CTI Special Feature on Immunopathobiology of Chronic Lung Disease
Special Feature Coordinators: Cecilia Prêle and Gerard Hoyne
The innate and adaptive immune system play critical roles in the maintenance of tissue homeostasis in the lung and in protecting the host from infection. Persistent and repetitive damage to the lung elicits an inflammatory response that can, if unregulated, contribute to the development of chronic lung disorders including interstitial lung diseases (ILDs) such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features (IPAF) and connective tissue associated-ILD (CTD-ILD), as well as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and lung cancer.
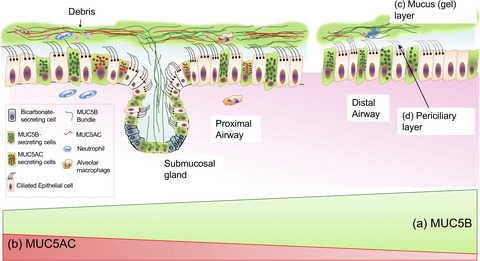
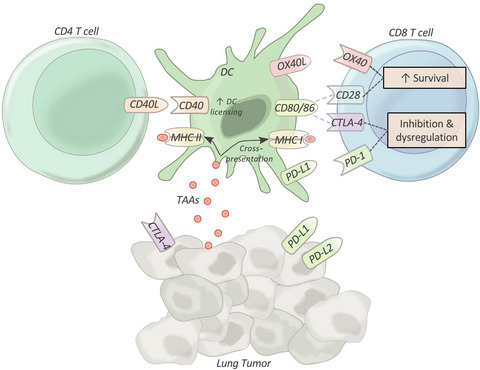
This Special Feature of Clinical & Translational Immunology covers a range of topics related to the role of the immune system in chronic lung diseases, including animal models, lung repair and regeneration, challenges with the clinical diagnosis of ILDs, in particular autoimmune-like IPAF, the role of the innate immune system and how mucins regulate the immune response in healthy lung and in chronic lung disease and the adaptive immune response in lung cancer and the potential for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy.
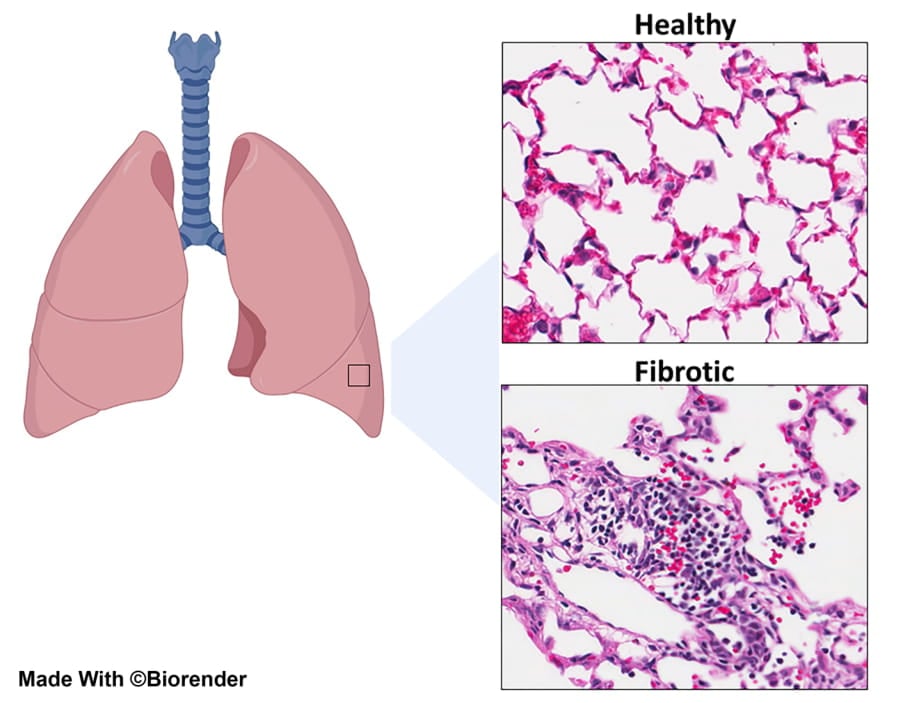 |
Image: Haematoxylin and eosin stained sections of mouse lung tissue showing open alveolar spaces within the healthy lung that allow efficient gas exchange. Chronic damage to the lung epithelium leads to increased recruitment of immune cells to the lung as shown at sites of tissue fibrosis. Image prepared by Ms Tylah Miles. |
EDITORIAL
SPECIAL FEATURE REVIEWS
Idiopathic and immune‐related pulmonary fibrosis: diagnostic and therapeutic challenges
Graphical Abstract
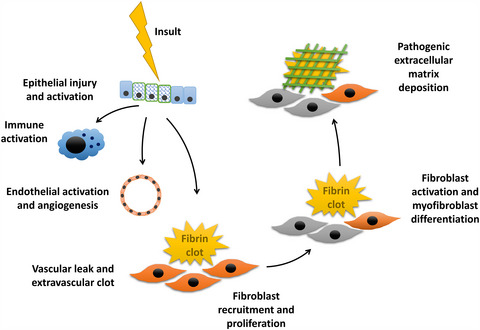
Interstitial lung diseases (ILD) are a large group of conditions causing morbidity and mortality in all age groups. In addition to highlighting the benefits of a multidisciplinary diagnoses, we review developments in ILD diagnostics, especially around autoimmune disease and current evidence for newer therapeutics.
