Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Original Articles
Autoimmunity
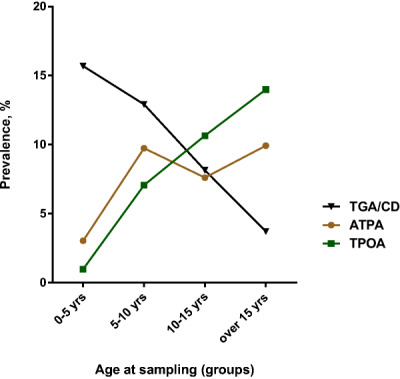
A quarter of patients with type 1 diabetes have co-existing non-islet autoimmunity: the findings of a UK population-based family study
- Pages: 251-258
- First Published: 12 February 2018
Diminished CXCR5 expression in peripheral blood of patients with Sjögren's syndrome may relate to both genotype and salivary gland homing
- Pages: 259-270
- First Published: 17 February 2018
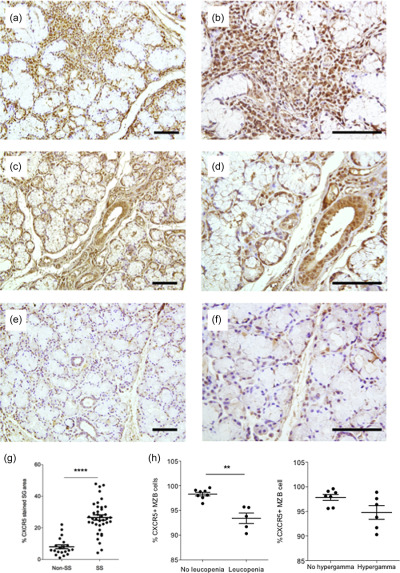
We link a genetic susceptibility allele for SS to a functional phenotype in terms of decreased CXCR5 expression. The decrease of CXCR5+ cells in circulation was also related to homing of B and T cells to the autoimmune target organ. Therapeutic drugs targeting the CXCR5/CXCL13 axis may be useful in SS.
Cancer immunology
Separation of plasma-derived exosomes into CD3(+) and CD3(–) fractions allows for association of immune cell and tumour cell markers with disease activity in HNSCC patients
- Pages: 271-283
- First Published: 12 February 2018
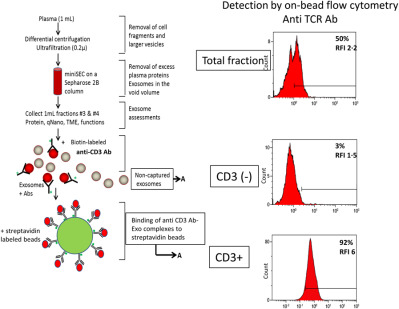
Exosomes from plasma of patients with HNSCC were separated by immunocapture with anti-CD3 Abs into CD3+ and CD3(-) fractions. Each fraction was evaluated for the content of immunoregulatory proteins by on-bead flow cytometry. The levels of immunoregulatory proteins carried by exosomes were correlated to disease activity and stage and lymph node positivity. CD3(-) CD44v3+ tumor-derived exosomes were more immunosuppressive than CD3(+) T cell-derived exosomes.
Immunodeficiency
The United Kingdom Primary Immune Deficiency (UKPID) registry 2012 to 2017
- Pages: 284-291
- First Published: 25 May 2018
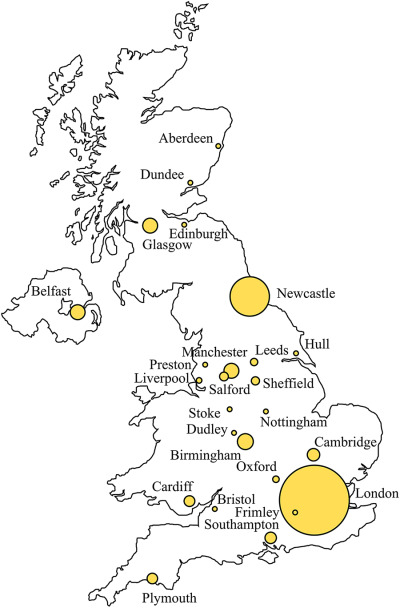
Since our first report in 2013, the number of patients entered into the UKPID registry has more than doubled to 4758 encompassing 97% of immunology centers within the United Kingdom. We believe this registry now represents virtually all patients with primary immunodeficiency within the UK. As such, this dataset continues to provide valuable information to clinicians, researchers, service commissioners and industry alike on PID within the UK, which may not otherwise be available without the existence of a well-established registry.
