Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Research Articles
Wafer reuse for repeated growth of III–V solar cells
- Pages: 155-159
- First Published: 11 March 2010
Optimal design of periodic surface texture for thin-film a-Si:H solar cells
- Pages: 160-167
- First Published: 11 March 2010
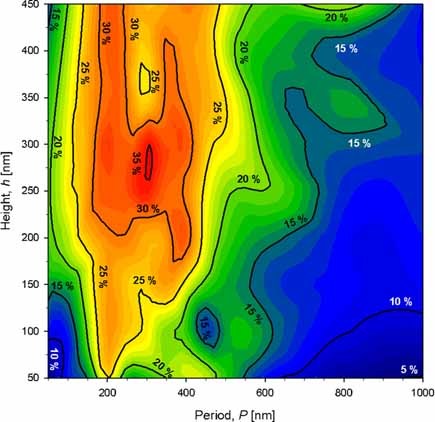
Optical effects of the rectangular-like periodic textures introduced at the interfaces of a-Si:H solar cells on the short circuit current and external quantum efficiency were studied by 2-D simulations. Three main interdependent effects that occur due to the periodic-texture were analysed in the paper. These three effects are the antireflective effect, improved light scattering and the optical losses in back metal layer and they strongly influence the overall performance of the cell.
Durability of Pb-free solder between copper interconnect and silicon in photovoltaic cells
- Pages: 168-182
- First Published: 11 March 2010
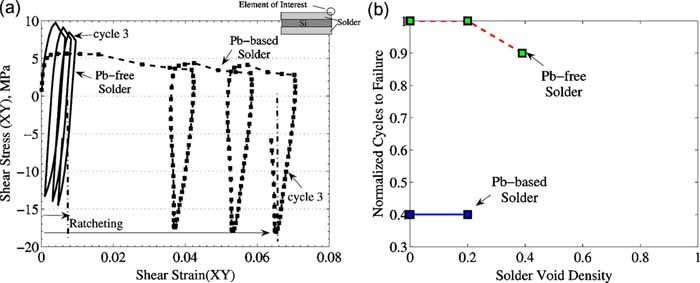
The superior thermal cycling fatigue durability of Pb-free cells was also confirmed with physics of failure (PoF) analysis, consisting of nonlinear finite element (FE) stress analysis and an energy-partitioning (E-P) solder fatigue model. FE models predict that even the most voided Pb-free cells modeled are twice as durable as void-free Pb-based cells, under the accelerated temperature cycle used in the test. The acceleration factor (AF) predicted by the PoF analysis for a typical service environment is three times higher for Pb-free cells than that for Pb-based cells.
Analysis of one-axis tracking strategies for PV systems in Europe
- Pages: 183-194
- First Published: 11 March 2010
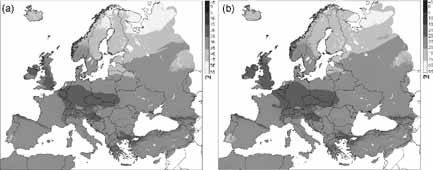
One-axis tracking PV systems can increase the energy output relative to fixed systems by about 30% in Southern Europe, and by up to 50% in Northern Scandinavia. These systems perform almost as well as true sun-tracking (two-axis) systems, with overall performance typically 1–4% lower, but with significant simplifications in design.
Optimization of moth-eye antireflection schemes for silicon solar cells
- Pages: 195-203
- First Published: 11 March 2010
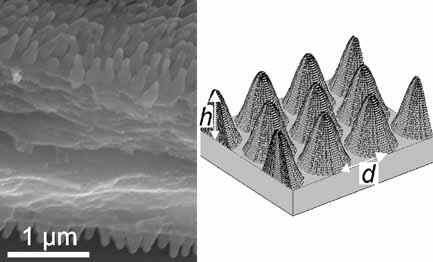
Nanostructured moth-eye antireflection schemes for silicon solar cells are simulated using rigorous coupled wave analysis and compared to traditional thin film coatings. The optimized moth-eye designs are predicted to outperform an optimized double layer thin film coating by approximately 2% for a laboratory cell and approximately 3% for an encapsulated cell. The predicted performance of the silicon moth-eye under encapsulation is particularly remarkable as it exhibits losses of only 0.6% compared to an ideal AR surface.