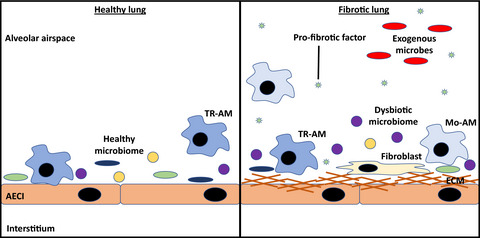
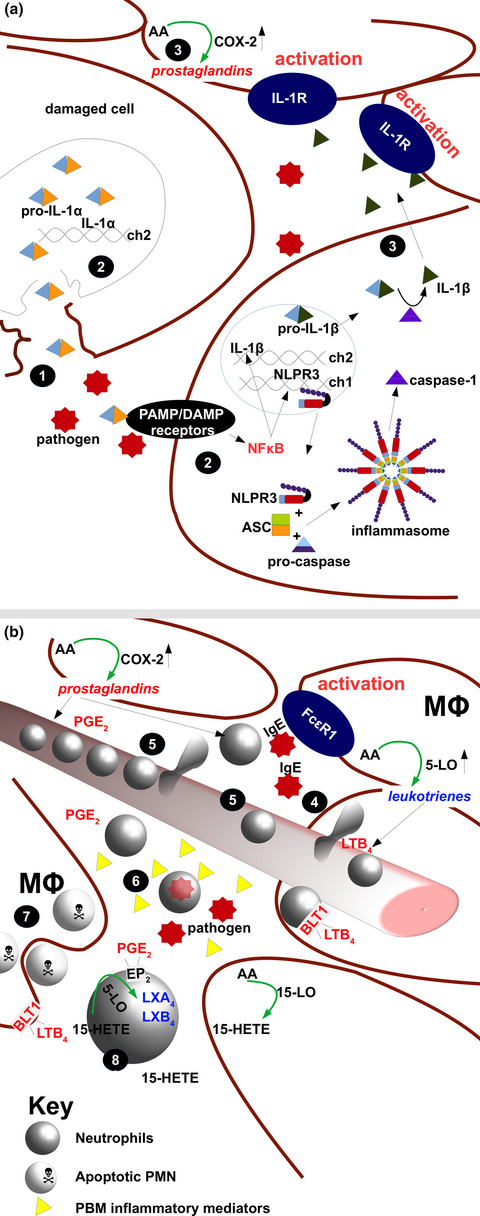
A pathologic two‐way street: how innate immunity impacts lung fibrosis and fibrosis impacts lung immunity
Graphical Abstract
The contribution of animal models to understanding the role of the immune system in human idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Graphical Abstract
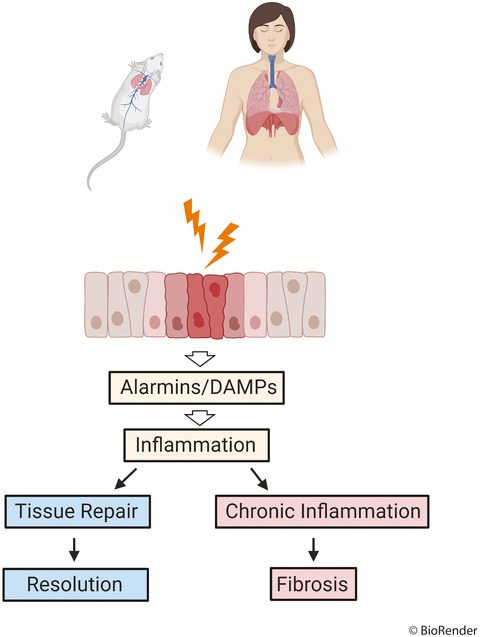
This review will compare some of the models used to investigate the pathogenesis and treatment of pulmonary fibrosis, in particular those used to study immune cell pathogenicity in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, highlighting their advantages, disadvantages and suitability in representing the human disease.