Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
Issue Information
- Pages: 2627-2629
- First Published: 05 September 2018

Cover of this issue. Drugs that induce ferroptosis are synthetic lethal with inactivation of fumarate hydrolase, the TCA cycle enzyme. See also Kerins et al. (pp. 2757–2766 of this issue).
IN THIS ISSUE
In this Issue: Volume 109, Issue 9, September 2018
- Pages: 2630-2631
- First Published: 05 September 2018
REVIEW ARTICLES
Tetraploidy in cancer and its possible link to aging
- Pages: 2632-2640
- First Published: 27 June 2018
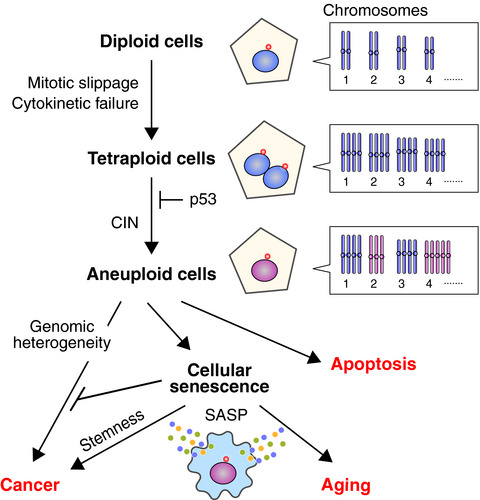
Tetraploidy, a condition in which a cell has four homologous sets of chromosomes, is often seen as a natural physiological condition but is also associated with cancer and possibly with aging. Here, we review recent findings about how tetraploidy is related to cancer and aging and discuss underlying mechanisms of the relationship, as well as how we can exploit the properties of cells exhibiting tetraploidy-induced chromosomal instability to control these pathological conditions.
Unveiling epigenetic regulation in cancer, aging, and rejuvenation with in vivo reprogramming technology
- Pages: 2641-2650
- First Published: 10 July 2018
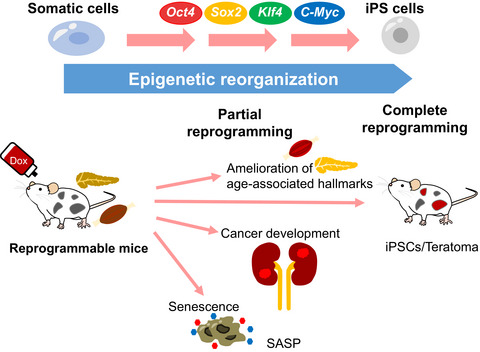
Recent studies using in vivo reprogramming technology to alter epigenetic regulation at organismal levels have revealed unappreciated epigenetic mechanisms in various biological phenomena in mammals. In this review, the authors review recent progress and future perspectives of in vivo reprogramming.
MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of glioma: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 2651-2659
- First Published: 27 June 2018

Review and meta-analysis to access diagnostic values of miRNAs in glioma. Overall miRNAs have an outstanding diagnostic accuracy of glioma. miRNAs detected in CSF and brain tissue largely improve the diagnostic accuracy. Panels of multiple miRNAs could enhance the pooled sensitivity. MiR-21 has a high sensitivity and specificity in detection of glioma.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
BASIC AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY
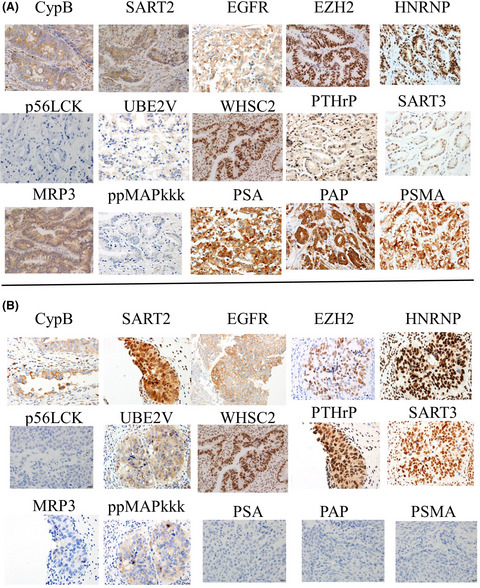
Survival analysis of multiple peptide vaccination for the selection of correlated peptides in urological cancers
- Pages: 2660-2669
- First Published: 25 June 2018
Lung-resident natural killer cells control pulmonary tumor growth in mice
- Pages: 2670-2676
- First Published: 21 June 2018
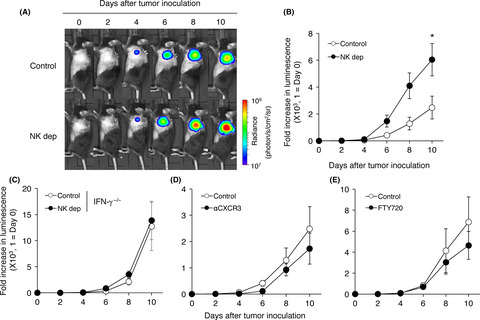
Although lung is a major organ where primary tumor develops and cancer cells metastasize, there is no clear evidence whether circulating NK cells and/or tissue-resident NK cells control tumor growth in lung. Presented results indicate the importance of lung-resident NK cells for controlling pulmonary tumor growth.
