Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Minimum spanning tree–based delay-aware mobile sink traversal in wireless sensor networks
- First Published: 30 January 2017
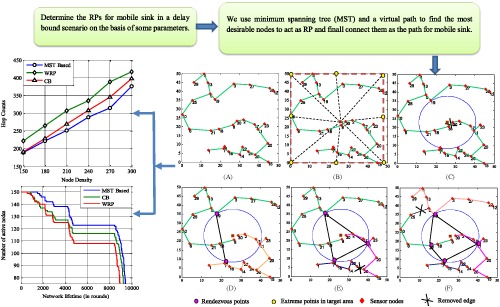
Considering the challenges of path design of mobile sink in any delay-bound application of wireless sensor networks, the article present an efficient algorithm for constructing an efficient rendezvous points–based mobile sink trajectory. The technique is based on a virtual path and minimum spanning tree. It considers several parameters to generate a cost function, which is latter used to select most suitable rendezvous points and is shown to outperform existing algorithms through simulation over various performance metrics.
D2D underlay massive MIMO hybrid networks with improved physical layer secrecy and energy efficiency
- First Published: 14 February 2017
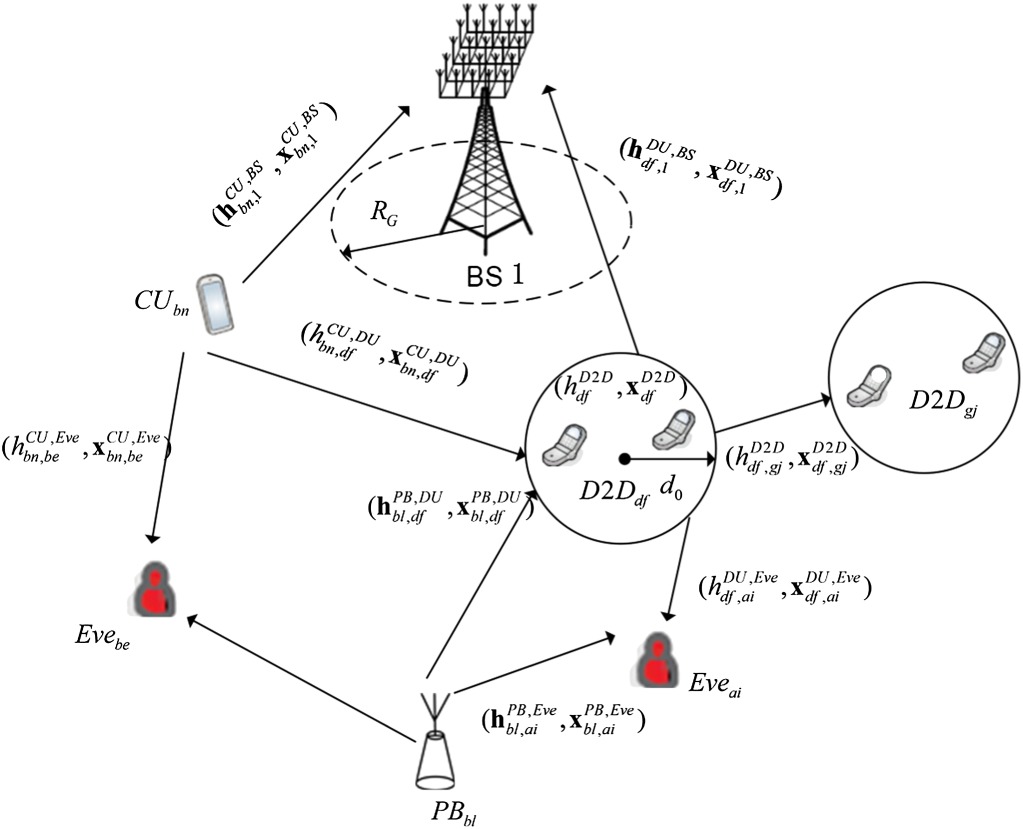
The hybrid network consists of device-to-device (D2D) user equipment and massive multiple-input multiple-output cellular infrastructure, where the D2D user and cellular user links are exposed to passive malicious eavesdroppers. The D2D transmitters harvest the power from the signals of dedicated power beacons, but also the ambient radio frequency interference of cellular user. The signals of PBs can be regarded as an artificial noise so that the secrecy performance of the D2D and cellular links is improved.
