Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Image
Cover Image, Volume 52, Issue 14
- Pages: i-ii
- First Published: 10 June 2014

Three commercial bis-benzoxazine monomers based on the aniline derivatives of bisphenol A, bisphenol F, and 3,3′-thiodiphenol are examined using a variety of spectroscopic, chromatographic, and thermo-mechanical techniques. On page 2068 (DOI: 10.1002/pola.27231), Ian Hamerton, Lisa T. McNamara, Brendan J. Howlin, Paul A. Smith, Paul Cross, and Steven Ward report the polymerization kinetics are well described by an autocatalytic model. The kinetic data are compared with parallel studies involving chemically initiated benzoxazine monomers. Molecular simulation is used to examine the rotational freedom of the central bridging units, which is related to the degree of conversion achieved.
Cover Image, Volume 52, Issue 14
- Pages: iii-iv
- First Published: 10 June 2014

Poly(ethylene glycol) end capped with biodegradable hydrophobic dipeptides shows versatile gelation behavior in a range of aqueous and organic solvents. On page 1917 (DOI: 10.1002/pola.27198), G. Rajesh Krishnan, Yuan Yuan, Ayesha Arzumand, and Debanjan Sarkar report this gelation characteristic is attributed to the aggregation of polymer chains induced by dipeptide end groups. These gels are biodegradable and possess physico-mechanical characteristics suitable for biomedical applications. Furthermore, proteins and hydrophobic model drugs can be encapsulated within the gels from aqueous and organic solvents, respectively, and can be released in a controlled fashion, indicating the potential application of the gels as drug delivery vehicles.
Articles
Gelation characteristics and applications of poly(ethylene glycol) end capped with hydrophobic biodegradable dipeptides
- Pages: 1917-1928
- First Published: 22 April 2014
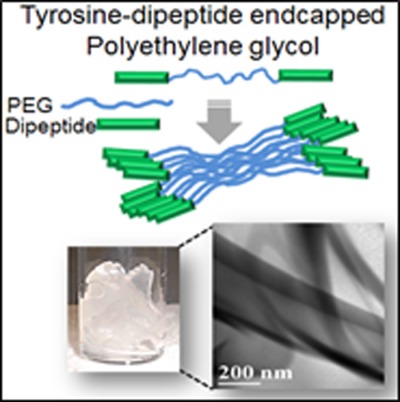
Aggregation of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) end capped with tyrosine-derived dipeptides in various solvents leads to the formation of both hydrogel and organogels. Noncovalent interactions between the end groups associate end functionalized PEG to form physically cross-linked networks in presence of solvents. Morphologically, the gels contain interpenetrating nanosheet structures. The gels are biodegradable and posses physico-mechanical properties suitable for delivery of small molecules and proteins.
Spotlight Article
Effects of donor unit and π-bridge on photovoltaic properties of D–A copolymers based on benzo[1,2-b:4,5-c']-dithiophene-4,8-dione acceptor unit
- Pages: 1929-1940
- First Published: 29 April 2014
![Effects of donor unit and π-bridge on photovoltaic properties of D–A copolymers based on benzo[1,2-b:4,5-c']-dithiophene-4,8-dione acceptor unit](/cms/asset/7ca27334-f81d-4e36-ae27-764a90291817/pola27209-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Four D-π-A type conjugated copolymers—PBDT-AT, PDTS-AT, PBDT-TT, and PDTS-TT—were designed and synthesized to investigate different donor and π-bridge effects on the optical and electrochemical properties, hole mobilities, and photovoltaic performance of the copolymers. The polymer solar cells based on PBDT-AT:PC70BM with methanol treatment showed a power conversion efficiency of 5.91%, under the illumination of AM 1.5 G 100 mW cm−2.
Efficient one-pot synthesis of water-compatible and photoresponsive molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles by facile RAFT precipitation polymerization
- Pages: 1941-1952
- First Published: 30 April 2014
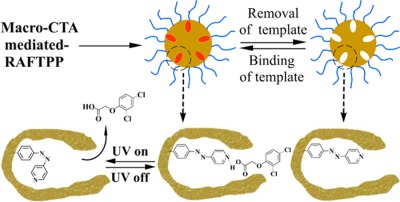
A facile, general, and highly efficient one-pot approach to obtain hydrophilic azobenzene (azo)-containing molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles with photoresponsive template binding and release properties in aqueous media is described. This involves the combined use of hydrophilic macromolecular chain transfer agentmediated reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) precipitation polymerization and easily available water-insoluble azo functional monomers.