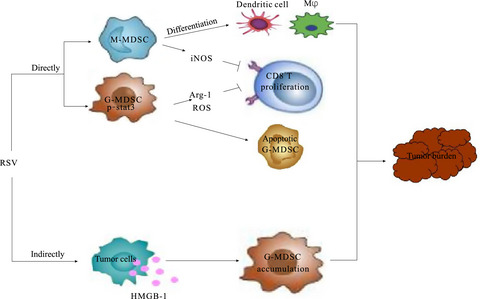
Resveratrol ameliorates Lewis lung carcinoma-bearing mice development, decreases granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cell accumulation and impairs its suppressive ability
- Pages: 2677-2686
- First Published: 30 June 2018
Novel chemical compound SINCRO with dual function in STING-type I interferon and tumor cell death pathways
- Pages: 2687-2696
- First Published: 07 July 2018
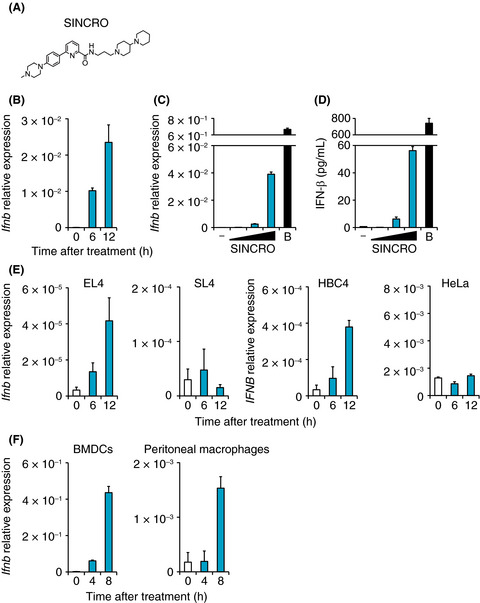
We find N-{3-[(1,4′-bipiperidin)-1′-yl]propyl}-6-[4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)phenyl]picolinamide (SINCRO; STING-mediated interferon-inducing and cytotoxic reagent, original) as a novel anticancer compound. SINCRO induces type I interferon gene expression through STING and exerts cytotoxic activity against cancer cells in a STING-independent method. Thus, SINCRO is an attractive compound with dual anticancer function.
Genetic and clinical characterization of B7-H3 (CD276) expression and epigenetic regulation in diffuse brain glioma
- Pages: 2697-2705
- First Published: 20 July 2018
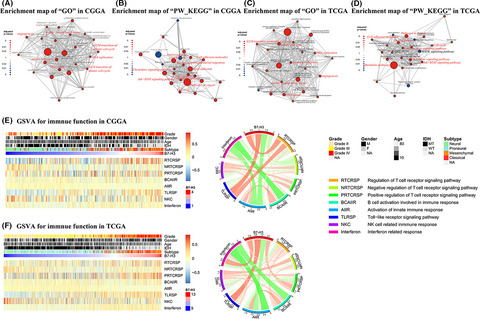
B7-H3 expression is regulated by multiple mechanisms and is mainly involved in the T-cell receptor signaling pathway. Higher B7-H3 expression indicates worse prognosis for glioma patients, which warrants further research into the development of inhibitors for targeting this immune checkpoint, but we still need to be cautious about immune checkpoint inhibition for central nervous system tumors.
