Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Special issue on progress in renewable energy
- Page: 571
- First Published: 17 March 2016
A critical review of the renewable portfolio standard in Korea
- Pages: 572-578
- First Published: 02 December 2015
A new concept in tidal turbines
- Pages: 579-586
- First Published: 29 October 2015
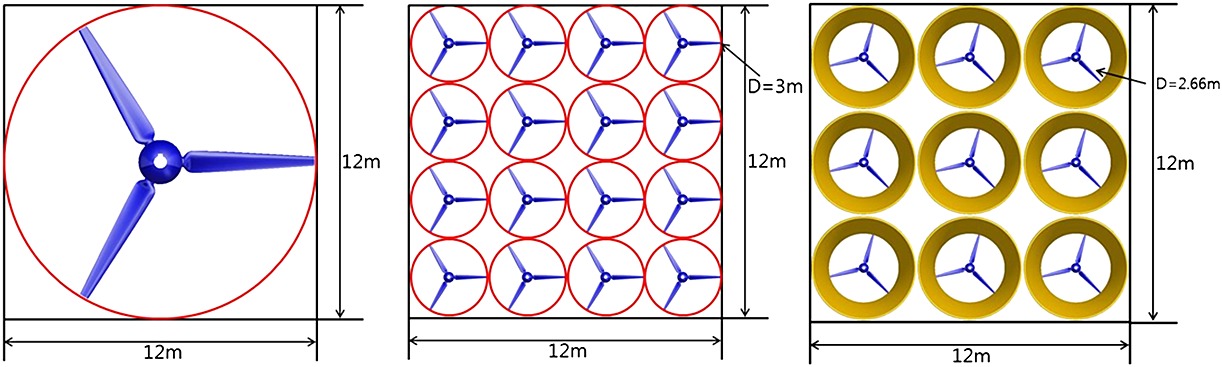
Vertical arrays of reduced- diameter tidal turbines enable power generation from low- velocity tidal flows. Using tidal stream data gathered in Hong Kong, it is demonstrated that vertical arrays increases power generation due to a reduced cut-in speed, harnessing flows that were previously deemed uneconomical. With the additional advantages of reduced cost of fabrication, installation, and maintenance from using smaller- diameter, modular tidal turbines, this concept greatly increases the potential for tidal energy generation worldwide.
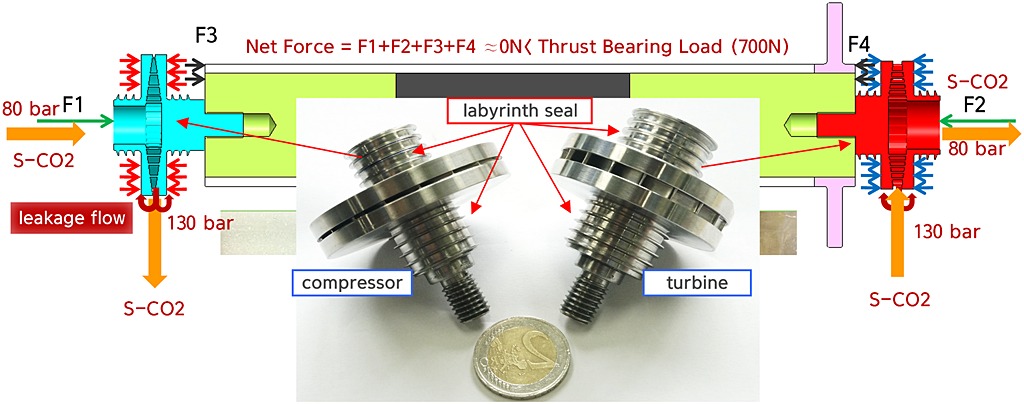
Development of the turbomachinery for the supercritical carbon dioxide power cycle
- Pages: 587-599
- First Published: 04 November 2015
Experiments on the hydrodynamic performance of horizontal axis tidal current turbine and desalination of sea water
- Pages: 600-609
- First Published: 11 November 2015
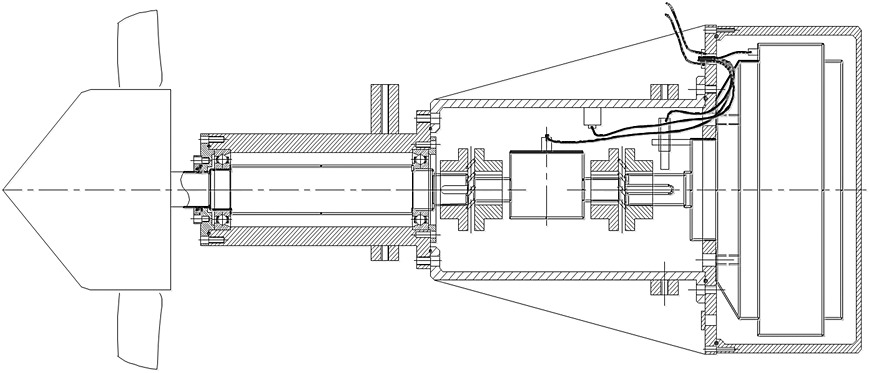
The comprehensive experiment rigs are built. The experimental results indicate that the efficiency of the newly developed turbine could reach up to 47.6%; the corresponding tip speed ratio is from 3.5 to 6. When the tidal current velocity exceeds 1.0 m/s, the pressure increases to 3.5 Mpa, and desalination of sea water can be carried out by our designed device.
