Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Unveiling New Clinical and Genetic Insights in Ultra-Rare Intellectual Disability Phenotypes: A Study of a Turkish Cohort
- Pages: 373-389
- First Published: 11 December 2024
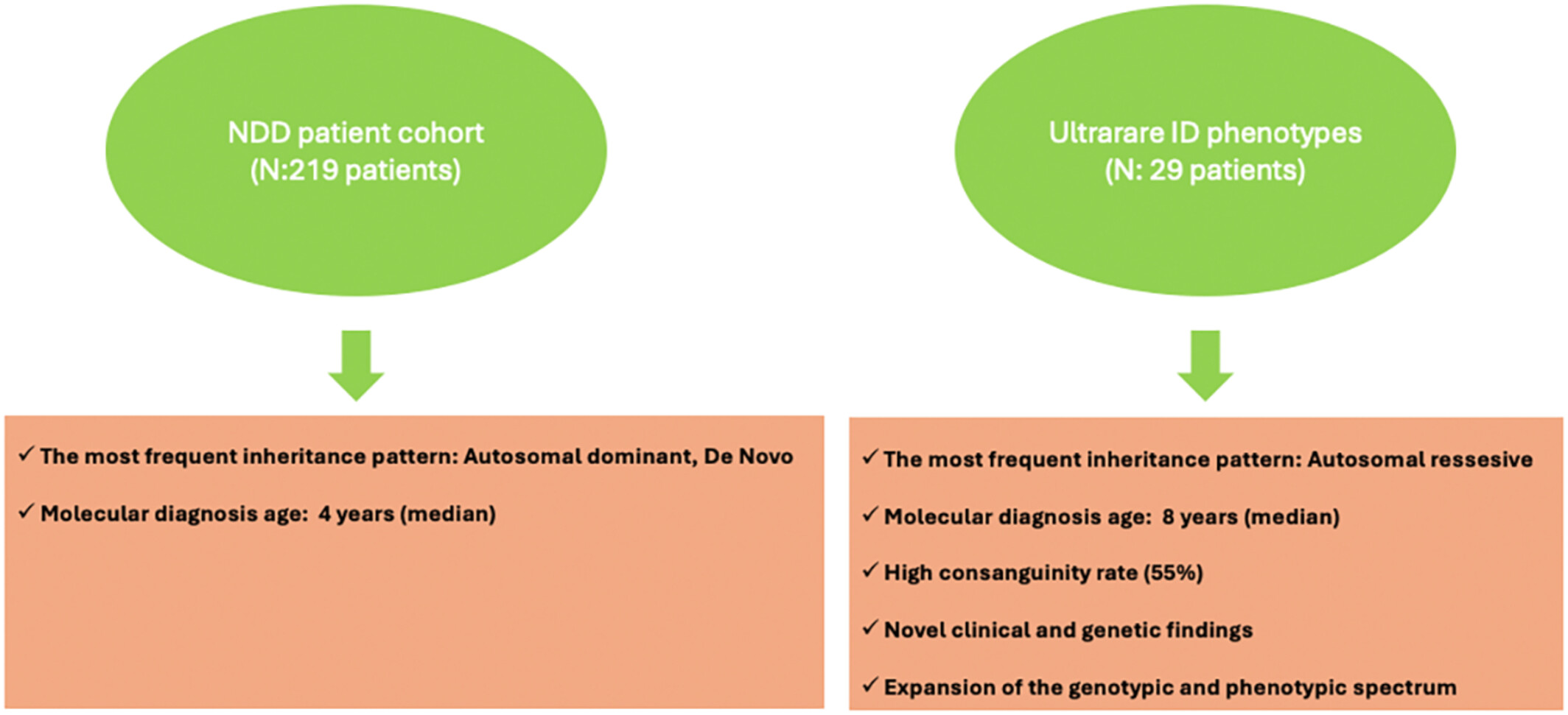
Novel clinical and genetic findings in the present study contribute to a better understanding of the genotypic and phenotypic spectrum. Newly described cases with ultrarare phenotypes help achieve a clearer description of the clinical and genetic manifestations of the syndromes and gain a better understanding of the molecular mechanisms.
Expanding the Clinical and Mutational Spectrum of Biallelic POC1A Variants: Characterization of Four Patients and a Comprehensive Review of POC1A-Related Phenotypes
- Pages: 390-401
- First Published: 11 December 2024
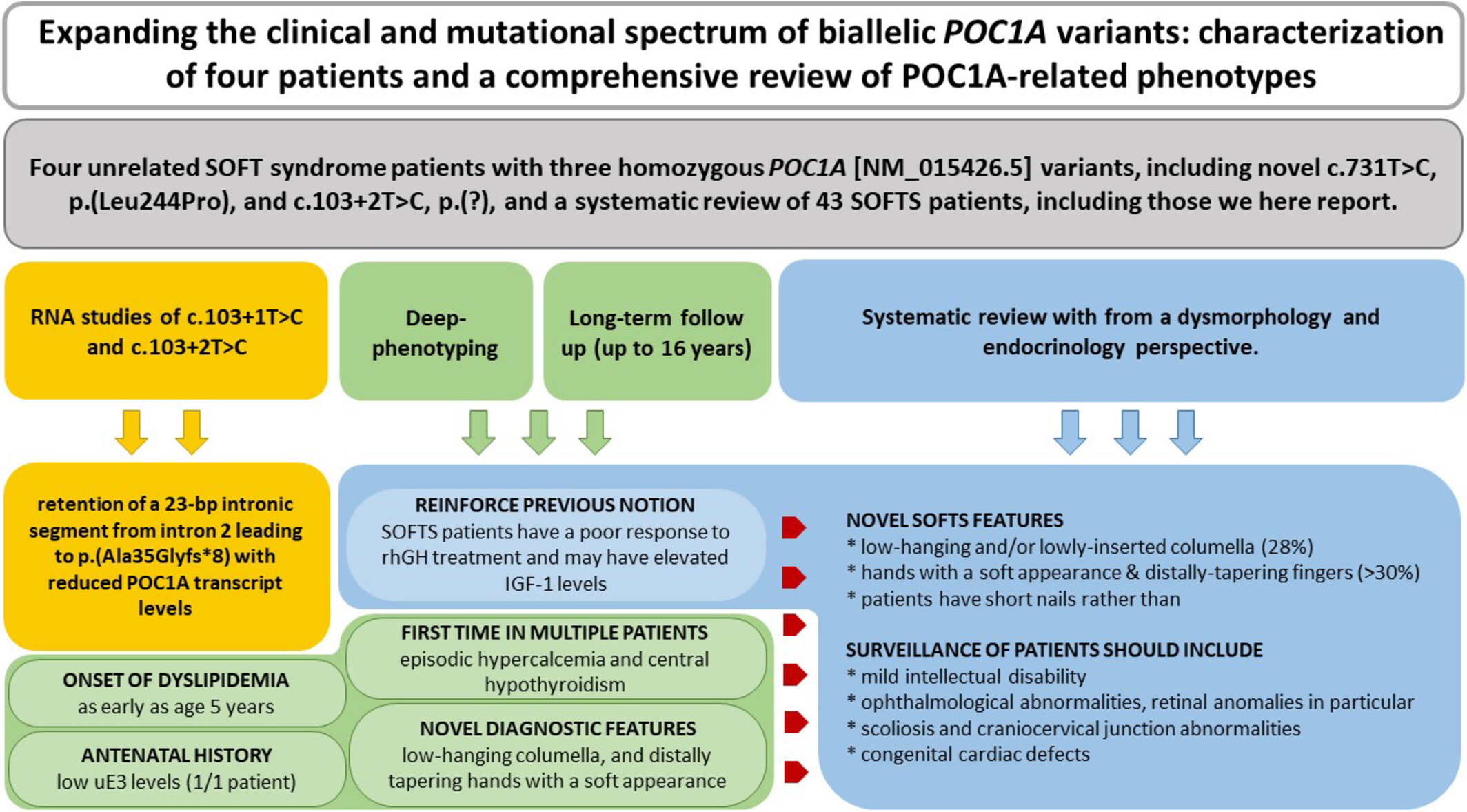
This study expands the POC1A-associated spectrum with four cases, detailing novel endocrine and dysmorphic features, dyslipidemia in the youngest SOFTS case, poor rhGH response, elevated IGF-1, and RNA impacts of two splice variants. A review of 43 cases highlights intellectual disability, craniocervical junction anomalies, and scoliosis, emphasizing comprehensive care needs.
