Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
FEATURED COVER
Featured Cover
- Page: i
- First Published: 14 April 2023

The cover image is based on the Review Article Clonal mast cell disorders and hereditary α-tryptasemia as risk factors for anaphylaxis by Mark Kačar et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/cea.14264.
ISSUE INFORMATION
COCHRANE CORNER
Increased inhaled corticosteroids for treating acute asthma exacerbations
- Pages: 388-391
- First Published: 28 March 2023
REVIEW ARTICLE
Clonal mast cell disorders and hereditary α-tryptasemia as risk factors for anaphylaxis
- Pages: 392-404
- First Published: 18 January 2023
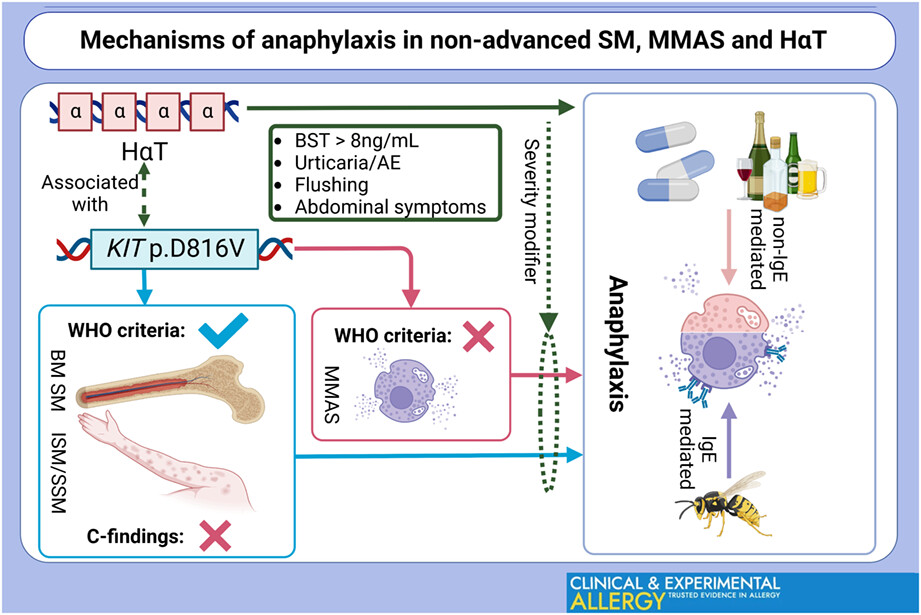
Non-clonal mast cell disease, hereditary alpha-tryptasemia, and anaphylaxis. Hereditary alpha-tryptasemia (HαT) is strongly associated with clonal mast cell disease (cMCD). Either of those conditions alone is a predisposing factor for severe IgE-dependent and IgE-independent anaphylaxis however, the presence of HαT in patients with cMCD serves to further increase the severity of anaphylactic reactions.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Progenitor cell-derived basophils: A novel barcoded passive degranulation assay in allergic diseases
- Pages: 405-416
- First Published: 16 November 2022
Efficacy of tezepelumab in patients with evidence of severe allergic asthma: Results from the phase 3 NAVIGATOR study
- Pages: 417-428
- First Published: 12 December 2022
Trajectories of cough without a cold in early childhood and associations with atopic diseases
- Pages: 429-442
- First Published: 01 December 2022
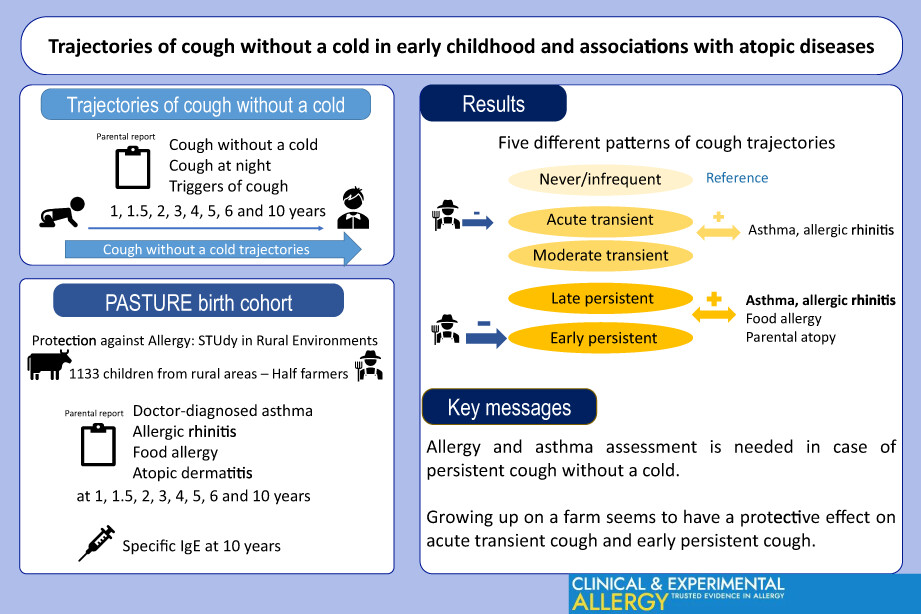
Five different patterns of cough trajectories during early childhood have been highlighted. Recurrent cough without a cold, with night cough and triggers should lead to allergy and asthma assessment. Growing up on a farm seems to have a protective effect on acute transient cough and early persistent cough.