Optimization of blade setting angles of a counter-rotating type horizontal-axis tidal turbine using response surface methodology and experimental validation
- Pages: 610-617
- First Published: 13 August 2015
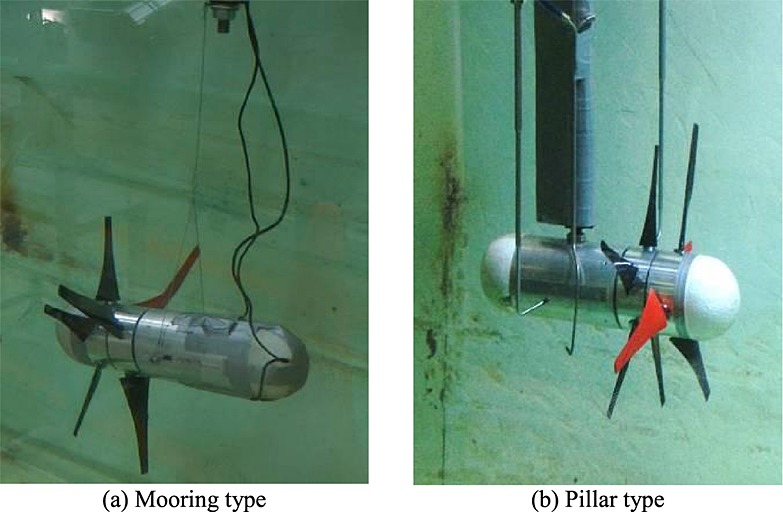
A model counter-rotating type horizontal-axis tidal turbine was designed based on the blade element momentum theory in order to exploit renewable energies form tidal currents. And a second-order response surface methodology (RSM) with the aid of three-dimensional Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes (RANS) analysis was employed to obtain the optimal match of front and rear blade setting angles. Furthermore, experimental tests in the wind tunnel were carried out to verify the numerical predictions. The performance of the optimal turbine has been proven to be greatly improved by both of CFD predictions and experimental results.
The effects of non-torque loads on a three-point suspension gearbox for wind turbines
- Pages: 618-631
- First Published: 27 July 2015
The effects of non-torque loads on the load sharing and distribution of planet gears for wind turbine gearboxes were investigated, using the experimental model of a 35-kW class gearbox of size one-fourth that of a 2-MW class three-point suspension gearbox. As a result, the load sharing became non-uniform when radial force and moments were added, while the effect of axial force was insignificant. The load distribution of the tooth face width did not show a clear difference for the non-torque loads.
