Frame Design of Moving Image Analysis System Based on Spatiotemporal Features
Abstract
In sports, kinematic image analysis is primarily concerned with the examination of space-time characteristics, such as image analysis of the speed and acceleration of related objects. Software and hardware make up the entire system. The medical scanner, scanning workstation, and DICOM server are all part of the hardware. Our self-developed scanner is used in the medical scanner, which can collect binary, 8-bit gray, 24-bit true color, 16-bit gray, and 48-bit color images. Kinematic image analysis is used to intuitively analyze sports technology, as well as to evaluate and diagnose its rationality. This paper investigates the kinematic-based framework design of a sports image analysis system. Image analyses of displacement, speed, and time are all used in the measurement of sports technology evaluation. Displacement analysis, for example, involves position coordinates, motion displacement, motion trajectory, and so on; speed class analysis, on the other hand, involves average and maximum speed.
1. Introduction
In the research of sports human body science, the most intuitive and concrete thing is the research of sports biomechanics. In this field, the athletes’ sports level in competition and training can be explained by data through experiments with high precision, the real sports level reflected by athletes in competition can be objectively and scientifically fed back, and the real kinematic parameters of technical movements can be reflected and compared and analyzed with reasonable kinematic parameters, so that coaches can revise training methods and improve athletes’ competition training level more effectively and quickly [1, 2]. Among them, the image analysis system has been widely used in the acquisition of competition data and training to check the level of athletes’ sports training because of its intuitive, vivid, and easy-to-use features, and various useful kinematics and dynamics parameters can be obtained through the image analysis system, which has become one of the important bases for improving technical movements, comparing the gaps and differences between existing technical movements and ideal technical movements to improve technical movements in order to achieve better sports results in the competition. The whole system consists of software and hardware. The hardware part includes medical scanner, scanning workstation, and DICOM server [3]. The medical scanner adopts our self-developed scanner, which can collect binary image, 8-bit gray image, 24-bit true color image, 16-bit gray image, and 48-bit color image [4, 5]. The interface of the scanner is USB2.0, which is universal and can realize high-speed acquisition. The traditional film storage management method has been increasingly unable to meet the demand, and there are many problems in itself, such as the high cost of film itself, a large amount of storage space, and easy damage during storage, which leads to the loss of image data. The processing steps are complicated, the image quality is poor, the window position and window width are fixed and cannot be changed, and a lot of information of the image itself has been lost, which is not conducive to doctors’ diagnosis. Manual management is inefficient and slow in retrieval, which is not conducive to transmission and sharing and requires a lot of manpower and material resources [6, 7].
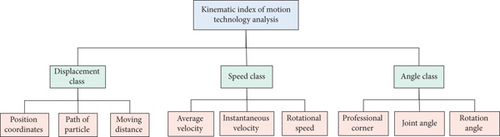
Kinematic image analysis in sports is mainly about the analysis of space-time characteristics, such as the image analysis of the speed and acceleration of related objects in sports. The purpose of kinematic image analysis is to intuitively analyze sports technology and evaluate and diagnose the rationality of sports technology. Human kinematics is a subject that describes human motion. It only discusses the details of the motion itself, not the internal and external forces that produce the motion [8]. The so-called kinematics based model means that the motion of an object is independent of the force producing motion. Its parameters include the position, velocity, and acceleration of the object. For example, in the kinematic-based model, the complete kinematic image analysis of any human bone segment needs 15 time-varying analyses. The measurement of motion technology evaluation involves the analysis of displacement, velocity, time, and other related images. Among them, displacement analysis involves position coordinates, motion displacement, and motion trajectory; speed analysis involves average speed and maximum speed; acceleration analysis involves instantaneous acceleration and average acceleration; the angle category involves attitude angle, rotation angle, and the best angle for evaluating a specific movement in a professional field; and the time category mainly involves the total time to complete an action, the time of a certain stage of an action, and the sequence and proportion of each stage [9, 10].