SNV/Indel and CNV Analysis in Trio-WES for Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities: Diagnostic Yield & Cost-Effectiveness
- Pages: 402-412
- First Published: 19 January 2025
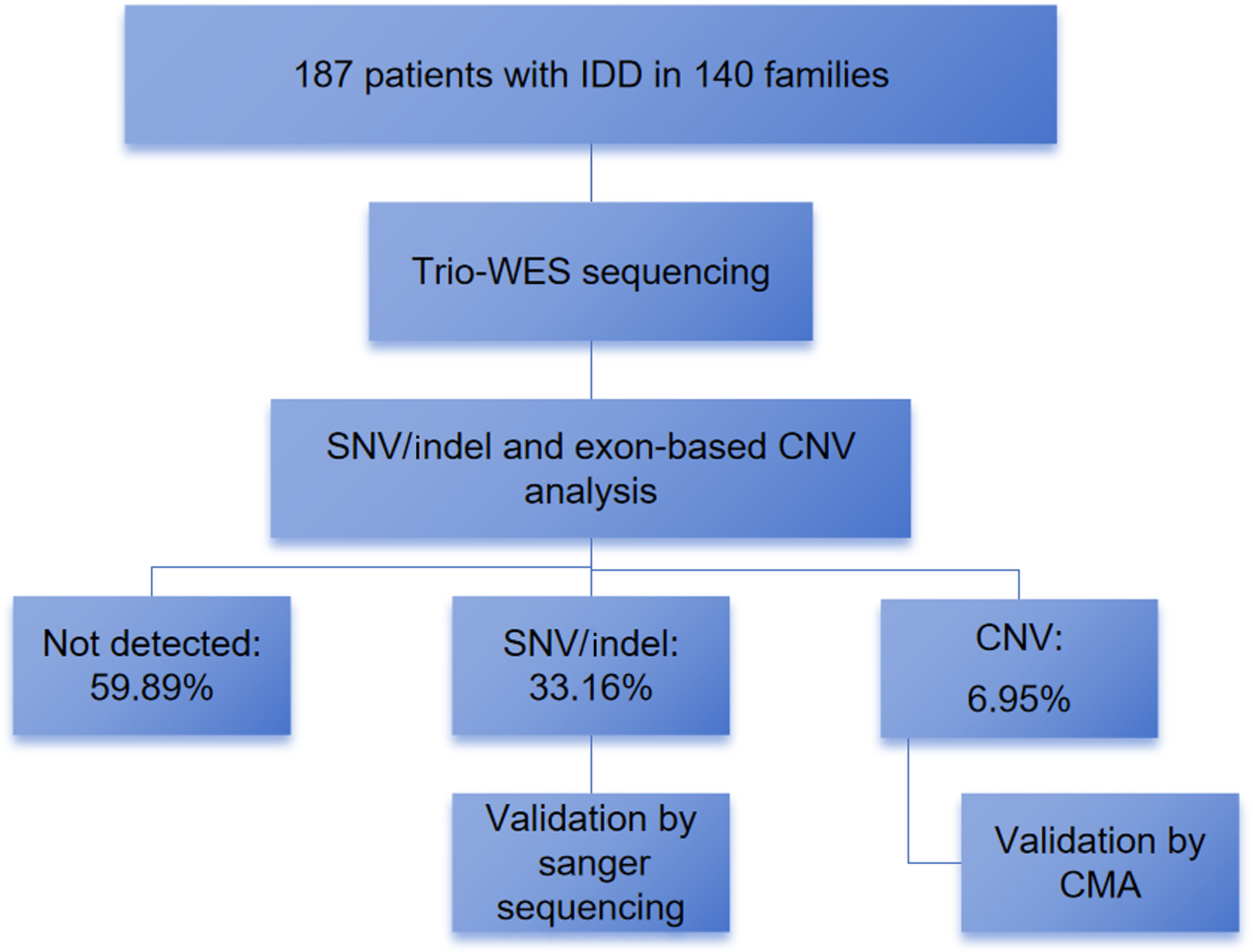
This flow diagram summarized the study of 187 IDD patients from 140 families. Trio-WES was performed, followed by analysis of SNV/Indel and exon-based CNV. The results showed that 59.89% of the patients were not detected, 33.16% detected SNV/Indel, and 6.95% detected CNV. Validation was carried out using Sanger sequencing and/or CMA.
