Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Not All Entangled States are Useful for Ancilla-Assisted Quantum Process Tomography (Ann. Phys. 5/2022)
- First Published: 08 May 2022

Quantum Entanglement
It has been shown that entanglement is not necessary for ancilla-assisted quantum process tomography. Surprisingly, by presenting two examples of two-qutrit entangled states, it is found by Cheng-Jie Zhang and co-workers in article number 2100550 that there also exist some entangled states which are useless for ancilla-assisted quantum process tomography. Moreover, experimental verification is performed on the IBM platform ibmq_athens.
Masthead
Review
On the Origin and the Amplitude of T-Square Resistivity in Fermi Liquids
- First Published: 26 February 2022
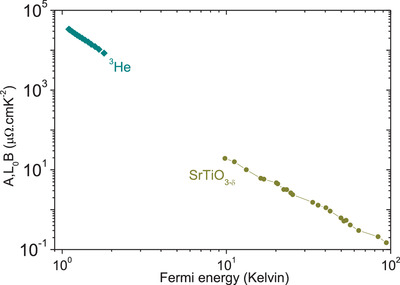
In a metal, the rate of collisions between electrons grows quadratically with temperature. This generates a T-square electric and thermal resistivity, even when these collisions conserve momentum. By comparing metals with the better understood case of 3He, the origin of T-square resistivity is tracked to the temperature dependence of diffusivity.
Research Articles
Quantum Version of the k-NN Classifier Based on a Quantum Sorting Algorithm
- First Published: 05 April 2022

A quantum k-NN (QK-NN) is developed. Its efficiency and performance are compared to those of the classical k-NN (CK-NN) and another quantum version proposed by Schuld. The efficiency of both quantum algorithms is similar to each other but superior to that of the classical algorithm, while the performance of present QK-NN algorithm is superior to that proposed by Schuld and similar to that of CK-NN.
Operational Detection of Entanglement via Quantum Designs
- First Published: 22 February 2022
By using quantum designs, this work explores the effects of the generalization of entanglement detection criteria based on symmetric informationally complete positive operator-valued measures (SIC POVMs). Counter-intuitively, no difference on the detection power is found between them. This highlights the unique role played by SIC POVMs in quantum information, meanwhile provides the minimal number of settings for experiments.
Not All Entangled States are Useful for Ancilla-Assisted Quantum Process Tomography
- First Published: 21 February 2022

It is shown that entanglement is not necessary for ancilla-assisted quantum process tomography. Surprisingly, by presenting two examples of two-qutrit entangled states, it is found that there also exist some entangled states that are useless for ancilla-assisted quantum process tomography. Moreover, experimental verification is also performed on the IBM platform.
Perfect Single-Magnon Generator Based on a Hybrid Cavity-Magnonic System
- First Published: 23 February 2022
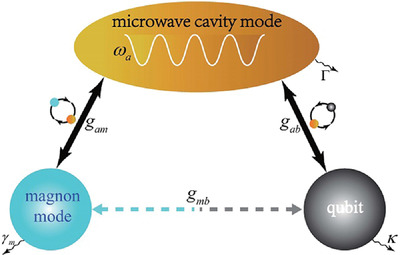
A scheme for as single-magnon generator is proposed in a hybrid cavity-magnonic system based on the coexistence mechanism of anharmonicity of energy levels and multipath interference. A global optimal condition of magnon blockade is obtained under which perfect magnon antibunching with a higher single-magnon number can be achieved. Based on the lithographically scalable and superconducting circuit compatible design, the scheme provides convenience for precisely and flexibly engineering in experiments.