Kinematic-based models have many advantages, the most important of which is that they can move according to the requirements of animation designers [11]. However, there are many limitations in the application of dynamic-based models. For example, for solving dynamic equations, we usually cannot get the closed analytical solution of kinematic equations, so we can only use numerical solution technology [12, 13]. At present, the analysis software on the market is generally designed based on motion video analysis system and infrared motion capture principle, and there are some products based on GPS satellite positioning system, and with the development of computer and measurement technology, various new softwares are constantly appearing [14, 15]. In the actual process of image analysis, there will always be various situations, especially when material images are collected, different site conditions, different relative positions of acquisition equipment, and different sports events will be encountered, which will result in some unknown and uncertain factors in the experiment, such as the athletes or equipment in some events have a large range of activities, 100-meter race, javelin throw, and hammer throw, which will increase the difficulties for image collection during analysis, and at the same time, it will affect the measurement results.
2. Related Work
Literature [16] pointed out that China’s sports image analysis industry started late and is still in the initial stage of development. At present, most sports still use old-fashioned film imaging equipment. In reference [17], through the big data analysis method, we use the sports image to analyze the two-dimensional information of the framework of the system with marked pictures. We restore the three-dimensional information of the athletes at this time and obtain the athletes’ sports parameters through the three-dimensional information. Then, through the three-dimensional virtual human model to reproduce the athlete’s posture at all times. According to a review of the literature [18], we should not only increase research on various imaging equipment in the field of sports image analysis but also vigorously develop various medical image processing technologies. The system’s core module is the sports image analysis and processing module. This module is the most commonly used and has a direct impact on the sports image analysis system’s framework. The distribution of each node of the photographic frame must be evenly distributed throughout the control field in the structural design of sports image analysis, according to literature [19], so that the human body has enough evenly distributed control points no matter where it moves in the control field. The application of various high and new technologies centered on computer technology in sports is promoted in literature [20], which promotes significant changes in sports image analysis through the big data analysis method and the application of various high and new technologies centered on computer technology in sports. The framework of a high-tech system centered on computer application will continue to be widely used in sports research in the future, which will encourage the development of a sports image analysis system framework. The main problem to be solved in the sports image analysis and processing module, according to literature [21], is how to realize effective sports image analysis processing and extract more framework information that can help find out the sports system from the original image data. Literature [22] proposes that sports pictures are introduced into the image analysis system to mark each joint point of the moving human body through manual marking method and automatic marking method to obtain two groups of two-dimensional information. In literature [23], with the help of big data analysis method, computer technology, and image processing technology, various useful and intuitive information can be extracted from the original complex data, and these information can be analyzed comprehensively, so that the analysis level can be greatly improved based on the current sports image analysis equipment. In literature [24], the interface of the scanner is USB2.0, which is universal and can realize high-speed acquisition. The traditional film storage management method has been increasingly unable to meet the demand, and there are many problems in itself, such as the high cost of film itself, a large amount of storage space, and easy damage during storage, which leads to the loss of image data. Literature [25] puts forward that two high-speed cameras are used to record the athletes’ technical movements synchronously when the two cameras form a certain angle and the generated images are saved in the form of pictures by video capture devices. The picture information is the athlete’s movement state at this moment.
This paper studies the framework design of sports image analysis system based on dynamics. The framework of sports image analysis system is to collect and analyze a certain section of action image continuously or at equal intervals. At the same time, collecting images in place at one time also meets the requirements that many other analysis methods cannot meet. For example, when collecting images, you can refer to the information of other images. During or after the analysis, the content of any analysis point on any screen can be modified arbitrarily, and the content of multimachine shot images at the same time can be displayed on the same screen by cutting the screen. It provides a powerful and systematic framework and means for rapid feedback information and vivid biomechanical teaching demonstration.
