Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
REVIEWS
Alcohol use and grey matter structure: Disentangling predispositional and causal contributions in human studies
- First Published: 29 August 2023
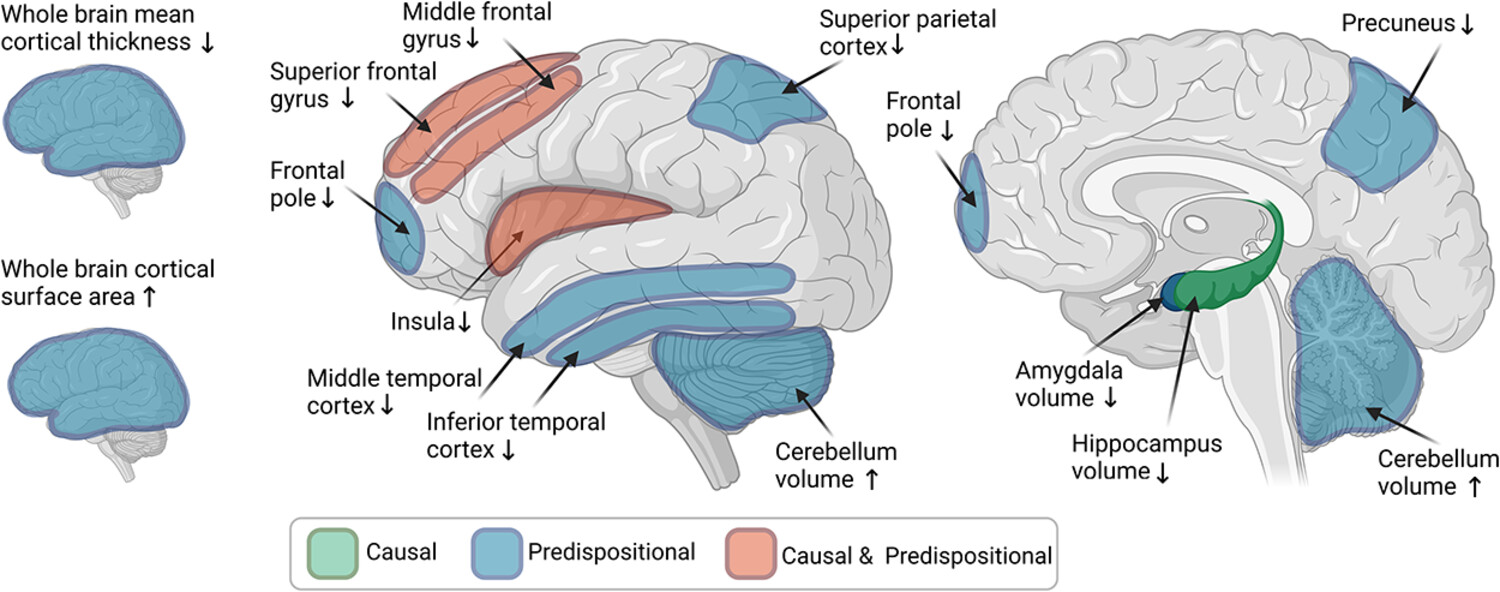
Here, we review evidence from human studies with designs (i.e., family-based, genomic and longitudinal) that allow them to assess the plausibility that grey matter correlates reflect predispositional risk factors and/or causal consequences of alcohol involvement. These studies provide convergent evidence that neural correlates of alcohol involvement largely reflect predisposing risk factors, with some evidence for potential alcohol-induced atrophy.