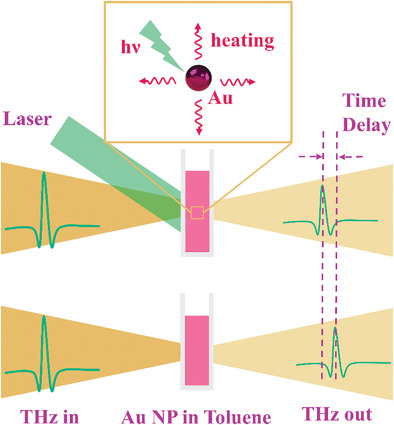
Large Terahertz Phase Shift Induced by Photothermal Effect of Gold Nanoparticles Incorporated with Toluene
- First Published: 24 February 2022
Nonlocal Correlation and Entanglement of Ultracold Bosons in the 2D Bose–Hubbard Lattice at Finite Temperature
- First Published: 02 March 2022
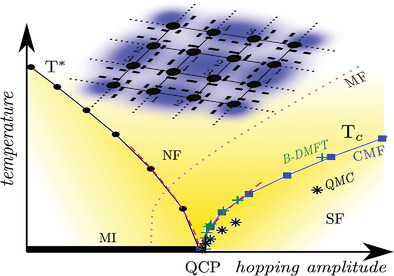
A temperature-dependent behavior, emerging in the vicinity of superfluid to Mott-insulator transition of interacting bosons in a two-dimensional Bose-Hubbard lattice at finite temperature, is investigated using a numerically inexpensive cluster-mean-field theory. Nonlocal correlations included within clusters, after an appropriate cluster-size scaling, leads to quantitative agreement of the phase boundaries and their critical exponents with quantum Monte-Carlo results and with experiments.
Lüders Bounds of Leggett–Garg Inequalities, - Symmetric Evolution and Arrow-of-Time
- First Published: 01 March 2022
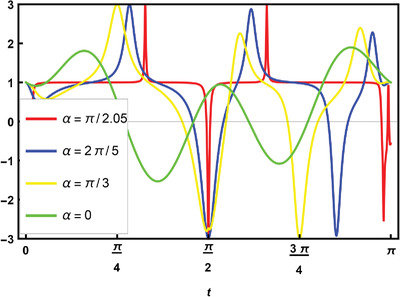
The Lüders bounds of the standard and variant of Leggett-Garg inequalities in unitary quantum mechanics requires the violation of no-signaling in time conditions. In PT-symmetric quantum mechanics the quantum violation of both form of Leggett-Garg inequalities exceeds their Lüders bound and reach their algebraic maxima. PT-symmetric evolution results in violation of arrow-of-time along with no-signaling in time.
Controllable Dispersive Wave Radiation from Pearcey Gaussian Pulses
- First Published: 02 March 2022
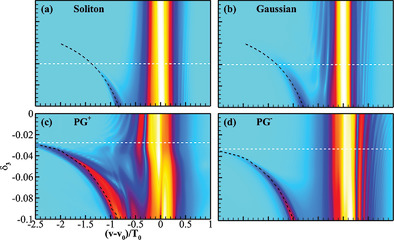
The process of dispersive waves emitted from Pearcey Gaussian pulses is investigated. Compared with the fundamental soliton, the minimum value of third-order dispersion required for the appearance of the dispersion wave is reduced by nearly 50%. The frequency, intensity, and energy conversion efficiency of the dispersive wave can be manipulated through the control of the Pearcey Gaussian pulse.
Photoluminescence and Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Spectroscopy for Revealing Visible Emission of ZnO Quantum Dots
- First Published: 02 March 2022
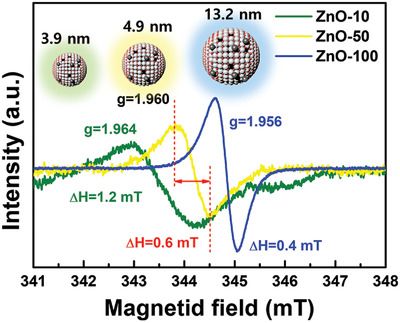
EPR peaks g = 1.964, 1.960, and 1.956 of ZnO quantum dots with sizes of 3.9, 4.9, and 13.2 nm emerge only under irradiation with light shorter than 400 nm, which is explicitly correlated with the photo-excited electrons trapped in the conduction band or the shallow donors participating in green luminescence.