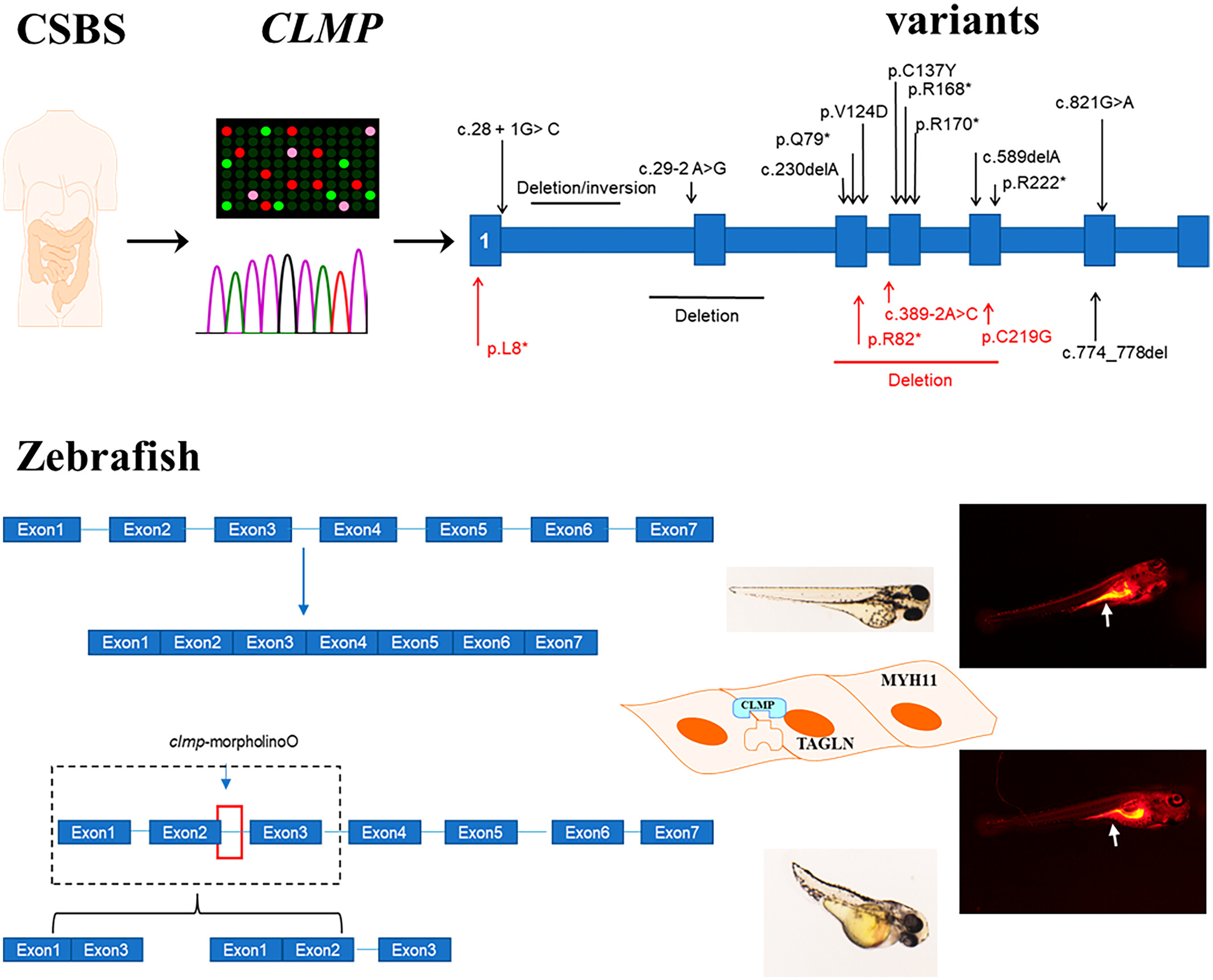
Loss-of-Function of CLMP Is Associated With Congenital Short Bowel Syndrome and Impaired Intestinal Development
- Pages: 413-424
- First Published: 06 January 2025
Exploring the Familial Phenotypic Variability Associated With TTN Truncating Variants in Cardiomyopathies: Variant Spectrum, Genotype–Phenotype Correlation and Consequences in Genetic Counseling
- Pages: 425-433
- First Published: 22 January 2025
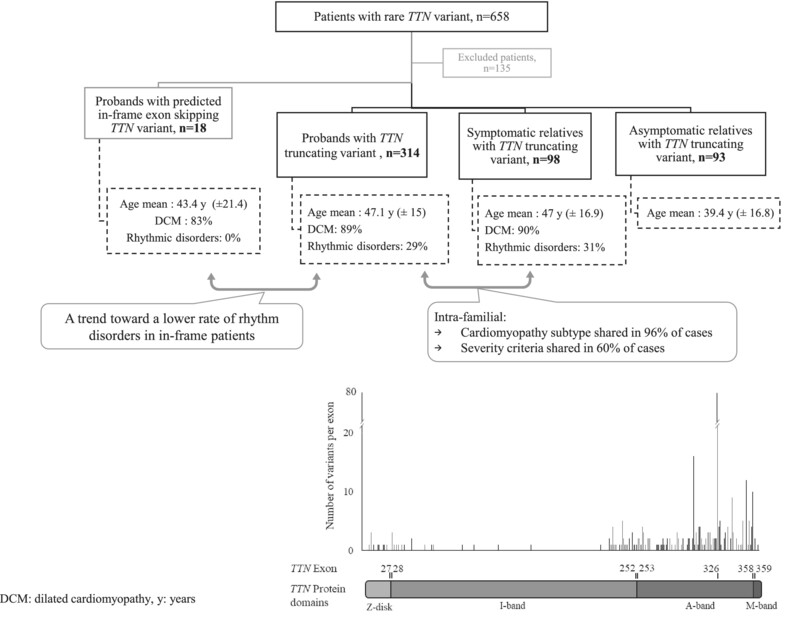
Within a family, the cardiomyopathy phenotype is homogeneous in 96% of cases but the expressivity varies. Patients with predicted in-frame exon skipping presented DCM (84%), but a trend toward a lower rate of rhythmic disorders than TTNtv patients (0% vs. 29% respectively). We extended the genetic spectrum of TTNtv associated with DCM.
SHORT REPORT
Unique Genetic Profiles in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Patients From São Miguel Island (Azores, Portugal)
- Pages: 434-440
- First Published: 28 November 2024
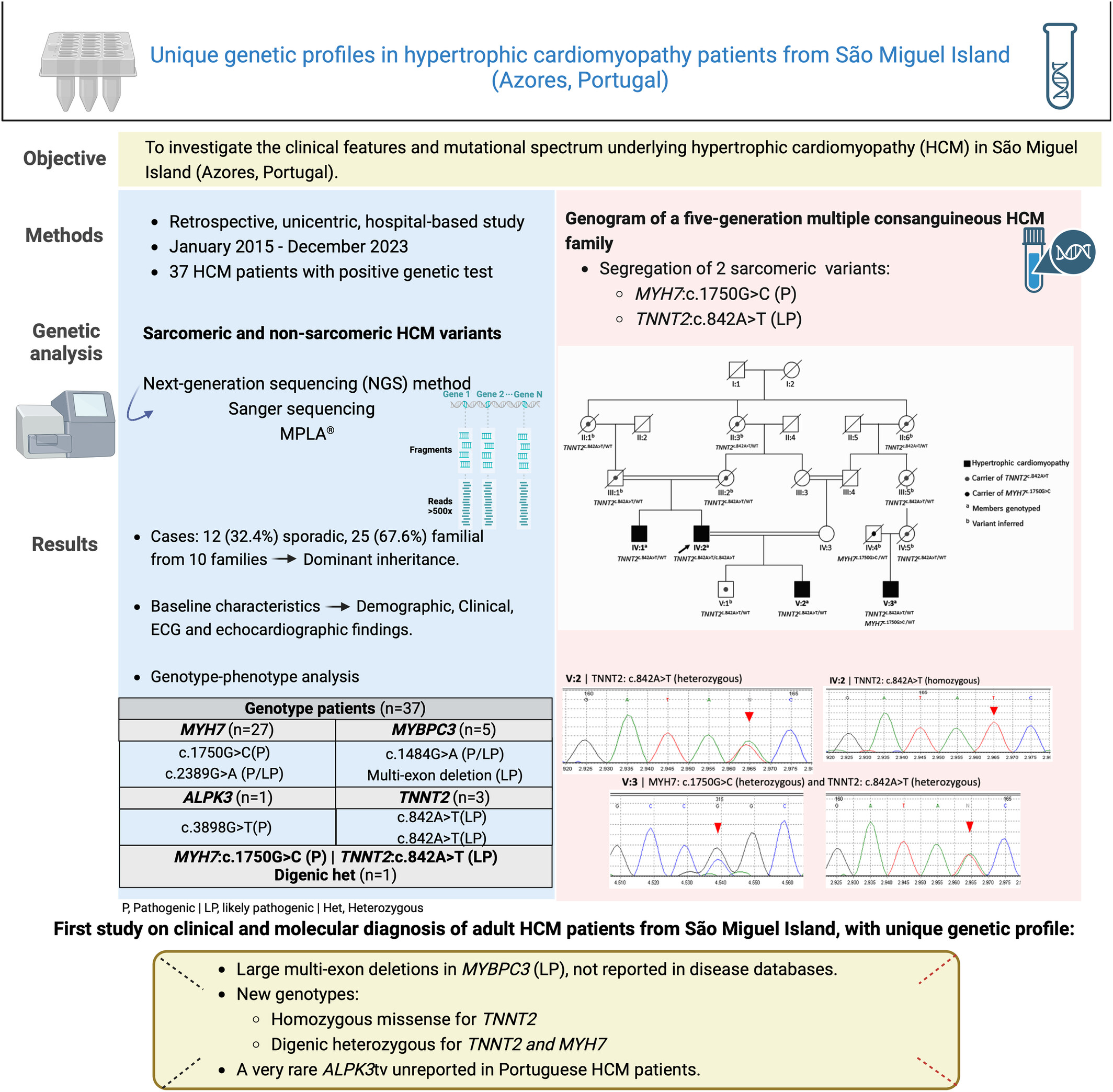
This is the first study to examine the clinical characteristics and molecular diagnosis of adult HCM patients from São Miguel Island. Novel variants and genotypes identified include large multi-exon deletions in MYBPC3, a homozygous missense variant in TNNT2, and a digenic heterozygous variant in TNNT2/MYH7.
