Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Introducing The Immunology Futures Special Series
Editorial
Immunology Futures: a dialog on our research discipline and careers
- Pages: 672-673
- First Published: 09 October 2022

Immunology Futures is a new articles series for Immunology & Cell Biology. Immunology Futures is designed as a forum to promote dialog with the immunology research community, in particular early-career researchers. The series aims to be a platform for career advice and to elevate the voices of diverse immunologists to provide multiple perspectives on a successful career in immunology.
Future Challenges
Gender inequities in medical research funding is driving an exodus of women from Australian STEMM academia
- Pages: 674-678
- First Published: 24 June 2022
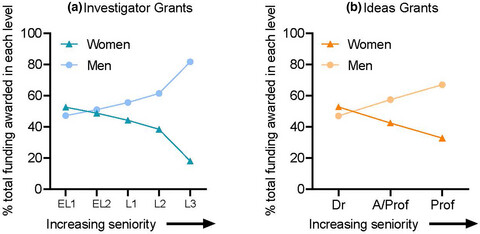
The retention of senior women in STEMM academia is a significant issue worldwide. Our analyses of publicly available funding outcomes from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (NHMRC) have revealed that gender bias is a significant contributor to the lack of retention of women.
A seat at the table is not enough: a perspective on Black women representation in academia
- Pages: 679-682
- First Published: 08 September 2022
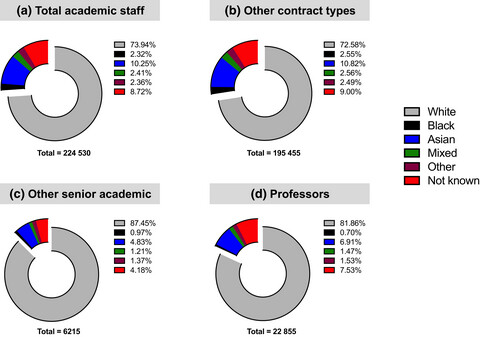
This article is a personal perspective on the double-dose effect of racism and sexism on Black females within the academic system. I present statistical evidence of the under-representation of this group in academic leadership positions and discuss some factors – systematic and cultural – that have contributed to the low numbers of Black women in academic leadership. The detrimental impact of this under-representation is supported by anecdotes from other Black women in academia. Finally, I propose some practical solutions to increase the representation of Black women in academia through the proactive inclusion of Black women in the design of frameworks and policies targeted to improve racial and gender-based inequality.
Rising Immunology Hubs
Pathways To Success
Training the next generation of Sudanese immunologists: a case for mentorship
- Pages: 687-690
- First Published: 15 September 2022

Lack of well-trained Sudanese immunologists hampers the ability of next generation of Sudanese students to get quality immunology training. By narrating my personal story, I highlight the challenges faced by students at home and argue for the importance of mentorship in helping them realize their dreams.
Original Articles
A novel ZsGreen knock-in melanoma cell line reveals the function of CD11b in tumor phagocytosis
- Pages: 691-704
- First Published: 18 July 2022
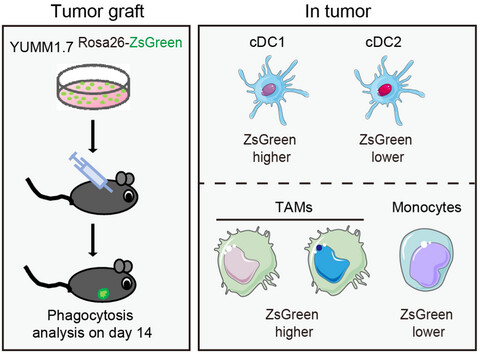
In this study, we developed a novel tool for assessment of tumor phagocytosis in vivo by knock-in expression of ZsGreen in YUMM1.7 melanoma cells. Our results showed that XCR1+ dendritic cells efficiently engulfed and trafficked tumor antigens and we also determined that a point mutation of CD11b lowering its surface expression was not affecting macrophagic phagocytosis.
CD137L and CD4 T cells limit BCL6-expressing pre-germinal center B cell expansion and BCL6-driven B cell malignancy
- Pages: 705-717
- First Published: 02 August 2022
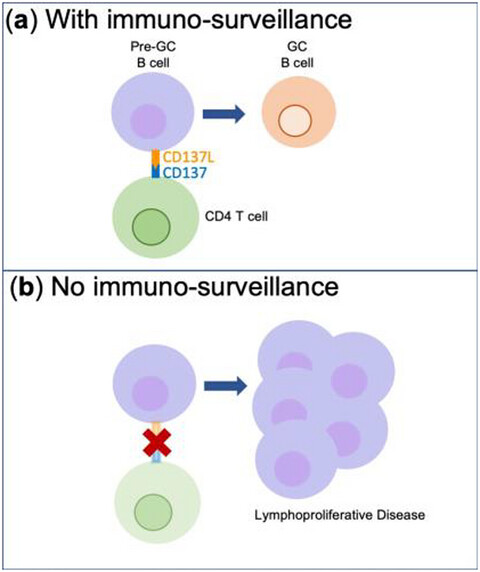
The mechanisms of immuno-surveillance in BCL6-driven B cell malignancy are poorly understood. In this study, we found that the CD137 ligand-mediated signaling pathway and CD4 T cells acted as additional layers in immuno-surveillance against BCL6-driven B cell malignancy by limiting the expansion of activated, pre-germinal center (GC) B cells.
METTL3 inhibition reduces N6-methyladenosine levels and prevents allogeneic CD4+ T-cell responses
- Pages: 718-730
- First Published: 25 August 2022
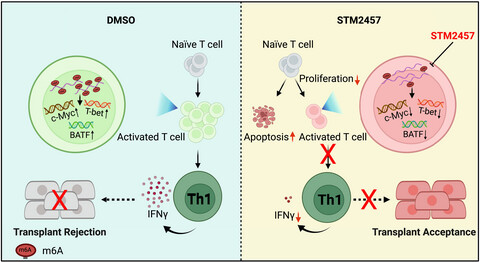
In this study, we found that STM2457 treatment reduced the levels of m6A RNA methylation, inhibited cell proliferation, induced G0 phase cell cycle arrest, promoted cell apoptosis and impaired effector differentiation of alloreactive TEa cells in response to alloantigen stimulation. The attenuated allogeneic T-cell responses were associated with diminished expression levels of key transcription factors (e.g. T-bet, c-Myc) that control the T-cell effector program. Therefore, METTL3 inhibition reduces the levels of m6A RNA methylation and inhibits allogeneic CD4+ T-cell responses.
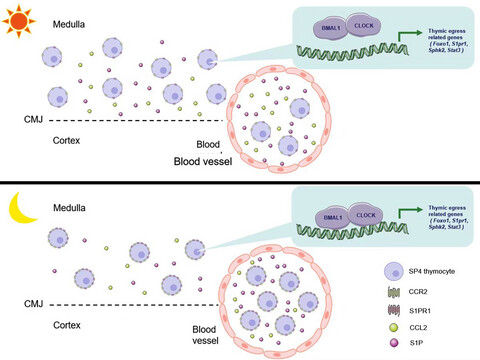
The circadian clock sets a spatial–temporal window for recent thymic emigrants
- Pages: 731-741
- First Published: 28 August 2022