Accessible Tuning of High Harmonics with Abruptly Auto-Focusing Beams
- First Published: 03 March 2022
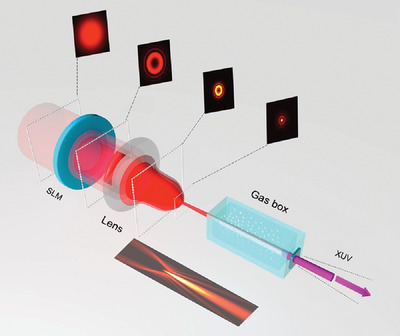
Ring-PeG beams are adopted as a driven beam to achieve a continuous increase of harmonic yield for a selected order within an effective interaction length of up to 1 cm. The underlying mechanism is attributed to the slowly diffracted propagation of the beams after their abrupt auto-focusing. The order of the phase-matched harmonic depends linearly on the beam intensity, indicating a phase-matching tuning scenario of high harmonic generation.
Simulating the Scattering Echo and Inverse Synthetic Aperture Lidar Imaging of Rough Targets
- First Published: 04 March 2022
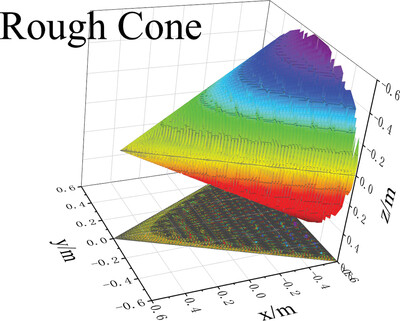
Although inverse synthetic-aperture lidar (ISAL) achieves high resolution, this is accompanied by high sampling rates and generates vast amounts of data. A process based on fast two-dimensional Fourier transforms to calculate the scattering echo under the Kirchhoff approximation is presented, achieving rapid real-time imaging of different large rough convex targets.
Topological Invariant of Velocity Field in Quantum Systems
- First Published: 09 March 2022
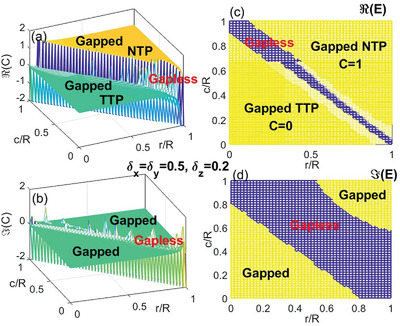
A velocity field approach is proposed to characterize the topological invariants of quantum states based on the Poincare–Hopf theorem. The global property of the zero modes dominates the topological invariants. The comparative study of the velocity field and the Chern number approaches for the quantum sphere and torus reveals novel insights into the topological invariant of quantum states.
The Simultaneous Ground-State Cooling and Synchronization of Two Mechanical Oscillators by Driving Nonlinear Medium
- First Published: 16 March 2022
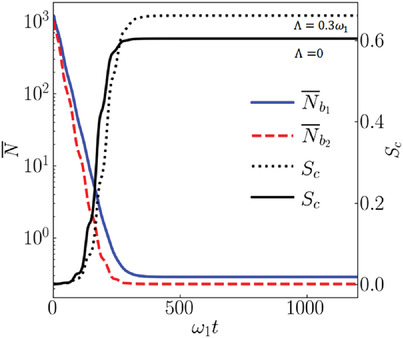
The influence of optical parametric amplifier on improving simultaneous ground-state cooling (SGC) and quantum synchronization of two mechanical resonators in a cavity optomechanical system is investigated. The relation between SGC and quantum synchronization shows that SGC must be accompanied by quantum synchronization, but quantum synchronization does not require SGC.
