Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
Left bundle branch area pacing in mildly reduced heart failure: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 713-720
- First Published: 05 May 2023
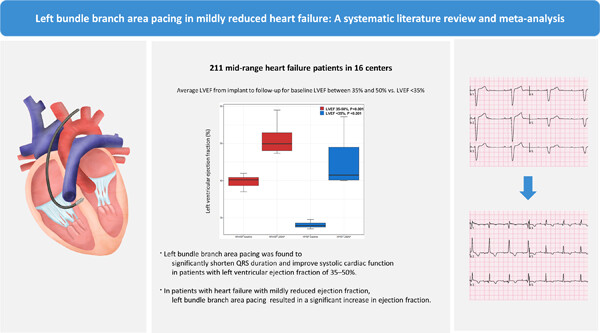
Average left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) from implant to follow-up for baseline LVEF between 35% and 50% versus LVEF <35%.
▪ Left bundle branch area pacing (LBBAP) was found to significantly shorten QRS duration and improve systolic cardiac function in patients with a LVEF of 35%−50%.
▪ In patients with heart failure with mildly reduced ejection fraction, LBBAP resulted in a significant increase in ejection fraction.
Association between vitamin D deficiency and vasovagal syncope: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 721-728
- First Published: 24 May 2023
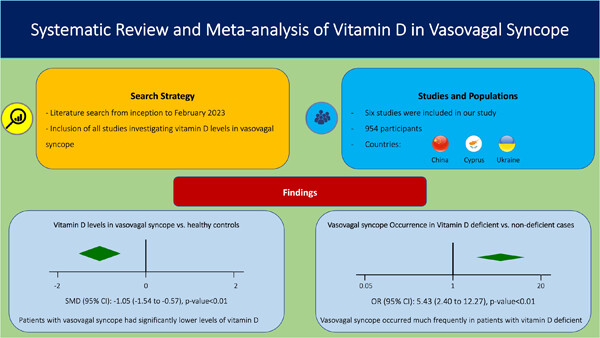
Studies have investigated vitamin D levels in patients with vasovagal syncope (VVS) and compared them with healthy controls. Our systematic review showed that patients with VVS have significantly lower levels of vitamin D. Also, VVS occurrence was significantly higher in vitamin D-deficient patients.
CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS
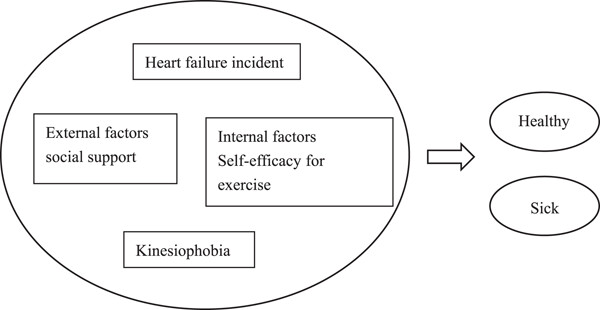
Influencing factors of kinesiophobia in older patients with chronic heart failure: A structural equation model
- Pages: 729-736
- First Published: 28 April 2023
Percutaneous closure of ventricular septal rupture after myocardial infarction: A retrospective study of 81 cases
- Pages: 737-744
- First Published: 15 May 2023
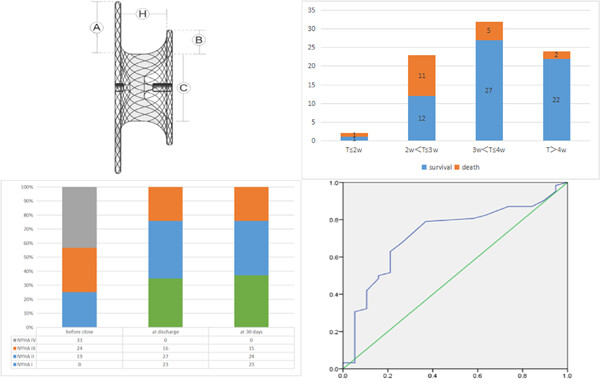
Ventricular septal rupture (VSR) is a rare but life-threatening complication of acute myocardial infarction (AMI). In this retrospective study of 81 patients, we investigated the efficacy and safety of percutaneous closure of postinfarction VSR. Our results show that delayed closure (3 weeks after AMI) is associated with a lower mortality rate and better clinical outcomes. We also found that percutaneous VSR closure can significantly improve cardiac function and hemodynamics. Notably, we identified that C-reactive protein and N-terminal pro brain natriuretic peptide elevation are independent risk factors for death at 30 days after VSR closure. Our study highlights the value of percutaneous closure as a viable treatment option for suitable VSR patients.
