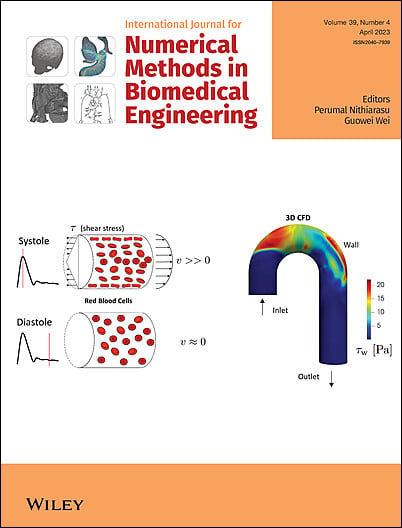
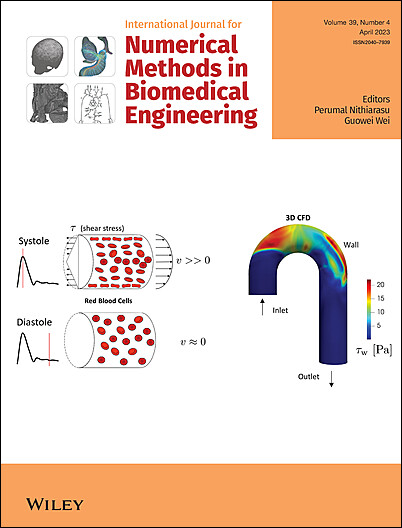
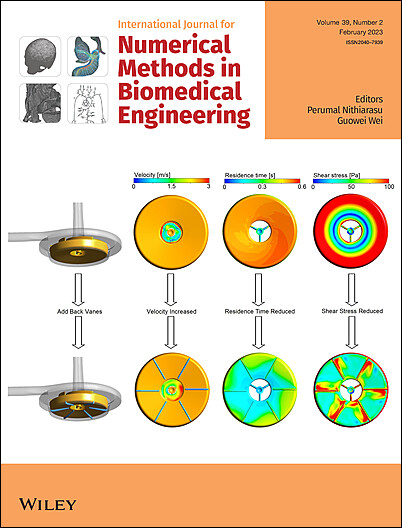
Edited By: Perumal Nithiarasu
The International Journal for Numerical Methods in Biomedical Engineering is where your work in computational methods can make a real difference to the good health and wellbeing of humans worldwide.
As a biomedical engineering journal with a core of applied mathematics, we publish papers on new mathematical models and numerical solutions, or those using existing numerical engineering methods to solve new biomedical problems.
Journal Metrics
- 4.6CiteScore
- 2.4Journal Impact Factor
- 10%Acceptance rate
- 6 days Submission to first decision
On the Cover
Articles