Rare Causes and Differential Diagnosis in Patients With Silver-Russell Syndrome
- Pages: 441-445
- First Published: 25 November 2024
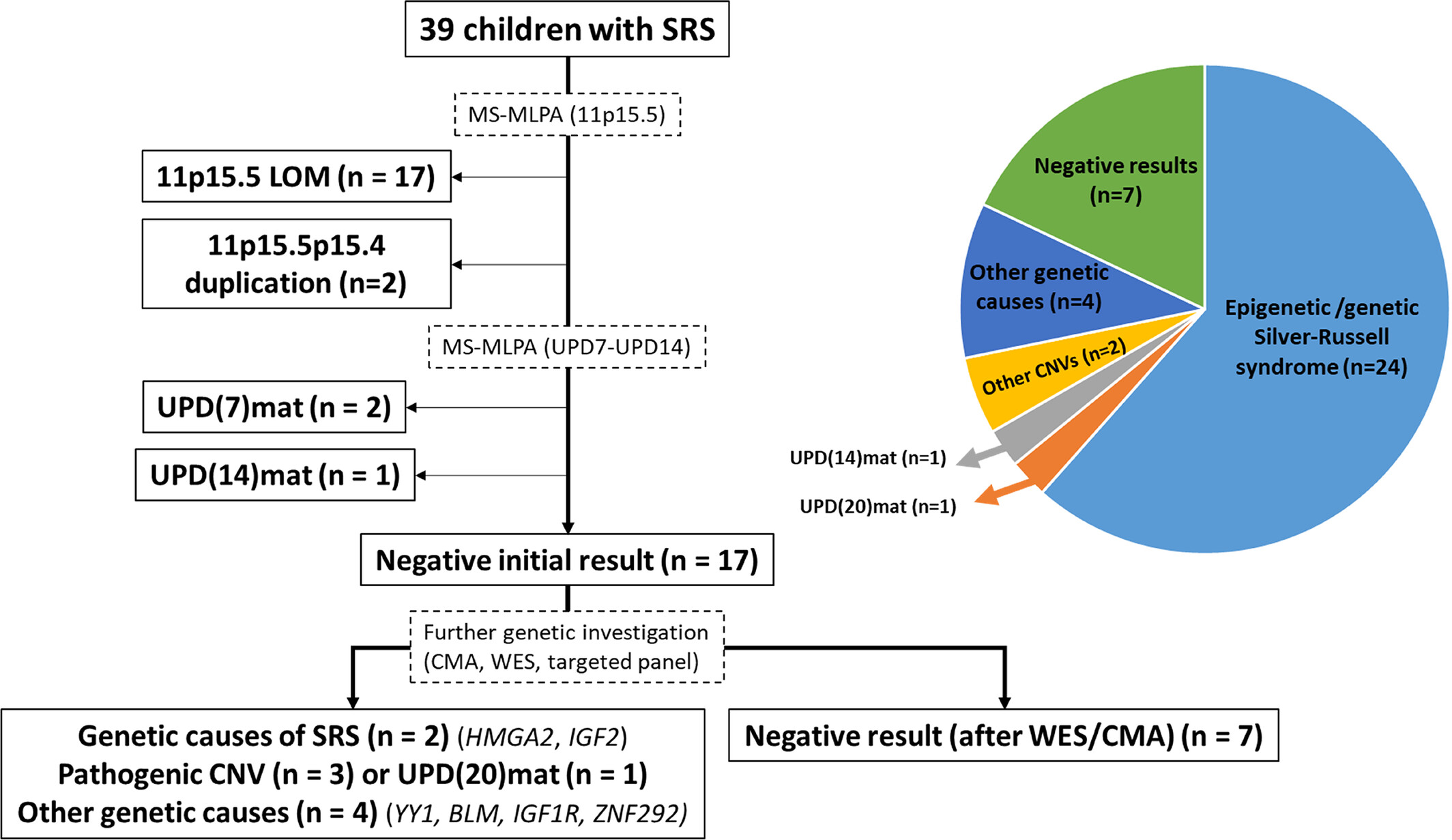
This study describes the molecular investigation of 39 children with clinical suspicion of Silver-Russell syndrome at a tertiary center specialized in growth disorders. The results included differential diagnoses for 8 patients and underscore the importance of establishing a molecular diagnosis in this context to enable adequate management and genetic counseling.