An experiment for the effects of the distance and rotational direction of two neighboring vertical Savonius blades
- Pages: 632-638
- First Published: 23 November 2015
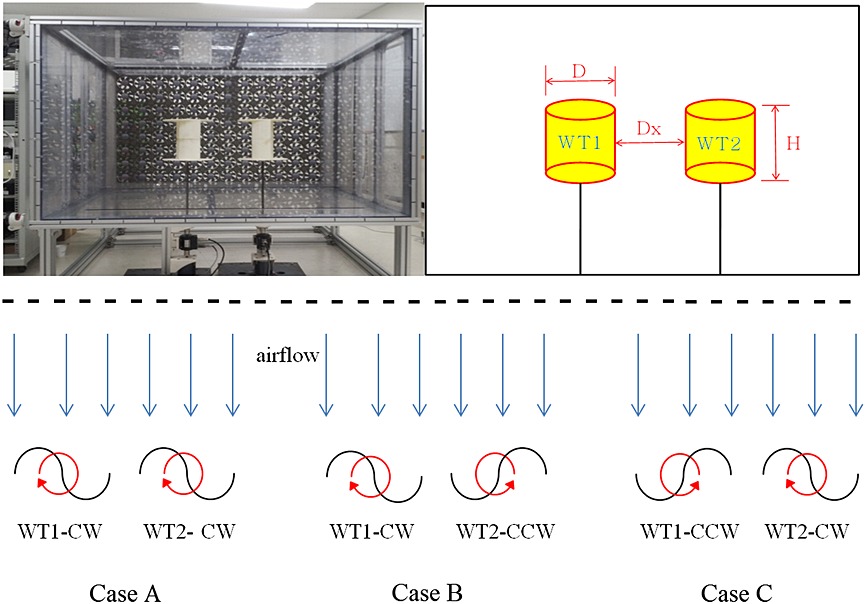
The array effect of the installing distance and rotational direction of two Savonius wind-turbine blades was studied using experimental method consisting of digital wind tunnel and scaled test model. The power coefficient was enhanced when a concave blade created positive torque using the turnaround accelerating flow in the asymmetric rotation. When the blade produced a positive torque by the inner blade using the accelerating airflow though the gap space, the power coefficient was greater for smaller distance of installation.
Ultimate load characteristics of NREL 5-MW offshore wind turbines with different substructures
- Pages: 639-650
- First Published: 16 October 2015
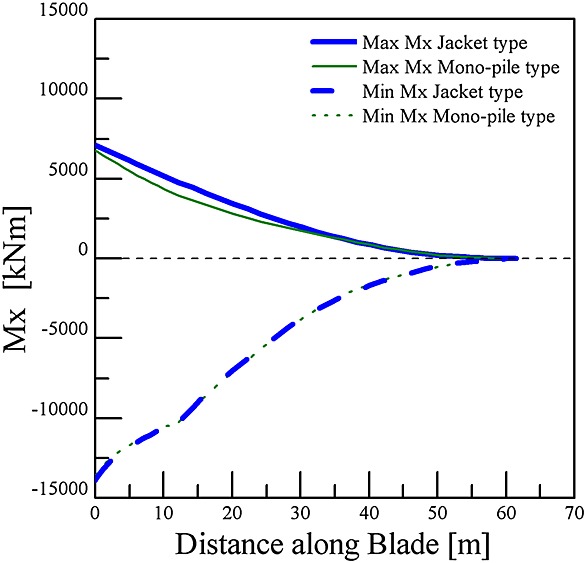
Table IX and Figures 11–13 give the modal analysis results regarding the model used in this research. Similar to the calculation results, the substructures used in the modeling were confirmed to be sufficient for the design margin region. The ultimate loads were compared for blade, tower, hub, and yaw bearing, as shown in Figures 15–18. Based on these results, the jacket-type was confirmed to have a structurally stable form.