CARCINOGENESIS
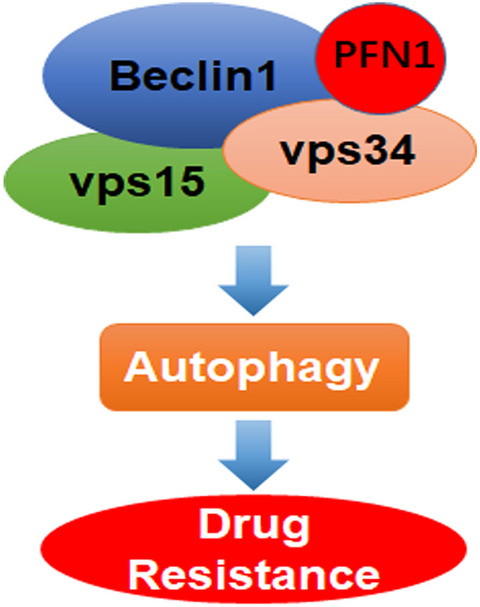
Profilin 1 induces drug resistance through Beclin1 complex-mediated autophagy in multiple myeloma
- Pages: 2706-2716
- First Published: 26 June 2018
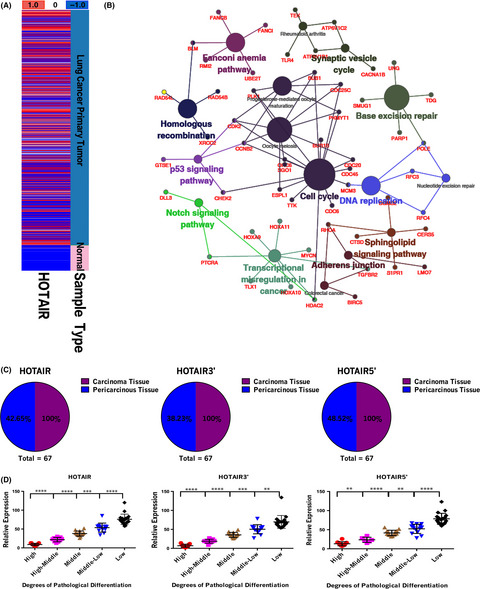
HOTAIR, a long noncoding RNA, is a marker of abnormal cell cycle regulation in lung cancer
- Pages: 2717-2733
- First Published: 26 July 2018
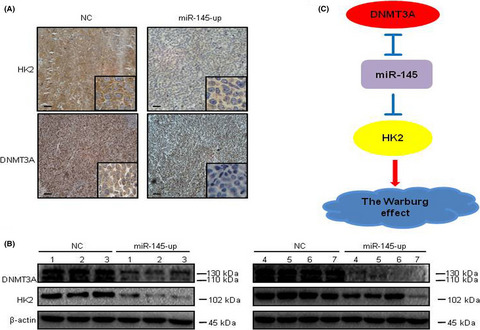
Double-negative feedback interaction between DNA methyltransferase 3A and microRNA-145 in the Warburg effect of ovarian cancer cells
- Pages: 2734-2745
- First Published: 11 July 2018
CELL, MOLECULAR, AND STEM CELL BIOLOGY
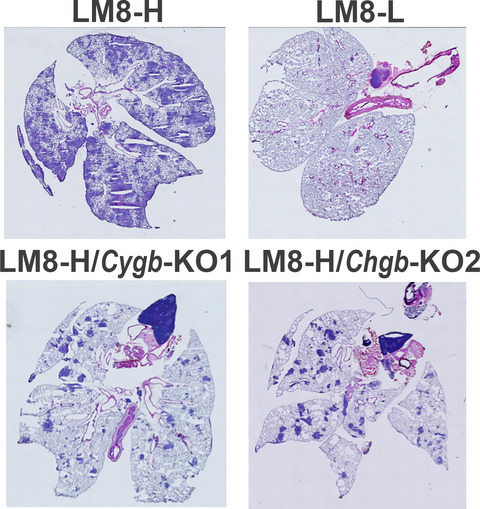
Novel lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1-cytoglobin axis promotes extravasation of osteosarcoma cells into the lungs
- Pages: 2746-2756
- First Published: 21 June 2018
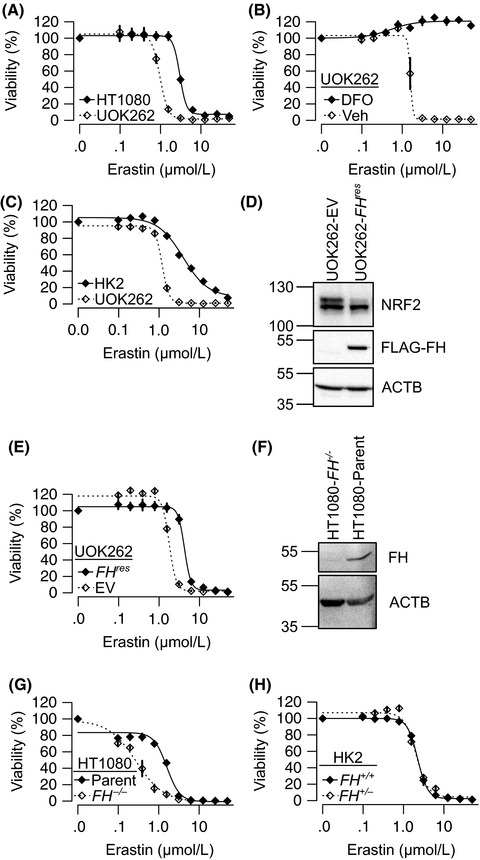
Fumarate hydratase inactivation in hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer is synthetic lethal with ferroptosis induction
- Pages: 2757-2766
- First Published: 19 June 2018
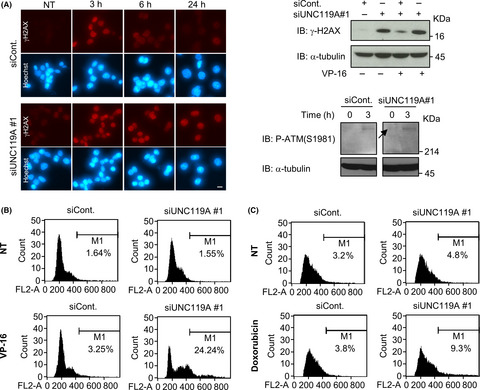
UNC119 is a binding partner of tumor suppressor Ras-association domain family 6 and induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by MDM2 and p53
- Pages: 2767-2780
- First Published: 21 June 2018
Transcriptional repression of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 by ClC-3 Cl−/H+ transporter inhibition in human breast cancer cells
- Pages: 2781-2791
- First Published: 27 June 2018