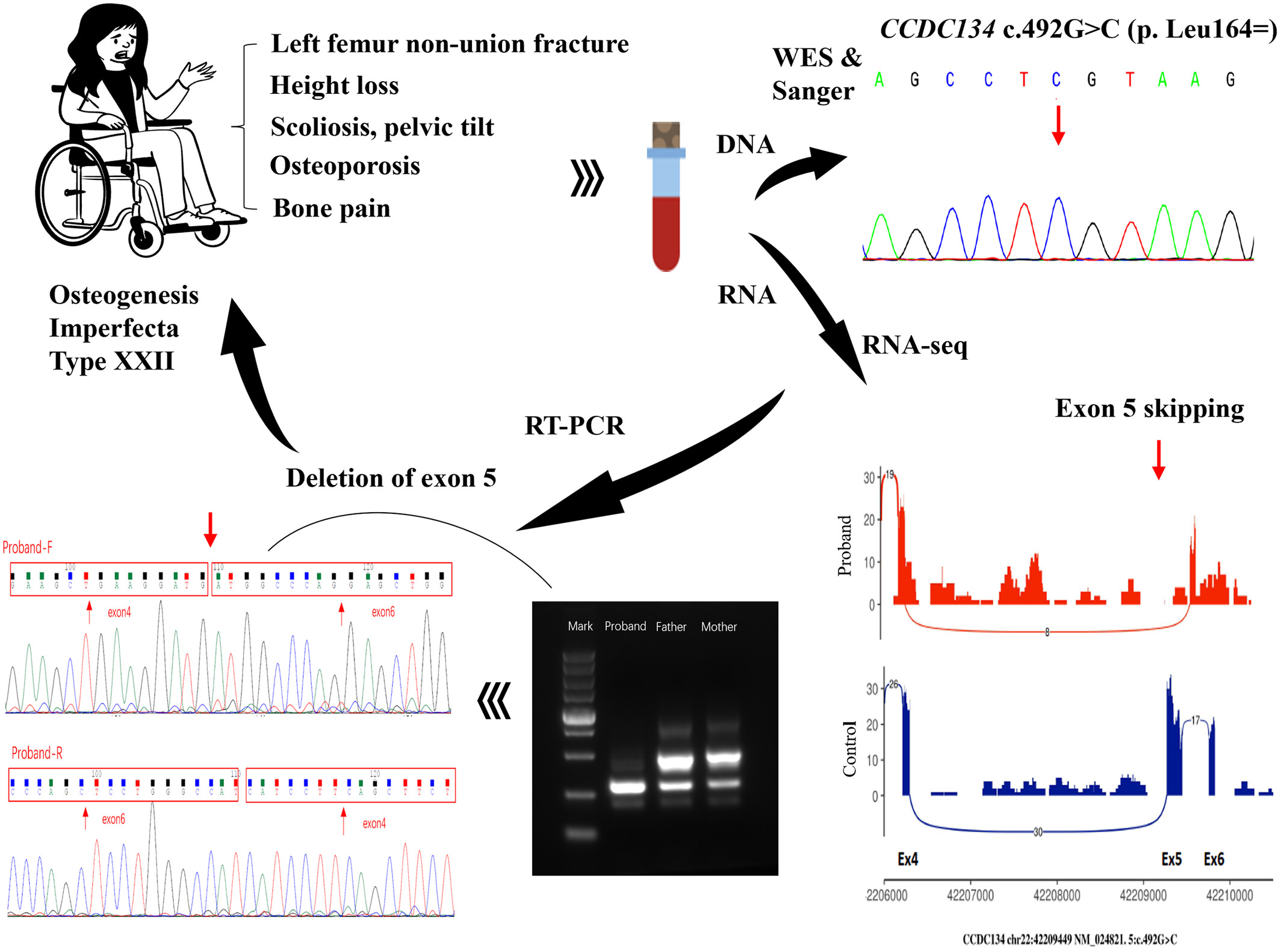
A Novel Homozygous Synonymous Variant in CCDC134 as a Cause of Osteogenesis Imperfecta Type XXII
- Pages: 446-452
- First Published: 02 December 2024
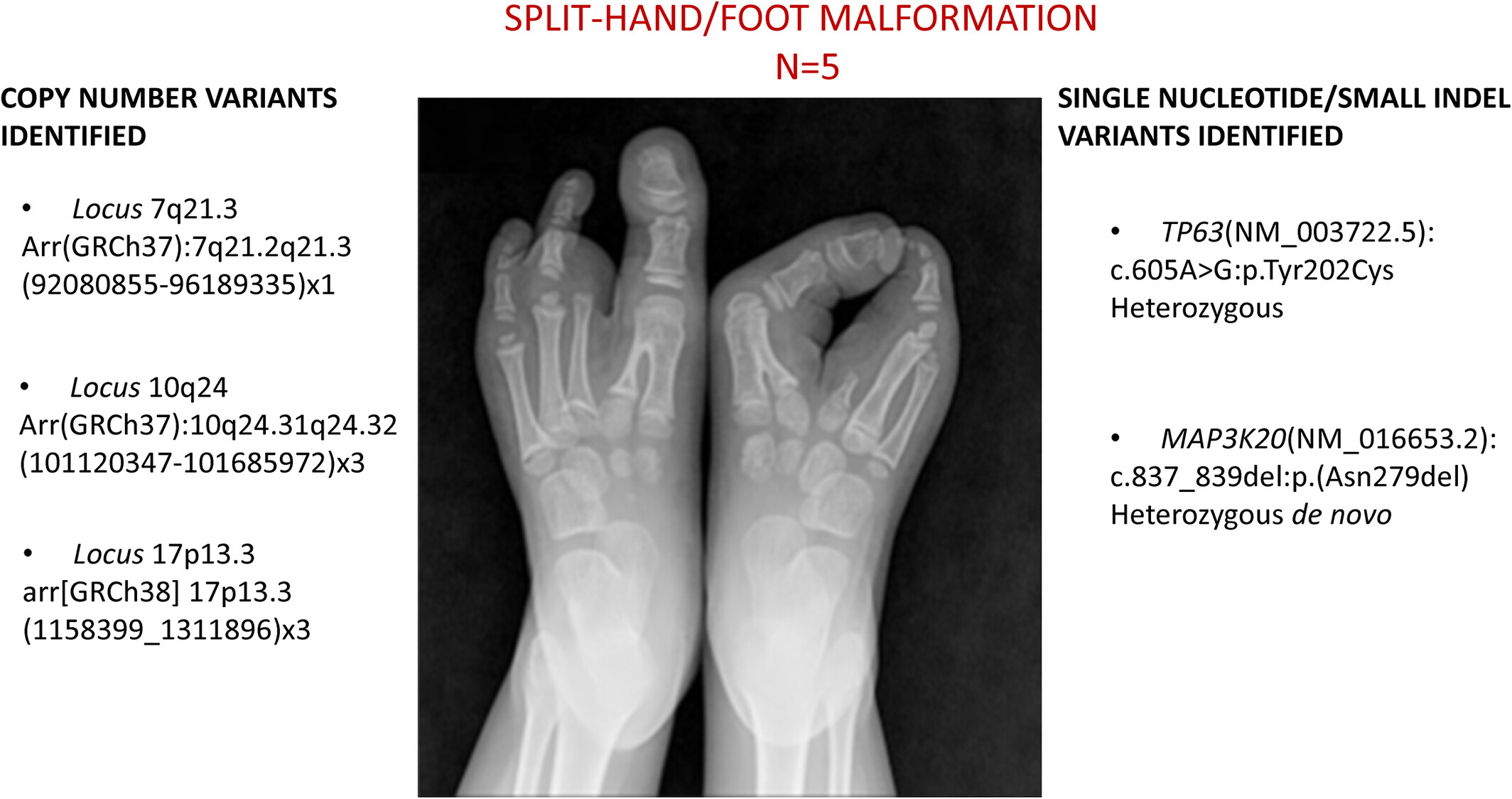
Split Hand-Foot Malformations—Unveiling Unique Molecular Diagnosis From a Brazilian Cohort
- Pages: 453-457
- First Published: 08 December 2024
Comprehensive Analysis of TEK Variants in Patients With Vascular Malformations
- Pages: 458-462
- First Published: 04 December 2024
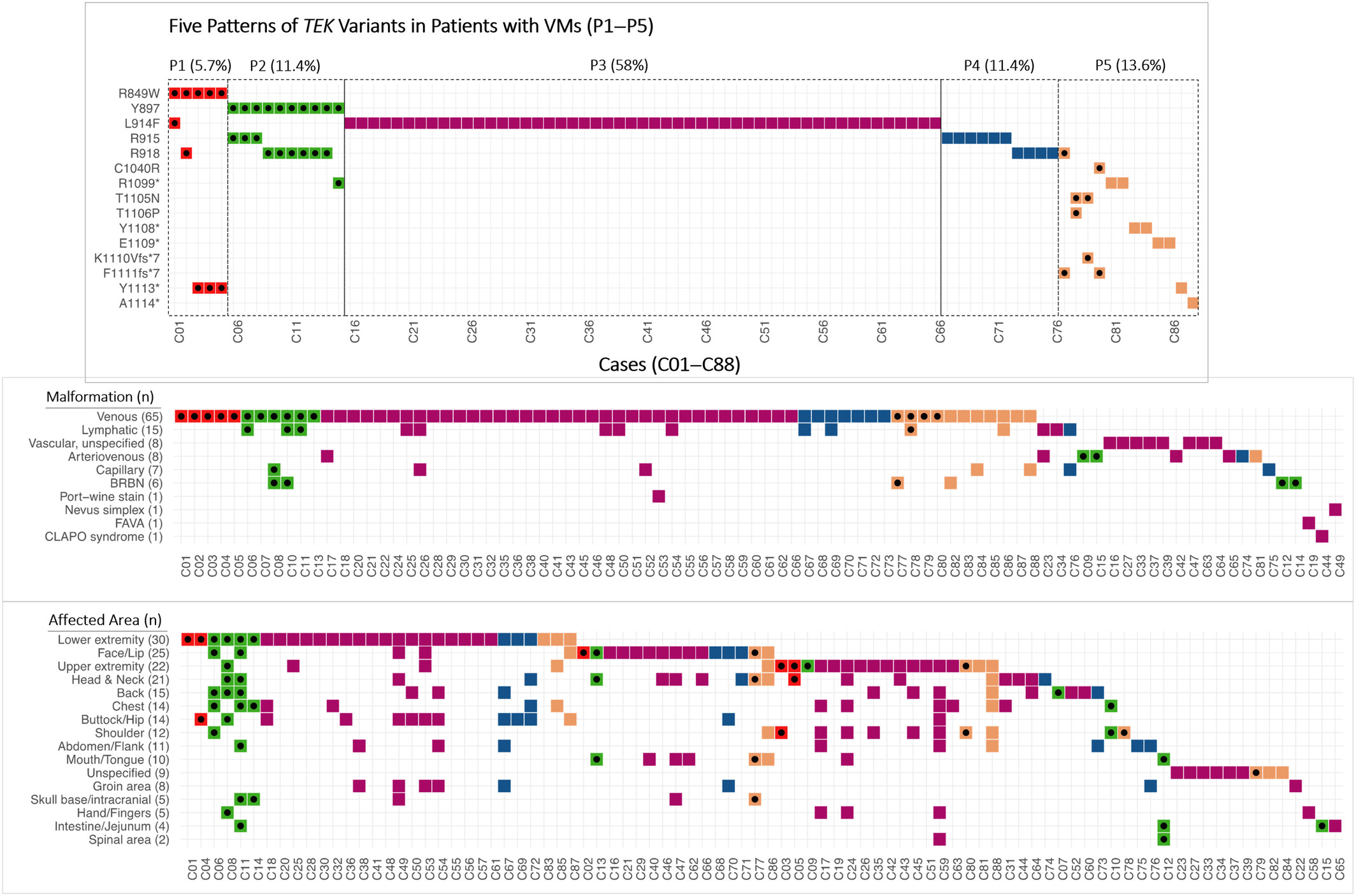