Generation and Enhancement of Mechanical Squeezing in a Hybrid Cavity Magnomechanical System
- First Published: 20 March 2022
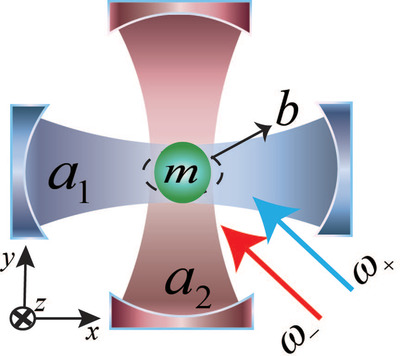
A scheme to generate strong mechanical squeezing by introducing two auxiliary cavities in a cavity magnomechanical system is proposed. It is found that mechanical squeezing can break the 3 dB limit even in the high dissipation rate of the magnon mode. This work provides an alternative way toward the practical implementation of mechanical squeezing in cavity magnomechanical systems.
Tripartite Quantum Correlations under Power-Law and Random Telegraph Noises: Collective Effects of Markovian and Non-Markovian Classical Fields
- First Published: 17 March 2022
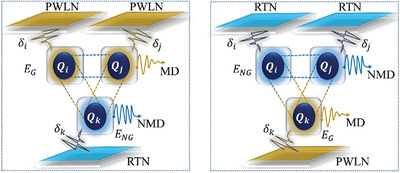
The combined implications of Markovianity and non-Markovianity on the dynamics of tripartite entanglement, purity, and coherence are investigated using mixed classical channels. In quantum information processing, classical channels have been discovered to be critical resources. For improved performance of local channels, parameter optimization and other strategies are being developed, allowing for longer information preservation.
Exponentially Enhanced Single-Photon Cross-Kerr Nonlinearity in Quantum Optomechanics
- First Published: 23 March 2022
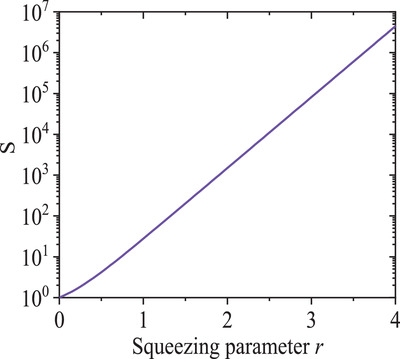
An efficient method is proposed to exponentially enhance the cross-Kerr nonlinearity in quantum optomechanics. Through periodically modulating the mechanical spring constant, a nonlinear two-phonon drive can be acquired to amplify the mechanical zero-point fluctuations. The exponentially enhanced single-photon cross-Kerr interaction between the two optical modes can be realized via the amplified mechanical motion.
Optimal Discrimination of Two Nonorthogonal States by Continuous Probing and Feedback Operation
- First Published: 30 March 2022
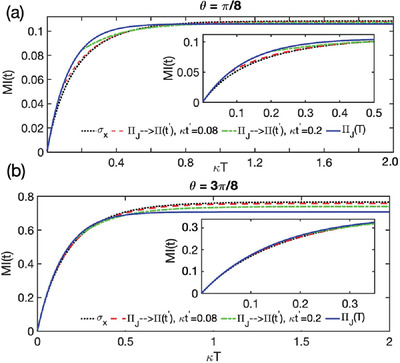
An optimal operator is found that could yield the maximal value of mutual information for a long-time measurement. It turns out that the error probability is minimized for any measurement moment by measuring the optimal operator. For a given finite duration, the proposal could determine the optimal measurement operator that maximizes the final value of mutual information.