Healable dual organic–inorganic crosslinked sol–gel based polymers: Crosslinking density and tetrasulfide content effect
- Pages: 1953-1961
- First Published: 25 April 2014
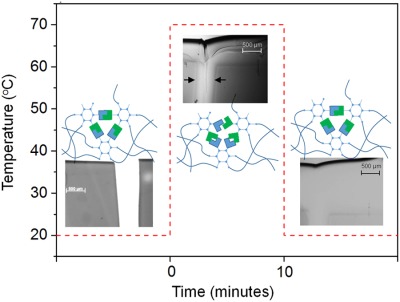
Novel organic–inorganic sol–gel based polymers restore their integrity by selective breaking of tetrasulfide groups upon moderate thermo-mechanical stimulus. The hybrid sol–gel architecture offers an attractive combination of a tuneable mesoscopic flow due to the presence of thermo-responsive reversible bonds while preserving relatively high mechanical properties during the healing stage as a result of the stable crosslinked network.
Self-immolative nanoparticles triggered by hydrogen peroxide and pH
- Pages: 1962-1969
- First Published: 22 April 2014
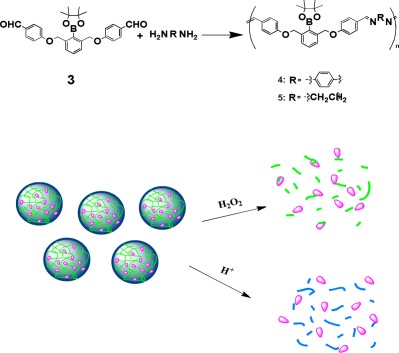
The azomethine-based oligomers bearing boronate groups and imine moieties in the main chain were synthesized from a dialdehyde monomer and p-phenylenediamine or ethylene diamine, respectively. Based on the oligomers, the nanoparticles with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and pH dual-responsive properties were constructed and encapsulated nile red inside. The degradation behavior of nanoparticles and the release of nile red triggered by H2O2 and pH were explored.
High-performance field-effect transistors based on furan-containing diketopyrrolopyrrole copolymer under a mild annealing temperature
- Pages: 1970-1977
- First Published: 22 April 2014
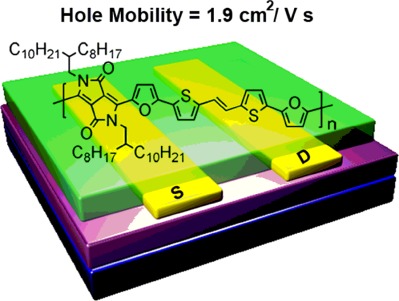
Two highly π-extended copolymers were designed and synthesized by copolymerizing furan-flanked diketopyrrolopyrrole units with (E)-2-(2-(thiophen-2-yl)vinyl)thiophene moieties for solution-processed polymer field-effect transistors (FETs). A typical nodular morphology with the ultrasmall lamellar distances of 16.84–19.15 Å had been demonstrated for the polymer thin films, therefore facilitating high-performance charge transport. The highest hole mobility without thermal annealing treatment reached 1.05 cm2 V−1 s−1. For the PDVF-8 thin films annealed at 100 ° C, moreover, an improved hole mobility of 1.90 cm2 V−1 s−1 was achieved, among the highest values of the reported polymer-based FETs fabricated from a mild temperature.
Intramolecular donor–acceptor copolymers containing side-chain-tethered perylenebis(dicarboximide) moieties for panchromatic solar cells
- Pages: 1978-1988
- First Published: 25 April 2014
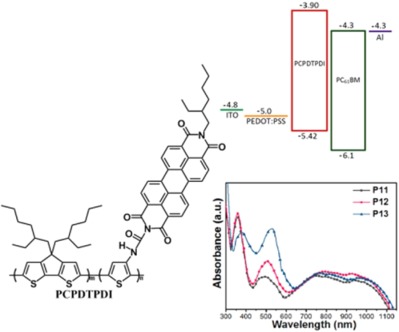
When increasing the molar ratio of the PDI unit, the Voc could be raised and the power conversion efficiency of the photovoltaic devices have shown a significant improvement. On the whole, the device based on the P13:PC61BM blend with a molar ratio of 1:3 displayed the best performance with the optimal power conversion efficiency of 1.66%, highest Voc of 0.573 V and Jsc of 6.82 mA/cm2 without annealing and any additives.
Electrochromic enhancement of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) films functionalized with hydroxymethyl and ethylene oxide
- Pages: 1989-1999
- First Published: 22 April 2014
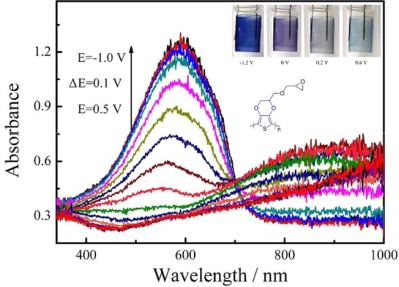
The electrosynthesis of poly(hydroxymethylated-3,4-ethylenedioxylthiophene) and ethylene oxide functionalized poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) are reported. In comparison with PEDOT, these polymers exhibit excellent electrochromic performances, including higher optical contrast ratio (57%), higher coloration efficiency (338 cm2 C−1), lower switching potential, fast response time, good electrochemical, and optical stability. They have promising potential applications in electrochromic devices and optical displays.