Five patterns of TEK variants (P1–P5) were identified from a retrospective review of 88 VM cases with a total of 107 clinically significant TEK variants. The correlation of clinical features among P1–P5 variant patterns was investigated from two different aspects: the malformation types and the affected anatomical locations.
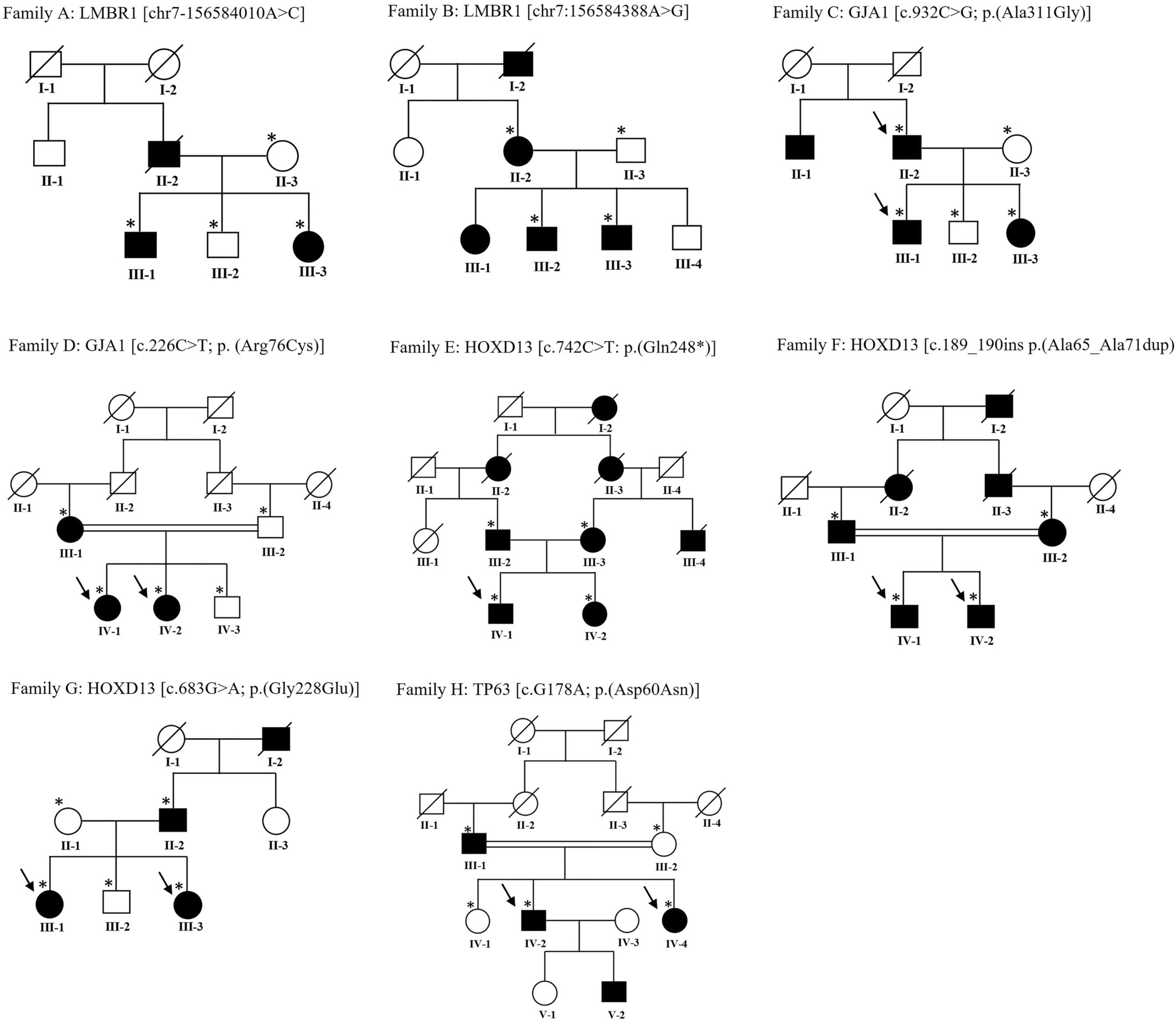
Unraveling the Genetic Basis of Congenital Limb Anomalies in Eight Families
- Pages: 463-468
- First Published: 05 December 2024