Research: Short Communication: Accelerated Publications
Determination of the bulk lifetime of bare multicrystalline silicon wafers
- Pages: 204-208
- First Published: 11 March 2010
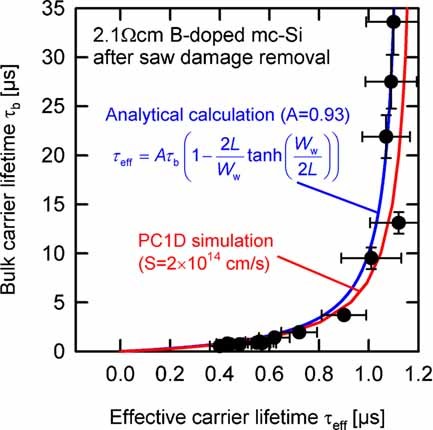
A detailed experimental study demonstrates the relationship between the effective carrier lifetime of unpassivated wafers and their bulk carrier lifetime. Numerical modelling is used to describe this relationship for different surface conditions taking into account the impact of a saw damage layers with poor electronic quality. A prediction of the bulk lifetime from measurements on bare wafers is possible. A simple procedure to implement the analysis for in-line inspection is presented.
Research: Short Communications
ZnO nanorod arrays as an antireflective coating for Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin film solar cells
- Pages: 209-213
- First Published: 11 March 2010
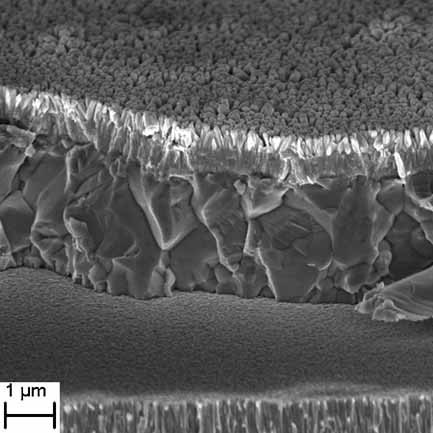
We report the successful application of ZnO nanorod arrays as an efficient antireflective coating for solar cells, in our case Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin film solar cells. We show a simple electrochemical approach for preparing ZnO nanorods on solar cells and give a detailed analysis of the solar cells' optical and electrical properties before and after the ZnO nanorods deposition as well as a brief comparison between the ZnO nanorod antireflective coating and a conventional single layer MgF2 coating. This novel approach is a solar cells substrate independent process.
Applications
RIE-induced carrier lifetime degradation
- Pages: 214-220
- First Published: 11 March 2010
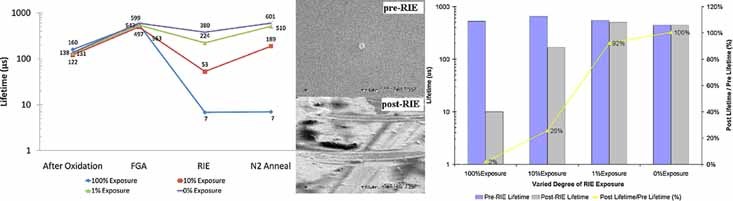
Lifetime degradation for samples where RIE etches into silicon is found to be permanent, while for samples where RIE etches only into dielectric layers of SiO2grown on the wafer, the lifetime degradation is found to be reversible. The reversible degradation in RIE-proc essed samples is associated with radiation damage. By reducing the proportion of a wafer exposed to RIE, the degradation of the effective lifetime of RIE-etched silicon samples can be minimised.
Wire bonding as a cell interconnection technique for polycrystalline silicon thin-film solar cells on glass
- Pages: 221-228
- First Published: 11 March 2010
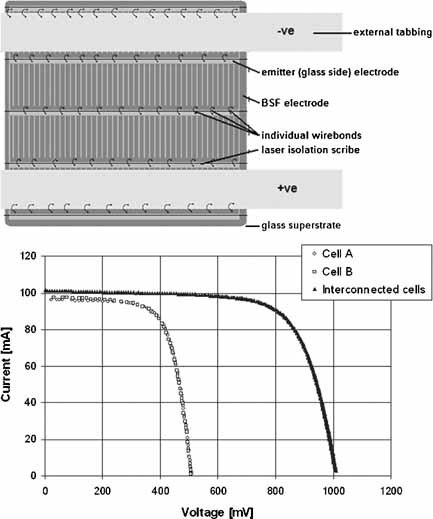
The use of wire bonding as an interconnection and cell tabbing technique for poly-silicon thin-film solar cells on glass is explored. A tabbed and series-interconnected mini-module with an efficiency of 8.3% has been fabricated, which represents a relative increase of 6.6% over the average efficiency of 7.75% for the individual cells prior to interconnection and tabbing. A 9.3% efficient single cell and an interconnected 4-cell mini-module with an efficiency of 5.6% are also reported.
Literature Survey
Photovoltaics literature survey (No. 77)
- Pages: 229-232
- First Published: 30 March 2010
In order to help keep readers up-to-date in the field each issue of Progress in Photovoltaics will contain a list of recently published journal articles most relevant to its aims and scope. This list is drawn from an extremely wide range of journals, including IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, Journal of Applied Physics, Applied Physics Letters, Progress in Photovoltaics and Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells. To assist the reader, the list is separated into broad categories, but please note that these classifications are by no means strict. Also note that inclusion in the list is not an endorsement of a paper's quality. If you have any suggestions please email Santosh Shrestha at [email protected].