Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
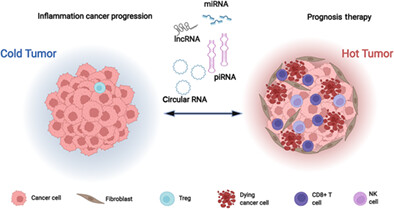
Impact of noncoding RNAs on cancer directed immune therapies: Now then and forever
- Pages: 981-992
- First Published: 30 April 2022
CANCER EPIDEMIOLOGY
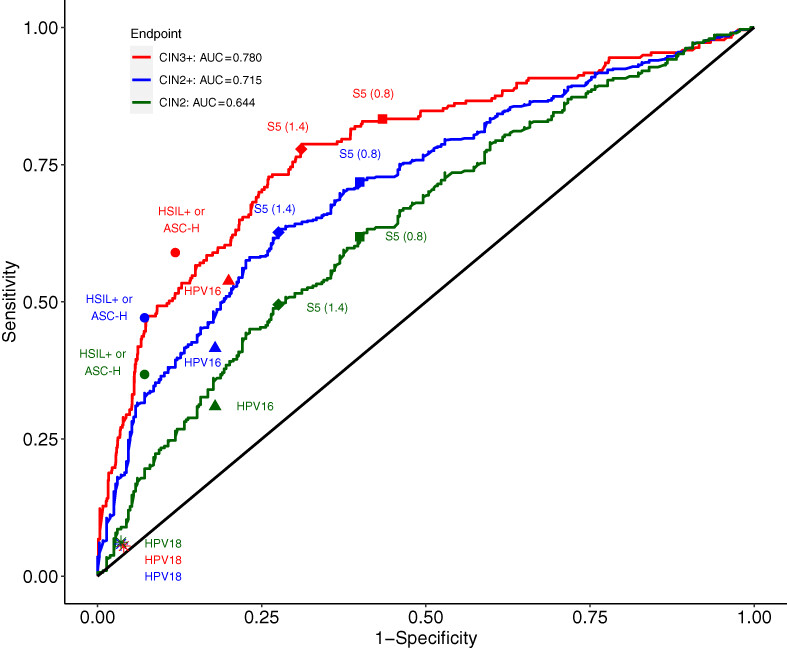
DNA methylation testing with S5 for triage of high-risk HPV positive women
- Pages: 993-1004
- First Published: 27 April 2022
What's new?
Human papillomavirus (HPV) testing is a more sensitive but less specific approach for cervical cancer screening than cytology. Methylation testing of host and viral genes has emerged as a promising approach for the triage of women with high-risk HPV. In this population-based study, using the DNA methylation S5 classifier as a triage test for high-risk HPV-positive women yields significantly greater sensitivity and similar positive predictive values for CIN3+ detection than HPV genotyping or cytology triage. Furthermore, S5 can improve discrimination between low- and high-grade cervical precancer, providing valuable information in the often complex and uncertain diagnosis of CIN2.
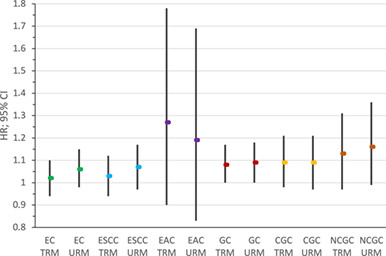
Meat consumption and risk of esophageal and gastric cancer in the Golestan Cohort Study, Iran
- Pages: 1005-1012
- First Published: 30 April 2022
What's new?
While high intakes of red meat and processed meat are risk factors for certain cancer types, especially colorectal cancer, associations with esophageal cancer (EC) and gastric cancer (GC) remain uncertain. Here, meat intake and EC and GC risk were examined in a population in northeast Iran with overall low meat intake, except for high consumption of organ and chicken meat. Hazards regression modeling reveals associations between red meat intake and elevated GC risk, particularly non-cardia GC. There was no association with EC or its subtypes. Further study is needed to determine possible etiological involvement of red meat in GC development.