An effective graph-theoretic approach towards simultaneous detection of fault(s) and cut(s) in wireless sensor networks
- First Published: 23 January 2017
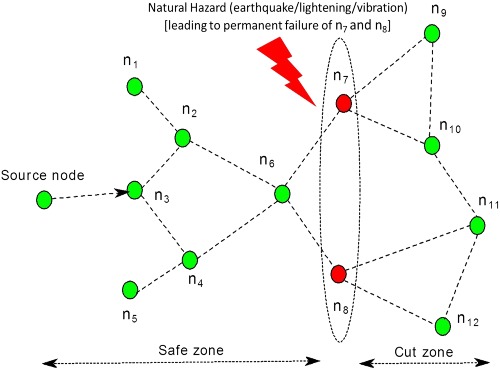
A simple-yet-effective graph-theoretic approach has been formulated to simultaneously detect distributed faults and cuts in the wireless sensor networks. This is an iterative approach where at every time-iteration, a sensor node updates its state by calculating a very important parameter, which we call as potential factor. Two terminologies have been introduced based on position of cuts in the network: safe zone and cut zone. Simulated results in network simulator shows promising results for problem of dense deployment of sensor nodes.
Analysis of multipoint transmission at higher frequencies using 3-D ray tracing
- First Published: 24 January 2017
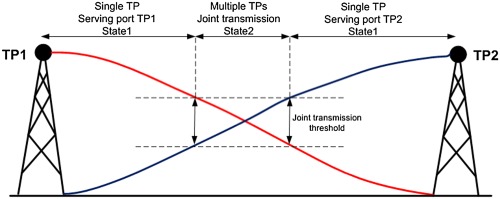
Joint transmission from two transmission ports provides up to 12.46% and 17.78% of the relative throughput gain with respect to the transmission from single port at 15 and 28 GHz, respectively. Utilization of 3-5 dB of joint transmission threshold avoids the unnecessary transmission from the multi ports. Joint transmission helped in making a smooth handover between the two cells, and the ping pong effect was efficiently handled by the joint transmission.
A high-performance belief propagation decoding algorithm for codes with short cycles
- First Published: 28 February 2017
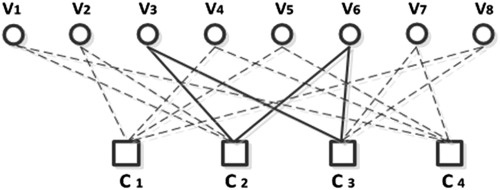
Belief propagation (BP) decoding algorithm is a well-known approach for decoding LDPC codes. We present 2 methods to improve the BP algorithm. In these methods, the calculation of variable nodes is controlled by using “multiplicative correction factor” and “additive correction factor” for 2 channels, namely, AWGN and BSC. Our methods have better performances in error correction.
An energy-efficient algorithm based on sleep-scheduling in IP backbone networks
- First Published: 21 February 2017
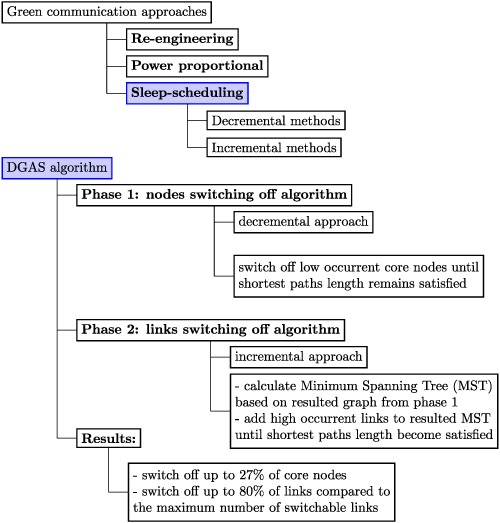
In this paper, we propose a new Distributed Green Algorithm based on Sleep-scheduling (DGAS) to save energy in Internet backbone networks. The DGAS switches off some low-occurrent network links and nodes in 2 consecutive decremental and incremental phases. Our solution does not depend on any centralized controller and any knowledge of traffic matrix.
