Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Recommendations From the Medical Education Editor
- Pages: 544-546
- First Published: 10 June 2025
Enhancing COPD Care for Women: A Predictive Tool for Palliative Needs
- Pages: 547-549
- First Published: 23 March 2025
See related article
Sliding Into Misdiagnosis? Distinguishing Bullous Emphysema From Pneumothorax With Lung Ultrasound
- Pages: 550-551
- First Published: 25 March 2025
See related article
COMMENTARY
World Bronchiectasis Conference 2025—Inclusive Lungs, Diverse Solutions
- Pages: 552-554
- First Published: 21 May 2025
Obstructive Sleep Apnoea Screening and Diagnosis Across Adult Populations: Are We Ready?
- Pages: 555-557
- First Published: 14 May 2025
INVITED REVIEW SERIES
Lung Cancer Screening—Preparedness, Toolkit for Nodule Service, Economic Implications, Lessons From International Counterparts
The TSANZ Practical Guide for Clinicians in the Management of Screen- and Incidentally-Detected Nodules
- Pages: 558-573
- First Published: 29 May 2025
INVITED REVIEW
Contemporary Concise Review 2024: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- Pages: 574-586
- First Published: 28 May 2025
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE
World Association for Bronchology and Interventional Pulmonology (WABIP) Guidelines on Airway Stenting for Benign Central Airway Obstruction
- Pages: 587-604
- First Published: 27 June 2025
POSITION STATEMENT
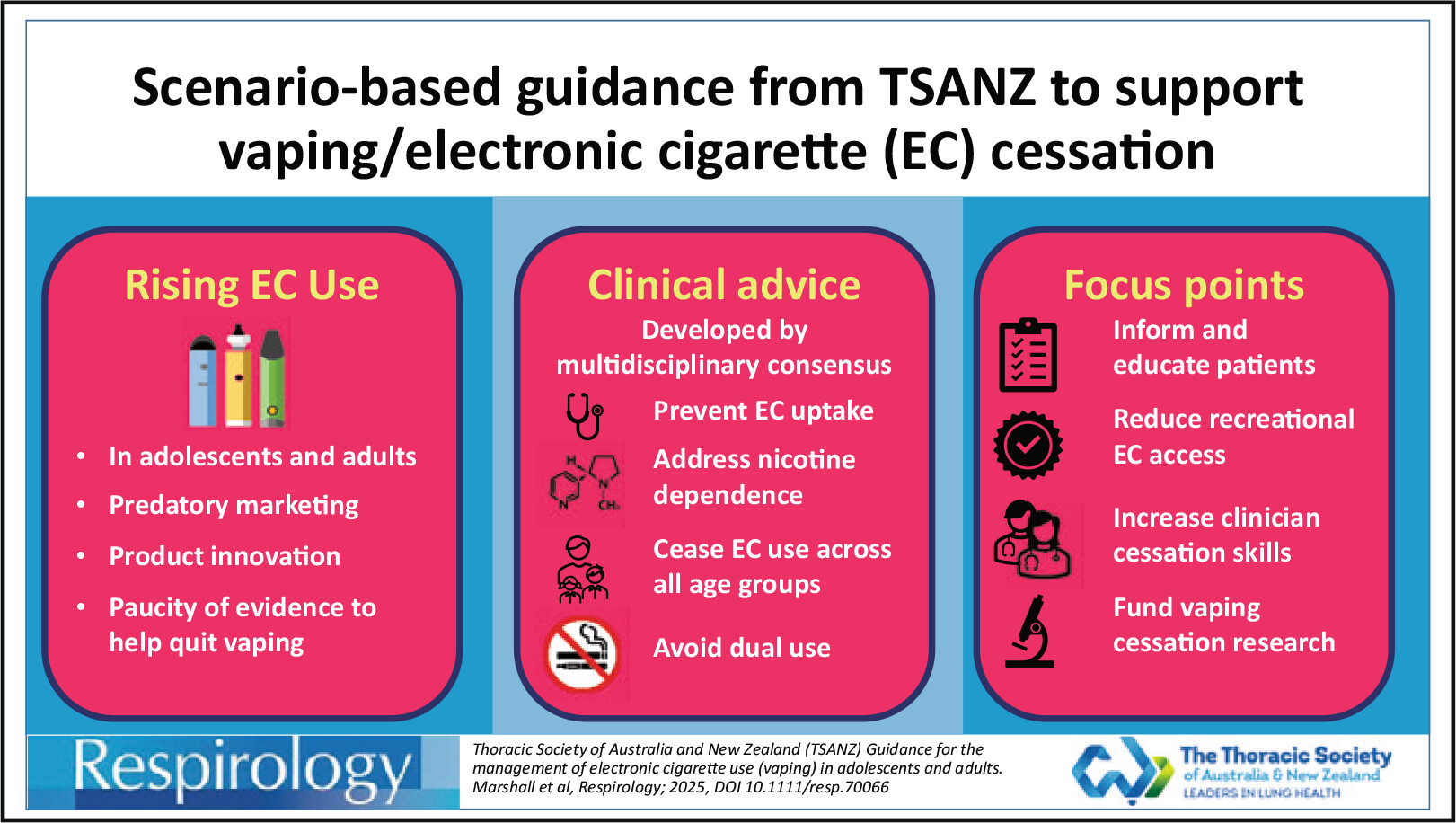
Thoracic Society of Australia and New Zealand (TSANZ) Guidance for the Management of Electronic Cigarette Use (Vaping) in Adolescents and Adults
- Pages: 605-622
- First Published: 28 May 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
COPD
Development and Validation of a Risk Prediction Model to Identify Women With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease for Proactive Palliative Care
- Pages: 623-632
- First Published: 16 February 2025