3. Principle and Model of System Kinematics
Sports image analysis system is a whole set of system that analyzes the video taken by kinematics sports image analysis video recorder, including image acquisition, image digitization, data smoothing, calculation and analysis, and result output. The system mainly consists of two parts: video shooting and image processing. At present, in many softwares, the motion model of virtual human is based on kinematics. It has become one of the important development directions of sports to improve the effect of sports training and sports performance with scientific training methods and technical monitoring means. At present, the moving image analysis system is mainly used in sports training technology monitoring. In the process of using kinematics to animate virtual human with these softwares, kinematics requires users to interactively set some key parameters and interpolate them. These key parameters are used to generate and control the movement change of the object, and the change of these parameters only relates to the magnitude of each parameter value at each moment and its change speed. For the analysis of motion technology, the structure diagram of kinematics technology commonly used is shown in Figure 1.
In the enlargement process, the overall size of the enlarged image must be calculated first, followed by the width and height of the enlarged image, and finally the pixels of the original image corresponding to each pixel of the enlarged image. The calculated x and y coordinate values are often not integers when inverse mapping the pixel coordinates (x, y) of the original image from the pixel coordinates (u, v) of the enlarged image, and some interpolation is required to determine the pixel coordinates corresponding to the original image.
If the coordinate of a pixel of the enlarged image is (u, v), the floating-point coordinate of the pixel corresponding to the original image is (x, y) after inverse operation. Now, four pixel points around the floating-point coordinate (x, y) are determined, and then, the values corresponding to the pixel points (u, v) of the enlarged image are calculated according to the distance relationship of the four pixel points. The specific process is described as follows.
The video shooting system can be divided into constant speed and high-speed systems based on kinematic classification, sports color can be divided into color and black-and-white systems based on kinematic classification, and sports image analysis system quality can be divided into ordinary quality video system and high-quality video system based on kinematic classification. Take pictures with multiple cameras, then analyze the sports images with multiple machines and synchronization, synthesize the three-dimensional spatial coordinates of the human body’s joint points and center of gravity, calculate the three-dimensional speed, posture angle, and joint angle of the human body, and then, depending on the characteristics of each sports event, the sports image analysis system uses biomechanics to analyze athletes’ movement technology and provides a diagnosis. The study of the mechanics that cause human motion is known as human dynamics of kinematics. Gravity, ground reaction, external force, muscle force, joint reaction, and the force between bones, for example, are the primary influences on the entire body. The so-called kinematic-based model states that an object’s motion is controlled by the force it receives, and that the relevant motion parameters are entirely determined by the dynamic equation. The user can use the remote data processing module to complete the calculation through the kinematics system after the frame design is selected by the hand sports image analysis system; if the network is not available, the processing module of the sports image analysis system is used to further strengthen the adaptability of the application, as shown in Figure 2.
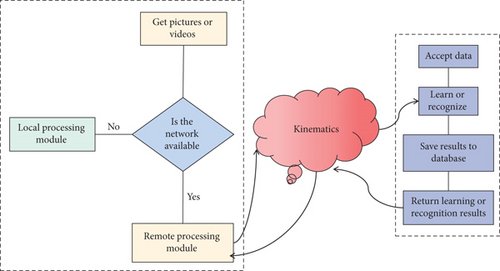
In the analysis system of sports assistant training, the trajectory of a joint at different times draws a curve in space. Sometimes, I want to make some subtle adjustments to a certain point on the curve, which means changing the posture of the human body at a certain moment. The key lies in two aspects: first, after adjusting the position of a certain point, it reflects how the positions of other points on the trajectory of this joint point will change. Secondly, with the change of the motion curve of this joint point, how will the motion curves of other joint points be adjusted to accurately reflect the motion characteristics of human body? The processing of sports image analysis system is to collect and analyze the motion images. The film analysis software is collectively referred to as analysis software. The kinematic motion image analysis system first reads in the original coordinate data obtained from digitizer and video image acquisition part and then eliminates the noise caused by systematic error and random error through data smoothing. The movement change of the object is caused by the breaking of its force equilibrium state. Therefore, the motion of an object is related to its interaction with the surrounding environment and the external force exerted on it by the outside world. In fact, the real motion of an object depends on its stress. Kinematic-based animation technology of virtual human is to introduce physical laws when establishing the animation model of virtual human, and its purpose is to improve the fidelity of computer animation.
