Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Editorial Board and Table of Contents
- Pages: 921-924
- First Published: 25 April 2019
Environmental Chemistry
Differences in Engineered Nanoparticle Surface Physicochemistry Revealed by Investigation of Changes in Copper Bioavailability During Sorption to Nanoparticles in the Aqueous Phase
- Pages: 925-935
- First Published: 30 January 2019
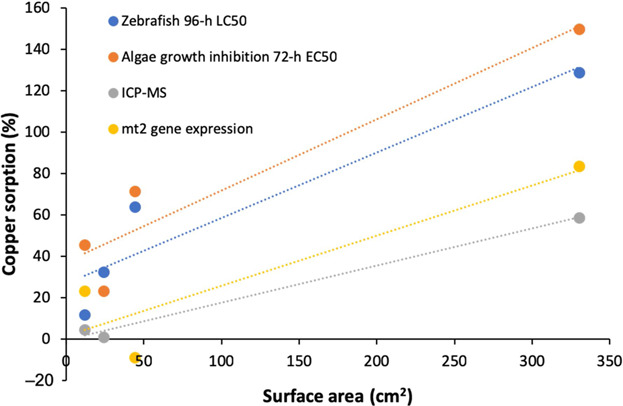
Copper sorption (%) as indicated by 4 independent analyses, conducted in the present study, show a positive correlation with the surface area (calculated by the reported manufactured particle diameter) of the nanoparticles (NPs) used in the present study (cm2). The analyses were as follows: the differences in the 72-h median effect concentration (EC50; Δ 72-h EC50) in the presence of NPs of different surface area generated by Chlorella vulgaris tests, the Δ 96-h median lethal concentration (LC50) of the zebrafish larvae tests, the differences in mt2 gene expression, and the curves generated by analytical chemistry (inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry [ICP-MS]), with R2 values of 0.90, 0.88, 0.81, and 0.99, respectively.
Identification of Toxicants from a Highly C10–C40-Contaminated Sediment Influenced by the Wood Industry: Petroleum Hydrocarbons or Biogenic Organic Compounds?
- Pages: 936-946
- First Published: 31 January 2019
Nontargeted Analysis of a Non-Aqueous-Phase Liquid From a Chemical Manufacturing Site Using Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
- Pages: 947-955
- First Published: 19 February 2019
Environmental Toxicology
Disinfection Byproducts Bind Human Estrogen Receptor-α
- Pages: 956-964
- First Published: 30 January 2019
Amitriptyline at an Environmentally Relevant Concentration Alters the Profile of Metabolites Beyond Monoamines in Gilt-Head Bream
- Pages: 965-977
- First Published: 31 January 2019
A Petri Net Approach to Physiologically Based Toxicokinetic Modeling
- Pages: 978-987
- First Published: 12 February 2019
Effects of Perfluoralkyl Substances on a Multigenerational Scale: A Case Study with Chironomus riparius (Diptera, Chironomidae)
- Pages: 988-999
- First Published: 20 February 2019
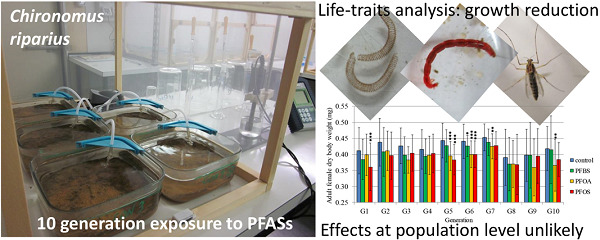
A 10-generation laboratory exposure of Chironomus riparius to perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS), perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorobutane sulfonate (PFBS) at concentrations comparable to maximum values found in European rivers highlighted a slight growth reduction. However, effects at the population level were not proved. PFASs = perfuoroalkyl substances.
Mitochondrial Toxicity of Selected Micropollutants, Their Mixtures, and Surface Water Samples Measured by the Oxygen Consumption Rate in Cells
- Pages: 1000-1011
- First Published: 19 February 2019
pH-Dependent Uptake and Sublethal Effects of Antihistamines in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos
- Pages: 1012-1022
- First Published: 19 February 2019
Developmental and Full-Life Cycle Exposures to Guanylurea and Guanylurea–Metformin Mixtures Results in Adverse Effects on Japanese Medaka (Oryzias latipes)
- Pages: 1023-1028
- First Published: 05 March 2019
Effects of Dissolved Organic Carbon on Copper Toxicity to Embryos of Mytilus galloprovincialis as Measured by Diffusive Gradient in Thin Films
- Pages: 1029-1034
- First Published: 06 March 2019
Land Use Contributions to Adverse Biological Effects in a Complex Agricultural and Urban Watershed: A Case Study of the Maumee River
- Pages: 1035-1051
- First Published: 18 March 2019
Hazard/Risk Assessment
Agrochemical Mixtures and Amphibians: The Combined Effects of Pesticides and Fertilizer on Stress, Acetylcholinesterase Activity, and Bioaccumulation in a Terrestrial Environment
- Pages: 1052-1061
- First Published: 30 January 2019
Creation of a Curated Aquatic Toxicology Database: EnviroTox
- Pages: 1062-1073
- First Published: 04 February 2019
A Vitellogenin Antibody in Honey Bees (Apis mellifera): Characterization and Application as Potential Biomarker for Insecticide Exposure
- Pages: 1074-1083
- First Published: 04 February 2019
Aquaculture Contributes a Higher Proportion to Children's Daily Intake of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Than to That of Adults in Eastern China
- Pages: 1084-1092
- First Published: 09 February 2019
Acute Effects of Binary Mixtures of Imidacloprid and Tebuconazole on 4 Freshwater Invertebrates
- Pages: 1093-1103
- First Published: 06 February 2019
The Use of Mechanistic Population Models in Metal Risk Assessment: Combined Effects of Copper and Food Source on Lymnaea stagnalis Populations
- Pages: 1104-1119
- First Published: 12 February 2019
Factors Affecting the Growth of Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata in Single-Species Tests: Lessons for the Experimental Design and the Reproducibility of a Multitrophic Laboratory Microcosm
- Pages: 1120-1131
- First Published: 19 February 2019
Di-(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate as a Chemical Indicator for Phthalic Acid Esters: An Investigation into Phthalic Acid Esters in Cultivated Fields and E-Waste Dismantling Sites
- Pages: 1132-1141
- First Published: 01 March 2019