We developed a predictive model to identify older women with COPD who are at a high risk of 1-year mortality. The model, based on six readily available, non-invasive, and inexpensive predictors, demonstrated excellent predictive accuracy. This can aid in identifying high-risk patients for timely palliative care interventions, potentially improving outcomes.
See related article
Mapping Bullous Emphysema With Lung Ultrasound: A Prospective Multicentre Study
- Pages: 633-643
- First Published: 09 March 2025
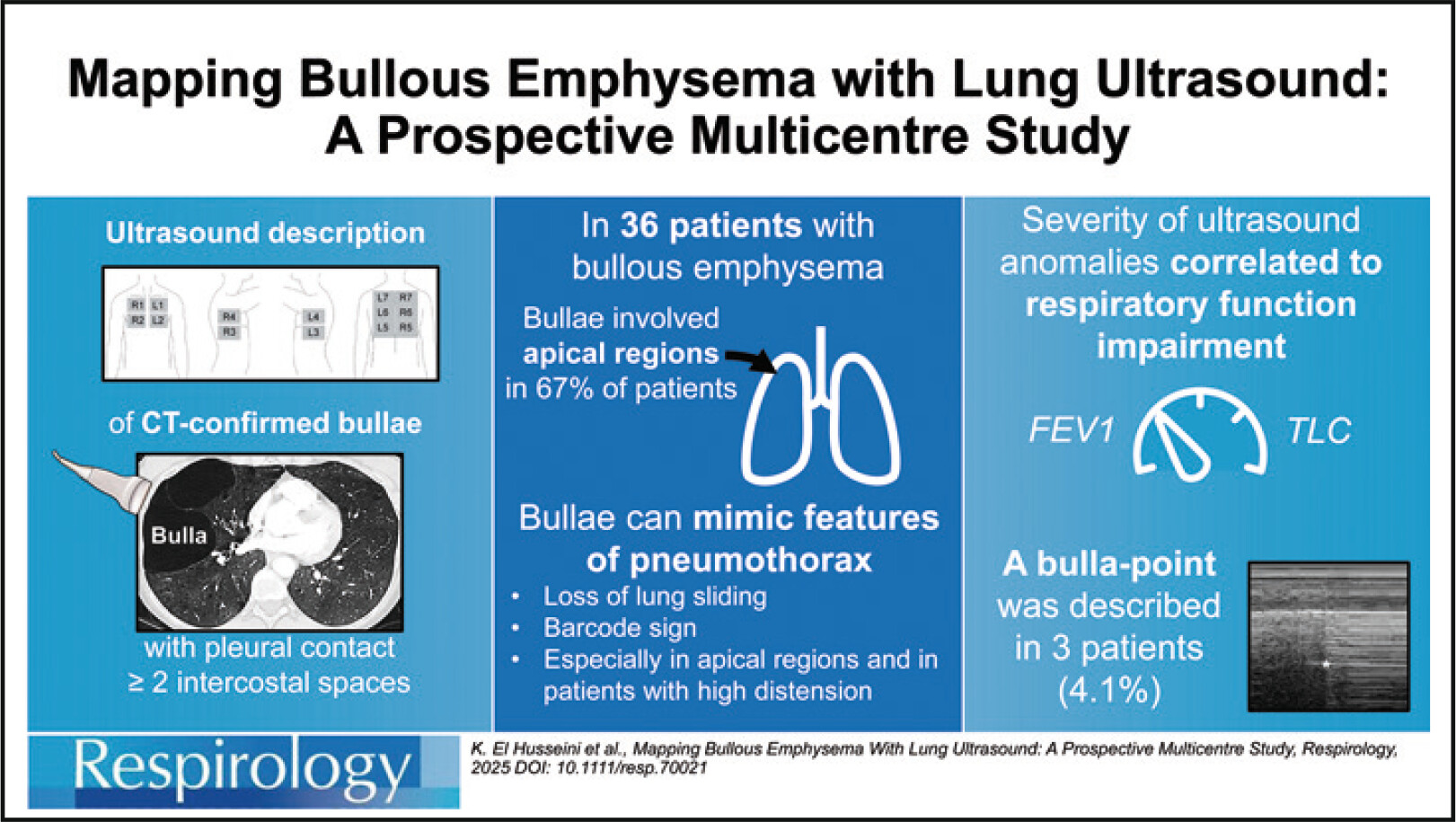
This study confirms the existence of the ‘bulla-point’, a sonographic sign echoing the lung-point associated with pneumothorax. Other signs of pneumothorax such as absent lung sliding or barcode sign are also prevalent in bullous emphysema, especially in patients with high pulmonary distension or in apical regions.
See related article
Interstitial Lung Disease
Objective Effects and Patient Preferences for Ambulatory Oxygen in Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Disease With Isolated Exertional Hypoxaemia: A Placebo-Controlled 6-Minute Walk Test Study
