Oral English Auxiliary Teaching System Based on Deep Learning
Abstract
In order to solve the problem of the oral English auxiliary teaching system, a research based on Deep Learning was proposed. Based on the theory of Deep Learning, the teaching mode of Deep Learning for college students built on information technology was investigated in the research. As for Shallow Strategy, the item “I think that the best way to pass the English examination is to keep high frequency words in mind” changed most significantly from 3.3 to 2.68. As for Deep Strategy, the most significant change was the item “It can be very interesting for almost all the oral English topics as long as you engage in it actively.” The value increased from 3.31 to 3.97, which was almost close to 4. From the comparison, it could be found that the students changed from memorizing English words mechanically and passively in order to pass the exam to engaging in the oral English situation actively to solve problems so as to obtain self-satisfaction. As a language, English can reflect a unique cultural heritage. It is different from Chinese culture, which can improve learners’ spiritual and cultural accomplishments subtly. In addition, we should try to solve problems with English logical thinking, which can train our critical thinking and oral expression ability, enhance our self-confidence, and improve our sense of self-efficacy. A design-based research paradigm was used in the research. Through the integrated use of information technology, it aimed at building out a deeply mixed teaching mode based on “Cloud Class and Offline Class.” A combination of quantitative and qualitative data collection methods was adopted to evaluate the practical effect. According to the experimental results, two rounds of mixed-mode iterative loop design were performed for the mixed teaching mode. In order to make it more operable, it was improved and perfected continuously.
1. Introduction
Words are the most important, most effective, most common, and easiest way to communicate with people. Speaking English is an important tool for identifying personal communication. The oral level is an important criterion for measuring conversational ability. English has become an international language, and teaching English is one of the most important studies of the language. With the advent of new curriculum adjustments, more and more attention has been paid to the promise of communication skills such as English listening and speaking. The oral English test has become an integral part of the academic examination for higher education students and the international examination for admission to general institutions of higher learning and accounts for 10% of the total score of all English examinations. With the development of international trade integration, as a global language, the relationship between English is getting higher and higher. In this context, English teachers are also more committed to revising the English curriculum. However, the inefficiency or inefficiency of English reading teaching has not been well addressed, affecting both English learners and English teachers. Reading is an important way to train students to obtain information and help them understand English culture. It plays an important role in English teaching, as shown in Figure 1.
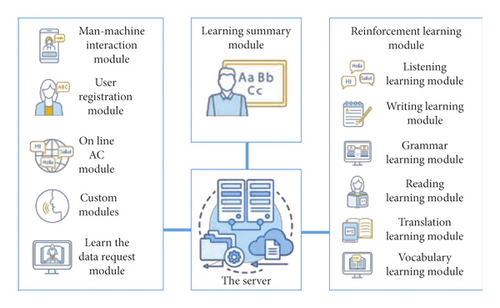
2. Literature Review
With the deepening of curriculum revision, confidence in communicative English has been paid more and more attention in English teaching. The importance of oral English teaching has become increasingly prominent and cannot be changed. In addition, with the advancement of science and technology, the integration of education and technology has become an important part of the role of computer-assisted English language teaching and has become more and more important in education [1].
Deep Learning was proposed by scholars Li et al. in the research “Essential Differences in Learning: Results and Process” jointly published after experimental research on students’ reading of academic articles [2]. Deep Learning was a concept opposite to Surface Learning, which was isolated memory and noncritical acceptance of knowledge. It emphasized learners’ active learning and flexible and skilled use of knowledge to solve practical problems. Meng believed that surface learning was oriented by mechanical memory to repeat isolated information. Deep Learning was comprehension-oriented [3]. Subsequently, Rooij et al. analyzed Deep Learning and Surface Learning on this basis. They believed that Deep Learning focused more on the meaning of texts, which was different from Surface Learning focusing on the superficial understanding of texts. It reflected learners’ application of different learning strategies. Namely, Surface Learning is more based on memory and recitation. On the other hand, Deep Learning focuses on high-level strategies such as concept association, comprehension elaboration, and critical thinking [4]. On this basis, Zhu established the influencing factor model of Deep Learning, and he believed that Deep Learning was a key strategy for extracting meaning and understanding from course materials and experiences [5]. Yuan and Zhu carried out the design and research of computer-aided translation teaching courses based on embedded microprocessors under the background of wireless communication, explored the use of high-tech systems to train college students, and promoted the reform of college classroom teaching. Using computers to assist translation and embedded microprocessors to perform related calculations in translation teaching courses in colleges and universities can improve students’ learning efficiency to a certain extent. The experimental results show that the student concentration on computer-assisted teaching is 20% higher than that of traditional teaching, and other relevant data is more than 8% higher. Students benefit from the teaching of computer-assisted translation courses [6].
