Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
FRONT COVER
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITOR'S CHOICE
The Mba1 homologue of Trypanosoma brucei is involved in the biogenesis of oxidative phosphorylation complexes
- Pages: 537-550
- First Published: 24 February 2023
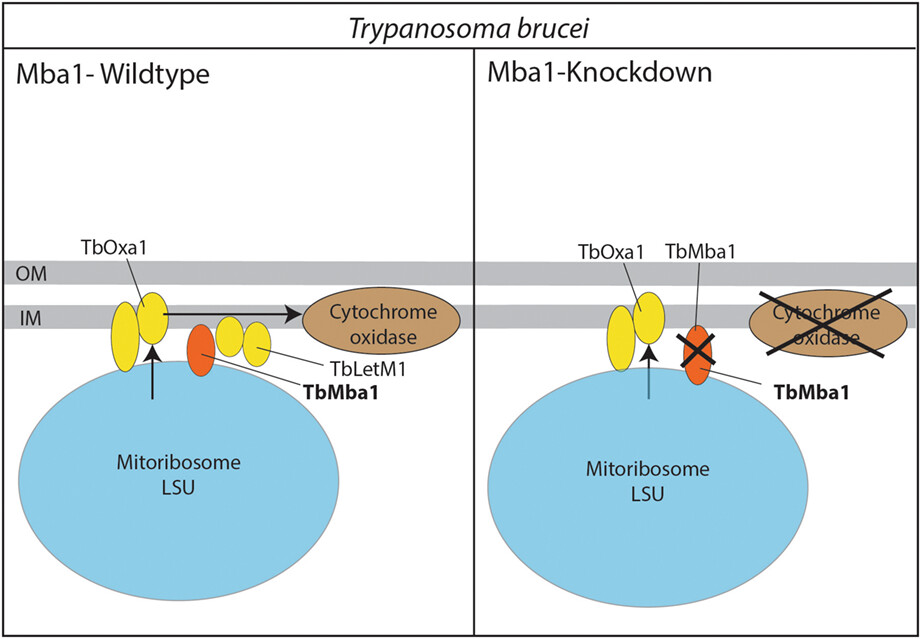
The trypanosomal orthologue of the mitoribosome receptor Mba1 (TbMba1) is essential for normal growth of procyclic trypanosomes. Proteomic analyses of TbMba1-depleted mitochondria revealed reduced levels of many components of the cytochrome c oxidase (Cox) complex, three subunits of which are mitochondrially encoded. Pull-down experiments showed that TbMba1 forms a dynamic interaction network that includes the trypanosomal Mdm38/Letm1 orthologue and a trypanosome-specific factor that stabilizes the CoxI and CoxII mRNAs.
MINI REVIEW
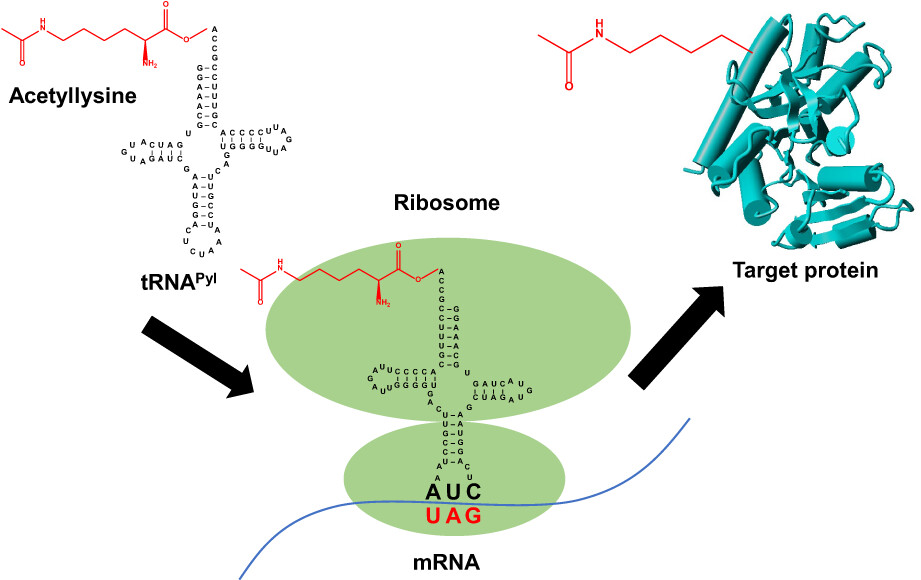
Studying lysine acetylation of citric acid cycle enzymes by genetic code expansion
- Pages: 551-559