A Computational Approach to Investigate the Structural Behavior of Bone Scaffold‐Implanted Proximal Femur in Routine Clinical Resolution
- 25 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
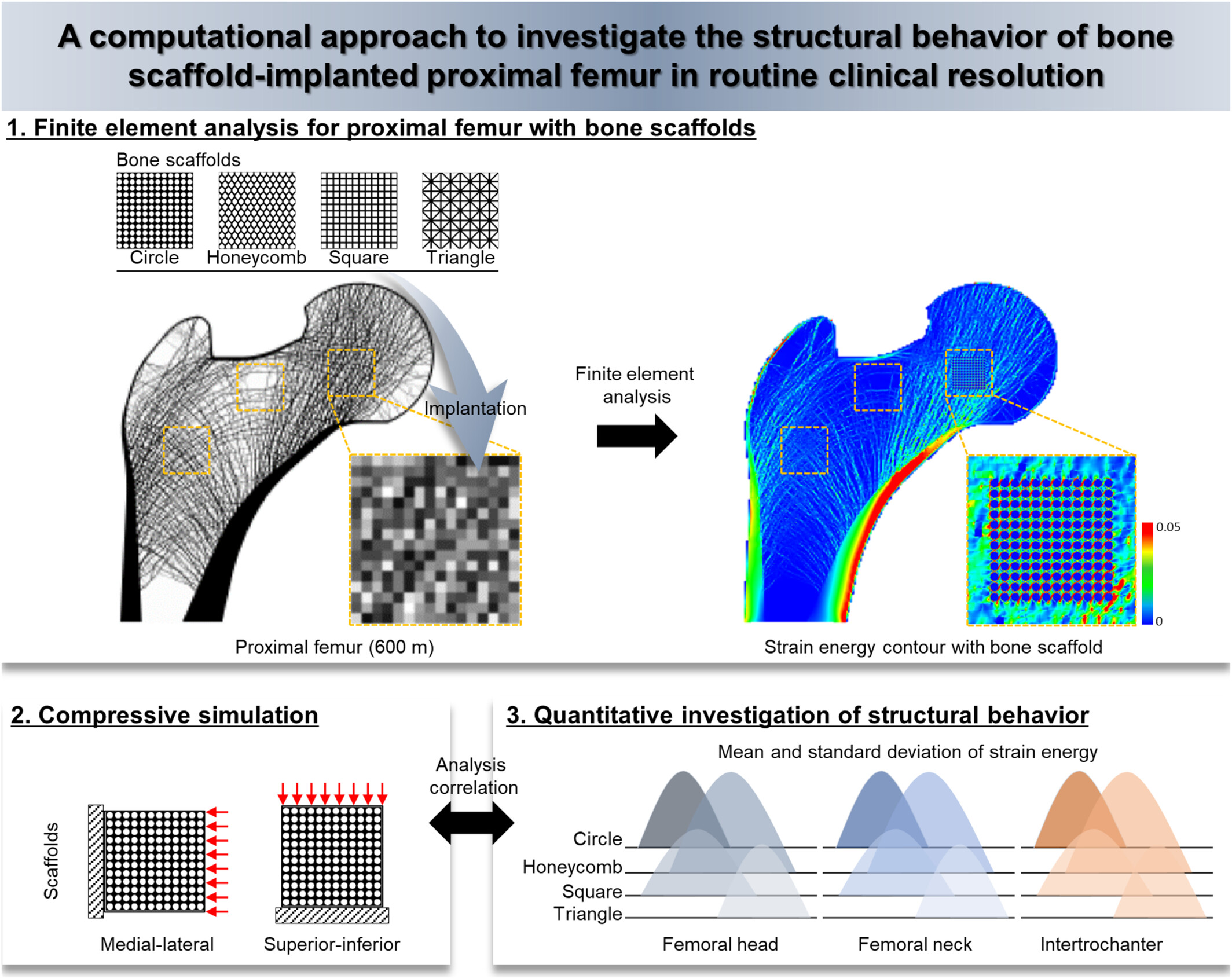
This study analyzed and compared the mechanical function of bone scaffolds under various conditions using the computational approach. Bone scaffolds play a crucial role in replacing damaged bone, supporting external loads, and transmitting mechanical stimuli to adjacent tissue. However, designing bone supports based solely on high apparent elastic moduli reduces their ability to transfer loads to the surrounding bone tissue. In contrast, a bone scaffold with an apparent elastic modulus similar to that of the adjacent bone at the implantation site ensures effective load transfer and structural support.