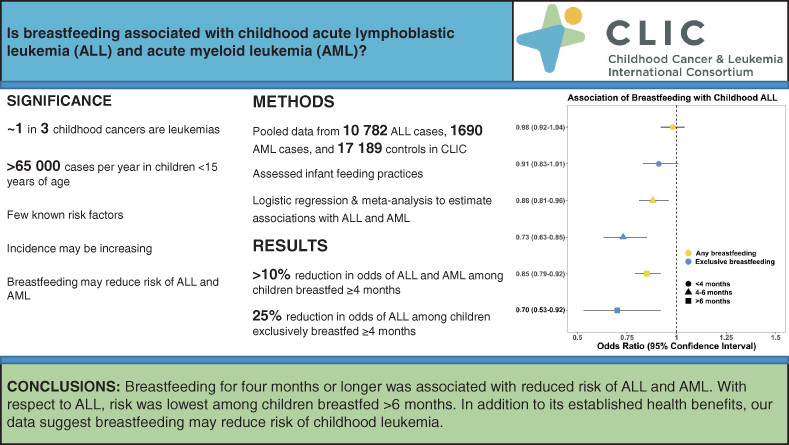
Infant feeding practices and childhood acute leukemia: Findings from the Childhood Cancer & Leukemia International Consortium
- Pages: 1013-1023
- First Published: 09 May 2022
What's new?
Breastfeeding may protect against childhood acute lymphoblastic and acute myeloid leukemia (ALL/AML), but few studies have examined exclusive breastfeeding or interactions with other early life exposures. In this international pooled analysis, breastfeeding was associated with reduced risk of ALL/AML. Risk of ALL was lowest among exclusively-breastfed children or breastfed children who also attended day care. The results indicate a dose-response relationship between breastfeeding and leukemia and highlight the potentially complex joint effects of early life exposures. Few risk factors for ALL and AML have been identified, and the findings support the need to promote breastfeeding for leukemia prevention.
Risk of secondary nonhematologic malignancies after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: A nationwide case-control cohort study
- Pages: 1024-1032
- First Published: 12 May 2022
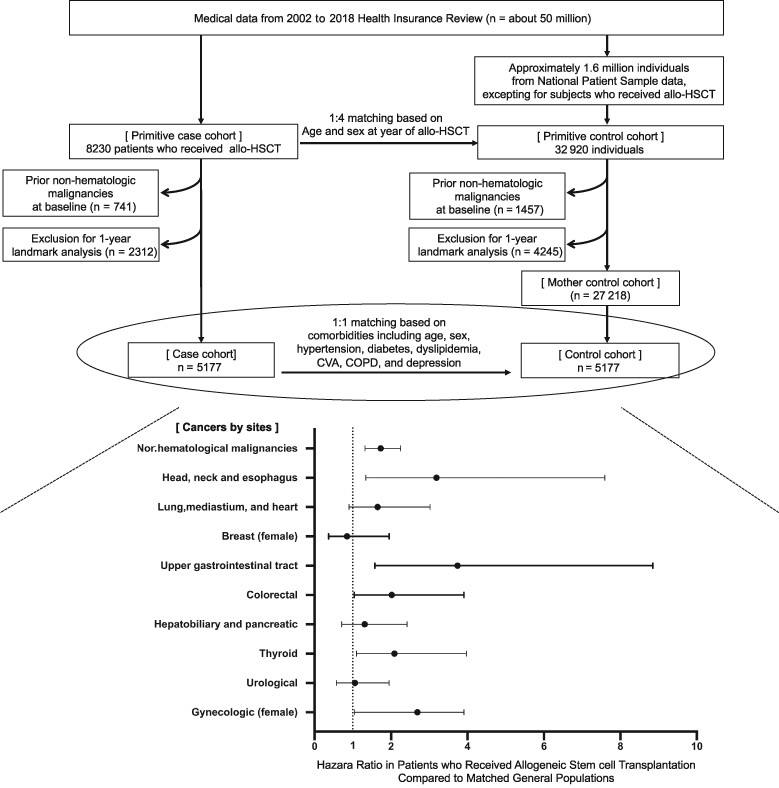
What's new?
While patients who received all ogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-SCT) are at increased risk of secondary nonhematological malignancies, the development of standardized screening strategies is hindered by regional and ethnic differences affecting cancer incidence and site. In this large nationwide, retrospective cohort study in Korea, the 10-year cumulative incidence of secondary nonhematological malignancies in allo-SCT was 4.23%. compared to the general population, the risk was higher for head, neck and esophagus cancers, upper gastrointestinal tract cancers, colorectal cancer, thyroid cancer and gynecological cancers following allo-SCT, suggesting the need to establish robust specific screening programs.
