Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
MR imaging in assessing cardiovascular interventions and myocardial injury
- Pages: 1-15
- First Published: 26 February 2007
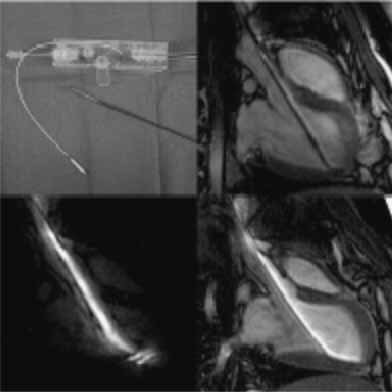
MR imaging provides information on myocardial viability, microvascular obstruction and real time imaging to guide minimally invasive intramyocardial injection of new therapies. MR contrast media and MR cell labeling allow assessment of myocardial viability and treatment effectiveness. Thus, they open up new avenues in molecular and cellular imaging.
Modified lipoproteins as contrast agents for imaging of atherosclerosis
- Pages: 16-23
- First Published: 23 February 2007
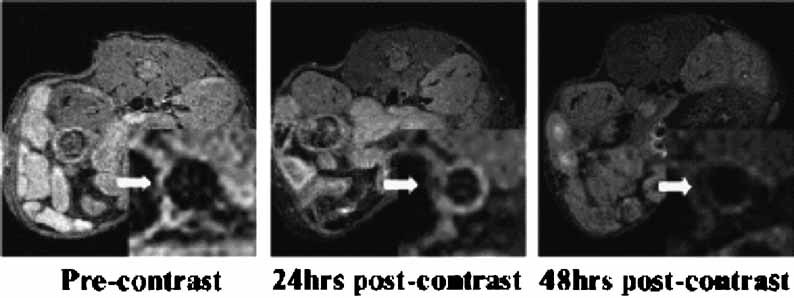
The modification of lipoproteins, mainly LDL and HDL, with radioisotopes for nuclear imaging, gadolinium chelates for magnetic resonance imaging, or other possible contrast agents for computed tomography, has helped to detect and characterize the atherosclerotic lesion. These specific contrast agents may enable initiation of therapy for atherosclerotic lesions prior to their becoming symptomatic.
A gadolinium triacetic monoamide DOTA derivative with a methanethiosulfonate anchor group. Relaxivity properties and conjugation with albumin and thiolated particles
- Pages: 24-34
- First Published: 08 February 2007
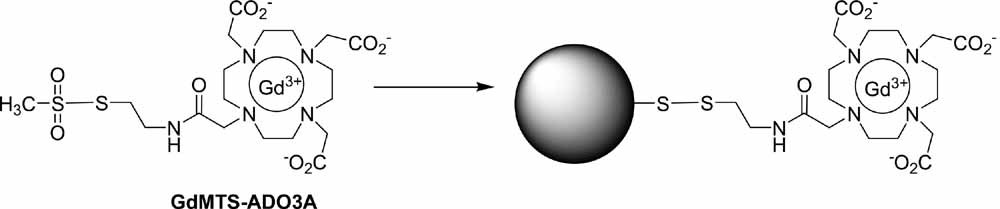
MTS-ADO3A is a new complexing agent of Gd(III) featuring a methanethiosulfonate group that readily reacts with thiol groups on native or reduced albumin and on thiolated silica particles. Its synthesis and relaxivity properties are reported. The isolated conjugates with albumin and particles display high relaxivity increases that remain limited by slow water exchange as shown by 17O NMR and NMRD. The reactivity of the disulfide bonds in presence of thiol derivatives has been investigated.
Phenylboronate 160Tb complexes for molecular recognition of glycoproteins expressed on tumor cells
- Pages: 35-41
- First Published: 16 February 2007
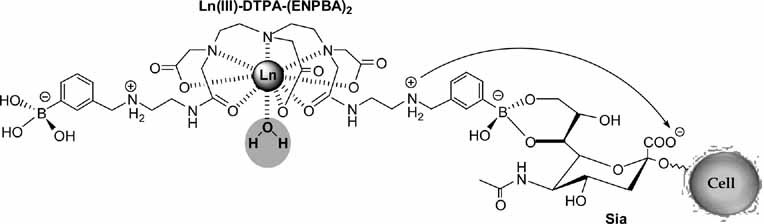
Phenylboronate funcionalized Ln(III)–DTPA complexes recognize sialic acid (Sia) on tumor cells. The cell recognition occurs by means of covalent binding between PBA and the diol-function of Sia and is assisted by an electrostatic interaction between an ammonium group and the negatively charged cell surface.
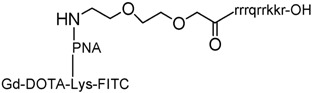
Synthesis and cellular uptake of a MR contrast agent coupled to an antisense peptide nucleic acid – cell– penetrating peptide conjugate
- Pages: 42-49
- First Published: 23 February 2007
A new temperature-sensitive contrast mechanism for MRI: Curie temperature transition-based imaging
- Pages: 50-54
- First Published: 16 February 2007
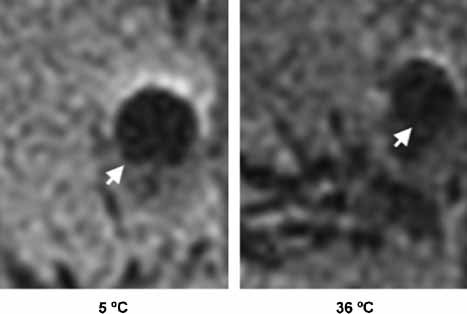
A temperature-sensitive MRI contrast mechanism is proposed based on the Curie temperature (Tc)—at which a ferromagnetic material transitions to paramagnetic state. In this study, magnetic susceptibility artifact area on MRI caused by pure, solid gadolinium (Gd) decreased with increasing temperature around Tc (20 °C) for Gd (p < 0.05). Potential applications of this mechanism may include MR thermometry and thermotherapy monitoring, using materials or alloys with desired Tc and magnetic susceptibility artifact versus temperature curves.
Spectral properties of a bifunctional PARACEST europium chelate: an intermediate for targeted imaging applications
- Pages: 55-58
- First Published: 26 February 2007
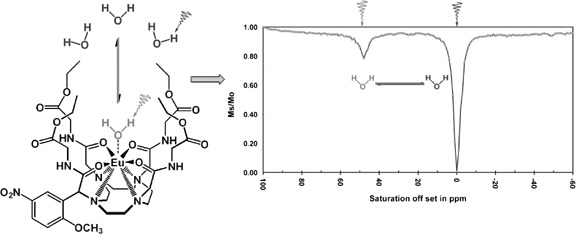
Lanthanide-based magnetization transfer (PARACEST) contrast agents offer great potential for probing physiological processes by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The versatility of these novel agents can be further augmented by introducing functionality that allows covalent attachment of the agent to biotargeting vectors for site specific and molecular imaging applications. The synthesis and CEST profile of a bifunctional PARACEST intermediate being developed for targeted nanoparticle applications is reported herein.
Current Awareness in Contrast Media and Molecular Imaging
- Pages: 59-66
- First Published: 07 March 2007