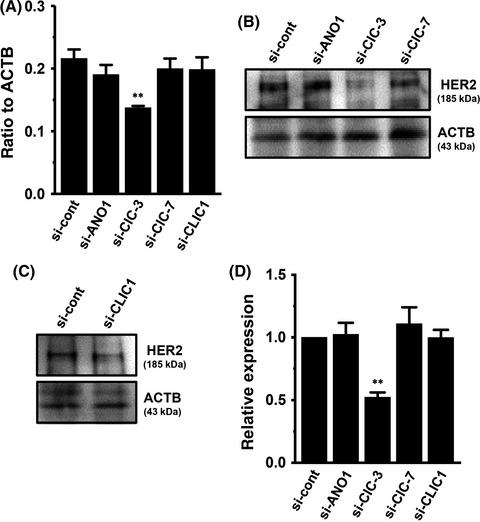
Inhibition of intracellular organelle ClC-3 Cl−/H+ transporter repressed HER2 transcription in breast cancer cells. Intracellular Cl- regulation participated in HER2 transcription, mediating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR and/or STAT3 signaling pathway(s) in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. ANO1/ClC-3 blockers may be potential therapeutic options for patients with resistance to anti-HER2 therapies.
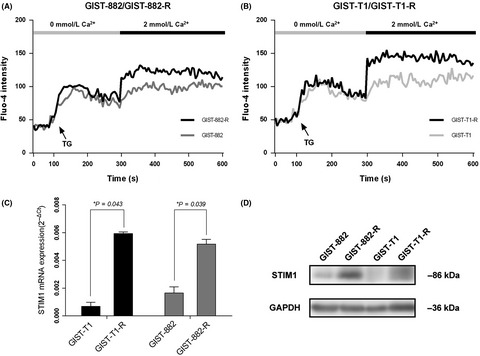
Inhibition of stromal-interacting molecule 1-mediated store-operated Ca2+ entry as a novel strategy for the treatment of acquired imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- Pages: 2792-2800
- First Published: 29 June 2018
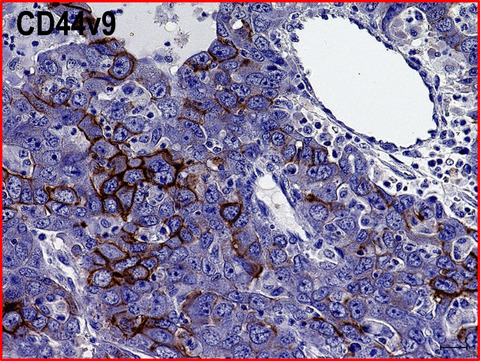
High expression of CD44v9 and xCT in chemoresistant hepatocellular carcinoma: Potential targets by sulfasalazine
- Pages: 2801-2810
- First Published: 07 July 2018
Identification of ENTPD8 and cytidine in pancreatic cancer by metabolomic and transcriptomic conjoint analysis
- Pages: 2811-2821
- First Published: 10 July 2018
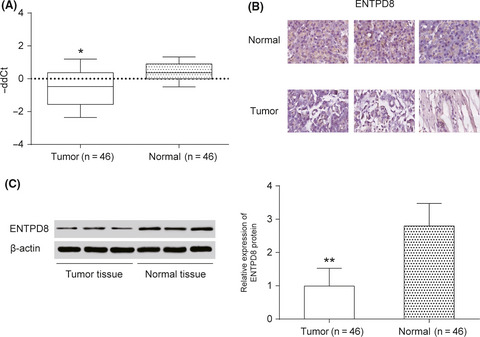
Seven biomarkers and first revealed that ENPTD8 engaged in CTP dephosphorization in pyrimidine metabolism was highly deregulated in pancreatic cancer (PC) tissue. The expression level of ENTPD8 was negatively related to PC tumor formation. ENTPD8 and cytidine were closely related to PC tumorigenesis, which could be a target for early detection and effective therapy of PC in the future.