Circulating free testosterone and risk of aggressive prostate cancer: Prospective and Mendelian randomisation analyses in international consortia
- Pages: 1033-1046
- First Published: 17 May 2022
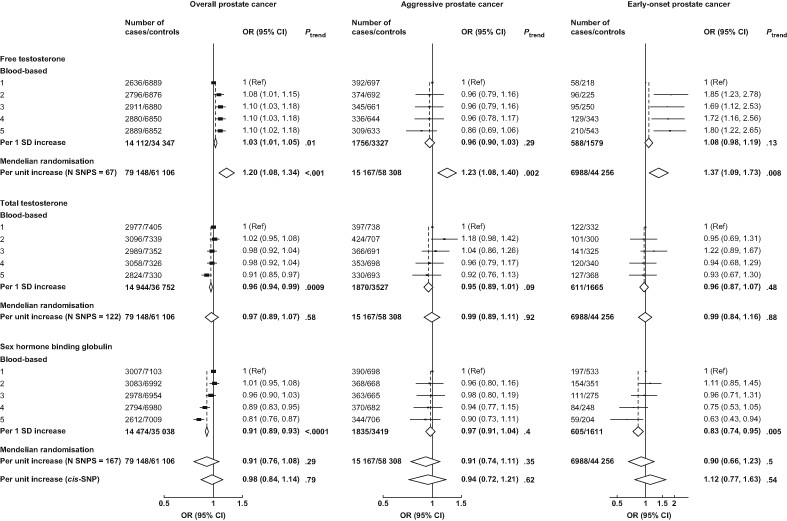
What's new?
The Endogenous Hormones, Nutritional Biomarkers and Prostate Cancer Collaborative Group (EHNBPCCG) is a pooled dataset of prospective studies of prostate cancer risk. Using this data, the authors conducted blood-based analysis and Mendelian randomisation analysis to determine the association between circulating testosterone and overall risk of prostate cancer, as well as looking at risk of aggressive disease and early-onset cancer separately. They found strong evidence that higher concentrations of circulating testosterone increases the risk of prostate cancer, including aggressive subtypes. This is the largest collection of prospective blood-based observational and genetic data on sex hormones and prostate cancer risk to date.
Performance of HPV E6/E7 mRNA assay as primary screening test: Results from the NTCC2 trial
- Pages: 1047-1058
- First Published: 17 May 2022
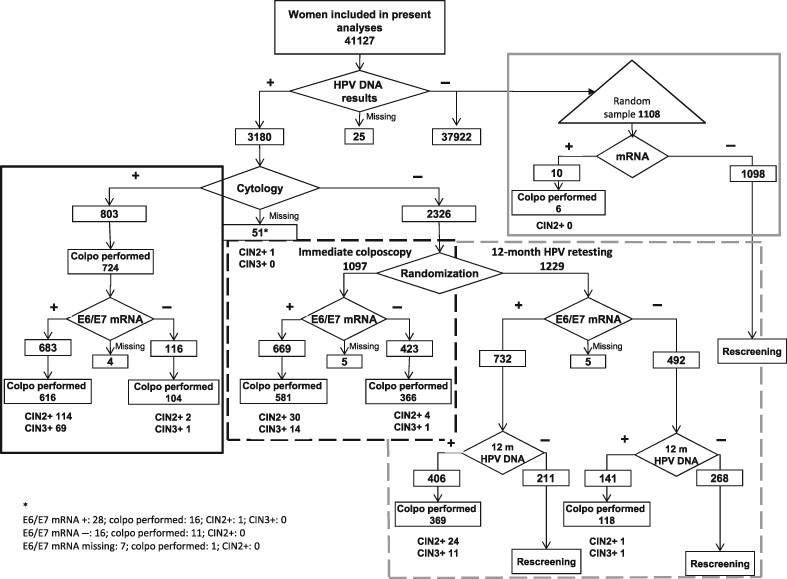
What's new?
Human papillomavirus (HPV) DNA-based assays are now widely recommended for cervical cancer screening, but they lack specificity. As a primary screening test, E6/E7 mRNA testing has shown a similar sensitivity for CIN3+ but a lower positivity rate than HPV DNA testing. This trial study shows that primary E6/E7 mRNA screening would miss about 3% of CIN3+ cases. Overall positivity would be 22% lower than that of HPV DNA. Triage with cytology or p16/ki67 dual staining would only marginally decrease overall colposcopy referral if retesting of E6/E7 mRNA-positive/triage-negative women was performed with HPV DNA assays after 12 months.
Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor: A multi-institutional study from the Pediatric Surgical Oncology Research Collaborative
- Pages: 1059-1067
- First Published: 23 May 2022
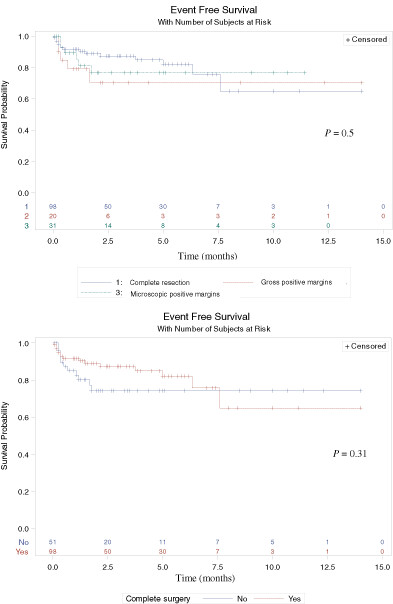
What's new?
Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT) is a heterogeneous malignancy with variable patterns of histology and behavior that primarily affects children and young adults. Owing to its rarity, however, IMT remains poorly understood. Here, data from a multi-institutional retrospective review of children and young adults with IMT was assessed to identify novel characteristics and thereby advance understanding of IMT. Analyses reveal a 5-year recurrence rate of 20%, wherein respiratory symptoms, tumor size and metastatic disease were linked to recurrence. Moreover, positive surgical margins did not correlate with event-free survival, calling into question the role of aggressive surgical resection in IMT.
Sleep duration and risk of cancer incidence and mortality: A pooled analysis of six population-based cohorts in Japan
- Pages: 1068-1080
- First Published: 26 May 2022
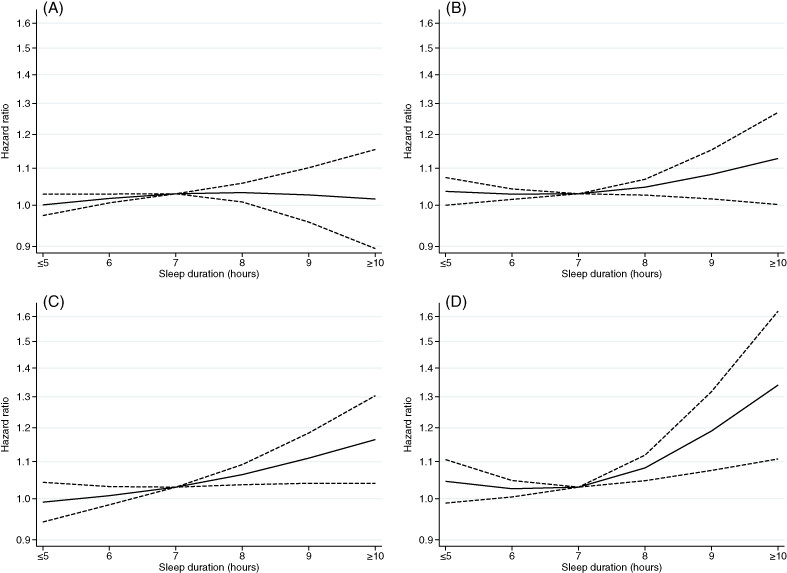
What's new?
Habitual sleep is a critical determinant of health and a potential indicator of cancer outcome. The relationship between sleep duration and cancer morbidity and mortality, however, remains unclear. In this assessment of data from the Japan Cohort Consortium, the authors show that excess sleep is associated with increased cancer mortality in both men and women, as well as with elevated cancer incidence specifically in women. Among postmenopausal women, both long and short sleep durations were linked to increased cancer mortality. The findings indicate that sleep duration is an important variable in cancer, with implications for cancer prevention.
Short Report
Detection of circulating tumor human papillomavirus DNA before diagnosis of HPV-positive head and neck cancer
- Pages: 1081-1085
- First Published: 09 March 2022
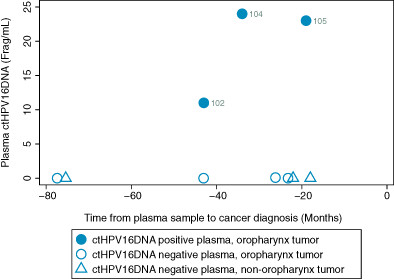
What's new?
Circulating tumor human papillomavirus (HPV) DNA (ctHPVDNA) is associated with tumor burden and response to treatment in HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). In this case-control study, ctHPVDNA was detected in plasma greater than 3 years prior to diagnosis of HPV-positive HNSCC. This is the first study to demonstrate that ctHPVDNA is detectable prior to clinical development of an HPV-positive cancer and thus, may allow for earlier diagnosis of HPV-positive HNSCC.