Histone deacetylase activity is a novel target for epithelial barrier defects in patients with eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps
- Pages: 443-454
- First Published: 01 December 2022
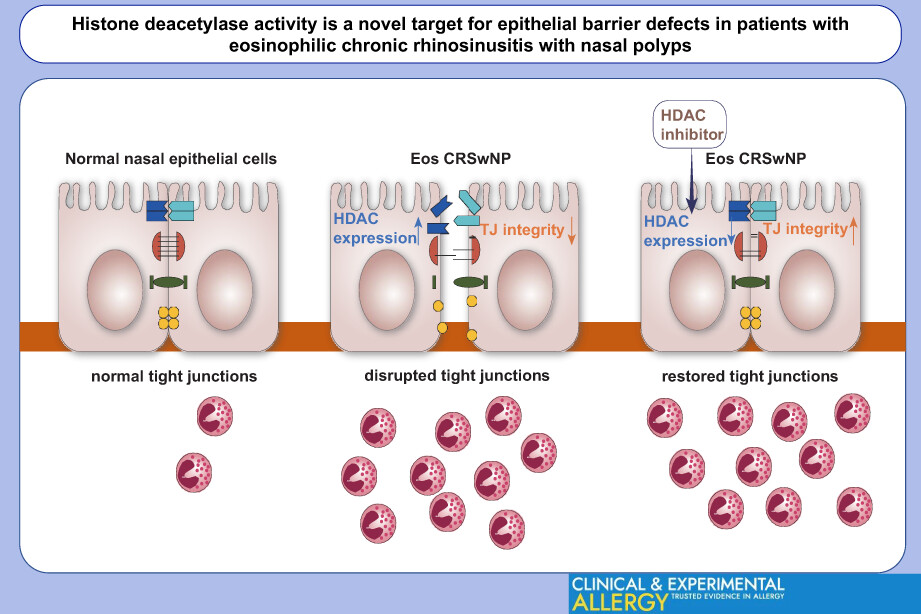
The integrated and continuous tight junctions (TJs) play a crucial role in maintaining normal epithelial barrier function of nasal mucosa. This could effectively prevent the invasion of foreign particles. The pathogenesis and development of chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) is associated with failure of barrier function in nasal mucosa, especially for the nasal polyps of patients with eosinophilic CRSwNP (Eos CRSwNP). In the meantime, expression of HDACs is increased in these patients and inhibition of HDACs activity may reconstitute the nasal epithelial barrier integrity in Eos CRSwNP.
RESEARCH LETTERS
Serum calprotectin, S100A9 and periostin levels in patients with newly diagnosed, controlled and uncontrolled asthma
- Pages: 455-458
- First Published: 11 January 2023
Mode of delivery and asthma in childhood and adolescence: Findings from the Millennium Cohort Study
- Pages: 459-464
- First Published: 16 January 2023
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist use is associated with lower serum periostin
- Pages: 469-473
- First Published: 17 January 2023
Prenatal household incense burning, air purifiers and cord blood IgE
- Pages: 474-478
- First Published: 17 January 2023
Prenatal antibiotic use, caesarean delivery and offspring's food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome: A National Birth Cohort (JECS)
- Pages: 479-483
- First Published: 20 January 2023