4. Research on Framework Design of Sports Image Analysis System
4.1. Sports Image Analysis System Based on Kinematics
With the rapid development of science and technology and the wide application of high-speed and high-definition cameras, the function, quality, test speed, and test accuracy of sports image analysis system have been greatly improved. In this field, the athletes’ sports level in competition and training can be explained by data through experiments with high precision, the real sports level reflected by athletes in competition can be objectively and scientifically fed back, and the real kinematic parameters of technical movements can be reflected and compared and analyzed with reasonable kinematic parameters, so that coaches can revise training methods and improve athletes’ competition training level more effectively and quickly. Nowadays, almost all colleges and training units in China have camera equipment, which can easily assist coaches and athletes to record and observe the sports process, but it is still difficult to calculate, analyze, and process conveniently. A set of moving image analysis system is not only very expensive but also easy to be eliminated by alternative products, and there are many El maintenance problems, which are the reasons that hinder the popularization of the system in China. When the coach needs to modify a joint point of the athlete at a certain time, in order to maintain the coordination of the whole action and the coherence of the front and rear actions, it is necessary to automatically match the other joint points of the frame and the actions of the front and rear frames. Kinematic sports image analysis system plays an extremely important role in the field of sports. It can accurately and real-time measure the motion curve of each part and the relative rotation angle of joints in the process of athletes’ action, which helps coaches correct athletes’ wrong actions, so as to prevent sports injury and improve kinematic sports performance. The original data obtained by the system only records the photoelectric position of the joint points concerned on the image, rather than recording the information of the whole picture like the kinematic motion video analysis system. It has the function of automatic tracking and capture and does not need to dot the image frame by frame. Motion capture system is generally composed of infrared camera system and processing software. Reflection markers, commonly known as mark points, are required during shooting.
This paper summarizes the research of kinematics sports image analysis system from five aspects: the development process of kinematics sports image analysis system, the research status of sports image analysis system, the comparison of performance and characteristics of sports image analysis system at home and abroad, the comparison between motion capture system and sports image analysis system, and the development trend of sports image analysis system. When analyzing, firstly, the centroid position of each marker point is calculated by using the frame, and then, the first amplitude is identified manually. The data from the same point at different times is summarized in the third step using the tracking method. Because of its intuitive, vivid, and easy-to-use features, the image analysis system has become one of the important bases for improving technical movements in the acquisition of competition data and training to check the level of athletes’ sports training. Various useful kinematics and dynamics parameters can be obtained through the image analysis system, which has become one of the important bases for improving technical movements. The three-dimensional spatial coordinates of the research object moving at various times can be obtained in this manner. The velocity curve is obtained through first-order frequency differentiation, and the acceleration curve is obtained through second-order differentiation in postprocessing. Our self-developed scanner is used in the medical scanner, which can collect binary, 8-bit gray, 24-bit true color, 16-bit gray, and 48-bit color images. The kinematic sports image analysis system has advanced significantly in comparison to previous versions, and its performance indexes have significantly improved in terms of capture frequency, image quality, data collection and analysis methods, and so on. However, the kinematic sports image analysis bottleneck problem, namely, the automatic identification of joint points, has yet to be solved, which has had a significant impact on the feedback speed of information and the effect of sports training and is an urgent problem that must be addressed. Although the sports image analysis system has become an indispensable sports biomechanic instrument and equipment for modern sports scientific research, sports training, sports teaching, medical rehabilitation and so on, its popularity in China is not high, and its owners are only sports institutes in several major provinces and cities and a few sports colleges and universities. The goal of kinematic sports image analysis is “higher, faster, and stronger”. In addition to the hard training of kinematics athletes, scientific training methods and means are also an effective way to improve athletes’ performance. With the deepening of the contemporary new technological revolution, the penetration of modern science and technology into sports is becoming more and more extensive and has become a strong driving force for the development of sports. In particular, the application of various high and new technologies centered on computer technology in sports has promoted great changes in sports. In the future, the high and new technology centered on computer application will continue to be widely used in sports research, which will promote the research of sports image analysis system to produce great changes.