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Prelimbic cortex dynorphin/κ opioid receptor system modulates methamphetamine-induced cognitive impairment
- First Published: 23 August 2023
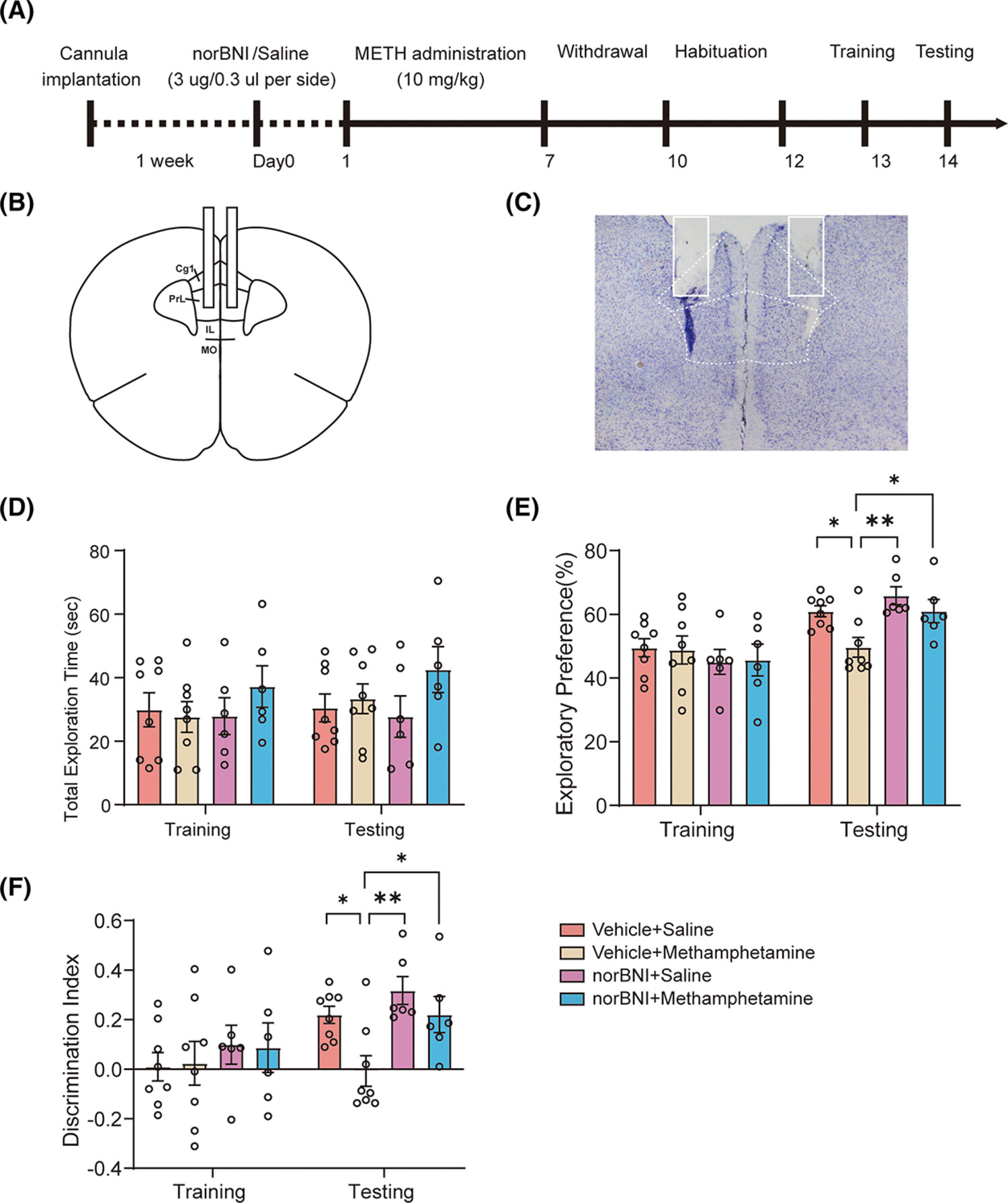
Blockade of κ opioid receptor (KOR) prevented METH-induced cognitive impairment. Chronic METH administration increased dynorphin and KOR mRNA level in prelimbic cortex (PL) but not infralimbic cortex (IL). KOR antagonist injections into PL but not IL attenuated cognitive impairment after METH exposure.
