Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Contents
RESEARCH ARTICLE
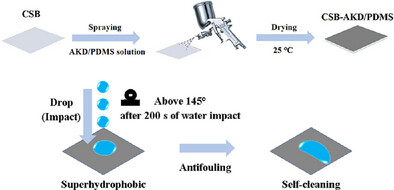
Alkyl Ketene Dimer/Polydimethylsiloxane Modified Starch-Based Materials With Superhydrophobicity and Wear Resistance
- First Published: 19 May 2025
α-Amylase Immobilization on Carbon Nanospheres: Influence of Size and Functionalization on Enzymatic Activity
- First Published: 09 February 2025
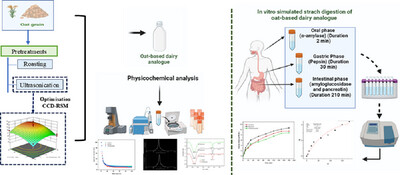
Investigating the Effects of Ultrasonication and Roasting on Starch Digestibility and Glycemic Index in Oat-Based Dairy Analog
- First Published: 18 April 2025
Impact of Antifreeze Protectant Addition on the Pore Structure Formation and Air Filtration-Related Properties of Konjac Glucomannan/Starch Aerogel
- First Published: 11 April 2025
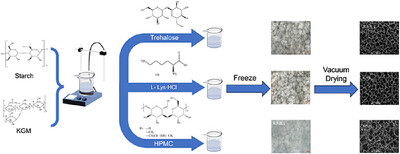
In this paper, the effects of three antifreeze protectants (trehalose, L-lysine hydrochloride, and HPMC) on the pore structure and air filtration performance of KGM/Starch aerogels were investigated. The results showed that the average pore size of the aerogel with trehalose addition (1.0% wt) was reduced, while the filtration efficiency of air particles was enhanced, which were better than the other two.
Insights Into the Digestibility, Properties, and Structure of Highland Barley Starch Using Dry Heat Treatment, Heat Moisture Treatment, and Annealing Treatment
- First Published: 14 April 2025
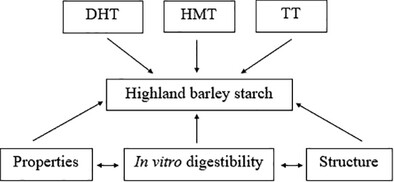
The manuscript reports the study on the changes of the digestibility, processing properties, and structure of highland barley starch induced by dry heat treatment, heat moisture treatment, and toughening treatment. And the interrelationship between modification conditions, structure, and functional properties of starch was also investigated.
REVIEW
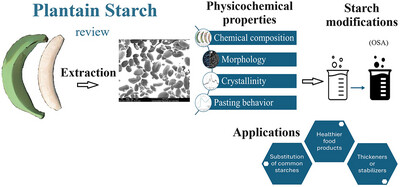
Extraction, Physicochemical Properties, and Potential Applications of Starches Isolated From Cooking Plantains
- First Published: 14 April 2025
Impact of High-Pressure Steam on Multilevel Structures of Rice Starch: A Review
- First Published: 24 May 2025
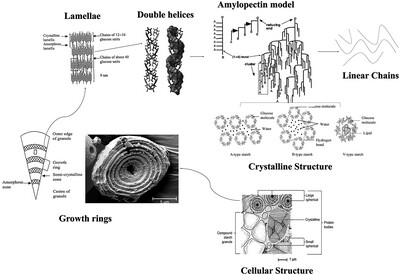
High-pressure steaming emerges as a promising technique due to its ability to uniformly heat rice while preserving its nutritional quality. The process notably affects starch structure across various levels, from the molecular level to the cellular system by disrupting starch structure significantly causing the leaching of amylose and losing the actual shape.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Concentration of Potato Fruit Juice From the Starch Industry Using Nanofiltration Membranes as Pretreatment Process Upstream an Evaporator for Energy Savings
- First Published: 02 May 2025
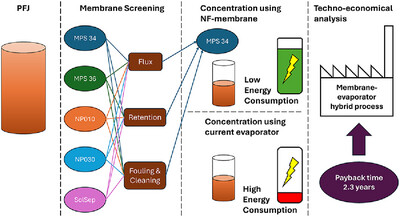
A nanofiltration membrane process was developed and evaluated for the concentration of potato fruit juice with low protein content upstream of an evaporator for energy savings. The study included membrane screening, pretreatment assessment, fouling and cleaning investigation, membrane concentration study, and a techno-economical analysis.
Characterization of Resistant Starch From Eleusine coracana and Evaluation of Its Prebiotic Potential
- First Published: 24 April 2025
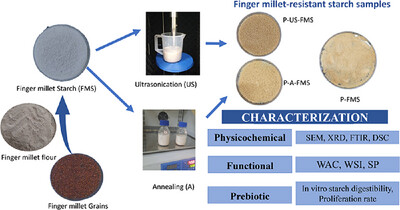
Physical treatments such as ultrasonication and annealing enhanced RS content in finger millet starch. The change of crystallinity to B-type enhanced enzymatic resistance to the simulated gastrointestinal environment and proliferation rate for Lactobacillus rhamnosus (MTCC 1423) compared to untreated samples. It fulfilled the criteria to be considered as prebiotics.
Effects of Staged Fermentation With Multistrains on the Physicochemical Characteristics and In Vitro Inhibitory Activity on Advanced Glycation End-Products (AGEs) Formation of Buckwheat
- First Published: 13 May 2025
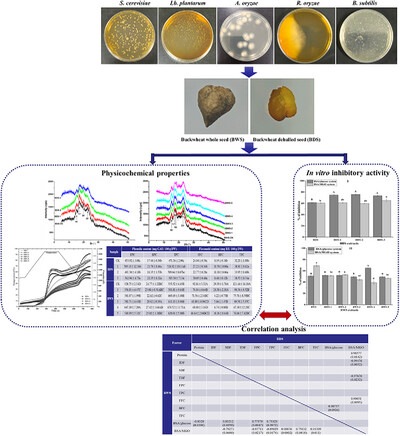
Staged fermentation was performed on BWS and BDS. Crystallinity of BDS increased while BWS decreased after fermentation. Breakdown viscosity was only detected in staged fermented BWS, indicating the higher fermentation level extended into endosperm. Phenolic, flavonoid, and soluble dietary fiber (SDF) played major roles in inhibition of AGE formation.
Saccharification Enhancing in Last Round of Maotai-Flavor Liquor Fermentation Using Fermented Glutinous Rice
- First Published: 13 May 2025
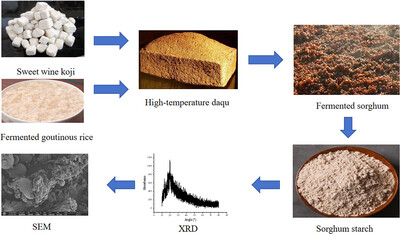
Fermented glutinous rice can promote the saccharification efficiency of the last round of Maotai-flavor liquor. Fermented glutinous rice changes the starch molecule from the last round of fermented sorghum, which reveals the mechanism of saccharification efficiency improvement. Fermented glutinous rice promoted microorganisms in the fermented sorghum above, further benefiting the liquor flavor.