Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information - Table of Contents
Free Access
free
Issue Information - Table of Contents
- Pages: 429-430
- First Published: 24 January 2017
Review Article
Full Access
full
Fate of microglia during HIV-1 infection: From activation to senescence?
- Pages: 431-446
- First Published: 26 November 2016
Research Articles
Open Access
oa
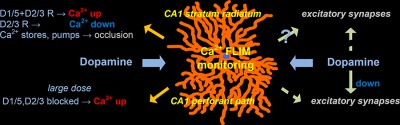
Dopamine elevates and lowers astroglial Ca2+ through distinct pathways depending on local synaptic circuitry
- Pages: 447-459
- First Published: 29 November 2016
Full Access
full
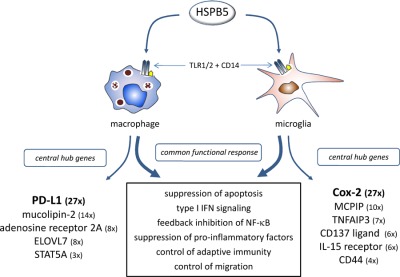
Identification of highly connected hub genes in the protective response program of human macrophages and microglia activated by alpha B-crystallin
- Pages: 460-473
- First Published: 07 January 2017
Full Access
full
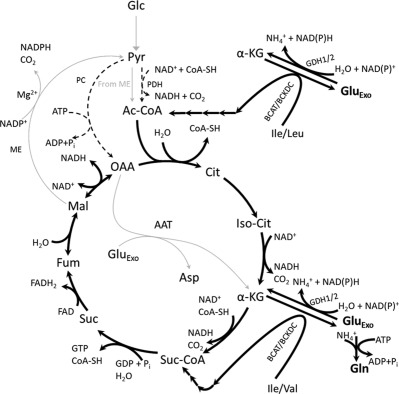
Expression of the human isoform of glutamate dehydrogenase, hGDH2, augments TCA cycle capacity and oxidative metabolism of glutamate during glucose deprivation in astrocytes
- Pages: 474-488
- First Published: 29 December 2016
Full Access
full
Conditional knockout of TOG results in CNS hypomyelination
- Pages: 489-501
- First Published: 07 January 2017
Main Points
- TOG is required for the expression of myelin basic protein (MBP).
- MBP transcripts level is not affected by the absence of TOG but in contrast to control they remain in the oligodendrocyte cell body.
- MBP regulates CNS myelin level.
Full Access
full
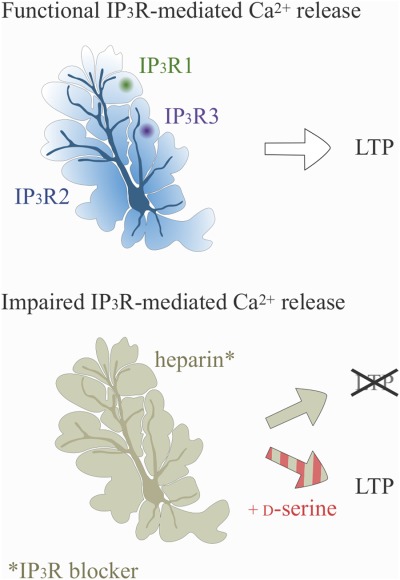
Astrocytic IP3Rs: Contribution to Ca2+ signalling and hippocampal LTP
- Pages: 502-513
- First Published: 07 January 2017
Full Access
full
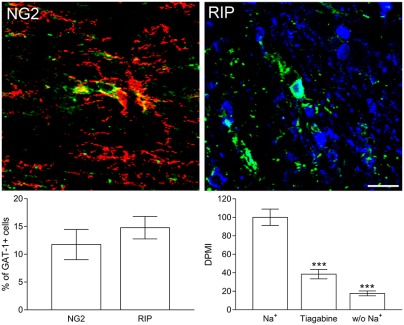
GAT-1 mediated GABA uptake in rat oligodendrocytes
- Pages: 514-522
- First Published: 10 January 2017
Full Access
full
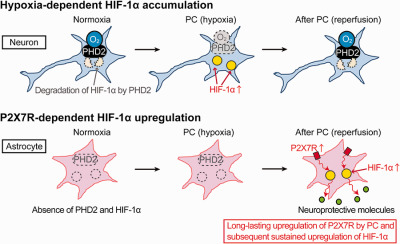
Hypoxia-independent mechanisms of HIF-1α expression in astrocytes after ischemic preconditioning
- Pages: 523-530
- First Published: 07 January 2017