- First Published: 08 March 2023
RESEARCH ARTICLES
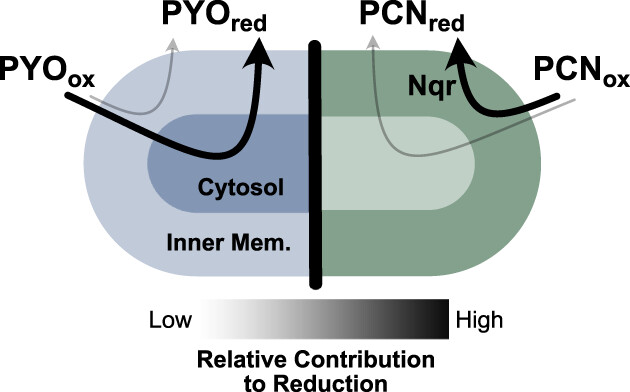
NADH dehydrogenases are the predominant phenazine reductases in the electron transport chain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Pages: 560-573
- First Published: 24 February 2023
Negative regulation of biofilm development by the CUG-Ser1 clade-specific histone H3 variant is dependent on the canonical histone chaperone CAF-1 complex in Candida albicans
- Pages: 574-585
- First Published: 28 February 2023
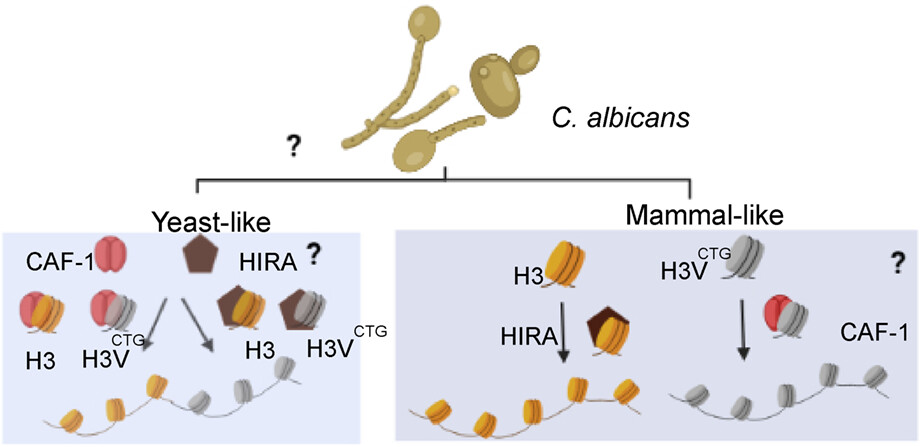
C. albicans possess both canonical and variant histone H3, and evolutionarily conserved histone H3 chaperone complexes, CAF-1 and HIR. The question remains whether both the histone chaperones assist the loading of histones or specific chaperones are designated for canonical and histone variants. While the CAF-1 complex is known to act as a major chaperone for canonical histone H3 loading, our studies suggest that it might act as a chaperone for variant histone H3, H3VCTG in C. albicans.