CANCER GENETICS AND EPIGENETICS
Somatic genomic landscape of East Asian epithelial ovarian carcinoma and its clinical implications from prospective clinical sequencing: A Korean Gynecologic Oncology Group study (KGOG 3047)
- Pages: 1086-1097
- First Published: 06 June 2022
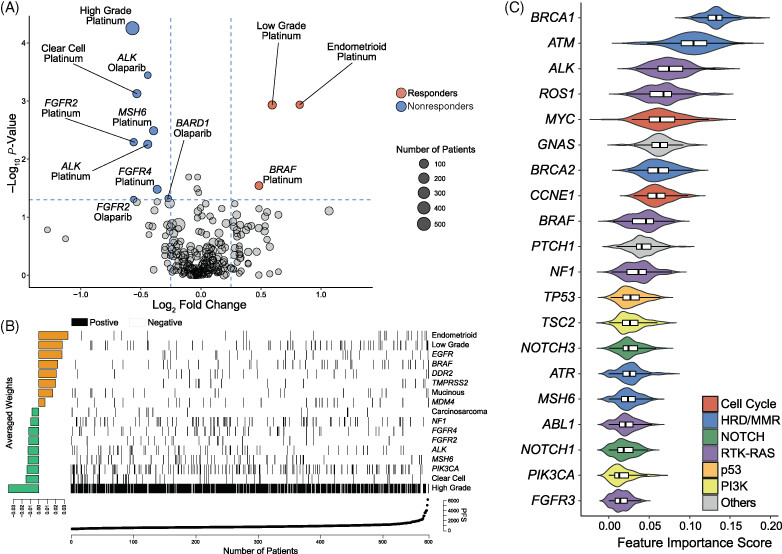
What's new?
Epithelial ovarian carcinoma has a high mortality rate, and as a heterogeneous disease, it can be difficult to treat. Here, the authors profiled the genetic characteristics of ovarian carcinomas among 652 patients in Korean hospitals. By sequencing the tumors, they determined that more than 80% of the cancers contained at least one actionable genetic alteration, most commonly in the genes TP53, BRCA1, BRCA2 or MYC. Machine-learning-based algorithms also uncovered correlations between certain molecular markers and response to platinum-based treatment and the PARP inhibitor olaparib. These results suggest that clinical sequencing could improve personalized treatment of ovarian carcinoma.
CANCER THERAPY AND PREVENTION
CANTO-RT: Skin toxicities evaluation of a multicentre large prospective cohort of irradiated patients for early-stage breast cancer
- Pages: 1098-1108
- First Published: 30 April 2022
What's new?
Cutaneous toxicities are a significant concern in the treatment of early-stage breast cancer. To minimise their occurrence, however, a greater understanding of factors influencing their development is needed. Here, using data from the prospective, multicentre CANTO study, occurrence of cutaneous toxicities was found to be influenced constantly over time by obesity and type of surgery received by patients, with both obesity and surgery acting as independent risk factors. Radiotherapy technique further impacted the occurrence of cutaneous toxicities. The results indicate that the modification of breast cancer treatment according to patient characteristics is a promising strategy for minimising cutaneous toxicities.
Association between medical androgen deprivation therapy and long-term cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality in nonmetastatic prostate cancer
- Pages: 1109-1119
- First Published: 30 April 2022
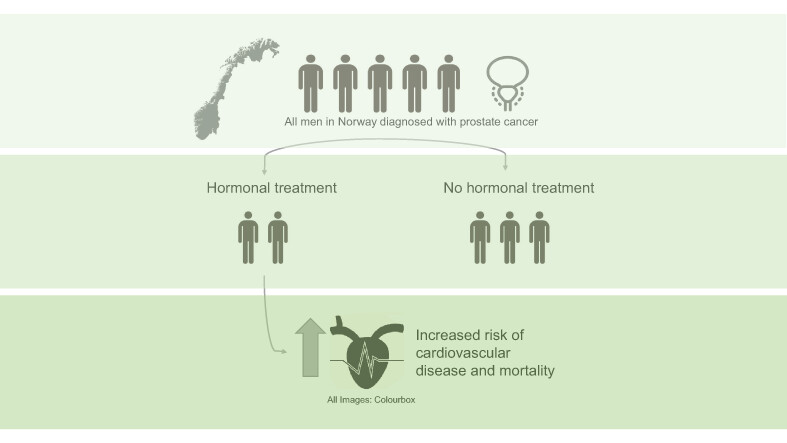
What's new?
Existing evidence suggests that prostate cancer patients receiving androgen deprivation therapy are at increased risk of cardiovascular disease. The relationship between prostate cancer treatment and cardiovascular disease remains unclear, however. Using longitudinal registry data for all prostate cancer patients in Norway, our study identifies an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality in patients treated with androgen deprivation therapy. The increased risk is most pronounced in patients with low or moderate prior risk of cardiovascular disease and longer duration of treatment. The findings contribute new evidence to the ongoing discussion about the use of hormonal therapy.