The Cdk5 inhibitor β-butyrolactone impairs reconsolidation of heroin-associated memory in the rat basolateral amygdala
- First Published: 18 August 2023
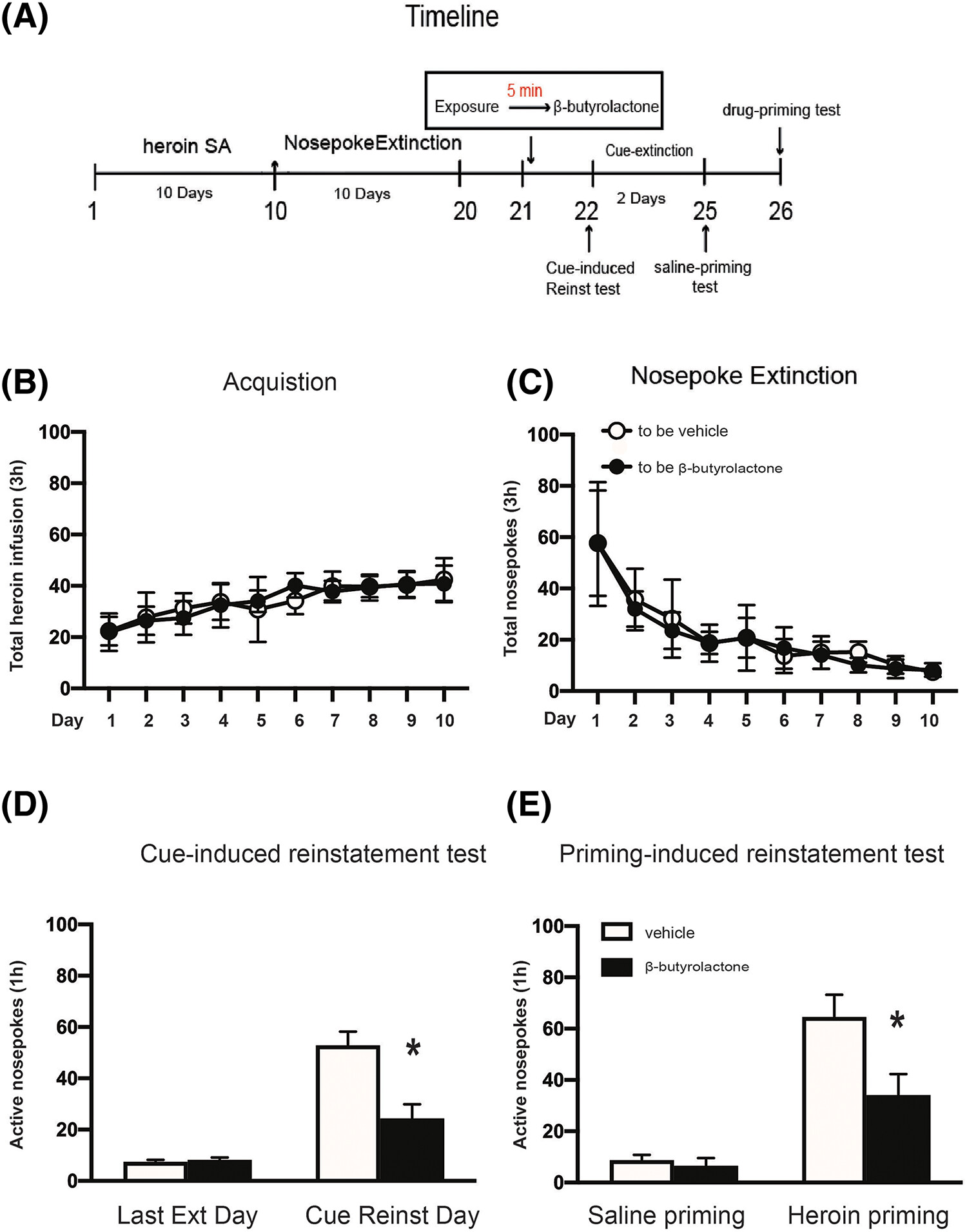
Intra-BLA infusion of β-butyrolactone immediately after memory retrieval effectively reduces cue- and heroin-induced reinstatement, with the observed effects persisting significantly for a minimum of 28 days. Inhibition of Cdk5 in the BLA for a duration of 6 h following the memory retrieval trial, or without it altogether, had no discernible impact. Cdk5 inhibition in the BLA can disrupt the reconsolidation of heroin-associated memory, thereby diminishing the reinstatement of heroin-seeking behavior.