Molecular insights into Escherichia coli Cpx envelope stress response activation by the sensor lipoprotein NlpE
- Pages: 586-598
- First Published: 15 March 2023
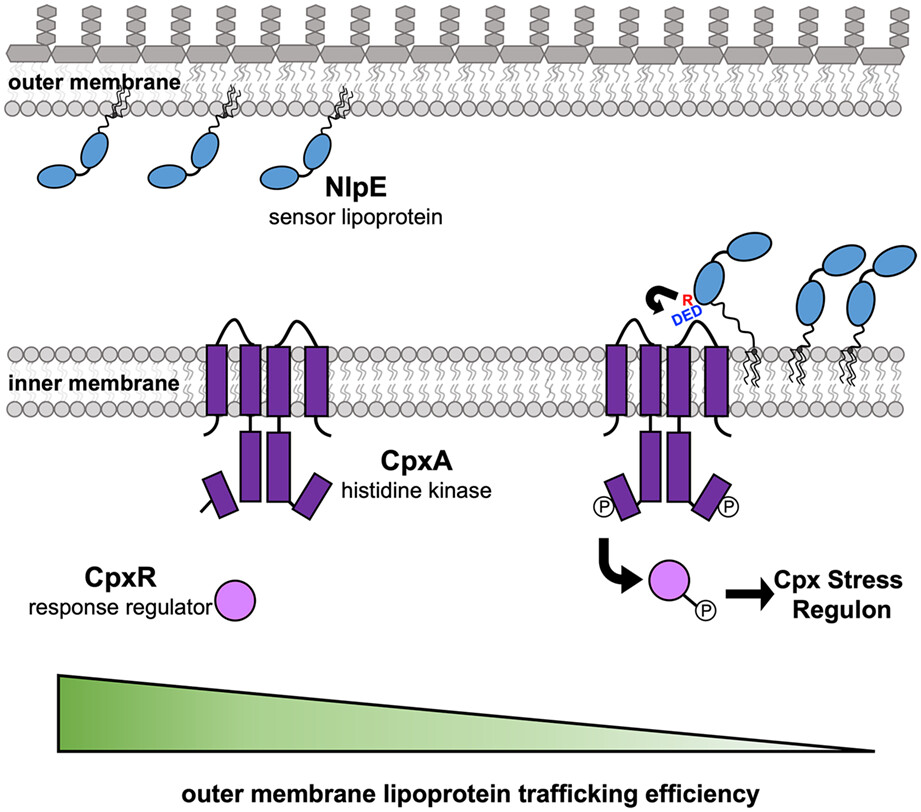
We reveal the molecular details of how the sensor lipoprotein NlpE activates the Cpx two-component stress response. Through complementary genetics, biochemistry, and AlphaFold2 modeling, we identified NlpE residues that are critical for binding the CpxA histidine kinase in the periplasm and activating the response. We also identify CpxA residues required for NlpE interaction. Remarkably, CpxA variants that are blinded to NlpE can respond to other stressors, showing that CpxA can uniquely recognize stress signals.
Two cyanobacterial response regulators with diguanylate cyclase activity, Rre2 and Rre8, participate in biofilm formation
- Pages: 599-611
- First Published: 16 March 2023
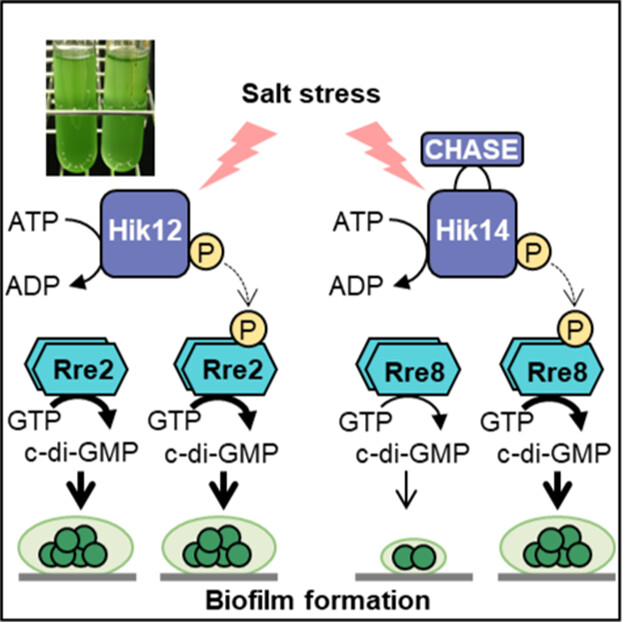
The model cyanobacterium, Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803, switches between a planktonic and a biofilm lifestyle in response to fluctuating environmental conditions. The two-component regulatory systems, Hik12-Rre2 and Hik14-Rre8, function in biofilm formation during high salt stress. Both response regulators, Rre2 and Rre8 catalyze the production of c-di-GMP and are involved in this process.