Deep Learning in College English refers to a curriculum in which learners critique new ideas and facts to make connections between old and new knowledge and transform existing knowledge into natural, new ways of solving creative problems through understanding and learning. The research, based on the research of Deep Learning, aimed at reconstructing the senior new concept of teaching and learning oral English classes, promoting building the corresponding support system through the learning process elements such as tools, resources, and means of integration and promoting the fundamental changes to the way the students learning, so as to effectively develop the students’ ability of senior deep cognition and high-level academic oral communication ability and enable students to express their views in written and spoken language in various occasions requiring language expression based on high-level thinking activities (logical reasoning, critical thinking, etc.) such as daily conversations, academic seminars, and public speeches, which can effectively promote interpersonal collaboration and communication.
3. Research on Oral English Auxiliary Teaching System Based on Deep Learning
3.1. Overview of Speech Evaluation Technology
With the emergence of cloud computing and the widespread use of 3G, the power of voice technology to adapt to the wave of the mobile Internet has developed rapidly. With the development of technology, the interaction of human-computer communication has been observed, making communication between people and technology and personal communication easier. Speech technology is a communication science that includes acoustics, organizational science, information science, language arts, and computer science. Technical communication usually includes verbal communication, speech skills, and speech measurement. Speech synthesis technology can convert unspoken words into natural and smooth speech, also known as Text-to-Speech, which solves the difficult problem of speech processing technology. As a speech technology, speech recognition is a tool that enables machines to convert speech signals into written or spoken commands through knowledge and understanding. In recent years, with the rapid development of cultural research and communication, speech assessment has achieved success and has been widely used. Phonetic measurement belongs to the field of computer-assisted language learning. It is a technology that receives speech scores, checks for errors, and provides corrective information from machines. Through the use of technology, Mandarin or English can be measured through computer models and faulty instructions. In English teaching, it can improve the efficiency and effect of students’ English learning [7]. Phonetic assessments include phonetic pattern development, prosodic quality assessment of pronunciation fragments, and book scoring mapping workshops. The principle of speech evaluation is shown in Figure 2.
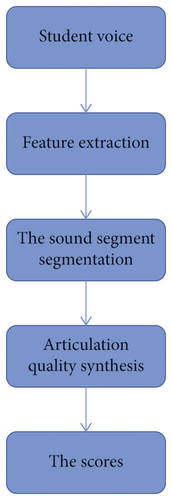
With the gradual maturity of speech technology and its wide application in language learning, computer-aided language learning (CAI) has become a hot topic in English teaching.
3.2. Intelligent Oral English System Based on Speech Evaluation
The Intelligent Tutoring System (ITS) works well in one-to-one teaching. Student standards are an important part of ITS, and student proficiency is the most important aspect of student standards, which can affect students’ knowledge and skill levels through assessment. Therefore, it is believed that the development of the student model depends on the measurement techniques used in the study [8]. Enrollment models and student models are the basis for the successful completion of the standard curriculum. This model is the bridge between the enrollment model and the student model. The purpose of this standard is to identify modifications and provide self-approval services. Their interaction is shown in Figure 3.

Linguistic research has found that reading and repetition are effective ways to improve English language skills. As a result, imitation reading, reading aloud, repetition, contextual discussion, and other English language practices are developed in science. As a speech measuring machine, the accuracy, precision, and fairness of spoken language will be its most important measurement criteria [9].
3.3. Innovation and Optimization Strategies of Oral English Reading Teaching Methods Based on Deep Learning
- (1)
Establishing the concept of student-centered education. In education and teaching activities, teaching concept plays a guiding role. Only by setting up correct educational ideas can teachers make the whole teaching activities move forward in the direction of high efficiency. Based on the perspective of Deep Learning, English teachers should establish the idea of student-centered education, highlight students’ subjectivity, and make students devote themselves to reading, so as to achieve the goal of Deep Learning. First of all, teachers should create a relatively loose and harmonious English environment for students according to the actual situation. In such an atmosphere of language expression, students’ learning enthusiasm and initiative will be fully mobilized. For example, teachers can use humorous language or create visual and interesting teaching situations with the help of multimedia equipment to stimulate students’ learning motivation. Secondly, teachers should strengthen their sense of service and put themselves in an equal position with students. During the teaching process, the teacher can use “Do you have a different point of view?” and “How do you understand this sentence?” Such discourses interact with students and make students feel understood and respected, which plays a positive role in promoting the construction of efficient classes [10].