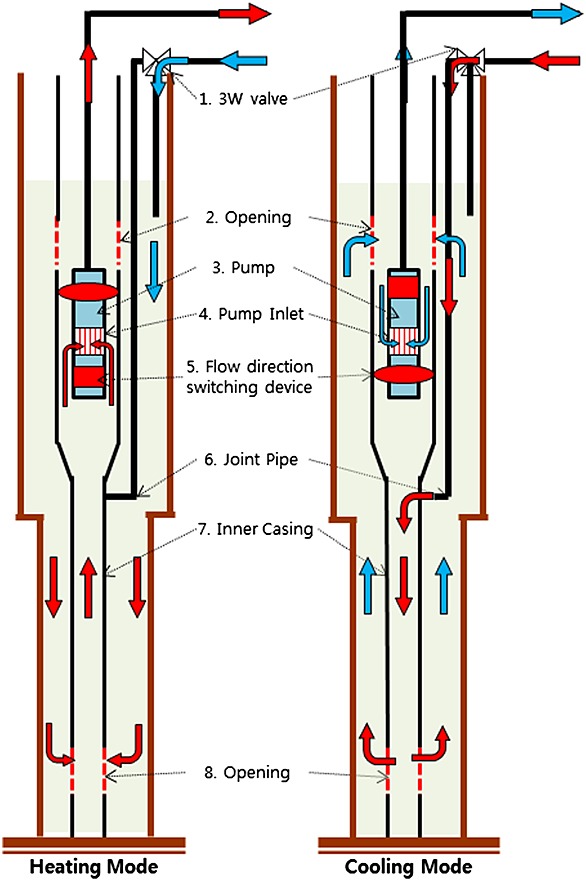
Optimum operation of open-loop ground heat exchanger considering subsurface temperature gradient
- Pages: 651-661
- First Published: 26 October 2015
Cu2ZnSnS4 solar cells with a single spin-coated absorber layer prepared via a simple sol–gel route
- Pages: 662-669
- First Published: 24 November 2015
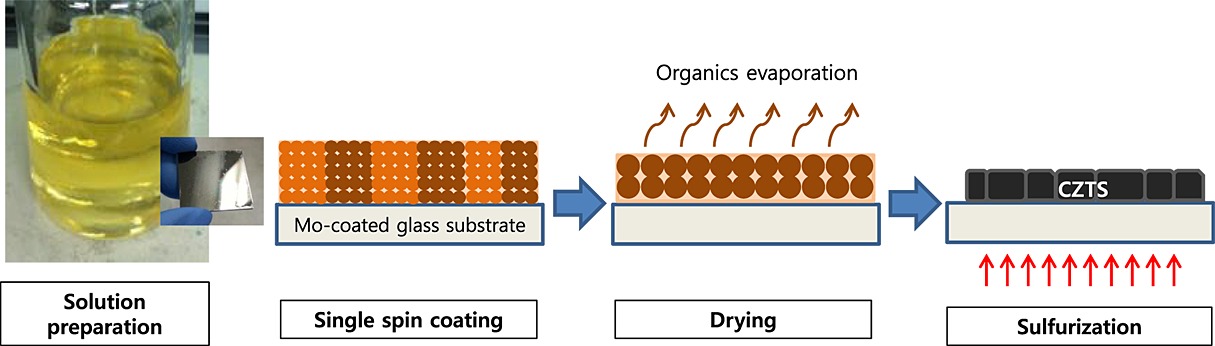
Nearly carbon-free Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) absorber layers were prepared via sulfurization of single spin-coated thin films deposited using a facile sol–gel technique. The best solar cell fabricated with a uniform CZTS absorber layer produced a conversion efficiency of 1.74% despite a porous microstructure of the absorber layer as well as the existence of several secondary phases, such as Cu2SnS3 and ZnS. Further research on CZTS grain growth without secondary phases by optimizing the post-annealing process will improve the photovoltaic cell performance.