CLINICAL RESEARCH
Pharmacodynamic analysis of eribulin safety in breast cancer patients using real-world postmarketing surveillance data
- Pages: 2822-2829
- First Published: 22 June 2018
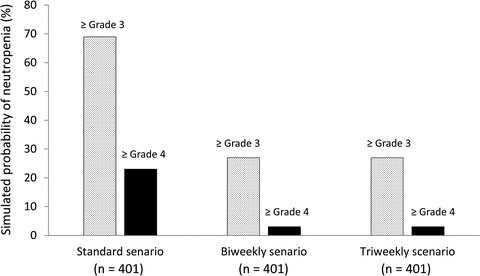
This article reports the first application of postmarketing real-world data on a mechanistic pharmacodynamic model for neutropenic profiles by eribulin. Low serum albumin and low baseline neutrophil counts were associated with severe neutropenia. The probability of grade ≥3 neutropenia was predicted in different dosing schedules, based on virtual simulations using the developed pharmacodynamic model.
R-High-CHOP/CHASER/LEED with autologous stem cell transplantation in newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma: JCOG0406 STUDY
- Pages: 2830-2840
- First Published: 29 June 2018
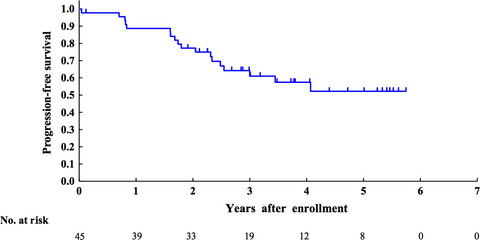
In this phase II study, an immunochemotherapy regimen (R-high-CHOP/CHASER) including high-dose cyclophosphamide and high-dose cytarabine with rituximab followed by high-dose chemotherapy (cyclophosphamide, etoposide, melphalan, and dexamethasone) and stem cell transplantation showed high efficacy and acceptable toxicity in younger patients (<65 years) with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma.
Periostin and CA242 as potential diagnostic serum biomarkers complementing CA19.9 in detecting pancreatic cancer
- Pages: 2841-2851
- First Published: 26 June 2018
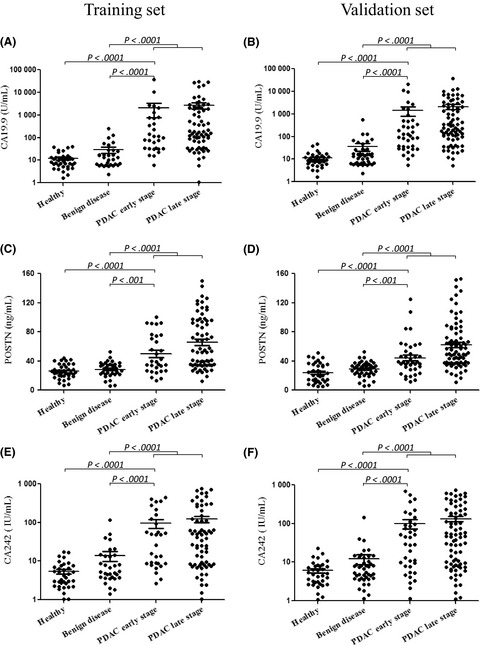
Serum levels of periostin (POSTN) were significantly increased in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Performances of carbohydrate antigen 19.9 (CA19.9) were improved by the marker panel composed of CA19.9, POSTN, and CA242, to discriminate early stage PDAC from control subjects. POSTN retained significant diagnostic capabilities to distinguish CA19.9-negative PDAC from control subjects.