Receiver design for multicarrier transmission systems in presence of Tx/Rx imperfections
- First Published: 09 February 2017
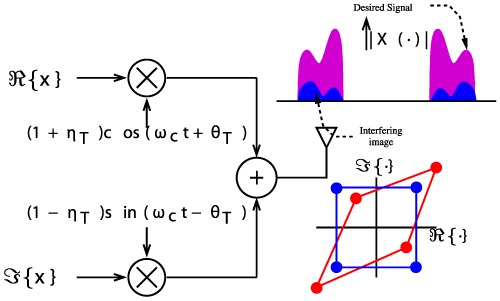
The aim of this article is to design a simple receiver, which can jointly estimate the frequency selective channel impulse response, frequency independent transmit/receive IQ imbalance, and carrier frequency offset with minimal training and implementation complexity. An scalable close-form CFO estimation technique and a novel doubly linear system model have been proposed to iteratively estimate Tx/Rx IQ imbalance and F CIR.
Recursive least square–based fast sparse multipath channel estimation
- First Published: 23 January 2017
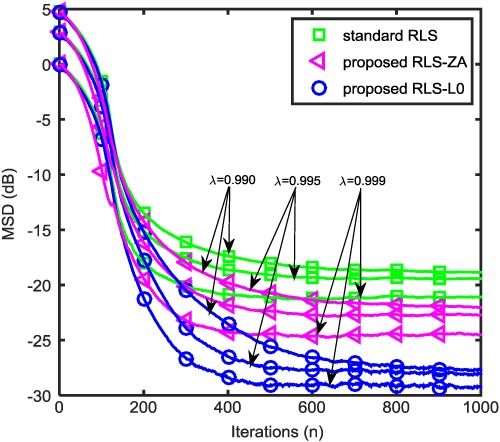
This paper proposes 2 recursive least square–based fast adaptive sparse channel estimation algorithms by introducing sparse constraints, L1-norm and L0-norm. To improve the flexibility of the proposed algorithms, this paper introduces a regularization parameter selection method to adaptively exploit the channel sparsity. Monte Carlo–based computer simulations are conducted to validate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithms.
Power optimization using optimal small cell arrangements in different deployment scenarios
- First Published: 26 January 2017
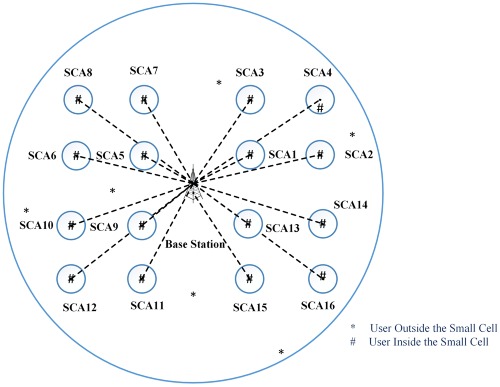
In this paper, a proposed mathematical approach for deployment of small cell access point is used for optimizing the power consumption in the massive multiple input and multiple output and small cell scenario. The new proposed mathematical approach will also help in deciding the optimal number of small cell access points and optimal location of these small cell access points for the particular deployment scenario like urban macro heterogeneous deployment scenario in the 3GPP LTE standard and different macro deployment scenarios in the ITU-R M.2135 standard like urban macro, suburban macro, and rural macro, for optimizing the power.
Cross-layer technique for boosting base-station anonymity in wireless sensor networks
- First Published: 26 January 2017
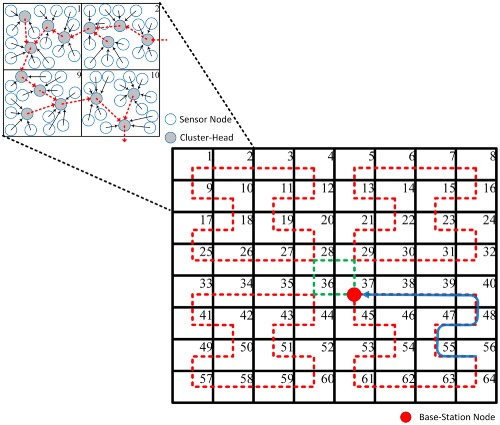
This paper presents a novel technique for boosting the base-station (BS) anonymity by grouping sensor nodes into clusters and creating multiple mesh-based routing topologies among the cluster-heads (CHs). By applying the closed space-filling curves such as the Moore curve, for forming a mesh, the CHs are offered a number of choices for disseminating aggregated data to the BS through inter-CH paths. Then, the BS forwards the aggregated data as well so that it appears as one of the CHs. The simulation results confirm the effectiveness of the proposed technique in boosting the anonymity of the BS.