Temperature-Controlled and Photoexcited Multitasking Janus Metasurface in the Terahertz Region
- First Published: 04 April 2022
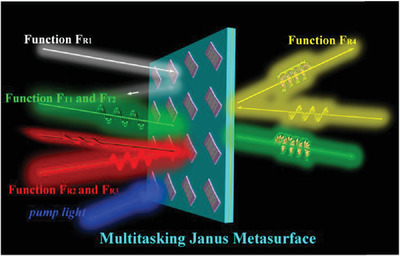
Tunable linear-to-circle (LTC) polarization conversion (PC) switches working band between 0.69–1.08 THz and 0.67–0.96 THz for normal incidence. In the reflection state, the operating band of the linear-to-linear PC changes from 1.23–1.91 THz to 0.98–1.91 THz. For backward incidence, it presents LTC PC with effective domain of 0.99–1.63 THz.
Optically Tunable Terahertz Metasurface Absorber
- First Published: 03 April 2022
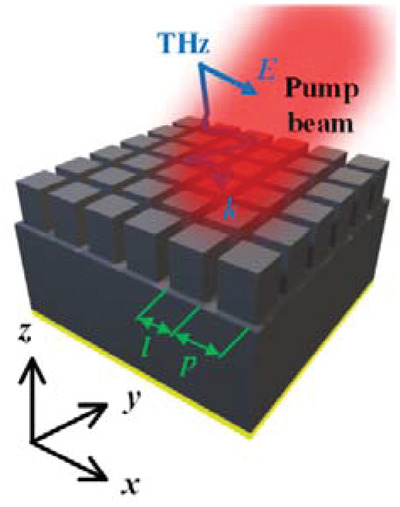
Terahertz absorbers have been widely explored in various fields because they are urgently required in THz shielding, stealth, sensing, and other fields. Here, a tunable THz perfect absorber consisting of high resistance silicon is proposed, which can realize the switch between perfect reflection and perfect absorption. The proposed scheme allows for more flexible design of THz absorbers, and the device is more easily fabricated.
Physical Implications of Pure Lovelock Geometry on Stellar Structure
- First Published: 31 March 2022

How is stellar structure influenced by the gravity theory in use? An exact model of an anisotropic star in the context of pure Lovelock gravity by prescribing a linear equation of state and a Finch-Skea potential is constructed. The general solution is found. Empirical evidence shows that mass-radius ratios, densities, and pressures are affected remarkably by higher curvature effects.
A Reputation Game Simulation: Emergent Social Phenomena from Information Theory
- First Published: 05 April 2022
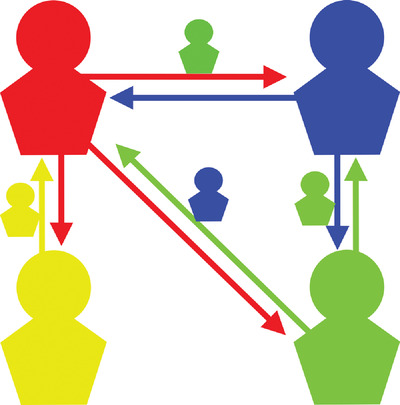
Sociophysical simulations of a reputation game are presented. The participating agents exchange honest or dishonest statements, which are about third agents or themselves, while trying to be perceived as being honest. Different social phases can be identified, in particular when malicious communication strategies are used.
The Gor'kov and Melik-Barkhudarov Correction to an Imbalanced Fermi Gas in the Presence of Impurities
- First Published: 05 April 2022
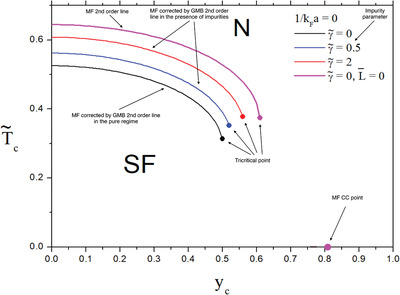
The Gor'kov and Melik-Barkhudarov (GMB) corrections to the mean-field first- and second- order lines and to the transition temperature (tricritical point) of balanced (imbalanced) Fermi gases are strongly supressed due to the presence of impurities. The GMB correction to the Chandrasekhar–Clogston limit of imbalanced Fermi gas at unitarity is found by means of the T-matrix approximation, in pure and impurity regimes.