4.2. Experimental Results and Analysis
In this paper, the superiority and significance of the system architecture are illustrated by comparing the time of kinematic calculation in sports image analysis system. Save the same 10 groups of learning results on the mobile phone and on the cloud computing platform server, respectively, and conduct 10 groups of experiments with 10 pictures, each group of experiments carries out 10 recognition calculations and records the average time. Three experiments were conducted for comparison, and the experimental results are shown in Figures 3–5.
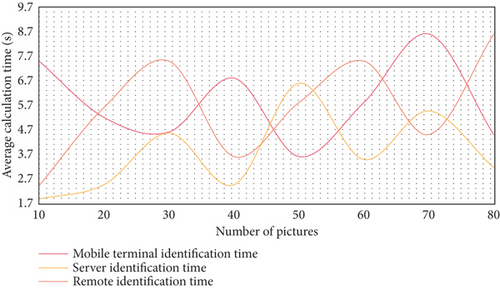
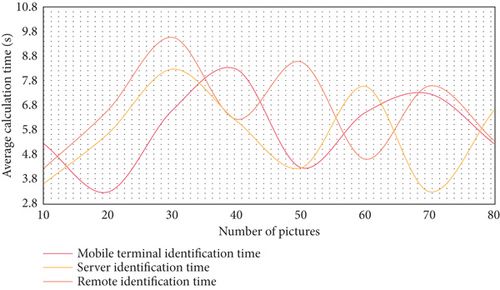
The experimental results show that the recognition time of kinematics server is about 4 to 5 times faster than that of mobile phone. Even with the network transmission time, remote recognition is about twice faster than simple mobile terminal recognition. The experimental results accurately reflect the characteristics of kinematic architecture’s high computing power, and they have practical implications for improving the user experience of mobile applications. The goal of sports image processing is to gather and analyze sports images. Analysis software refers to all types of sports image analysis software. When analyzing sports images, read the original coordinate data obtained from the digitizer and video image acquisition part first, then use data smoothing to remove noise caused by system error and random error. Video shooting systems can be divided into two types based on their shooting speeds: constant speed and high-speed. Color systems and black-and-white systems are the two types of sports image color systems. There are two types of sports image quality video systems: ordinary quality video systems and high-quality video systems.
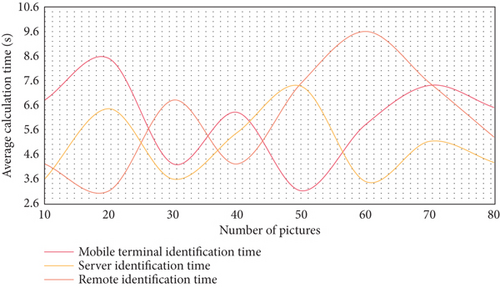
The one legged jump starts from the last step of the run-up, the swing leg kicks off the ground, and the take-off leg quickly and actively pedals. The whole process includes taking off, landing on the ground, moving the body’s center of gravity over the vertical support point, and stepping off the ground. The technical requirements are that the connection between the run-up and take-off actions of athletes is reasonable and consistent, the take-off angle should not be too large, the take-off direction should be more forward, and the loss of horizontal speed should be reduced as much as possible on the premise of ensuring a certain distance. Three experiments were carried out in this experiment for comparison. The experimental results are shown in Figures 6–8.