Mismatch Repair Proficient Colorectal Adenocarcinoma in Two Patients With Lynch Syndrome
- Pages: 469-474
- First Published: 11 December 2024
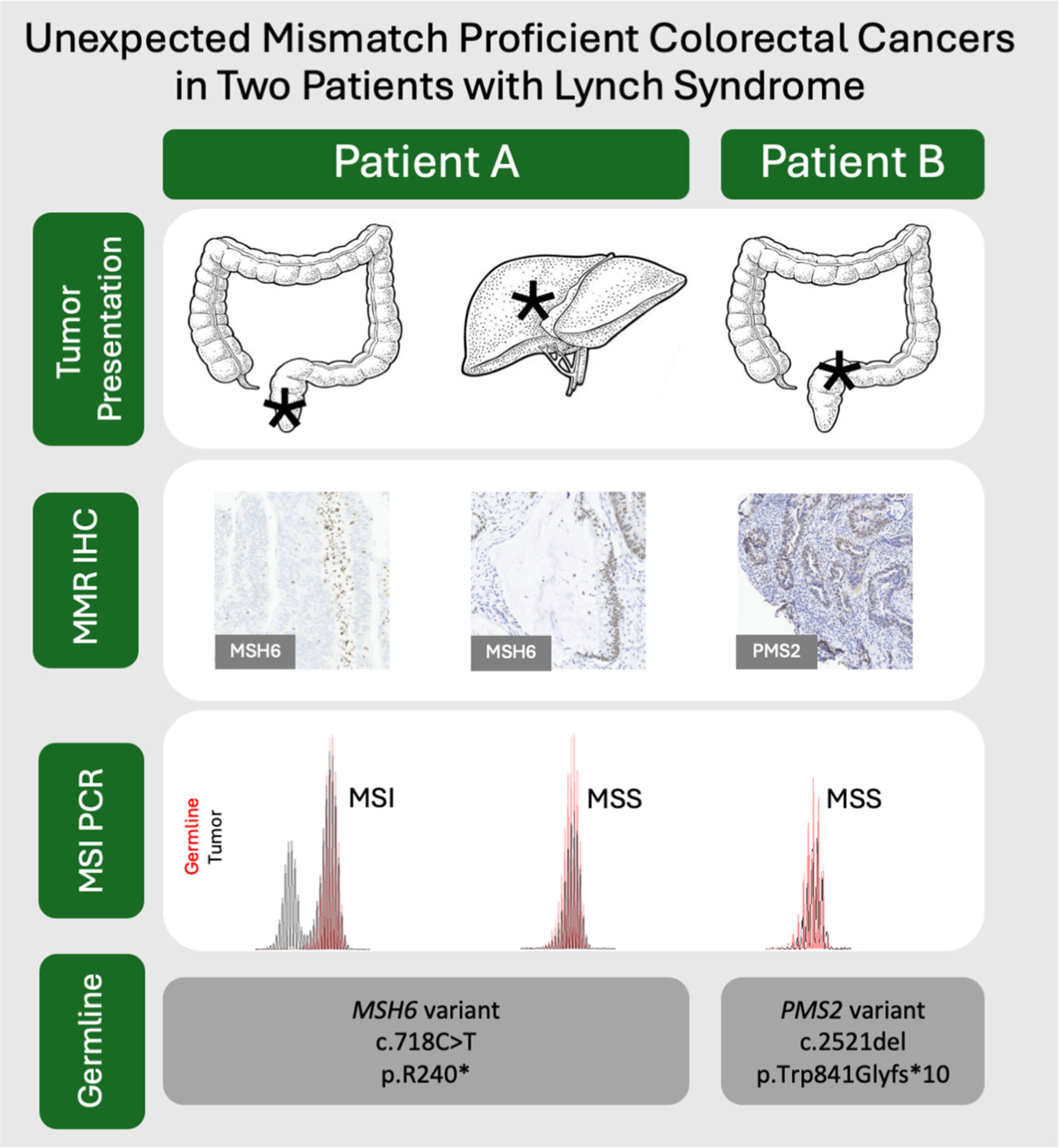
This paper reports two Lynch syndrome (LS) patients with mismatch repair proficient (MMRp) colorectal carcinomas (CRCs), challenging typical diagnostic methods reliant on MMR deficiency (MMRd) and microsatellite instability (MSI). It underscores the importance of comprehensive molecular testing, including germline analysis and reevaluation of MMR status in recurrent or metastatic CRCs.