On Implementation of a Finite Element Visco‐Hyperelastic Material Model for Spinal Ligaments in Explicit Time Integration Method With an Infinite Impulse Response Filtering Technique
- 22 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
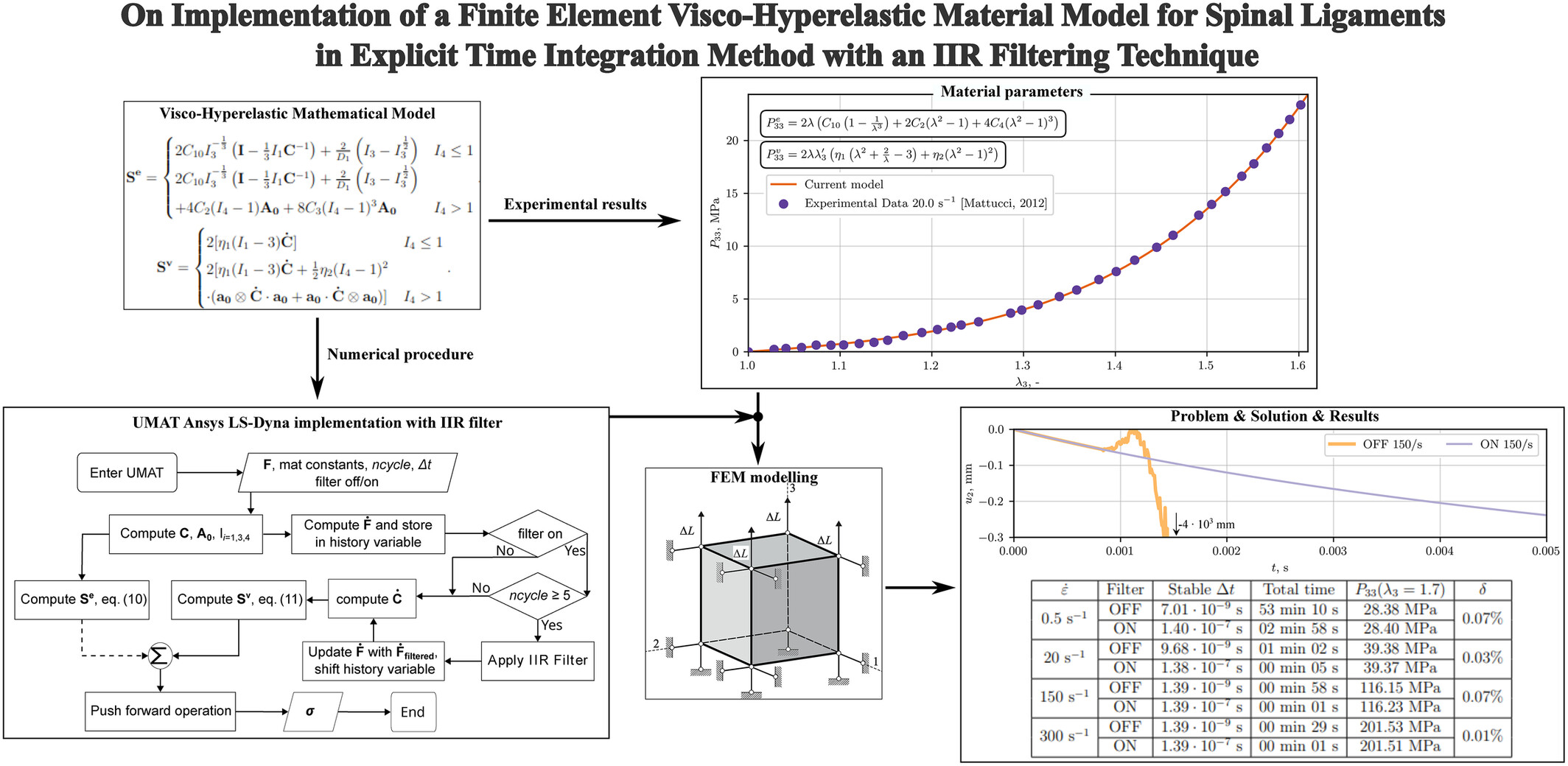
This figure illustrates the newly proposed visco-hyperelastic material model for spinal ligaments under dynamic loads. It highlights both the Neo-Hookean matrix and transversely isotropic fibers, enhanced by viscous terms. The model is supplemented by an IIR filter to eliminate numerical oscillations at high strain rates, ensuring stable and accurate FEM simulations.