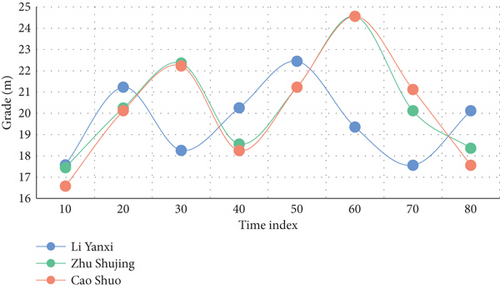
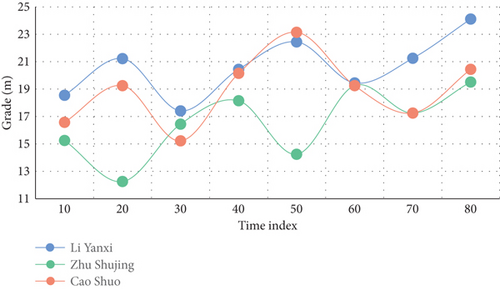
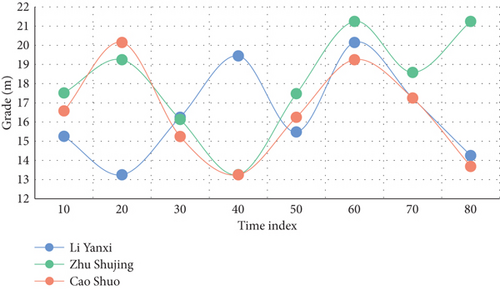
Distance athletes’ instantaneous average speed is 9.47 m/s and 9.52 m/s, respectively, according to the experimental results. The average speed when leaving the plate is 9.34 s/m, and the average speed when entering the plate is 9.48 s/m. 3.21 percent and 2.84 percent, respectively, are the rates of speed loss. The take-off time is 0.12 s and 0.14 s, respectively; the center of gravity rising angle is 16.5 and 15.4. The loss rate of athletes’ horizontal speed is large; the center of gravity leaps at a large angle, as can be seen from these data. To maintain a good rising direction and horizontal speed during the single-foot jump stage, the rising angle of the athlete’s body center of gravity is crucial. If the rising angle is too large, it will affect the speed, amplitude, and angle of the stride jump and the final jump, which will have a certain influence on the successful completion of the follow-up actions. Although the sports image analysis system has become an indispensable sports biomechanical instrument and equipment for modern sports research, sports training, sports teaching, medical rehabilitation, etc., its popularity in China is not high, and its owners are only sports institutes in several major provinces and cities and a few sports colleges. When analyzing sports images, first read in the original coordinate data obtained from digitizer and video image acquisition part and then eliminate the noise caused by systematic error and random error through data smoothing. After the data frame is calibrated, the three-dimensional spatial coordinates are obtained by the fixed-point three-dimensional direct linear transformation method. In this way, according to the shooting frequency, the original data can get the velocity curve by primary differentiation and the acceleration curve by secondary differentiation.
5. Conclusions
Nowadays, sports image analysis information systems play a critical role in the analysis and processing of sports images, as well as the dissemination of information. The image analysis and processing module is an important part of the sports image information system’s core structure. The size of the hard disk determines the image acquisition time, which can range from several hours to several days based on kinematics. The kinematic sports image analysis system has advanced significantly in comparison to previous versions, and its performance indexes have significantly improved in terms of capture frequency, image quality, data collection and analysis methods, and so on. It can be used to investigate the entire set of technical movements, analyze the entire game of ball games, and perform other tasks that take a long time, comparing and contrasting gaps and differences between existing and ideal technical movements in order to improve technical movements and achieve better sports results in competition. The kinematic analysis accuracy is ideal when the analyzed image part is within the calibration range of 3 M. The calibration accuracy is reduced to some extent when the radius of the analyzed image part is within the calibration range of 4.5 m; when the radius of the analyzed image part is within the calibration range of 6 m and 7.5 m, the calibration accuracy decreases noticeably, but the accuracy at the radius of 6 m is still ideal. At the same time, the x-axis and z-axis calibration accuracy is lower than the y-axis calibration accuracy.
Conflicts of Interest
The author does not have any possible conflicts of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.