Clinical activity of ASP8273 in Asian patients with non-small-cell lung cancer with EGFR activating and T790M mutations
- Pages: 2852-2862
- First Published: 04 July 2018
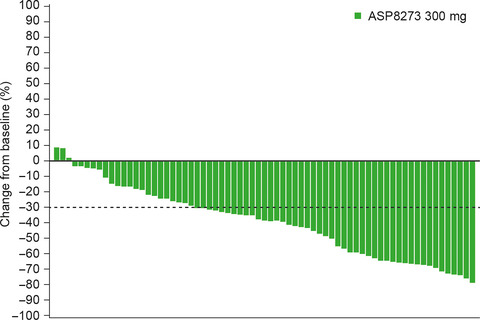
This dose-escalation/dose-expansion study (NCT02192697) was carried out in two phases to assess the clinical activity of ASP8273 in Asian patients with non-small-cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-activating and T790M mutations. ASP8273 is a highly specific, irreversible, once-daily, oral, EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor that inhibits both activating and resistance mutations. ASP8273 300 mg was generally well tolerated and showed antitumor activity in Asian patients with both EGFR-activating and T790M mutations.
Phase II study of ceritinib in alectinib-pretreated patients with anaplastic lymphoma kinase-rearranged metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer in Japan: ASCEND-9
- Pages: 2863-2872
- First Published: 30 June 2018
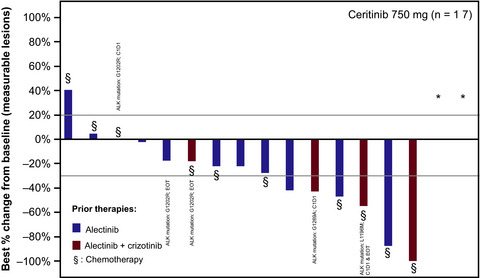
Clinical experience of ceritinib in patients who progressed on alectinib is limited. In this prospective phase II study, we evaluated the activity of ceritinib in alectinib-pretreated patients with anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-rearranged metastatic (stage IIIB/IV) non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in Japan.
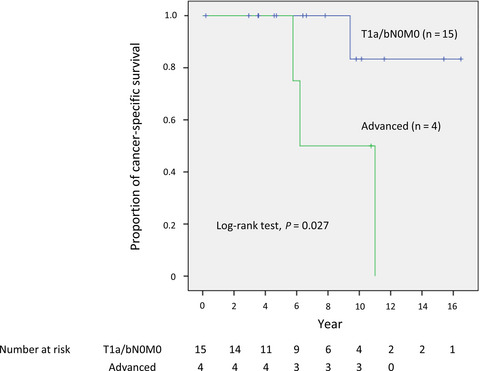
Updated long-term outcomes after carbon-ion radiotherapy for primary renal cell carcinoma
- Pages: 2873-2880
- First Published: 07 July 2018
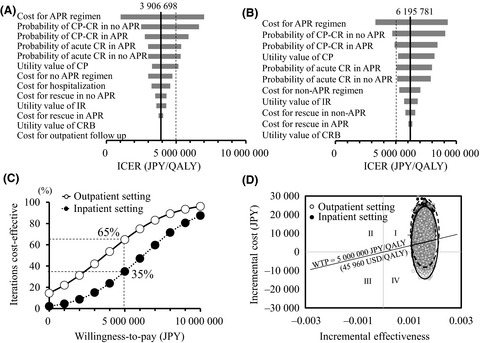
Cost-effectiveness of aprepitant in Japanese patients treated with cisplatin-containing highly emetogenic chemotherapy
- Pages: 2881-2888
- First Published: 12 July 2018
DRUG DISCOVERY AND DELIVERY
Changes in plasma membrane damage inducing cell death after treatment with near-infrared photoimmunotherapy
- Pages: 2889-2896
- First Published: 27 June 2018
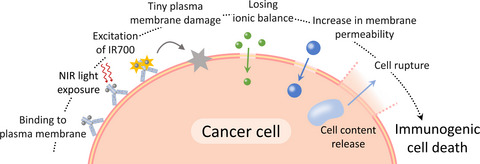
In the present study, the cytotoxic mechanism of photoimmunotherapy was investigated. As a result, we found that minute irreversible damage of the cell plasma membrane was produced after near-infrared light irradiation. This damage was not recovered in the usual biological process, but it was expanded to cause fatal cell death.
