Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Image
Cover Image, Volume 33, Issue 32
- Pages: i-ii
- First Published: 16 November 2012

Deoxythymidine, a deoxyribonucleoside, is presented separated into the high and low layers used by the ONIOM-ccCA methodology. The chemically relevant O4 position is highlighted, along with the adjacent atoms to be included in the high layer calculation. As presented by Amanda G. Riojas, Joshua R. John, T. Gavin Williams, and Angela K. Wilson on page 2590, by determining the proton affinities of deoxyribonucleosides and the location of preferred protonation sites, insight into the protonation of DNA may be attained, leading to a better understanding of a mechanism of DNA breakage that can result in carcinogenic or mutagenic effects.
Inside Cover, Volume 33, Issue 32
- Pages: iii-iv
- First Published: 16 November 2012

The molecular mechanics-Poisson- Boltzmann surface area (MM-PBSA) and MM-generalized-Born surface area (MM-GBSA) approaches are commonly used in molecular modeling and drug design. Four critical aspects of these approaches are investigated for their effect on calculated binding energies: (1) the atomic partial charge method used to parameterize the ligand force field, (2) the method used to calculate the solvation free energy, (3) inclusion of entropy estimates, and (4) the protonation state of the ligand. As presented on page 2566 by David J. D. Wilson and colleagues, HIV protease is used as a test case with six structurally different inhibitors covering a broad range of binding strength to assess the effect of these four parameters.
Full Papers
A QTAIM-based energy partitioning for understanding the physical origin of conformational preferences: Application to the Z effect in O=C-X-R and related units
- Pages: 2533-2543
- First Published: 23 August 2012
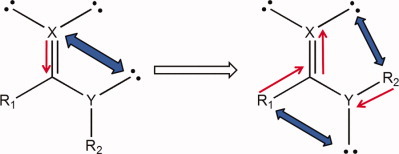
Energy partitioning based on QTAIM analysis indicates that the most important interaction in the stabilization of the Z conformer in formic acid is the attraction of the oxygen carbonyl electron density by the acid hydrogen nucleus. This method also reveals important shortcomings in the explanation provided by the hyperconjugative method.
Static hyperpolarizability of the van der Waals complex CH4N2
- Pages: 2544-2553
- First Published: 20 August 2012
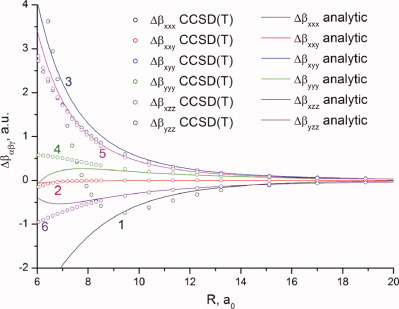
The first hyperpolarizability of the CH4N2 complex has been calculated in the approximation of rigid interacting molecules for six configurations at CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ level of theory with the BSSE correction. Calculations in the long-range classical approximation were also carried out, including terms up to R−6. Under stable complex formation, the intensity and degree of depolarization of the hyper-Rayleigh scattering are noticeable decreased (by ∼10%) in comparison with free CH4 and N2 molecules.
Original Article
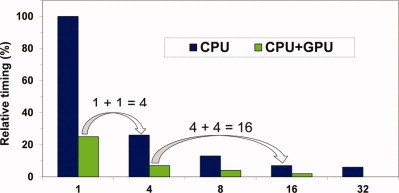
Fast force field-based optimization of protein–ligand complexes with graphics processor
- Pages: 2554-2565
- First Published: 22 August 2012
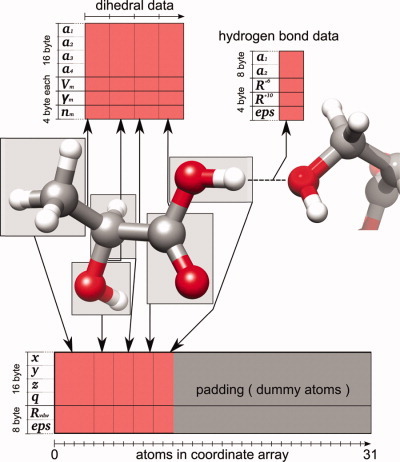
The numerical postoptimization of ligand poses is typically the most time-consuming step in protein–ligand docking calculations. An algorithmic approach is presented for massively speeding up force field-based protein–ligand complex optimizations with GPUs. The method, customized to pose-optimization, performs at least 100 times faster than widely used CPU-based optimization tools. An improvement in RMSD compared to the original docking pose of up to 42% can be achieved.
Full Papers
Effect of atomic charge, solvation, entropy, and ligand protonation state on MM-PB(GB)SA binding energies of HIV protease
- Pages: 2566-2580
- First Published: 23 August 2012
Accelerating VASP electronic structure calculations using graphic processing units
- Pages: 2581-2589
- First Published: 20 August 2012
Proton affinities of deoxyribonucleosides via the ONIOM-ccCA methodology
- Pages: 2590-2601
- First Published: 01 September 2012
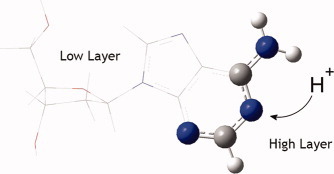
Utilizing the ONIOM-ccCA methodology, the proton affinities of anime systems and deoxyribonucleosides were predicted and compared with experiment. A protocol for the determination of the model system size was also established, and density functionals were investigated for description of the real system (low layer). ONIOM-ccCA predicts the proton affinities of the amine set to within 1 kcal mol−1 of experimental values, on average, and is used to predict the protonation sites of deoxyribonucleosides.
Software News and Updates
SIMONA 1.0: An efficient and versatile framework for stochastic simulations of molecular and nanoscale systems
- Pages: 2602-2613
- First Published: 10 August 2012
Molecular simulation methods have increasingly contributed to our understanding of molecular and nanoscale systems. Here, the development of a generic, versatile simulation package is reported for stochastic simulations and its application to protein conformational change, proteinprotein association, small-molecule protein docking, and simulation of the growth of nanoscale clusters of organic molecules is demonstrated. Simulation of molecular and nanoscale systems is easy to use for standard simulations via a graphical user interface and highly parallel both via MPI and the use of graphical processors.
Retraction
Retracted: Predicting protein folding rates using the concept of Chou's pseudo amino acid composition
- Page: 2614
- First Published: 04 October 2012