Interaction of lactate/albumin and geriatric nutritional risk index on the all-cause mortality of elderly patients with critically ill heart failure: A cohort study
- Pages: 745-756
- First Published: 24 May 2023
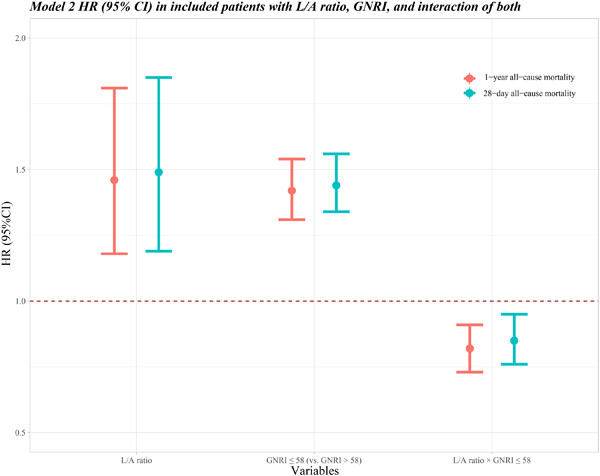
Graphical abstract showed that high lactate/albumin (L/A) ratio or geriatric nutritional risk index (GNRI) ≤ 58 was associated with the high risk of 28-day and 1-year all-cause mortality. There was a significant multiplicative interaction effect between L/A ratio and GNRI score on the 28-day and 1-year all-cause mortality.
Prognostic role and relationship of thyroid dysfunction and lipid profile in hospitalized heart failure patients
- Pages: 757-767
- First Published: 25 May 2023
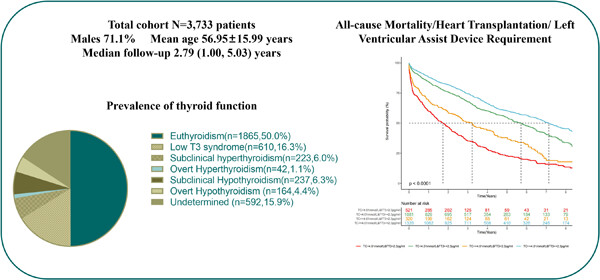
The study performed a large single-center retrospective cohort study to investigate the prognostic role of thyroid dysfunction and the relationship with lipid profile in hospitalized heart failure (HF) patients. Among enrolled 3733 patients, low fT3 and elevated TSH independently increased the risk of composite endpoint defined as the combination of all-cause mortality, heart transplantation, or left ventricular assist device requirement. Higher total cholesterol was still a protective factor in HF patients and showed good risk stratification combined with fT3 in Kaplan–Meier survival curves.
