Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
Cover Picture: Arch. Pharm. Chem. Life Sci. (9/2019)
- First Published: 02 September 2019
EDITORIAL BOARD
Editorial Board: Arch. Pharm. Chem. Life Sci. (9/2019)
- First Published: 02 September 2019
REVIEW ARTICLE
Quinolone derivatives: Potential anti-HIV agent—development and application
- First Published: 05 July 2019
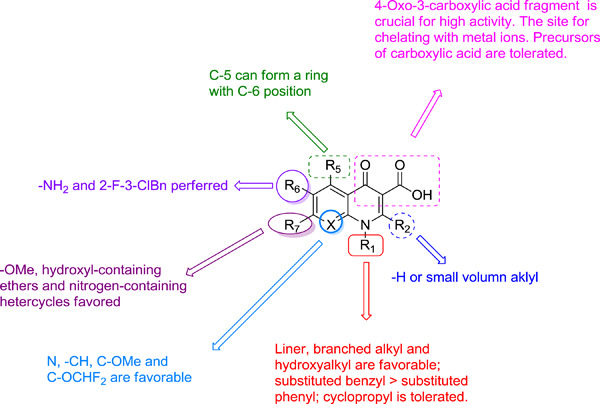
Quinolone represents a significant class of privileged heterocycles, and its derivatives possess promising in vitro and in vivo anti-HIV properties. This review emphasizes quinolone derivatives as potential anti-HIV agents and discusses the structure-activity relationship for the further rational design of this kind of derivatives.
FULL PAPERS
Synthesis and biological evaluation of heteroalicyclic cyanoguanidines at histamine receptors
- First Published: 29 July 2019
Heterocyclic exchange of aromatic imidazole by aliphatic six-membered heterocycles did not improve the binding affinity at the four histamine receptor subtypes. In addition, a variation of the spacer length (C3-C5) did not achieve receptor subtype selectivity, as shown in previous studies. Moderate affinities at the hH3R could be obtained for piperidine-containing compounds, with 2-cyano-1-(3-phenylpropyl)-3-[5-(piperidin-1-yl)pentyl]guanidine (53) having a pKi of 5.66.
Sulfonylpiperazines based on a flavone as antioxidant and cytotoxic agents
- First Published: 24 July 2019
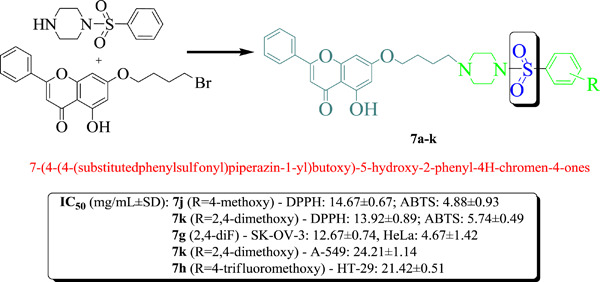
Natural product based semisynthetic chrysin-sulfonylpiperazines were synthesized and subjected to antioxidant and anticancer assays. They exerted better antioxidant and anticancer efficacies then previously studied chrysin-piperazine precursors. For example, compounds 7h, 7j, and 7k with 4-OCF3, 4-OCH3, and 2,4-diOCH3 groups exhibited the best antioxidant potential against 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) and 2,2′-azino-bis-3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS) radicals.
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of 6-substituted quinolines derived from cabozantinib as c-Met inhibitors
- First Published: 15 August 2019
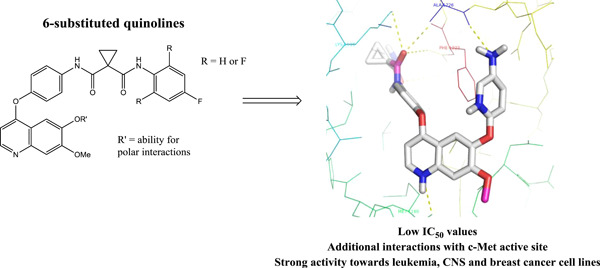
Based on cabozantinib and the limited knowledge of structure-activity relationship (SAR) for the quinoline 6-position, novel kinase inhibitors were designed. Structural modifications were made with an emphasis on the introduction of groups capable of engaging in polar interactions with the c-Met active site. Several of the compounds showed potent c-Met affinity. The para-amino substituted 15b and 18b showed additional hydrogen bonding in silico and potent antiproliferative effect toward the NCI60 cancer cell lines.
Quinazoline based 1,3,5-triazine derivatives as cancer inhibitors by impeding the phosphorylated RET tyrosine kinase pathway: Design, synthesis, docking, and QSAR study
- First Published: 05 August 2019
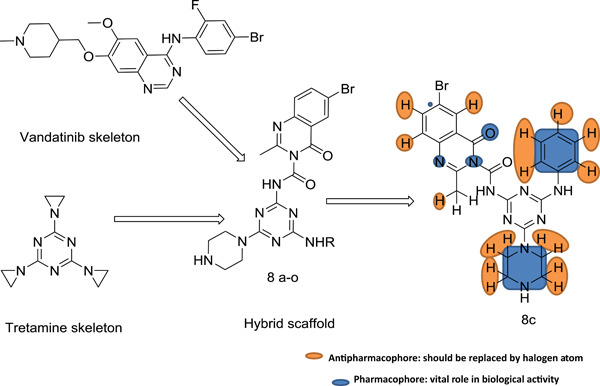
A quinazoline skeleton was designed, framed via 1,3,5-triazine derivatives (QBT) through field mapping and alignment studies. The QBT derivatives were evaluated for anticancer potency against TPC-1 and MCF-7 cells. Molecular docking in the adenosine triphosphate binding site of the RET tyrosine kinase domain was studied to elucidate vital structural residues necessary for bioactivity.