Evaluation of effectiveness, acceptability and safety of thermal ablation in the treatment of cervical neoplasia in Burundi
- Pages: 1120-1126
- First Published: 14 May 2022
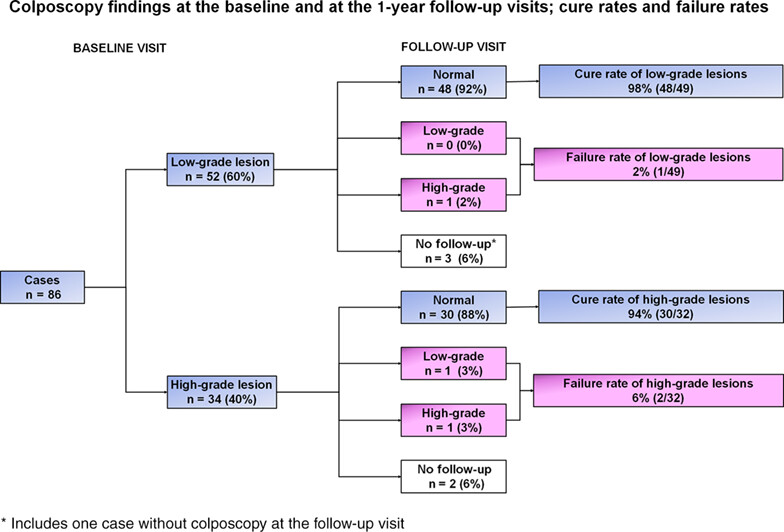
What's new?
Cervical cancer remains a major public health issue in resource-constrained settings. Appropriate management of precancer lesions is a key strategy to achieve cervical cancer elimination. Many low-income countries provide cryotherapy as an ablative treatment, but thermal ablation may be a more practical and sustainable alternative. This longitudinal study reports the efficacy of thermal ablation in the treatment of cervical neoplasia in Burundi. Thermal ablation had a high cure rate at 12 months and was found to be safe and acceptable, supporting its potential use at the primary health care level in a ‘screen-and-treat’ approach.
INFECTIOUS CAUSES OF CANCER
Systematic analysis of Kaposi's sarcoma (KS)-associated herpesvirus genomes from a KS case-control study in Cameroon: Evidence of dual infections but no association between viral sequence variation and KS risk
- Pages: 1127-1141
- First Published: 24 May 2022
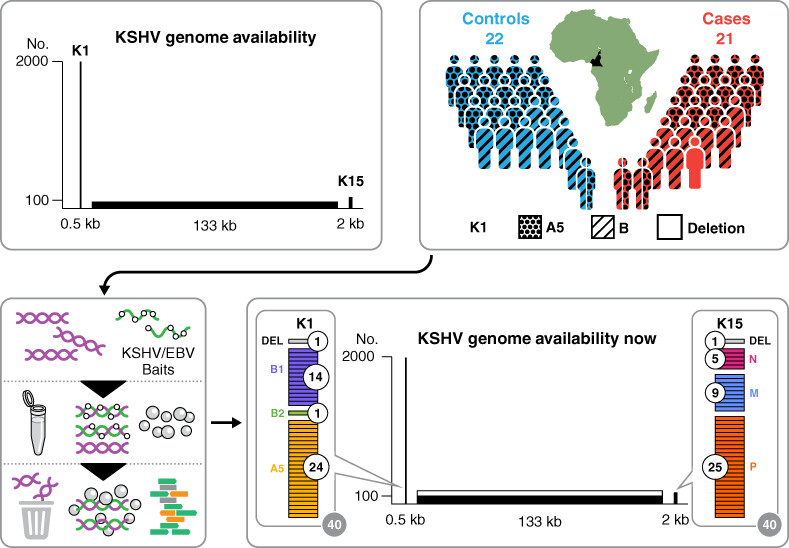
What's new?
Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), the cause of Kaposi sarcoma (KS), is classified into different subtypes based on genetic variation. Little is known, however, about whether variations in KSHV genomes differ among KS patients in the same geographic region. Here, no link was found between viral sequence variations and KS risk, based on comparison of KSHV genomes from KS patients in the same population. Several participants exhibited evidence of at least two divergent KSHV genomes, indicating dual infection with distinct KSHV subtypes. The observation of highly recombinant KSHV sequences and KSHV coinfection contributes to improved understanding of KSHV epidemiology.