Profiling the Pyrenophora tritici-repentis secretome: The Pf2 transcription factor regulates the secretion of the effector proteins ToxA and ToxB
- Pages: 612-629
- First Published: 14 April 2023
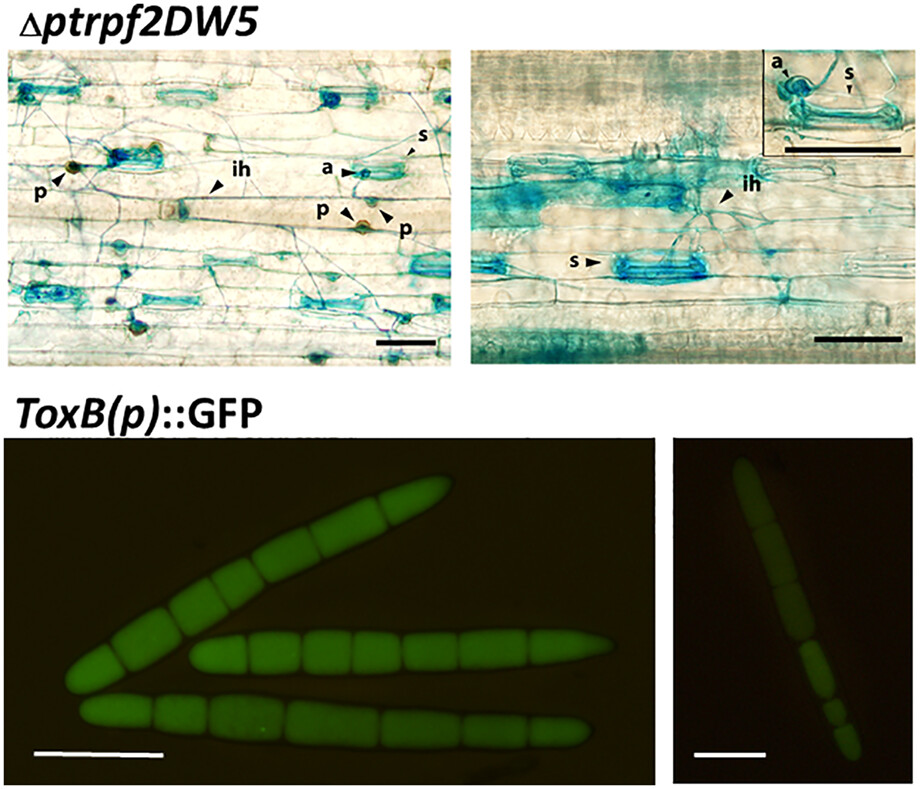
In this study, we show that the transcription factor Pathogenicity factor 2 (Pf2) is a positive regulator of the fungal necrotrophic effector ToxB within the global wheat pathogen Pyrenophora tritici-repentis (Ptr). We investigate the function of Pf2 in different Ptr races via profiling of the secreted fungal proteins and examine the significant promoter motifs identified via GFP report assays.