Effect of Pulsatile Blood Flow Parameters on Membrane Oxygenator Performance: A Cross‐Scale Simulation Study
- 22 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
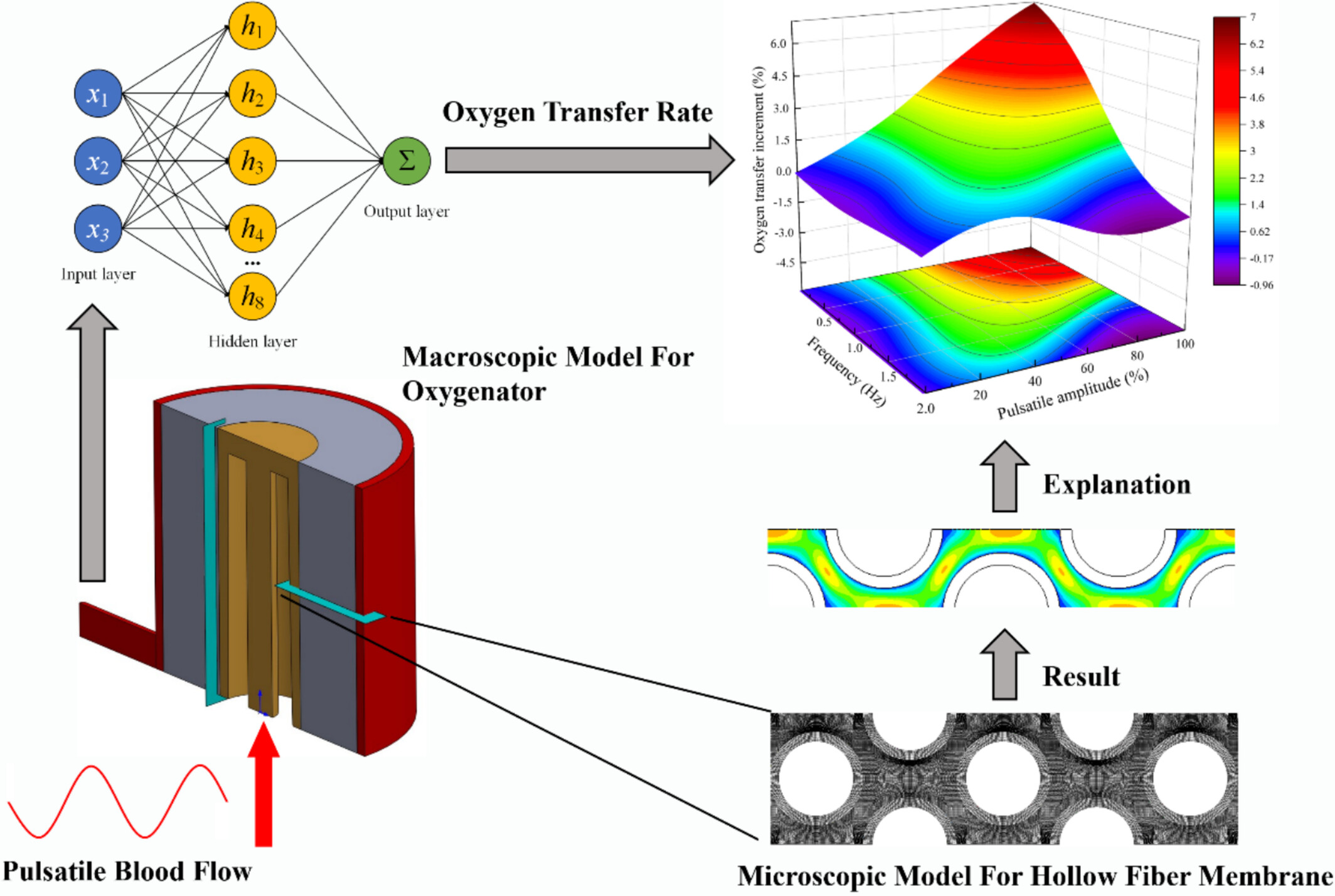
This study developed a novel transient simulation model of the oxygenator to calculate the oxygen transfer rate under various pulsatile blood flow conditions. To address the high computational resource demands of the transient simulation model, we employed a BP neural network to extrapolate the simulation results. Then the extended findings were interpreted from a mechanistic standpoint by using a hollow fiber microscale simulation model.
