Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
An overview of unsolved deficiencies of direct methanol fuel cell technology: factors and parameters affecting its widespread use
- Pages: 1367-1390
- First Published: 18 February 2014
Process simulation and analysis of a five-step copper–chlorine thermochemical water decomposition cycle for sustainable hydrogen production
- Pages: 1391-1402
- First Published: 13 January 2014
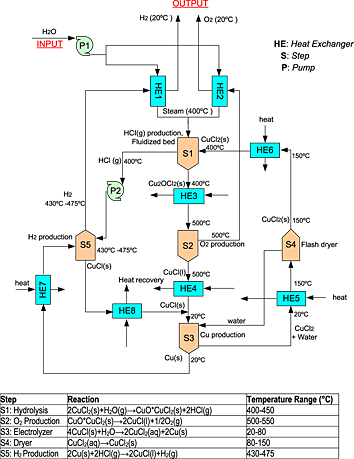
- An Aspen Plus simulation of a five-step Cu–Cl cycle is developed.
- A more realistic user-defined electrolyzer model is simulated using Fortran.
- The effect of production yields on reaction heats in each step is evaluated.
- To achieve high CuO · CuCl2 yields, an excess amount of steam is needed.
- Efficiency of the Cu–Cl cycle is calculated as 44% on the basis of the lower heating value of hydrogen.
Study on zero CO2 emission atmospheric pressure SOFC hybrid power system integrated with OTM
- Pages: 1403-1415
- First Published: 23 January 2014
Power generation using polyaniline/multi-walled carbon nanotubes as an alternative cathode catalyst in microbial fuel cells
- Pages: 1416-1423
- First Published: 29 January 2014
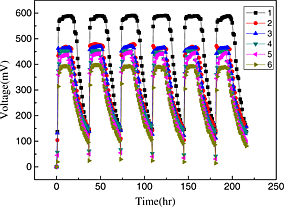
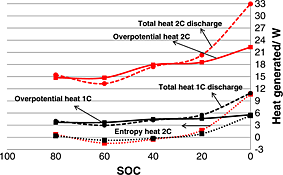
Heat generation in high power prismatic Li-ion battery cell with LiMnNiCoO2 cathode material
- Pages: 1424-1437
- First Published: 10 February 2014
Bridging TiO2 nanoparticles using graphene for use in dye-sensitized solar cells
- Pages: 1438-1445
- First Published: 04 February 2014
Thermodynamic performance analysis of the coal-fired power plant with solar thermal utilizations
- Pages: 1446-1456
- First Published: 19 February 2014
Methodology to estimate the economic, emissions, and energy benefits from combined heat and power systems based on system component efficiencies
- Pages: 1457-1466
- First Published: 18 February 2014
Evaluation of GTHTR300A nuclear power plant design with dry cooling
- Pages: 1467-1477
- First Published: 22 January 2014
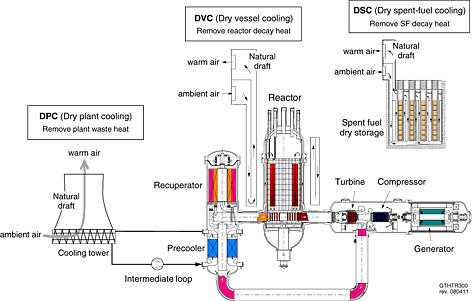
GTHTR300A is a high-temperature gas-cooled reactor power plant design with exclusive dry cooling. The reactor coolant is used to drive a direct-cycle gas turbine, and further dry systems are provided to meet the three general cooling requirements. By reliance on economic and safe dry cooling, the design succeeds in making inland construction feasible even without source of cooling water, and the resulting benefit to safety and environment is compelling as described in the article.
Latent heat energy storage characteristics of building composites of bentonite clay and pumice sand with different organic PCMs
- Pages: 1478-1491
- First Published: 12 March 2014
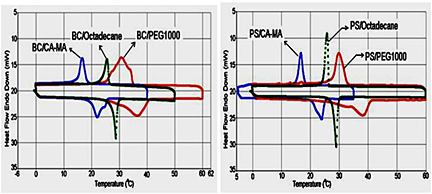
In this study, six new kinds of BCPCMs, BC/PEG1000, PS/PEG1000, BC/octadecane, PS/octadecane, BC/CA–MA, and PS/CA–MA composites, were prepared. The BCPCMs were characterized by SEM, FT-IR, DSC, and TG techniques. The DSC measurements indicated that the LHTES properties make them promising BCPCMs for low temperature-passive TES applications in buildings. Thermal cycling test and TG analysis indicated that they have good thermal reliability, chemical stability, and thermal durability. In addition, the thermal conductivity of BCPCMs was enhanced considerably by addition of EG.
Synthetic and physical characterization of phase change materials microencapsulated by complex coacervation for thermal energy storage applications
- Pages: 1492-1500
- First Published: 10 January 2014