INNOVATIVE TOOLS AND METHODS
Redesign of a rapid, low-cost HPV typing assay to support risk-based cervical screening and management
- Pages: 1142-1149
- First Published: 06 June 2022
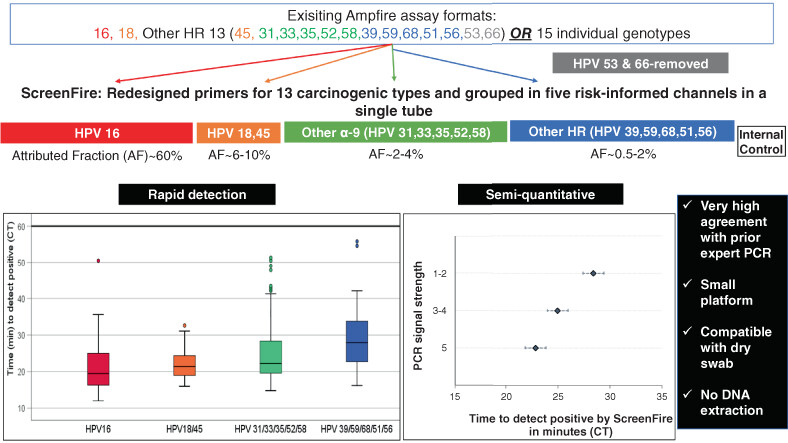
What's new?
Due to cost and perceived complexity, most existing human papillomavirus (HPV) assays for cervical cancer screening are designed to yield a pooled result for the carcinogenic HPV types. Here, to promote rapid, affordable and risk-based cervical screening, an existing isothermal DNA amplification test was redesigned to group the carcinogenic HPV types into four channels based on clinical importance (HPV16; HPV18/45; HPV 31/33/35/52/58 and HPV 39/51/56/59/68). In masked retesting of 453 Nigerian specimens, the new ScreenFire assay showed good-to-excellent type group agreement with prior PCR testing. When validated, the redesigned test could support risk-based screening in resource-limited settings.
MOLECULAR CANCER BIOLOGY
Amplified Ca2+ dynamics and accelerated cell proliferation in breast cancer tissue during purinergic stimulation
- Pages: 1150-1165
- First Published: 03 June 2022
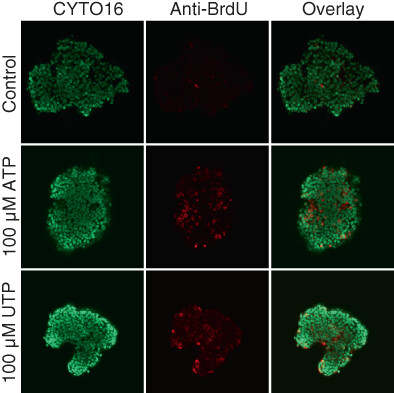
What's new?
Molecular mechanisms influencing intracellular Ca2+ dynamics are deregulated in cancer cell lines. However, many implications of deregulated Ca2+ signaling during carcinogenesis remain unclear. Using fresh human and murine tissue biopsies, here the authors show that resting intracellular Ca2+ levels, organellar Ca2+ storage and intracellular Ca2+ responses to nucleotides and cholinergic stimuli are elevated during breast, but not colon, carcinogenesis. Nucleotides stimulate proliferation in breast cancer tissue within the elevated nucleotide concentration range observed in the tumor microenvironment, whereas cell death is induced only at higher concentrations. The authors propose that amplified Ca2+ signals facilitate breast malignancy.
TUMOR MARKERS AND SIGNATURES
Predictive value of chromosome 18q11.2-q12.1 loss for benefit from bevacizumab in metastatic colorectal cancer: A post hoc analysis of the randomized phase III-trial AGITG-MAX
- Pages: 1166-1174
- First Published: 30 April 2022
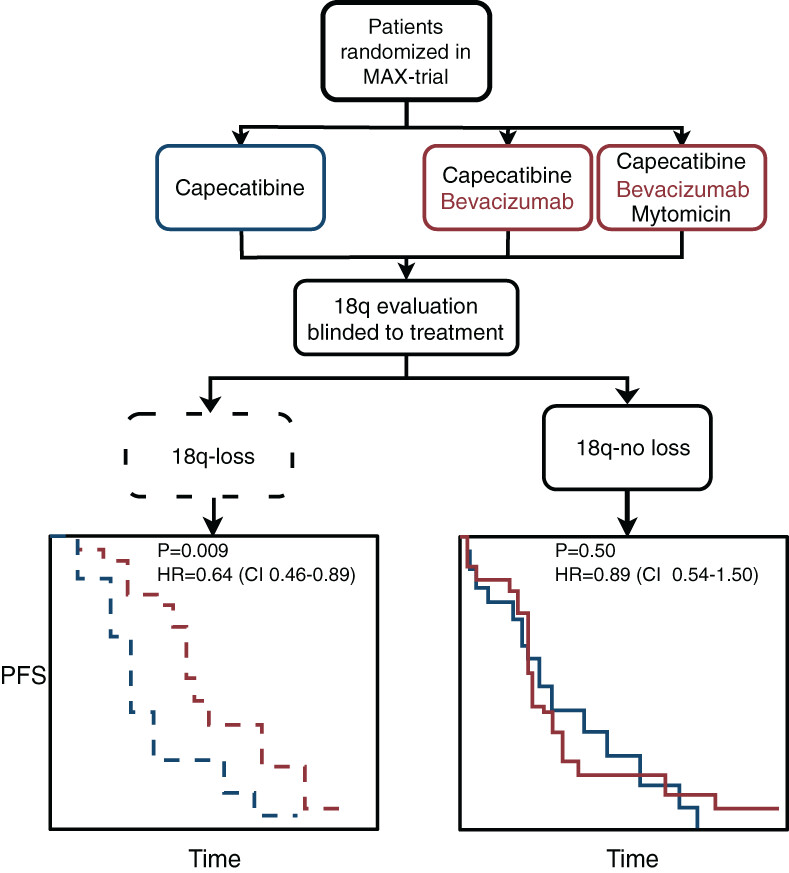
What's new?