EPIDEMIOLOGY AND PREVENTION
Branched rolling circle amplification method for measuring serum circulating microRNA levels for early breast cancer detection
- Pages: 2897-2906
- First Published: 07 July 2018
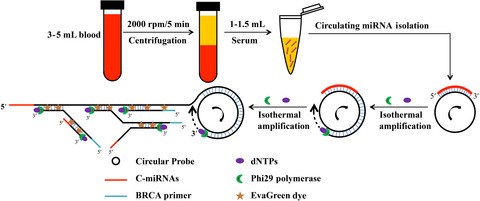
This is the first study to detect serum circulating miRNA biomarkers by branched rolling circle amplification in clinical research. Serum c-miR16, c-miR21, c-miR155, and c-miR195 could be used as biomarkers to improve early diagnosis of breast cancer, and distinguish different breast cancer molecular subtypes. Branched rolling circle amplification assay can be used to measure the serum levels of circulating miRNAs for the screening and detection of early breast cancer, which has high accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity.
GENETICS, GENOMICS, AND PROTEOMICS
EWS-FLI1 regulates a transcriptional program in cooperation with Foxq1 in mouse Ewing sarcoma
- Pages: 2907-2918
- First Published: 26 June 2018
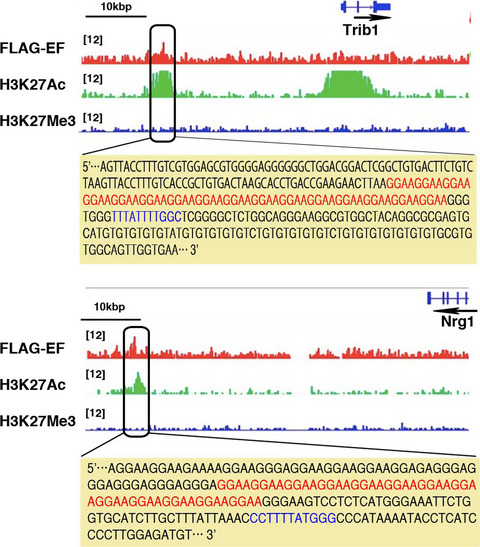
GGAA microsatellites and enhancer regions were identified as EWS-FLI1-binding loci in a mouse model for Ewing sarcoma. Foxq1 was identified as a cooperative partner of EWS-FLI1, and interaction between Foxq1 and EWS-FLI1 was observed. Trib1 and Nrg1 were identified as direct target genes for EWS-FLI1 and Foxq1 collaboration.
Regulation of antitumor miR-144-5p targets oncogenes: Direct regulation of syndecan-3 and its clinical significance
- Pages: 2919-2936
- First Published: 03 July 2018

Our study showed that expression of miR-144-5p and miR-144-3p was downregulated, and these microRNAs (miRNAs) acted as antitumor miRNAs in renal cell carcinoma. SDC3 was directly controlled by miR-144-5p, and its expression enhanced cancer cell aggressiveness. Clustered miRNAs (miR-451a, miR-144-5p, and miR-144-3p) acted as antitumor miRNAs, and their targets were intimately involved in renal cell carcinoma pathogenesis.