Combined effects of methadone and quetiapine on respiratory rate, haemodynamic variables, and temperature in conscious rats
- First Published: 18 August 2023
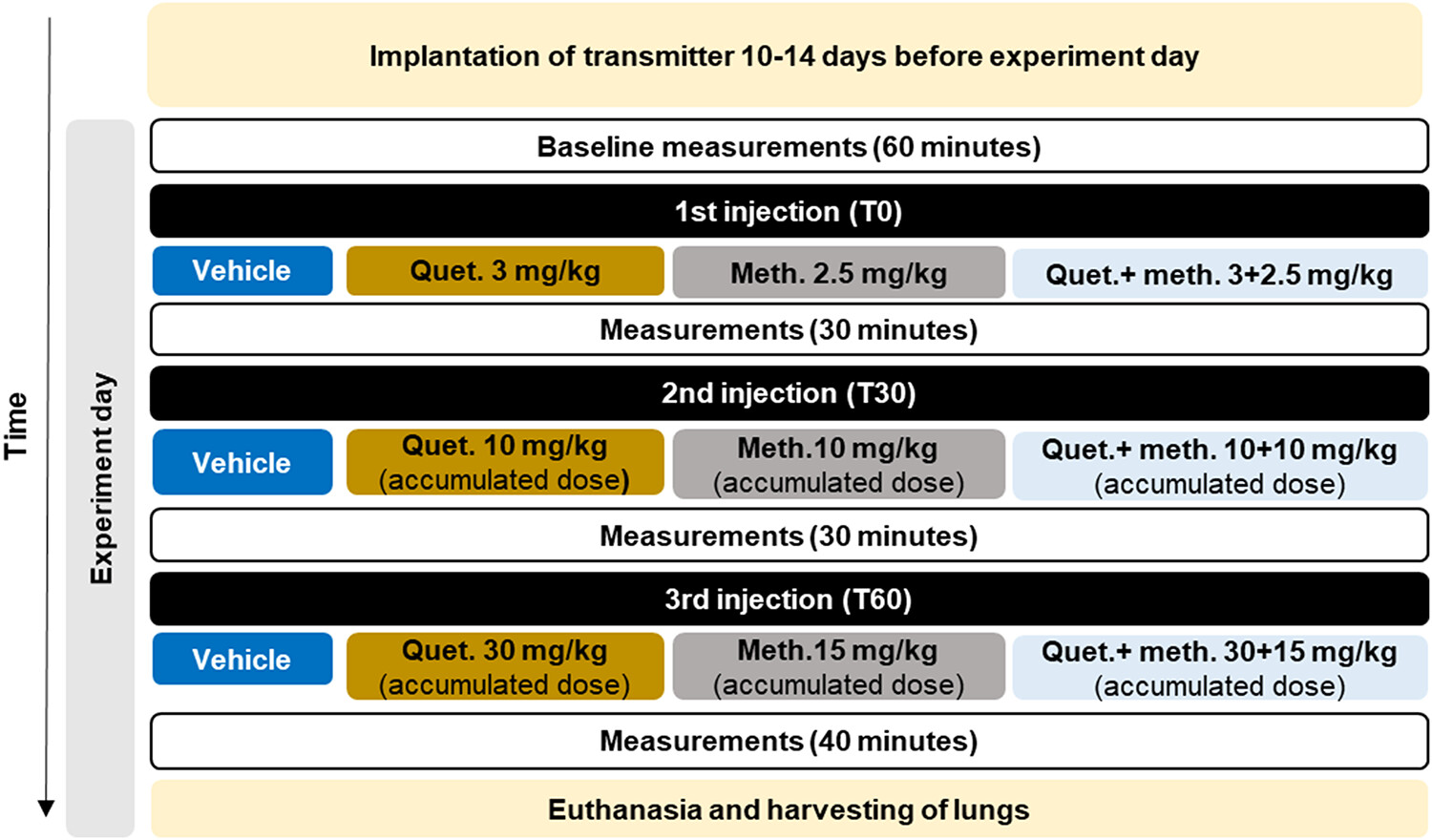
As it is unclear whether quetiapine increases the risk of fatal methadone poisoning, the combined effects of three accumulated doses of methadone, and quetiapine was investigated in conscious freely moving rats using telemetry and compared to vehicle and treatment with each drug alone. No additive effects on respiratory rate or haemodynamic variables were observed. However, the two drugs seemed to lower body temperature synergistically. We suggest studying this finding further in human settings.