Association of race and in-hospital outcomes following acute pulmonary embolism: A retrospective cohort study
- Pages: 768-776
- First Published: 31 May 2023
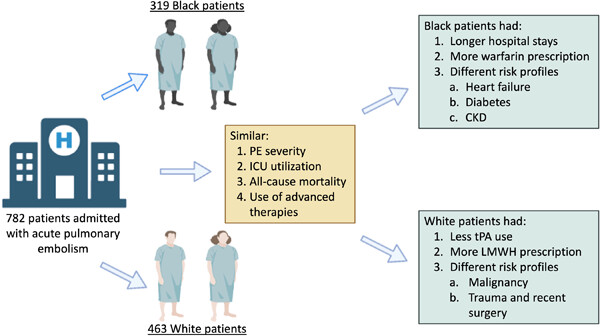
During index hospitalization for acute pulmonary embolism (PE), Black and White patients had similar PE severity with no difference in all-cause mortality. However, malignancy, trauma, and recent surgery were more common risk factors in White patients, while Black patients more often had heart failure, diabetes, and kidney disease. Black patients had longer hospitalizations and were more frequently discharged on warfarin. CKD, chronic kidney disease; ICU, intensive care unit; LMWH, low molecular weight heparin; PE, pulmonary embolism; tPA, tissue plasminogen activator.
CLINICAL STUDY DESIGN
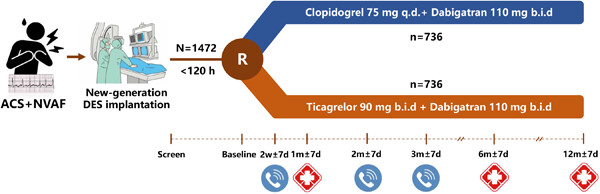
Rationale and design of the optimal antithrombotic treatment for acute coronary syndrome patients with concomitant atrial fibrillation and implanted with new-generation drug-eluting stent: OPtimal management of anTIthroMbotic Agents (OPTIMA)-4 trial
- Pages: 777-784
- First Published: 16 May 2023
CLINICAL TRIAL
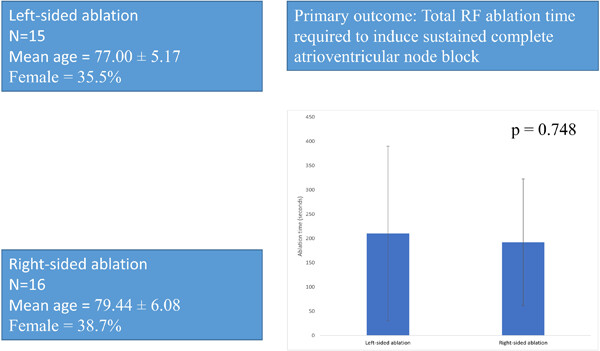
A randomized comparison of retrograde left-sided versus anterograde right-sided ablation of the atrioventricular junction
- Pages: 785-793
- First Published: 26 May 2023
CLINICAL TRIAL RESULT
Safety and efficacy of ablation index-guided atrial fibrillation ablation in octogenarians
- Pages: 794-800
- First Published: 18 May 2023
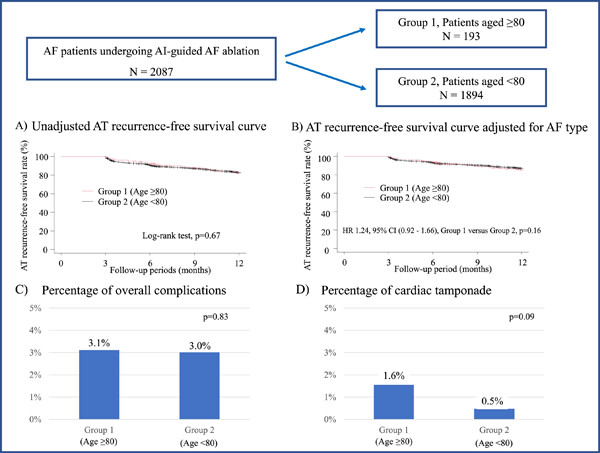
Catheter ablation guided by the ablation index achieved a similar AT recurrence rate between elderly AF patients aged ≥80 years and patients <80 years. The overall complication rate was similar among them. However, the percentage of cardiac tamponade in AF patients aged ≥80 years was almost three times as high as those <80 years.
Catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation in patients with autoimmune disease: A propensity score matching study based on the China Atrial Fibrillation Registry
- Pages: 801-809
- First Published: 22 May 2023
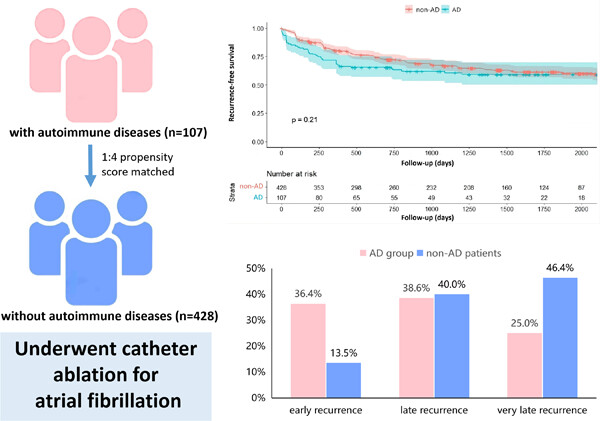
In this study conducted at Beijing Anzhen Hospital, we investigated the association between autoimmune diseases (AD) and procedural characteristics and recurrence after catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation in 107 patients with AD (AD group) and 428 propensity score-matched patients without AD (non-AD group). During the index procedure, a higher proportion of AD patients received nonpulmonary vein trigger ablation. Over a median follow-up of 36.3 months, patients with AD experienced a similar risk of recurrence with the non-AD group despite a higher incidence of early recurrences.
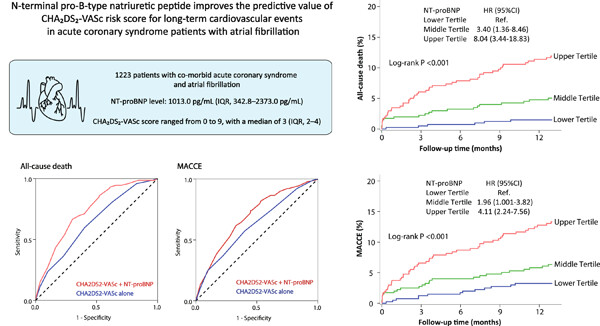
N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide improves the predictive value of CHA2DS2-VASc risk score for long-term cardiovascular events in acute coronary syndrome patients with atrial fibrillation
- Pages: 810-817
- First Published: 22 May 2023
Correlation between serum laminin level and prognosis of acute heart failure
- Pages: 818-822
- First Published: 31 May 2023
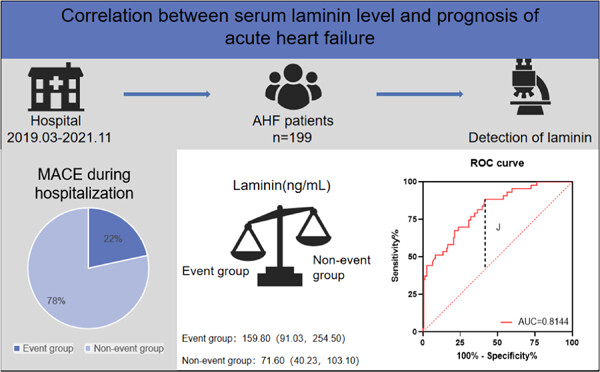
Among 199 patients with acute heart failure (AHF) in our hospital from March 2019 to November 2021, 43 cases developed major adverse cardiovascular events during hospitalization. We found that laminin (LN) levels were significantly elevated in this group of patients (p < .001). LN was independently associated with poor prognosis of AHF by receiver operating characteristic curve and multivariate analysis.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Antipyretics and vaccine-induced myocarditis
- Pages: 823-824
- First Published: 30 May 2023
CORRESPONDENCE
Postvaccine myocarditis and the use of antipyretics: Is there any relation?
- Pages: 825-826
- First Published: 30 May 2023