RESEARCH LETTER
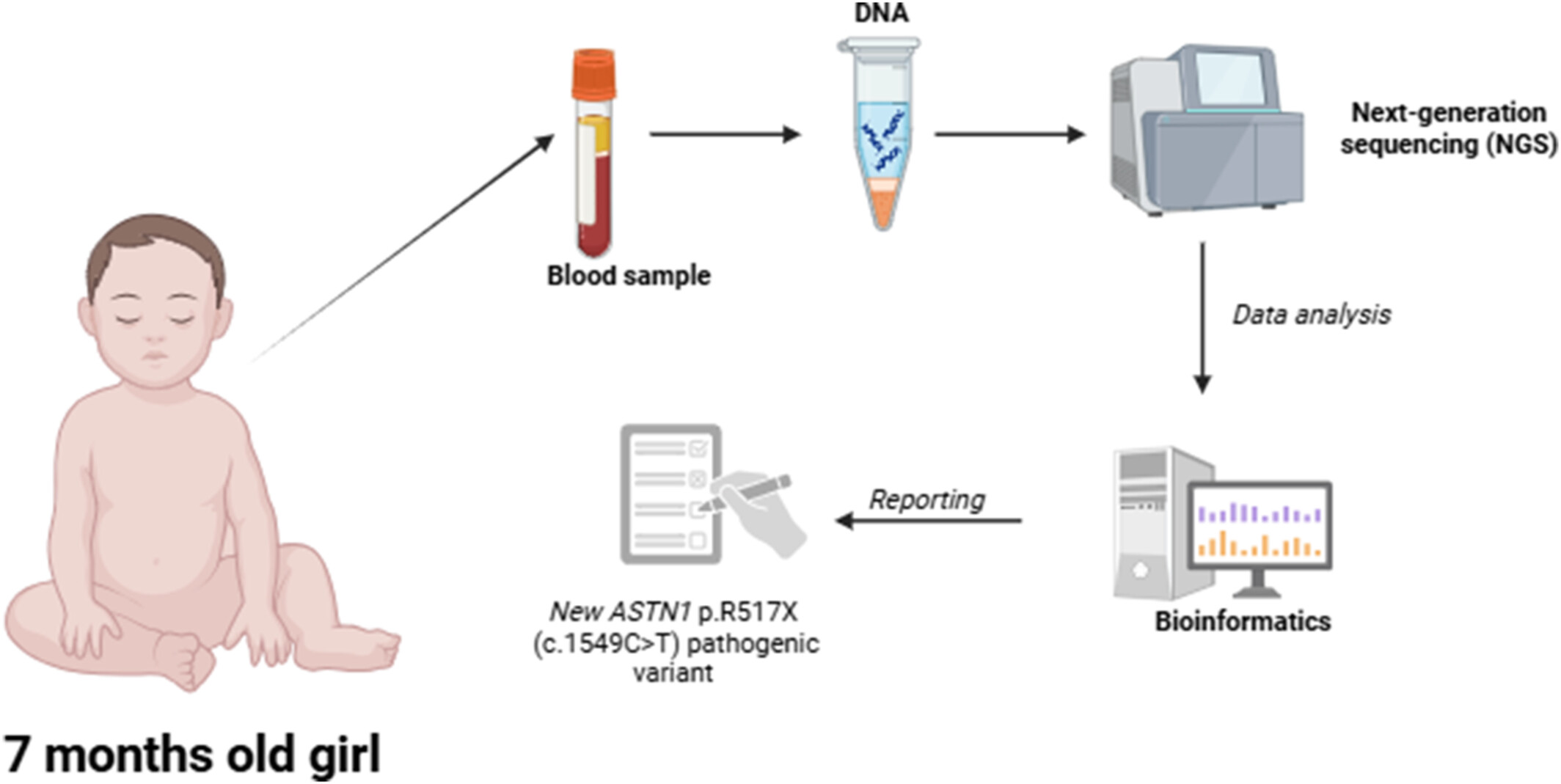
Homozygous ASTN1 Nonsense Variant Linked to Epileptic Encephalopathy: A Detailed Report With Unique Clinical Presentation
- Pages: 475-476
- First Published: 12 December 2024
Biallelic Loss of Function Variant in SEC31A Is Associated With Lethal Neurodevelopmental Disorder, Dysmorphic Features, and Skeletal Defects
- Pages: 477-479
- First Published: 26 December 2024
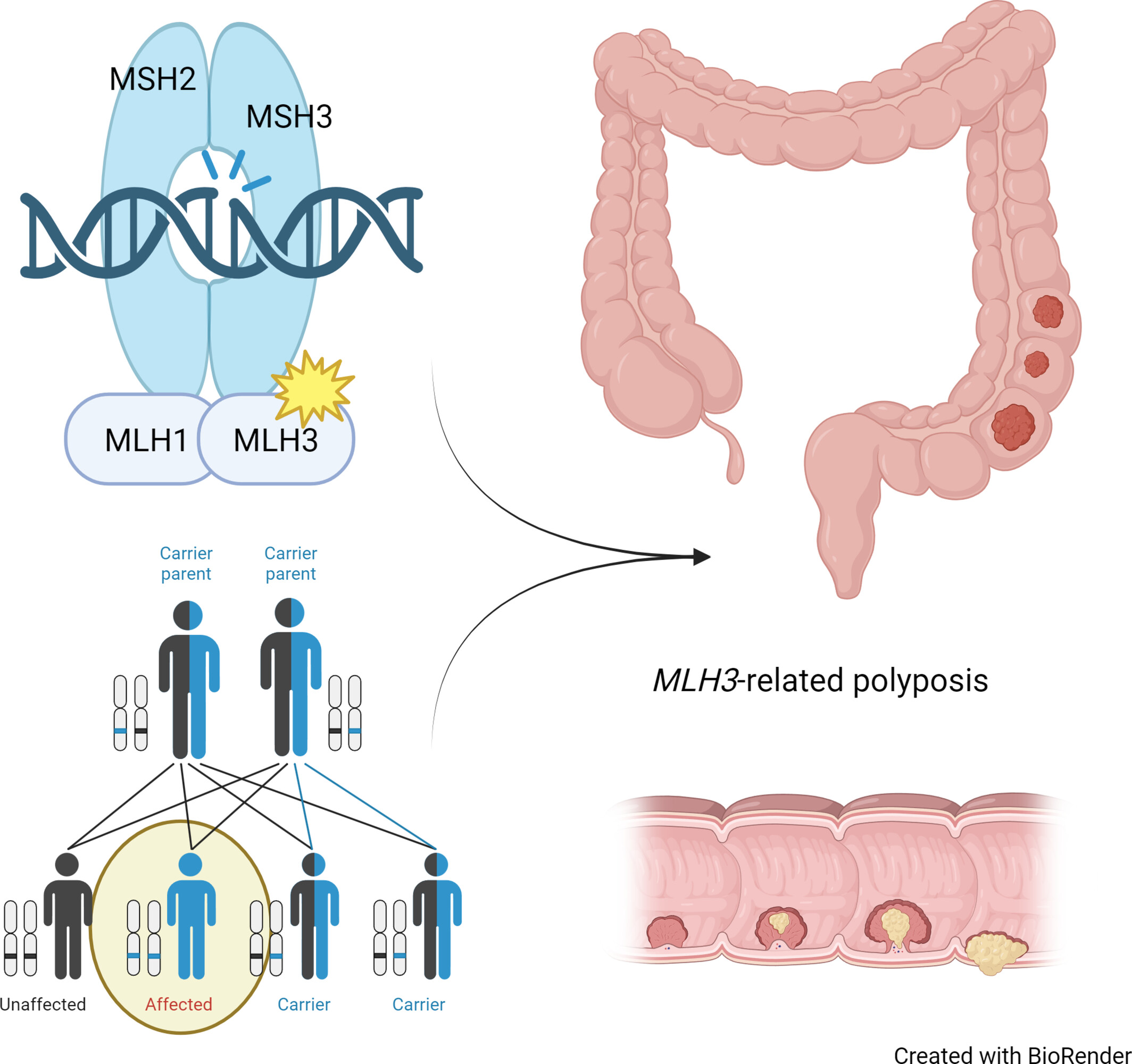
A Novel Case of Biallelic MLH3 Variants in a Patient With Rectal Cancer and Polyps
- Pages: 480-482
- First Published: 09 January 2025