Disruption of Dcp1 leads to a Dcp2-dependent aberrant ribosome profiles in Aspergillus nidulans
- Pages: 630-639
- First Published: 06 April 2023
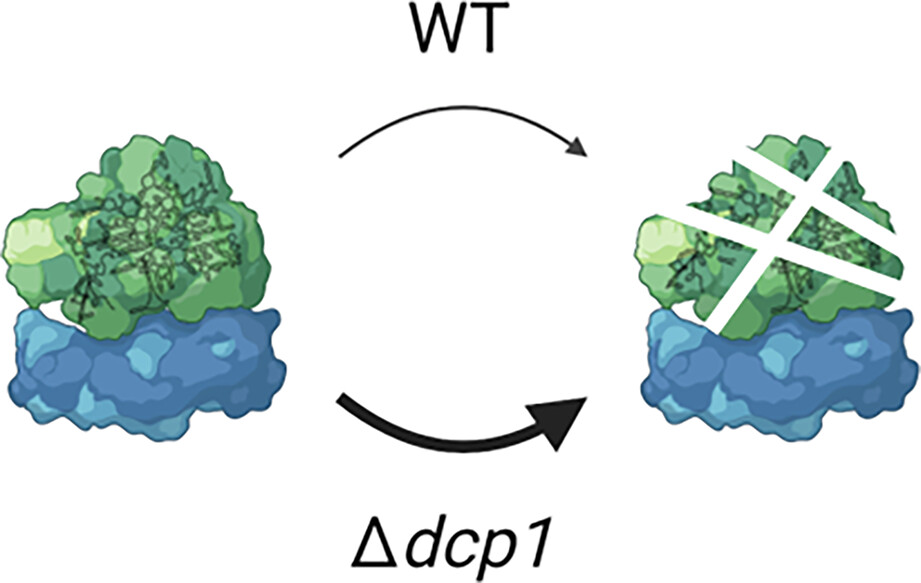
In yeast but not plant and animal systems, the rapid degradation of transcripts with premature termination codon is dependent on mRNA decapping and the cytoplasmic exonuclease, Xrn1. We show the fungus, Aspergillus nidulans does not fit the yeast model, suggesting as yet unidentified RNA degradation mechanisms are involved. Surprisingly, disruption specifically of the regulatory component of the decapping complex, Dcp1, leads to an accumulation of rRNA degradation products.
Apoptosis-inducing factor-like protein-mediated stress and metronidazole-responsive programmed cell death pathway in Entamoeba histolytica
- Pages: 640-658
- First Published: 10 April 2023
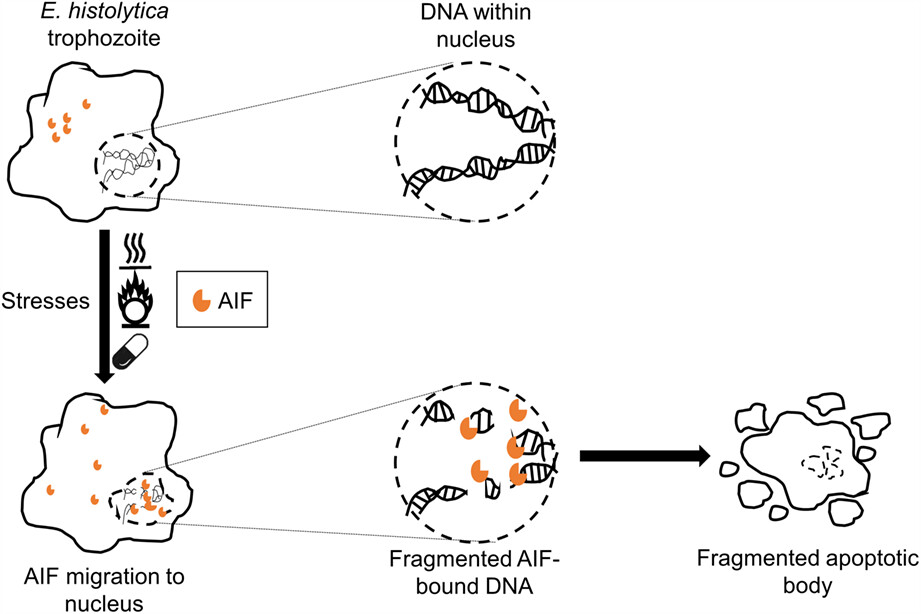
The apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) present in the protoplasm of the Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites, migrates to the nucleus when the trophozoites are stressed with heat shock, oxidative shock or drug treatment. Once the AIF is in the nucleus, they cause the peripheral chromosome condensation and DNA degradation. These ultimately lead to the apoptosis of the E. histolytica, the pathogen of amoebiasis.