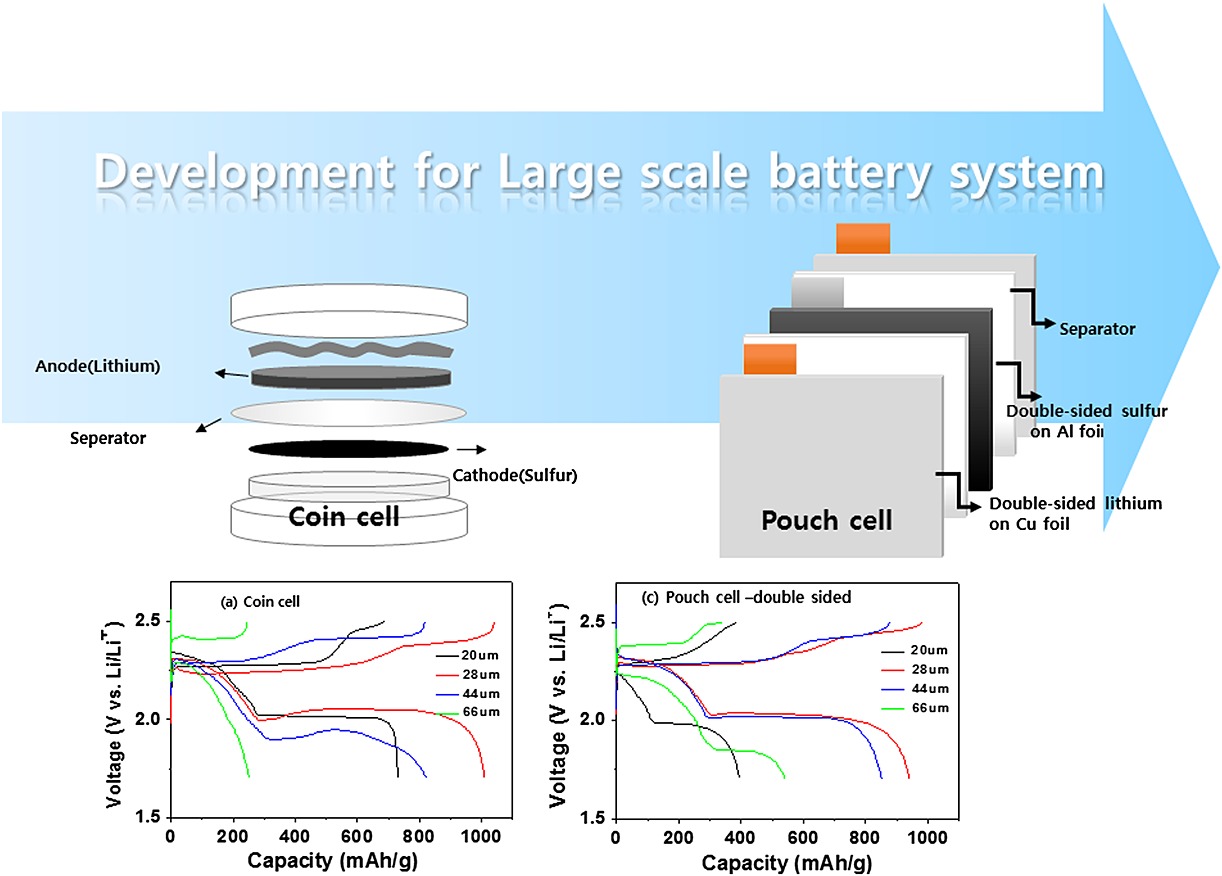
Optimized cell conditions for a high-energy density, large-scale Li–S battery
- Pages: 670-676
- First Published: 03 November 2015
Improved performance of inverted polymer solar cells using pentacene
- Pages: 677-684
- First Published: 16 October 2015
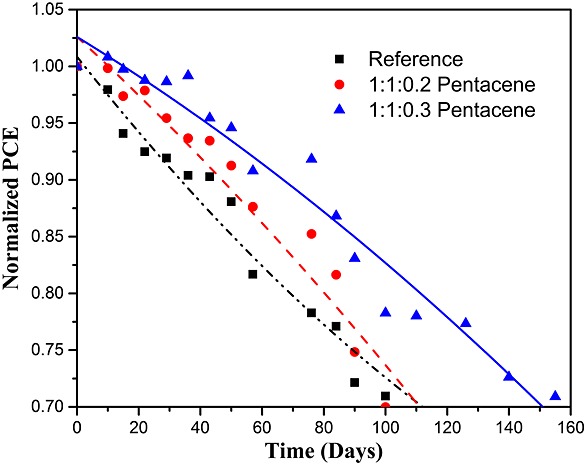
We investigated the role of pentacene in inverted polymer solar cells based on the blends of poly(3-hexylthiophene) (P3HT), (6,6)-phenyl C61-butyric acid methyl ester (PCBM), and pentacene. The performance of organic solar cells with pentacene improved in terms of power conversion efficiency (PCE), thermal stability, and lifetime in the ambient air. The pentacene in the P3HT:PCBM blends modified the crystallization of P3HT and PCBM. The donor–acceptor interface of devices with pentacene was found to be more stable than that without pentacene in the active layer, which was characterized by optical microscopy, atomic force microscopy and ultraviolet–visible absorption spectra. The PCE of pentacene based as-fabricated device was 4.3%, and the PCE of non-encapsulated pentacene device reduced just by about 25% after 4 months.
