Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Issue Information
Contents
Original Papers
Model of a relativistic oscillator in a generalized Schrödinger picture
- Pages: 871-882
- First Published: 22 August 2011
In a generalized Schrödinger picture, the authors consider the motion of a relativistic particle in an external field (like in the case of a harmonic oscillator). In this picture the analogs of the Schrödinger operators of the particle are independent of both the time and the space coordinates. These operators induce operators which are related to Killing vectors of the Anti de Sitter (AdS) space. The nonrelativistic limit is also considered.
On the nature of a*kak and the emergence of the Born rule†
- Pages: 883-897
- First Published: 13 September 2011
This paper is intended to show that a review in the concept of the game theoretical utility, the revised utility to be applied to the definition of the utility of a wave function representing an object subsystem relative to its observer subsystem, both within an isolated system, leads to the emergence of Max Born's rule as a profit under a von Neumann good measure game.
Electron on a cylinder with topological defects in a homogeneous magnetic field
- Pages: 898-909
- First Published: 20 September 2011
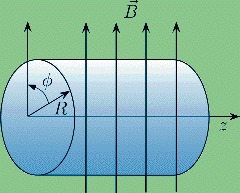
In this work the authors study the effects of the geometry and topology of a cylinder on the energy levels of an electron moving in a homogeneous magnetic field. They consider the existence of topological defects as a screw dislocation and a disclination. When they take the region of movement as the full cylindrical surface, they find that, by increasing the strength of the screw dislocation, the dispersion on the electronic energy levels is affected and monotonically increasing.
Relativistic Anandan quantum phase in the Lorentz violation background
- Pages: 910-918
- First Published: 20 September 2011
The authors study the influence of a classical background based on the violation of the Lorentz symmetry on the relativistic Anandan quantum phase. They show that the choice of the Lorentz symmetry violation background provides an abelian contribution for the relativistic Anandan quantum phase.
Next-to-next-to-leading order post-Newtonian spin(1)-spin(2) Hamiltonian for self-gravitating binaries
- Pages: 919-924
- First Published: 20 September 2011
The authors present the next-to-next-to-leading order post-Newtonian (PN) spin(1)-spin(2) Hamiltonian for two self-gravitating spinning compact objects. If both objects are rapidly rotating, then the corresponding interaction is comparable in strength to a 4PN effect. The Hamiltonian is checked via the global Poincaré algebra with the center-of-mass vector uniquely determined by an ansatz.
Quantum anticentrifugal potential in a bent waveguide
- Pages: 925-930
- First Published: 20 September 2011
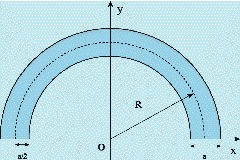
The authors show the existence of an anticentrifugal force for a quantum particle in a bent waveguide. This effect may be observed in interference experiments which are sensitive to the additional phase of the wavefunction gained in the bent regions and can find application in distinguishing between straight and bent geometries.
Quantum mechanics needs no consciousness
- Pages: 931-938
- First Published: 13 October 2011
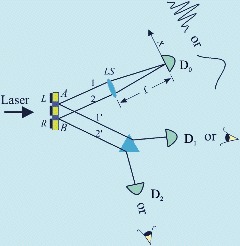
It has been suggested that consciousness plays an important role in quantum mechanics as it is necessary for the collapse of wave function during the measurement. Here the authors formulated several predictions that follow from this hypothetical relationship and that can be empirically tested. Experimental results that are already available suggest falsification of these predictions. Thus, the suggested link between human consciousness and collapse of wave function does not seem viable.
Neutron bound states in a supersymmetric double Dirac delta electrostatic potential
- Pages: 939-945
- First Published: 13 October 2011
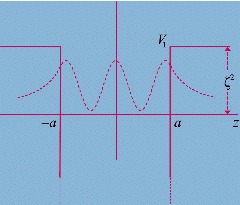
The authors study neutron bound states in a particular (1+1)-supersymmetric configuration. A simple physical setup is chosen so that the effective interaction becomes a particular kind of double Dirac delta potential. In this configuration it is shown that the neutron distinguishes between positive and negative electric charge as a consequence of a purely quantum mechanical effect. The theoretical background is presented and a possible application to a real-life physical system is discussed.
Comment
Comment on “Strong signature of the active Sun in 100 years of terrestrial insolation data” by W. Weber
- Pages: 946-950
- First Published: 20 September 2011
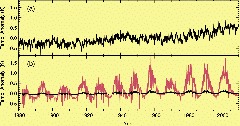
An analysis of ground-based observations of solar irradiance was recently published in this journal, reporting an apparent increase of solar irradiance on the ground of the order of 1 % between solar minima and maxima [1]. Since the corresponding variations in total solar irradiance on top of the atmosphere are accurately determined from satellite observations to be of the order of 0.1 % only [2], the one order of magnitude stronger effect in the terrestrial insolation data was interpreted as evidence for cosmic-ray induced aerosol formation in the atmosphere. In the author's opinion, however, this result does not reflect reality. Using the energy budget of Earth's surface, he shows that changes of ground-based insolation with the solar cycle of the order of 1 % between solar minima and maxima would result in large surface air temperature variations which are inconsistent with the instrumental record. It would appear that the strong variations of terrestrial irradiance found by [1] are due to the uncorrected effects of volcanic or local aerosols and seasonal variations. Taking these effects into account, the author finds a variation of terrestrial insolation with solar activity which is of the same order as the one measured from space, bringing the surface energy budget into agreement with the solar signal detected in temperature data.
Reply
Reply to the Comment of G. Feulner
- Pages: 951-956
- First Published: 20 September 2011
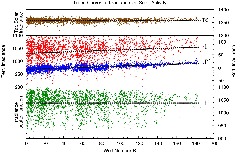
In his reply the author present a re-analysis of the data of the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO). For this, a new data reduction method is introduced, allowing a drastic lowering of data scatter, so that the time series of the reduced data clearly shows the ≈︁ 1 % variation of the terrestric solar irradiance in parallel with solar activity. The implications are discussed.
Erratum
Erratum: Optical properties of nitride nanostructures
- Page: 957
- First Published: 13 October 2011
The set of InN nanocolumn samples discussed in the article was not grown using Au as a catalyst. Instead, the growth was performed catalyst-free by plasma-assisted molecular beam epitaxy.