Measurement of Typhi Vi antibodies can be used to assess adaptive immunity in patients with immunodeficiency
- Pages: 292-301
- First Published: 29 January 2018
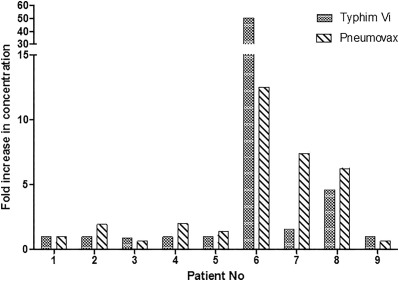
Responses to Pneumovax II are used to assess the response to polysaccharide antigens but interpretation may be complicated.
Measurement of IgG antibodies raised in response to the polysaccharide vaccine Typhim Vi® maybe a useful additional test to accompany Pneumovax II responses for the assessment of antibody deficiencies.
IgG responses to Typhim Vi® vaccination can be measured using the VaccZyme Salmonella typhi Vi IgG ELISA.
Correction of T cell deficiency in ZAP-70 knock-out mice by simple intraperitoneal adoptive transfer of thymocytes
- Pages: 302-314
- First Published: 12 February 2018
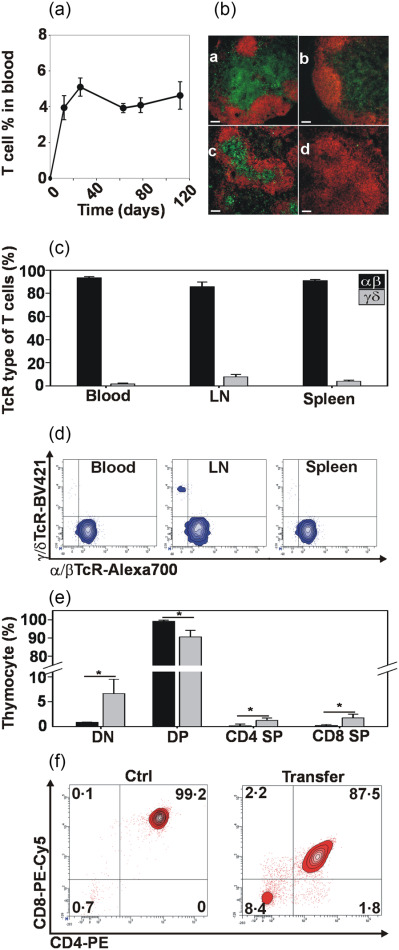
In the absence of ZAP-70 kinase, T cell development is arrested in the CD4+CD8+ double positive stage, thus ZAP-70 homozygous knockout (ZAP-70-/-) mice have no mature T cells in their peripheral lymphoid organs and blood, causing severe immunodeficiency. Here, we demonstrate that a simple, intraperitoneal injection of ZAP-70+/+ thymocytes is a feasible method for the long-term reconstitution of T cell development in ZAP-70 deficient mice.
Inflammation/Inflammatory disease
Human lactoferrin attenuates the proinflammatory response of neonatal monocyte-derived macrophages
- Pages: 315-324
- First Published: 02 February 2018
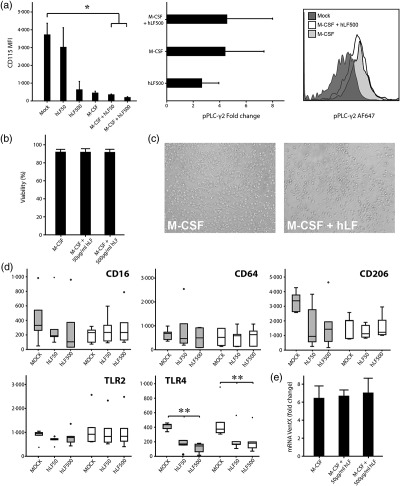
Neonatal intestinal macrophages display a pro-inflammatory profile that might contribute to inflammatory mucosal injury. The human bioactive milk component lactoferrin attenuates the pro-inflammatory immune response of neonatal monocyte-derived macrophages by interference with TLR-pathways. Thus, the anergic/anti-inflammatory properties of human lactoferrin might contribute to the prevention of harmful TLR-mediated inflammatory disorders in the developing gut of premature infants.