A multivariate approach to understanding the genetic overlap between externalizing phenotypes and substance use disorders
- First Published: 23 August 2023
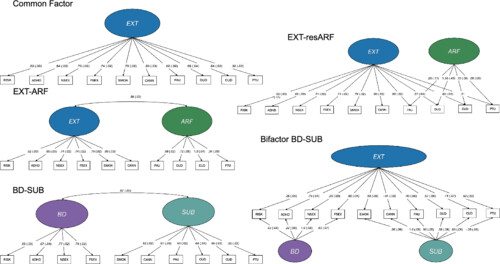
In this study, we investigated the shared genetic architecture between externalizing and addiction risks. We explored alternative structural models that capture their covariation, examined their correlations with external traits and quantified their degree of polygenic overlap. Overall, we found that externalizing and addiction risks share a substantial proportion of their genetic influences in common while also retaining meaningful unique genetic variance.
Gegen-Qinlian decoction—A traditional Chinese medicine formula—Alleviates methamphetamine withdrawal induced anxiety by targeting GABAergic interneuron-pyramidal neuron pathway in mPFC
- First Published: 30 July 2023
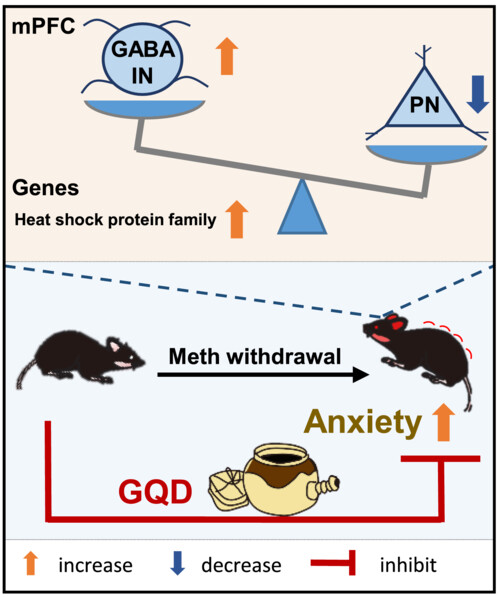
GQD treatment during Meth withdrawal period efficiently alleviates anxiety, partially through regulating the local GABA IN-PN pathway and transcriptomic profile of mPFC. The present study confirms that TCM, such as GQD, will be a desirable therapeutic approach in the treatment of drug withdrawal symptoms.
Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol modulates pain sensitivity among persons receiving opioid agonist therapy for opioid use disorder: A within-subject, randomized, placebo-controlled laboratory study
- First Published: 30 July 2023
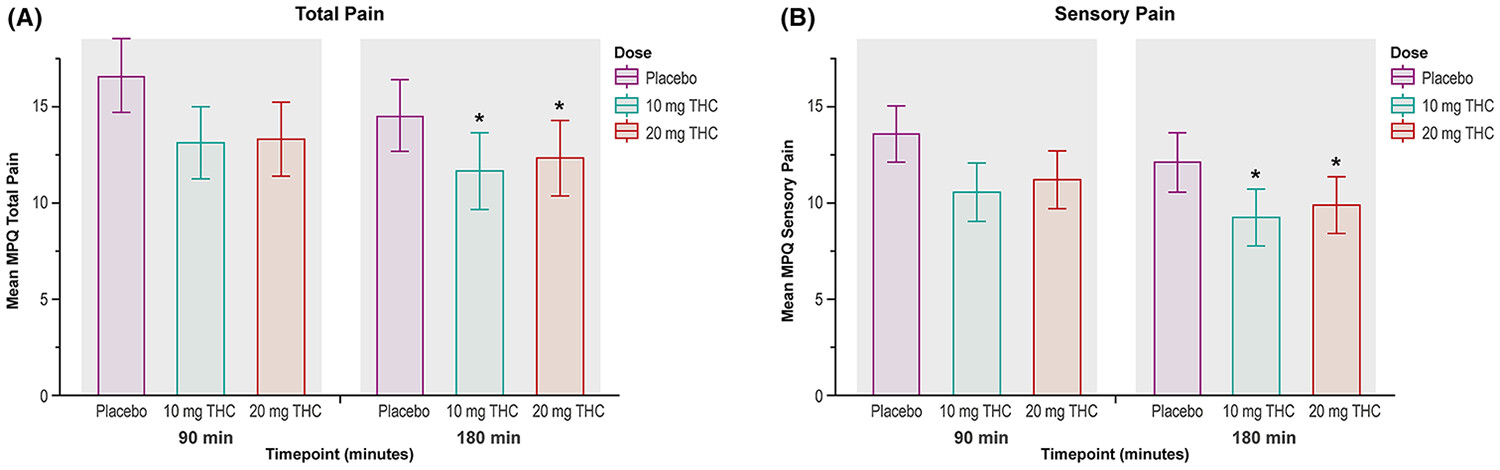
This randomized, placebo-controlled, human laboratory study examined the acute effects of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) in individuals receiving methadone therapy for opioid use disorder (OUD). The 25 participants were given varying oral doses of THC and placebo, with measures taken for pain sensitivity, abuse potential, cognitive performance and physiological effects. The study found that lower doses of THC provided greater subjective pain relief without significant evidence of abuse potential, highlighting a potential avenue for future studies on pain management in OUD therapy.