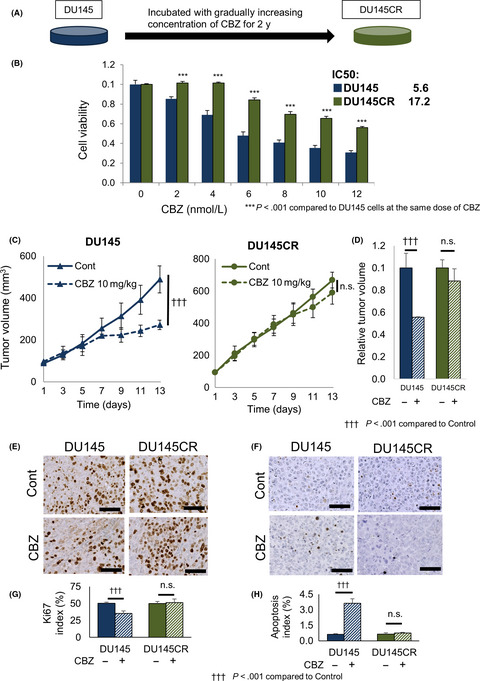
Analysis of cabazitaxel-resistant mechanism in human castration-resistant prostate cancer
- Pages: 2937-2945
- First Published: 10 July 2018
Exosomal zinc transporter ZIP4 promotes cancer growth and is a novel diagnostic biomarker for pancreatic cancer
- Pages: 2946-2956
- First Published: 14 July 2018
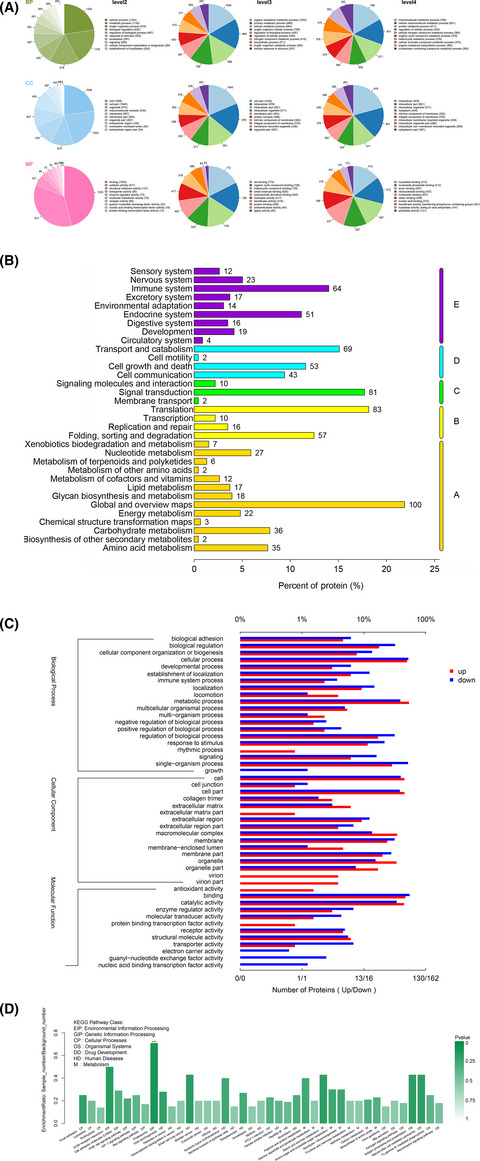
Using proteomic analysis, we identified that ZIP4 was the most upregulated exosomal protein in PC-1.0 cells. In vitro and in vivo experiments showed that exosomal ZIP4 could promote pancreatic cancer growth. Validation with clinical samples proved that exosomal ZIP4 could be a novel diagnostic biomarker for pancreatic cancer.
PATHOLOGY
Programmed cell death ligand-1 protein expression and CD274/PD-L1 gene amplification in colorectal cancer: Implications for prognosis
- Pages: 2957-2969
- First Published: 27 June 2018
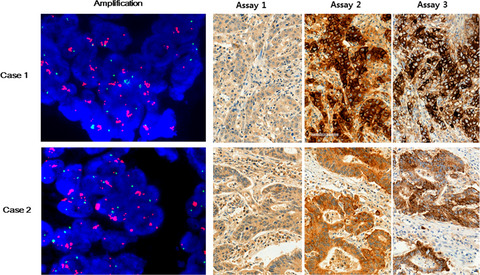
We undertook this study to evaluate programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) expression in colorectal cancer with immunohistochemistry using 3 different antibodies as well as multiple cut-off points for denoting PD-L1 positivity. We also evaluated the CD274/PD-L1 gene copy number in colorectal cancers using FISH.
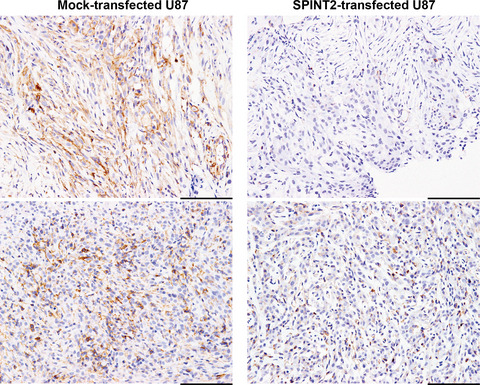
Aberrant methylation and silencing of the SPINT2 gene in high-grade gliomas
- Pages: 2970-2979
- First Published: 10 July 2018
REPORTS
Clinical practice guidance for next-generation sequencing in cancer diagnosis and treatment (Edition 1.0)
- Pages: 2980-2985
- First Published: 05 September 2018
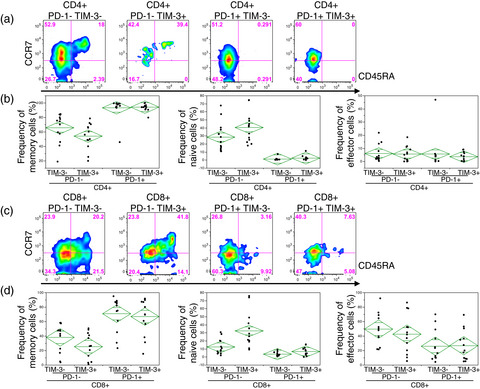
PD-1+ TIM-3+ T cells in malignant ascites predict prognosis of gastrointestinal cancer
- Pages: 2986-2992
- First Published: 05 September 2018