A Continuum Approach With Adaptive Mesh Refinement for Platelet Plug Formation
- 19 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
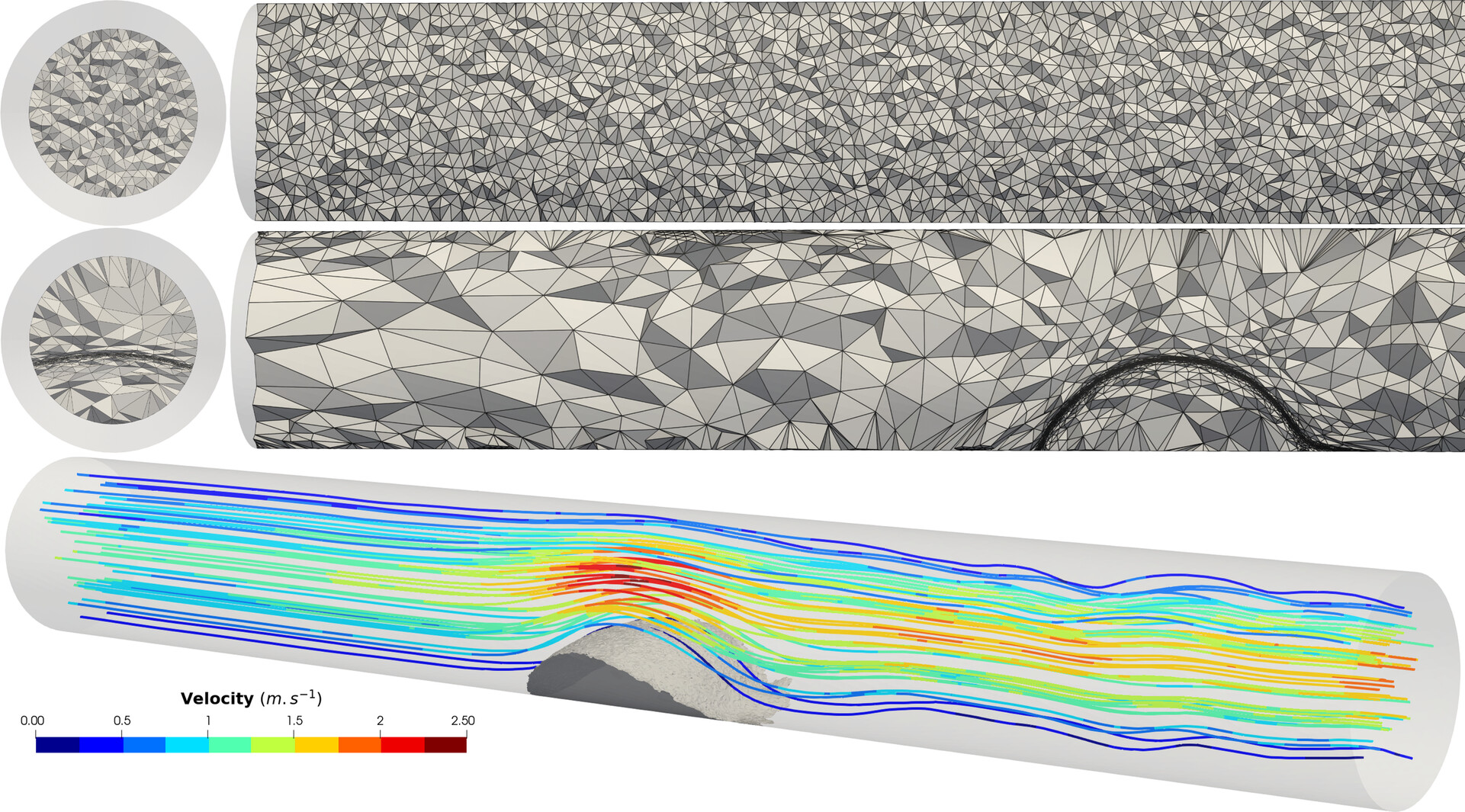
This study introduces a computational framework coupling stabilized finite element methods with dynamic anisotropic mesh refinement to simulate platelet plug formation in complex hemodynamic environments. The model is validated on 2D and 3D benchmarks, demonstrating accurate predictions of plug growth and reduced computational costs. It offers a scalable tool for thrombosis simulation, with potential applications in patient-specific treatments.