- Pages: 644-651
- First Published: 11 March 2025
In a double-blind, placebo-controlled 6-minute walk test study, patients with Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Diseases and exertional breathlessness with hypoxaemia experienced less dyspnoea and fatigue, walked farther, and preferred ambulatory oxygen at a flow rate preventing desaturation, compared to medical air at the same flow rate.
Quantitative Assessment of Systemic Sclerosis–Related Interstitial Lung Disease via 3D-Imaging
- Pages: 652-661
- First Published: 17 March 2025
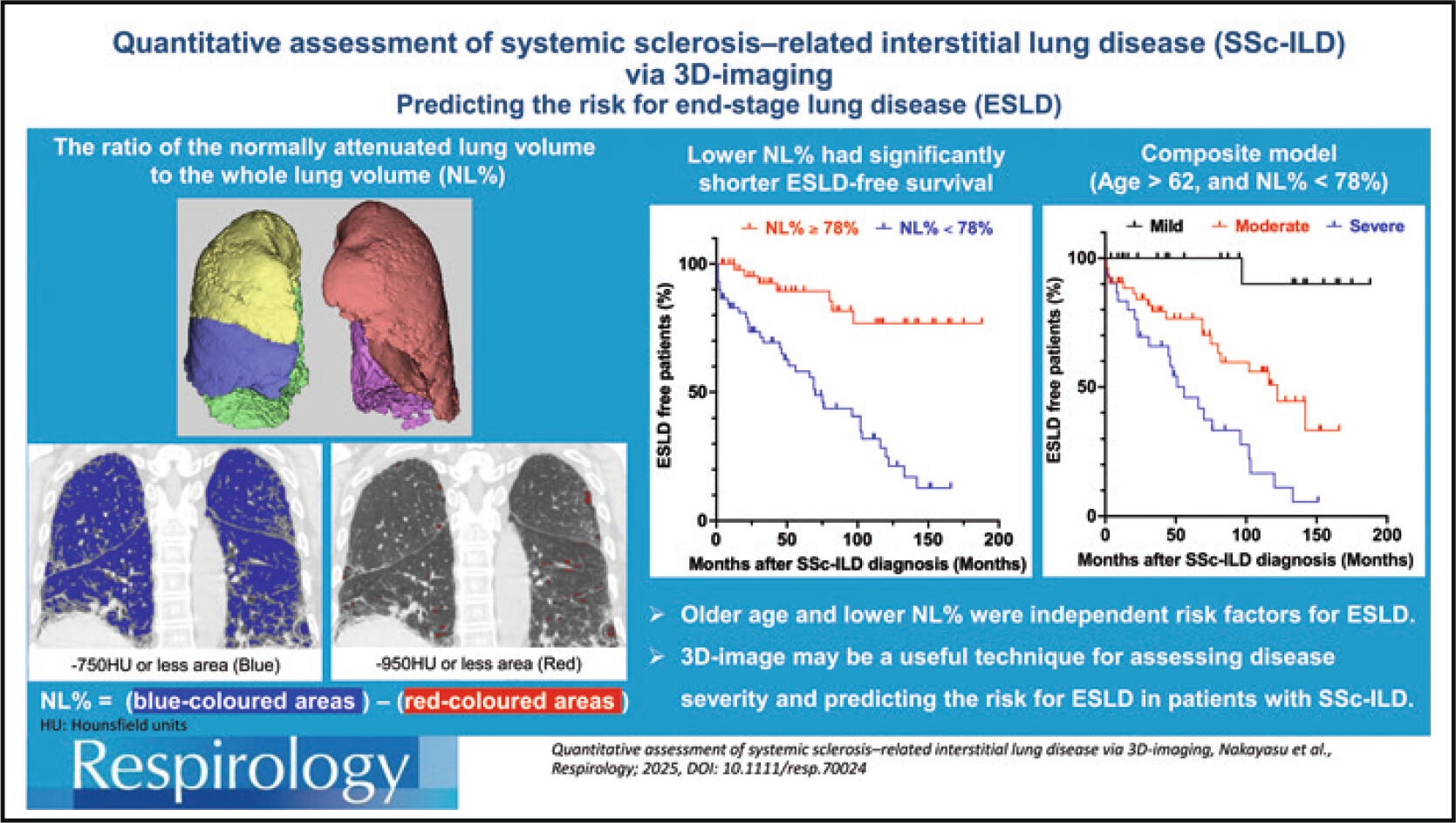
Three-dimensional imaging (3D-image) can quantitatively measure disease extent and volume loss in patients with systemic sclerosis–related interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD). Volume loss and disease extent were associated with disease progression. The application of 3D-image analyses can help determine disease severity and mortality risk in patients with SSc-ILD.