Efficient energy storage method by multistage pump of the energy storage system using CFD
- Pages: 685-691
- First Published: 09 October 2015
Design and implementation of communication architecture in a distributed energy resource system using IEC 61850 standard
- Pages: 692-701
- First Published: 13 October 2015
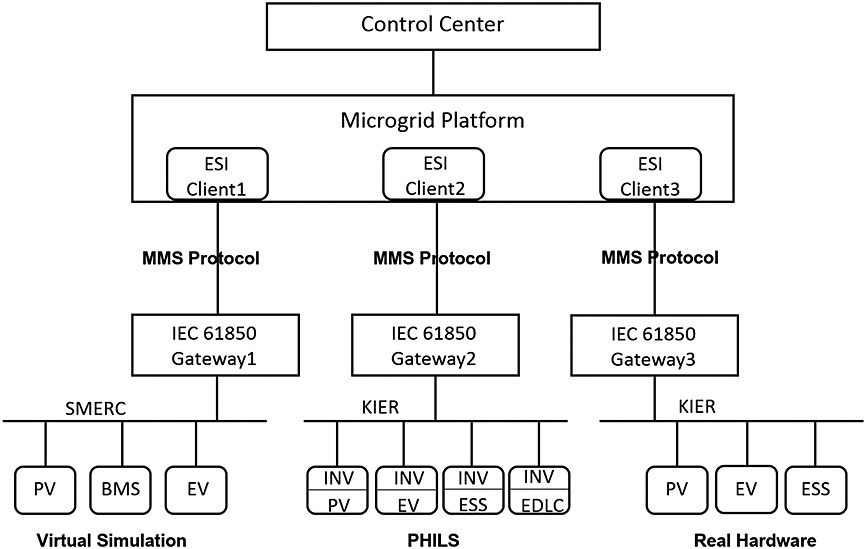
The goal of this paper is to study and propose a common approach to standardize the communication network in the DER system using IEC 61850 and includes a design and implementation of the communication architecture. Two prototypical testbeds for the DER system have been developed in the SMERC laboratory and at KIER, with the aim to demonstrate a case study using the proposed approach. The research results and data collected from the current testbeds indicate a quality integration of the IEC 61850 standard with stable power flow and unified communication architecture in the DER system.
Comparative life cycle assessment of diesel production from crude palm oil and waste cooking oil via pyrolysis
- Pages: 702-713
- First Published: 04 November 2015
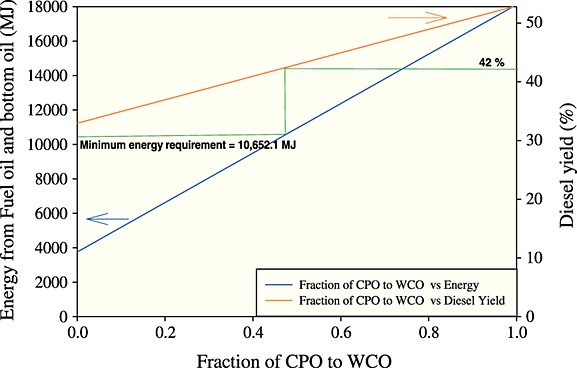
Life cycle assessment for the production of crude palm oil-based and waste cooking oil-based diesel using pyrolysis process is developed to analyze resource uses, energy consumption inputs, and air emissions. We combined actual data from the pilot plant and informative data from the leader organization of Thailand to estimate energy gain and environmental impacts. Blending feedstocks were recommended to be applied for reducing greenhouse gas impact and energy requirement from non-renewable fuel.