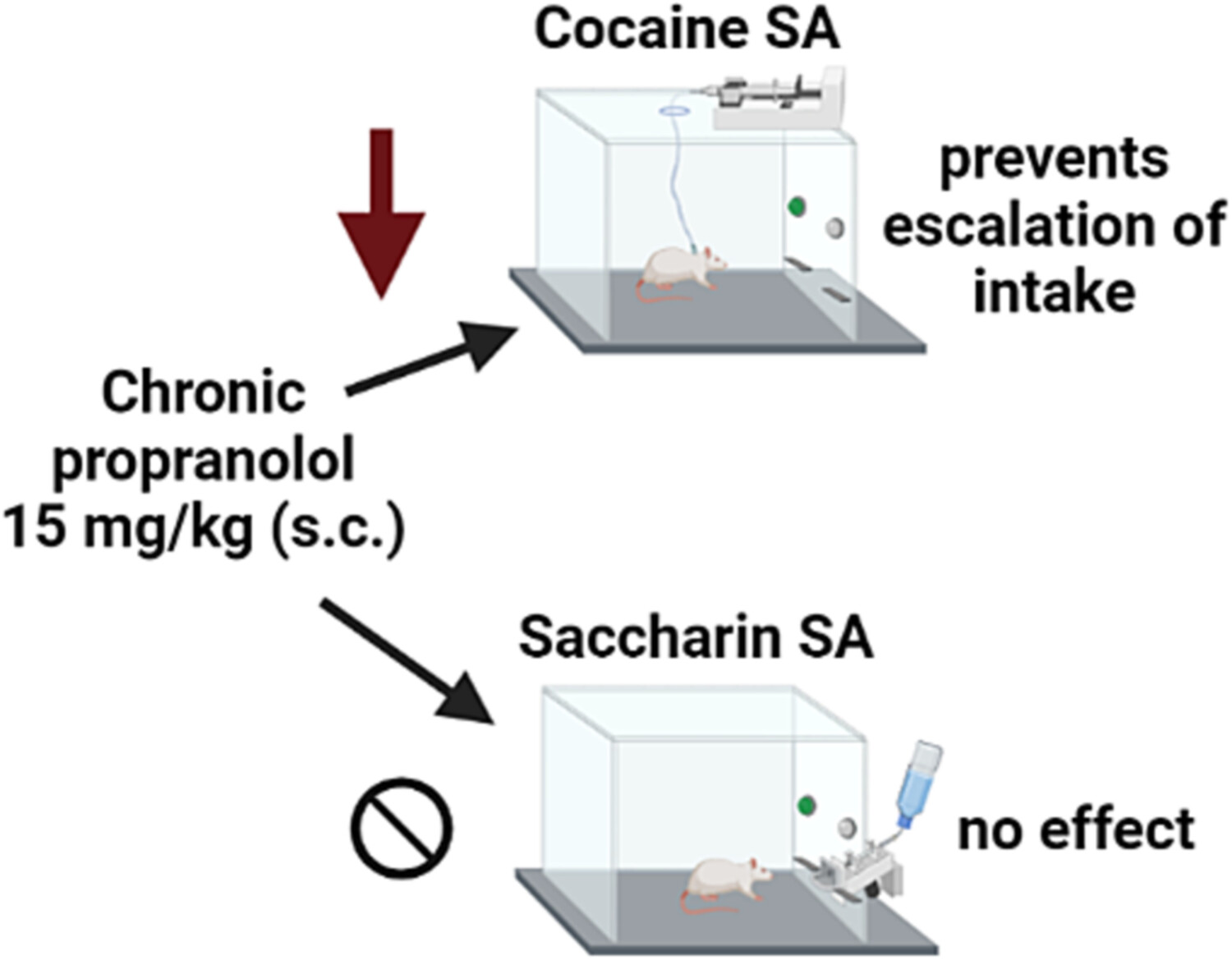
Chronic administration of a norepinephrine antagonist prevents and partially reverses escalation of cocaine self-administration