Disulfide-centered star-shaped polypeptide-PEO block copolymers for reduction-triggered drug release
- Pages: 2000-2010
- First Published: 22 April 2014
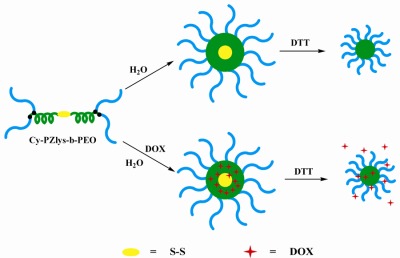
Disulfide-centered star-shaped polypeptide-based block copolymers Cy-PZlys-b-PEO were successfully synthesized by combining ROP and thiol-yne chemistry. Despite a liquid crystal phase transition behavior, the inner α-helical PZlys blocks greatly suppressed the crystallinity of the outer PEO blocks. Cy-PZlys-b-PEO self-assembled into nearly spherical micelles, and these micelles were progressively reduced to smaller micelles in 10 mM 1,4-dithiothreitol, exhibiting a reduction-sensitivity. The DOX-loaded micelles presented a reduction-triggered profile, enhancing them useful for intracellular GSH-triggered drug delivery systems.
Spotlight Article
Pyrrolidone-functional smart polymers via nitroxide-mediated polymerization
- Pages: 2011-2024
- First Published: 30 April 2014
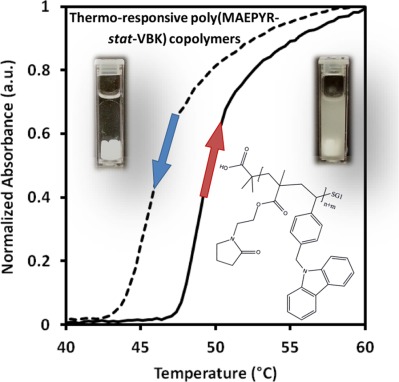
A viable route toward thermoresponsive, pyrrolidone-functional polymers via nitroxide-mediated polymerization is presented. Pyrrolidone-rich poly(N-(2-methacryloyloxyethyl)-pyrrolidone-stat-9-(4-vinylbenzyl)-9H-carbazole) (MAEPYR-stat-VBK) statistical and block copolymers with water-soluble poly(dimethylacrylamide) were synthesized and controlled relatively well by low amounts of VBK comonomer in the feed (1–5 mol %). UV–Vis and dynamic light scattering were used to evaluate thermoresponsive behavior in aqueous media. Cloud point temperatures (CPTs) were tuned by altering VBK composition, heating rate, and solution concentration.
Reversible fixation and release of carbon dioxide with a binary system consisting of polyethylene glycol and polystyrene-bearing cyclic amidine pendant group
- Pages: 2025-2031
- First Published: 02 May 2014
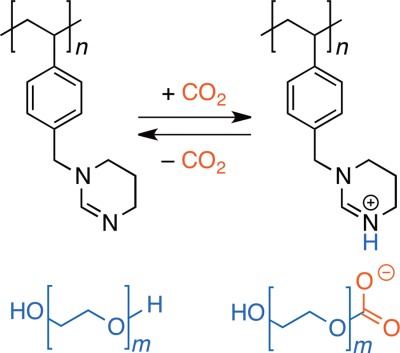
The polystyrene bearing cyclic amidine pendant groups was synthesized via free radical polymerization of the HCl salt of the corresponding styrene monomer followed by neutralization. For comparison, the polystyrene bearing N-formyl-1,3-propanediamine pendant groups was prepared through hydrolysis of the amidine polymer. It was found that the binary system of the amidine polymer and PEG captured and released CO2 more efficiently than that of the N-formyl-1,3-propanediamine polymer and PEG.