The induced RNA-binding protein, HuR, targets 3′-UTR region of IL-6 mRNA and enhances its stabilization in periodontitis
- Pages: 325-336
- First Published: 02 February 2018
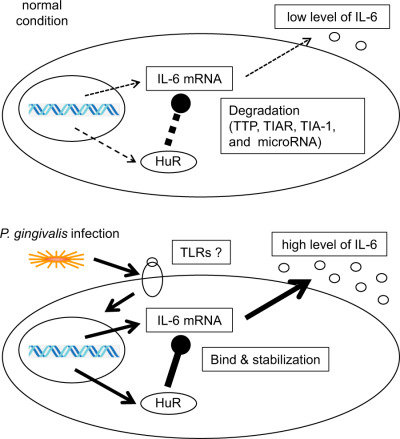
This illustration is showing the proposed mechanism of IL-6 elevations by HuR with a Pg stimulation. Up-regulated HuR stimulated by P. gingivalis binds to the 3'-UTR of IL-6 mRNA, and this binding results in an increase in the stability of IL-6 mRNA. On the other hand, the mRNA expression of IL-6 and HuR is not induced under normal conditions (without a stimulation).
A triglyceride-rich lipoprotein environment exacerbates renal injury in the accelerated nephrotoxic nephritis model
- Pages: 337-347
- First Published: 06 February 2018
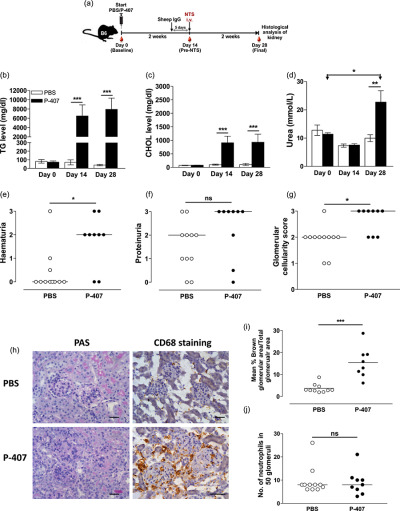
Dyslipidaemia accompanies various metabolic and non-metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes and systemic lupus erythematosus, where renal complications are common. Here we show that the induction of hypertriglyceridaemia in mice renders the kidney more susceptible to damage in the advent of an immune complex-mediated inflammatory insult. This was demonstrated by a higher degree of haematuria and glomerular cellularity in the hypertriglyceridaemic animals compared to the normolipidaemic controls. This hypersensitive response appears to be mediated, at least in part, by macrophages given the higher infiltration of CD68+ cells in the kidneys of hypertriglyceridaemic mice.
Immunoassay methods used in clinical studies for the detection of anti-drug antibodies to adalimumab and infliximab
- Pages: 348-365
- First Published: 12 February 2018
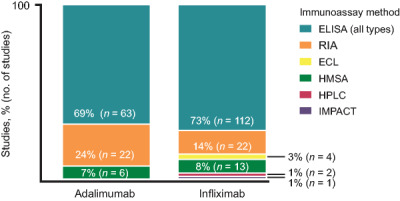
We conducted a literature review to examine the assay formats used to detect anti-drug antibodies (ADA) in clinical studies of the anti-TNF monoclonal antibodies adalimumab and infliximab in chronic inflammatory disease. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays and radioimmunoassays were used in 93% and 87% of adalimumab and infliximab studies, respectively. ADA incidence varied from 0 to 87% in adalimumab studies and 0 to 79% in infliximab studies across assays and inflammatory diseases. The presence of ADA was associated with reduced serum concentrations and efficacy and increased rates of infusion-related reactions, independent of the assay format and biologic used.
Infection
Defective RNA sensing by RIG-I in severe influenza virus infection
- Pages: 366-376
- First Published: 17 February 2018
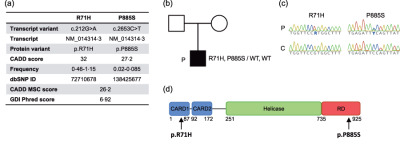
By whole exome sequencing of patients with severe influenza virus type A (IAV) infection we identified a patient with mutations in DDX58 encoding the RNA sensor RIG-I. These variants significantly impaired the signaling activity of RIG-I and patient cells demonstrated decreased antiviral responses to RIG-I ligands as well as increased pro-inflammatory responses to IAV, suggesting dysregulation of the innate immune response with increased immunopathology. We suggest that these RIG-I variants may have contributed to severe influenza in this patient and advocate that RIG-I variants should be sought for in future studies of genetic factors influencing single-stranded RNA virus infections.