- First Published: 16 August 2023
COMMENTARIES
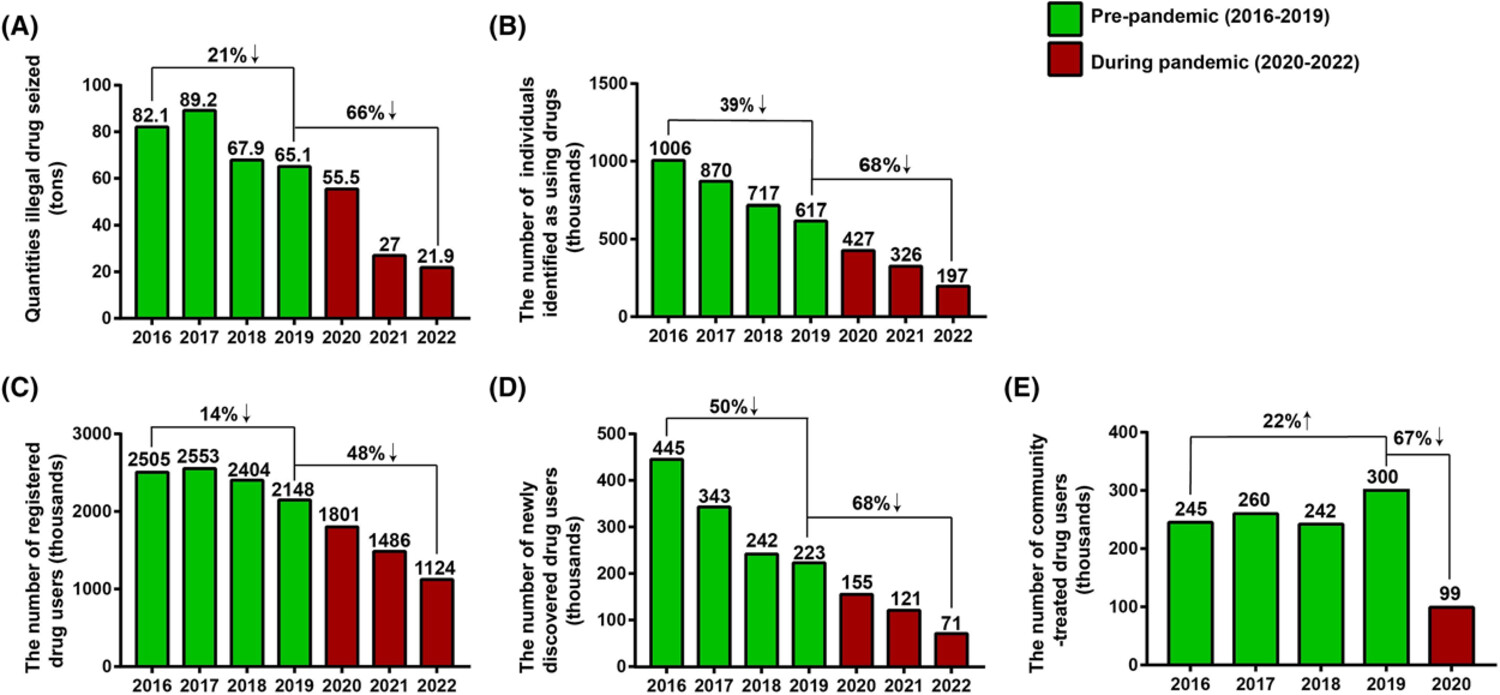
COVID-19 control accelerates the decline in illegal drug use in China
- First Published: 01 August 2023