A Parameterized Cross‐Sectional Model for Simulating Balloon Angioplasty in Atherosclerotic Arteries
- 18 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
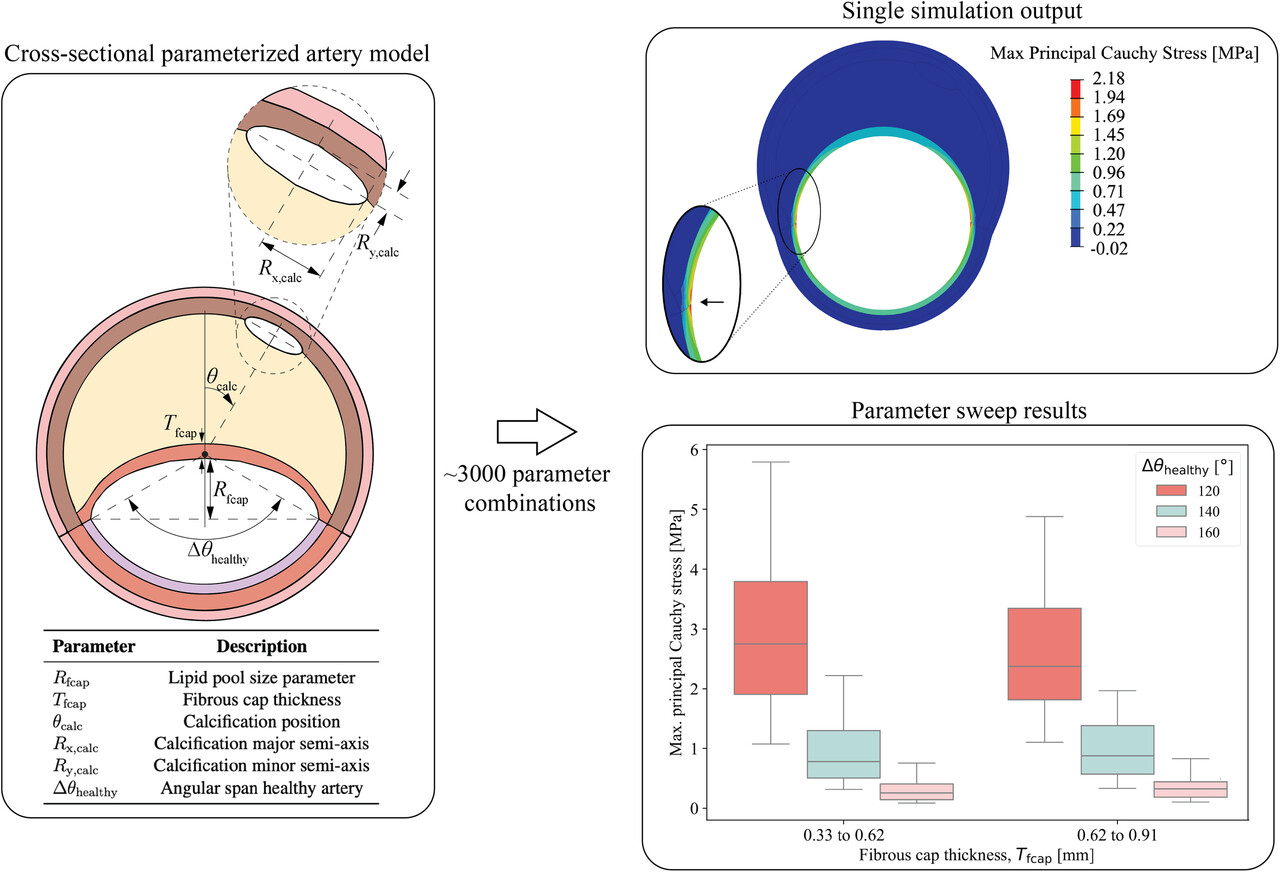
The parameterized cross-sectional model allows assessment of the effect of geometric variability in iliac atherosclerotic arteries during angioplasty balloon inflation. The size of the lipid pool and the thickness of the fibrous cap primarily control, respectively, the magnitude and location of the maximum principal stress in the artery. Our study highlights the importance of using a parameterized finite element model over deterministic approaches.