Survival among metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) patients can be significantly improved with the monoclonal antibody bevacizumab, though patient selection is needed in order to ensure favorable cost-benefit ratio. A promising marker for this task is chromosome 18q11.2-q12.1 loss. Here, the predictive capacity of 18q loss was evaluated in mCRC samples from bevacizumab-treated patients enrolled in the AGITG-MAX randomized trial. Data show that, compared to patients without 18q loss, those lacking 18q had better progression-free survival following bevacizumab therapy. The study highlights the utility of 18q as a predictive marker for bevacizumab response and cost-benefit assessment in mCRC patients.
Diagnostic potential of nanoparticle aided assays for MUC16 and MUC1 glycovariants in ovarian cancer
- Pages: 1175-1184
- First Published: 09 May 2022
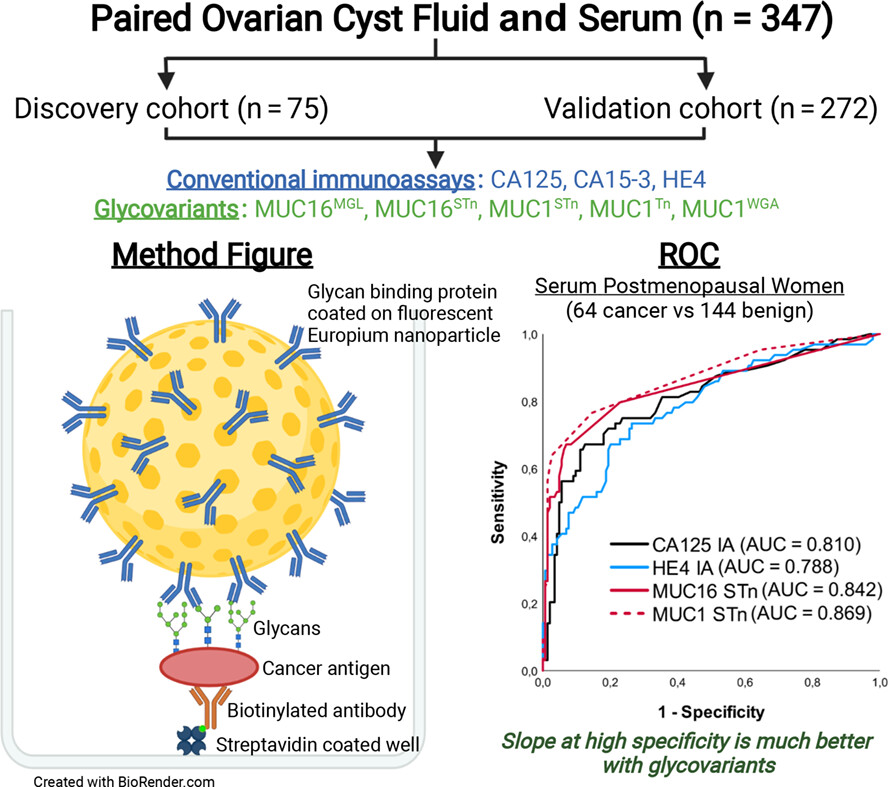
What's new?
While MUC16 represents a promising serum marker for epithelial ovarian cancer, its inadequate specificity has impeded clinical applications. Our study using a novel immunoassay with fluorescent nanoparticles coated with glycan structure-specific binders shows that cancerous sub-forms of MUC16 and MUC1 can be quantitated while suppressing mucin signals from confounding benign conditions. In ovarian cyst fluids, immunoassays for MUC16 and MUC1 STn glycovariants were superior to conventional CA125 and CA15-3 immunoassays. In paired serum samples, the main benefits were seen in postmenopausal and early-stage patients. The results pave the way for improved routine differential diagnostics of epithelial ovarian cancer.