Bis(4-nitrophenyl) phosphate as an efficient organocatalyst for ring-opening polymerization of β-butyrolactone leading to end-functionalized and diblock polyesters
- Pages: 2032-2039
- First Published: 02 May 2014
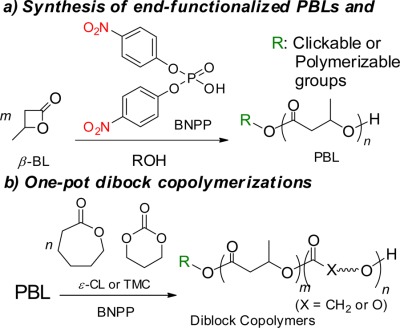
The bis(4-nitrophenyl) phosphate-catalyzed ring-opening polymerization of β-butyrolactone (β-BL) efficiently proceeded via monomer and initiator/chain-end activation, leading to well-defined poly(β-butyrolactone) (PBL) with controlled molecular weight and polydispersity. Functional initiators were applicable for synthesizing various end-functionalized PBLs. In addition, diblock copolymerization of ε-caprolactone or trimethylene carbonate with β-BL proceeded successfully in a one-pot synthesis.
Spotlight Article
Thiol-epoxy polymerization via an AB monomer: Synthetic access to high molecular weight poly(β-hydroxythio-ether)s
- Pages: 2040-2046
- First Published: 25 April 2014
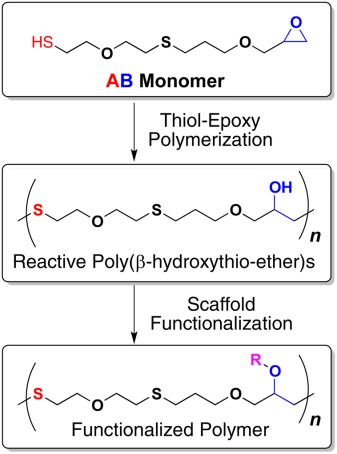
An AB type of monomer carrying an epoxy and a thiol group is synthesized. Base-catalyzed thiol-epoxy polymerization of this monomer gave access to reactive and functionalizable poly(β-hydroxythio-ether)s. The molecular weight of the polymers resulting from the present AB monomer route was found to be five times higher than the molecular weight of the polymers prepared through a previously reported AA/BB approach.
Suppressing charge recombination by incorporating 3,6-carbazole into poly[9-(heptadecan-9-yl)-9H-carbazole-2,7-diyl-alt-(5,6-bis-(octyloxy)-4,7-di(thiophen-2-yl)benzo[1,2,5]-thiadiazole)-5,5-diyl]
- Pages: 2047-2056
- First Published: 04 May 2014
![Suppressing charge recombination by incorporating 3,6-carbazole into poly[9-(heptadecan-9-yl)-9H-carbazole-2,7-diyl-alt-(5,6-bis-(octyloxy)-4,7-di(thiophen-2-yl)benzo[1,2,5]-thiadiazole)-5,5-diyl]](/cms/asset/97ab90d1-bde6-4189-9316-eb600c7c2dc8/pola27214-toc-0001-m.jpg)
A series of copolymers were synthesized based on alkoxy-bis(bromothienyl)benzo-thiadiazole with various amounts of 3,6-carbazole. P0.02, which incorporated 2% of 3,6-carbazole, exhibited a good photovoltaic performance (3.8–5.3%). This improvement largely arose from suppressed nongeminated recombination owing to the strong intermolecular interactions of the 3,6-carbazole moieties. Appropriate quantities of the 3,6-carbozole units enhanced the hole mobility by introducing conjugation breaks that improved the intermolecular interactions; however, an excess appeared to hamper hole transport, thereby increasing recombination reactions in the polymer solar cells.
Tuning amphiphilicity/temperature-induced self-assembly and in-situ disulfide crosslinking of reduction-responsive block copolymers
- Pages: 2057-2067
- First Published: 29 April 2014
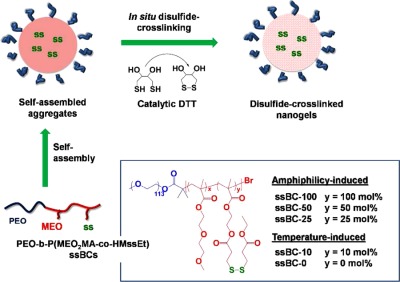
Reductive- and thermo-responsive poly(ethylene oxide)-based block copolymers with tunable amphiphilicity/temperature induced self-assembly were synthesized by ARGET ATRP. By varying the ratio of hydrophilic to pendant disulfide containing monomers, the amphiphilicity and in-situ disulfide crosslinking of reduction-responsive copolymers could be tuned to yield self-assembled nanogels via temperature induced self-assembly exhibiting enhanced colloidal stability upon dilution.
Examining the kinetics of the thermal polymerization of commercial aromatic bis-benzoxazines
- Pages: 2068-2081
- First Published: 14 May 2014
Three bis-benzoxazine monomers based on the aniline derivatives of bisphenol A (BA-a), bisphenol F (BF-a), and 3,3′-thiodiphenol (BT-a) are examined using a variety of spectroscopic, chromatographic and thermo-mechanical techniques. The kinetics of the polymerization of BA-a were found to be well described using an autocatalytic model.