The following is a list of the most cited articles based on citations published in the last three years, according to CrossRef.
Neural‐network‐based approximations for solving partial differential equations
- 195-201
- March 1994
A systematic comparison between 1‐D and 3‐D hemodynamics in compliant arterial models
- 204-231
- 24 September 2013
Graphical Abstract
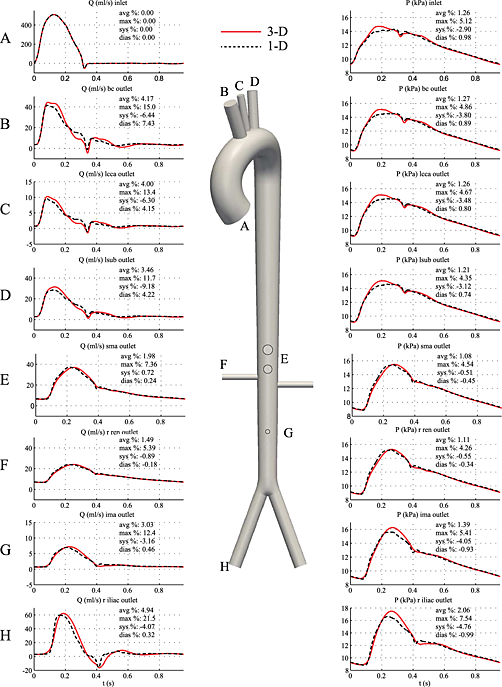
We present a systematic comparison of computational hemodynamics in a one-dimensional and a three-dimensional formulation with deformable vessel walls. The formulations share identical inflow and outflow boundary conditions and have compatible material laws. The results show good agreement between the two formulations, especially during the diastolic phase of the cycle.
Near infrared optical tomography using NIRFAST: Algorithm for numerical model and image reconstruction
- 711-732
- 15 August 2008
A review of personalized blood glucose prediction strategies for T1DM patients
- 19 September 2016
Graphical Abstract
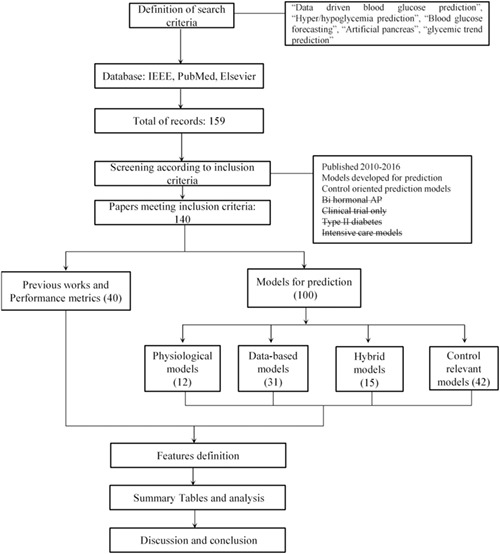
This paper presents a methodological review of models for predicting blood glucose (BG) concentration, risks, and BG events. The surveyed models are classified into three categories, and they are presented in summary tables containing the most relevant data regarding the experimental setup for fitting and testing each model as well as the input signals and the performance metrics. Each category exhibits trends that are presented and discussed. This document aims to be a compact guide to determine the modeling options that are currently being exploited for personalized BG prediction.
A generalization of two-dimensional theories of laminated composite plates†
- 173-180
- May/June 1987
Recent issues
- Volume 41, Issue 7July 2025
- Volume 41, Issue 6June 2025
- Volume 41, Issue 5May 2025
- Volume 41, Issue 4April 2025