Impact of Pulmonary Artery Pressure on the Response to Oxygen Administration for Exertional Desaturation in Interstitial Lung Disease
- Pages: 662-670
- First Published: 20 May 2025
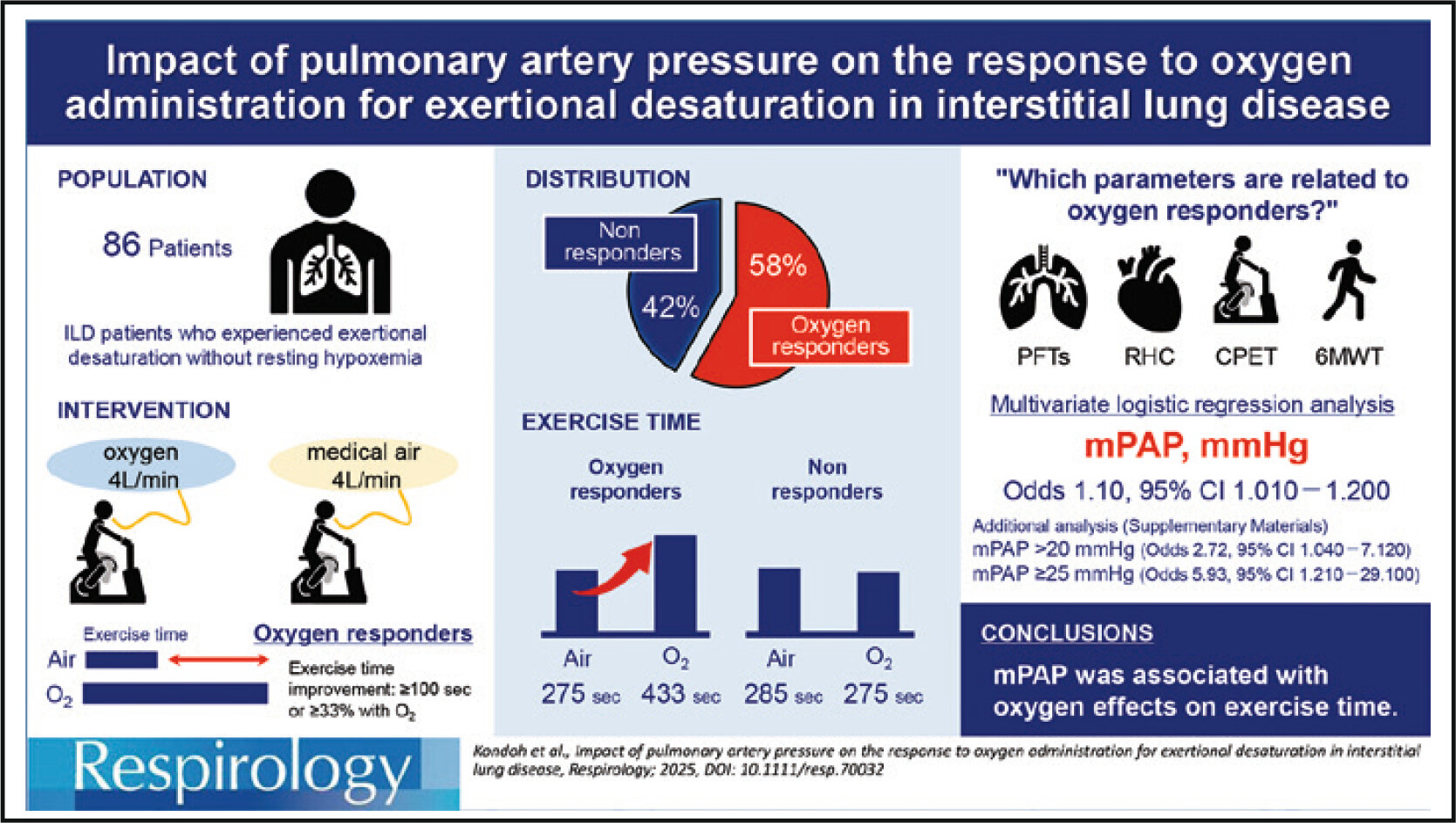
Patients with progressive ILD often experience exertional desaturation without resting hypoxemia. Among 86 ILD patients, 58.1% responded to oxygen therapy, with these patients showing higher mPAP and differences in cardiovascular and gas exchange parameters. Logistic regression identified mPAP > 20 mmHg as a possible biomarker predicting the response to oxygen therapy.
Paediatric Lung Disease
Clinical Presentation and Diagnostic Evaluation of Vaping Related Lung Injury in Youth
- Pages: 671-677
- First Published: 26 March 2025
FORUM AND DEBATE
Respirology Column
Correspondence
Fixed CPAP at 10 cmH2O for OSA: A One-Size-Fits-All Approach?
- Pages: 680-681
- First Published: 23 May 2025
See related article
Response to “Fixed CPAP at 10 cmH2O for OSA: A One-Size-Fits-All Approach?”
- Pages: 682-683
- First Published: 23 May 2025
See related article












-1652674259.png)