Agent-based secure routing for underwater acoustic sensor networks
- First Published: 01 February 2017
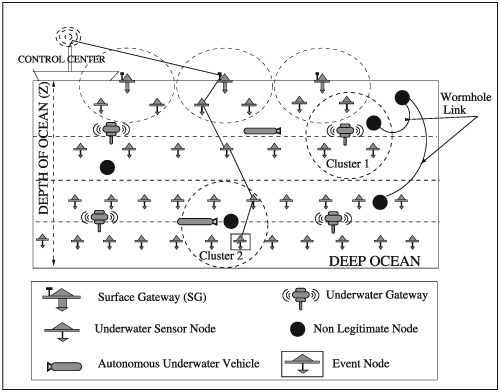
The proposed agent-based secured routing scheme enhances the quality of service by discovering trustworthy neighbors and establishing secured routes using software agents. The secured neighbors are identified based on authentication and Direction of Arrival (DoA) estimation. Authentication mechanism alone sometimes fail to detect the wormhole links; thus, DoA estimation combined with authentication reduces the probability of establishing neighboring relationship with false neighbors. The proposed scheme avoids void conditions and improves scalability.
Analysis of downlink power control and cooperation scheme for two-tier heterogeneous cellular network
- First Published: 14 February 2017
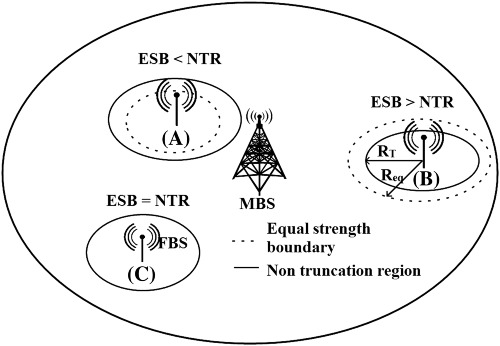
In this work, a mathematical framework is developed to mitigate the cross-tier interference of the macro base station (MBS) tier by using proposed power control scheme (PCS) for femto base station tier. This PCS operates on path loss inversion and location-based power level rule. Moreover, a cooperation scheme and an association policy with MBS (cooperation scheme and an association policy with MBS) is suggested that makes up the loss in performance of femto base station tier due to applied PCS. The effectiveness of proposed PCS and cooperation scheme and an association policy with MBS on outage performance and area spectral efficiency are numerically demonstrated.
Distributed fuzzy logic based energy-aware and coverage preserving unequal clustering algorithm for wireless sensor networks
- First Published: 02 February 2017
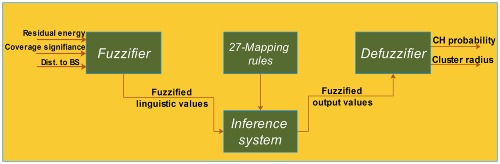
In this paper, a distributed fuzzy logic based energy-aware and coverage preserving unequal clustering algorithm is proposed for WSNs bearing in mind two key aspects: firstly it needs to be energy efficient and secondly it should maximize complete coverage duration of the target area. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first attempt to combine energy and coverage parameters using a fuzzy logic approach also addressing the hot spot problem.
Topology control in the presence of jammers for wireless sensor networks
- First Published: 14 February 2017
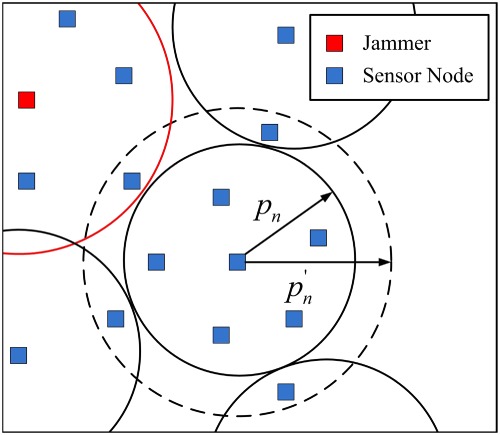
The problem of ensuring packet delivery ratio and high network lifetime in wireless sensor networks in the presence of single or multiple jammers is studied using single-leader-multiple-followers Stackelberg game theory. A scheme, named TC-JAM, for ensuring packet delivery ratio, while avoiding jammers and increasing network lifetime in WSNs, is proposed. Using TC-JAM, the energy consumption of the overall network reduces by up to 62% and the network lifetime increases by 56% to73%.