1,3,5,8-Tetrahydroxy-9H-xanthen-9-one exerts its antiageing effect through the regulation of stress-response genes and the MAPK signaling pathway
- First Published: 17 July 2019
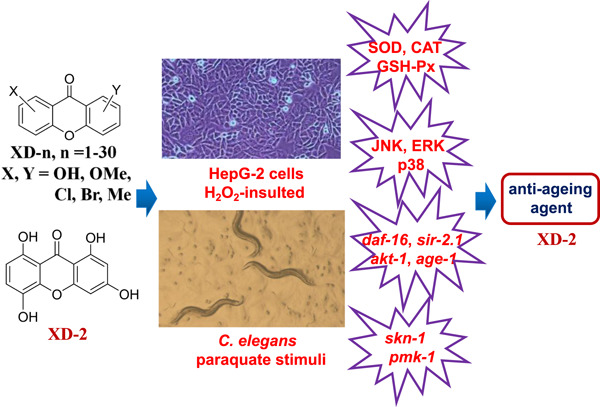
The antioxidative effects of 30 xanthone derivatives (XD-n, n = 1–30) were evaluated in HepG2 cells. All derivatives showed antioxidant activity, with 1,3,5,8-tetrahydroxy-9H-xanthen-9-one (XD-2) being the most active. XD-2 extended the lifespan of wild-type N2 nematodes under paraquat-induced oxidative stress and may be a promising antiageing agent.
Design and synthesis of leucine-linked quinazoline-4(3H)-one-sulphonamide molecules distorting malarial reductase activity in the folate pathway
- First Published: 05 August 2019
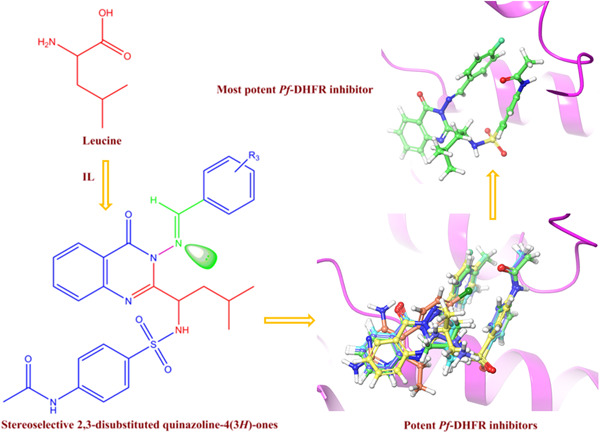
Quinazolinone derivatives incorporating an amino acid and sulfonamide were synthesized utilizing [Bmim][BF4]-H 2O as a neutral ionic liquid catalyst. The resulting 2,3-disubstituted quinazolinones were predominantly the E-stereoisomers derived from leucine. The synthesized leucine-linked sulfonamide-clubbed hybrid quinazolinone motifs showed inhibitory potency against Plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductase.
Anticancer properties of novel pyrazole-containing biguanide derivatives with activating the adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase signaling pathway
- First Published: 24 July 2019
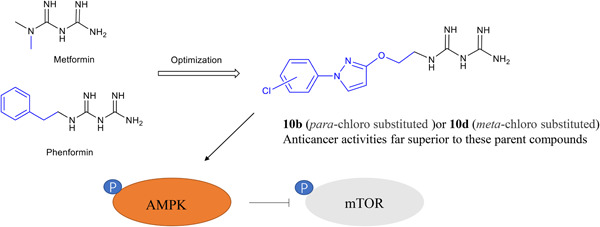
Pyrazole-containing biguanide derivatives were synthesized and screened for in vitro cytotoxicity against human cancer cell lines. Clonogenic assays and scratch wound healing assays demonstrated that these new derivatives profoundly inhibit cell proliferation and migration, revealing their therapeutic potential for the treatment of bladder and ovarian cancer.
Synthesis and mycobacterial evaluation of 5-substituted-6-acetyl-2-amino-7-methyl-5,8-dihydropyrido-[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one derivatives
- First Published: 24 July 2019
![Synthesis and mycobacterial evaluation of 5-substituted-6-acetyl-2-amino-7-methyl-5,8-dihydropyrido-[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one derivatives](/cms/asset/3bdc8f5c-51c6-4b13-92b1-0ae1fc696ec9/ardp201900068-gra-0001-m.jpg)
The 5-substituted-6-acetyl-2-amino-7-methyl-5,8-dihydropyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one derivatives were assayed for their antibacterial and cytotoxic potentials, showing activity in the range of 1.95-125 µg/ml against Mycobacterium tuberculosis but no activity against Mycobacterium aurum, Escherichia coli, and Staphylococcus aureus revealing selectivity towards slow-growing mycobacterial pathogens and they exhibited low cytotoxicity. Derivative 2l identified as an antituberculosis hit molecule could be used to yield more potent lead molecules.