- (2)
Using a variety of teaching methods. A single course cannot meet the needs of current English reading teaching. To achieve the goal of Deep Learning, English teachers need to receive a variety of teaching materials based on classroom facts. According to the author’s personal teaching, in addition to the multimedia teaching process, teachers can also adopt various teaching methods such as layered teaching, participation in teaching groups, and state design guidance [11].
- (3)
Paying attention to the infiltration of Western culture. From the perspective of Deep Learning, English teachers should not only focus on the explanation of basic knowledge such as vocabulary and grammar but also pay attention to the infiltration of Western culture when analyzing texts. Only in this way can students better grasp the connotation of the text. For example, in analyzing the “Good Morning!” text, the teacher should not only tell westerners how to greet each other but also make a comparison between Chinese and Western ways of greeting so as to penetrate Western culture on this basis [12].
3.4. Teaching Design
- (1)
Constructing the teaching design of an advanced oral English course oriented to deep learning: under the traditional teaching mode, a large number of repetitive tasks, excessive teaching content, and delayed feedback lead to students’ repetitive work and lack of opportunities for independent thinking, which cannot meet students’ personalized needs for development. College non-English major undergraduates also have strong English test capability, but they lack the academic oral communication ability such as oral presentations, speeches, and debates. Especially, the problems of Deep Learning for indications of speculative ability, information integration, knowledge construction, migration, problem-solving-oriented active learning, and lifelong learning are particularly acute. The Deep Learning mechanism, which is oriented by critical learning, knowledge construction, and problem-solving, solves this problem effectively. The research aimed at improving learning effectiveness by expanding the learning space, building integrated learning inside and outside the classroom, and exploring the new and new information technology-supported mixed teaching mode, which relied on the “Cloud Class” learning platform. Based on the “Cloud Class” platform, the teaching process of a unit was as follows. Before class, teachers designed and developed teaching resources and uploaded them to the learning platform. And students learn independently. According to their own learning needs, learning habits, learning strategies, and learning objectives, students could use the teaching resources of listening, reading, and watching on the self-learning platform to form a personal understanding of the topic and find problems timely. During the class, teachers and students shared discussions. Through scenario simulation, role-playing, project training, case discussion and analysis, exchange and debate, problem discussion, and other activities, under the guidance of teachers, group discussion was performed based on the problem to form a conclusion and the teacher summarized. After class, reflection and evaluation were necessary. This part included evaluating your classmates and reflecting on yourself to further deepen the learning content. In this process, teachers and students evaluated and reflected together to modify teaching tasks and requirements [14].
- (2)
Reshaping course objectives and knowledge structure and improving the knowledge connotation of Advanced Oral English course. The teaching objective connotation of the “Advanced Oral English” course is optimized. Through the training of this course, students will basically reach the oral English ability stipulated in “Higher Requirements” of “College English Course Teaching Requirements,” that is, they can express their opinions and thoughts clearly and logically with the basic language knowledge they have mastered. They are able to conduct accurate and fluent conversations or discussions with Native English speakers on general or professional topics and to carry on the conversations or discussions effectively. They are able to use English flexibly and effectively to express one’s own ideas, such as feelings and intentions, for personal or social purposes. They are able to summarize a longer, more difficult text or speech in brief language and give a longer explanation or explanation on a subject. They are able to express their views and opinions freely in academic conferences or professional exchanges, with outstanding focus, complete content, and fluent language. Based on students’ learning needs and following the rules of second language acquisition, the research aimed to improve the effectiveness of College English teaching by reconstructing the curriculum knowledge structure, perfecting the knowledge connotation of Advanced Oral English course, optimizing the teaching content, and teaching mode and innovating the construction and application of teaching materials. The fragmentation, multitask, and shallow graph reading caused by digital and networked learning brought diversity and convenience to learning and limited students’ thinking at the same time, resulting in the lack of Deep Learning and low classroom effectiveness. To solve the problem, the curriculum connotation characterized by Deep Learning should be reconstructed to help students build a knowledge system [15].
- (3)
Exploring new assessments based on in-depth research. SOLO (Structure of the Observed Learning Outcome) was selected as one of the measurement tools. To influence students’ understanding of the problem, SOLO dissociation theory divides the answer to the problem into five different thinking levels, namely, the preceding model, conceptual language, multiple meanings, social model, problem-solving model, and the SOLO classification theory. The new assessments not only look at the benefits of short-term learning but also focus on improving students’ academic and emotional well-being, promoting learning, and applying what they have learned. Intimidation and self-assessment severely limit students’ initial learning and interest. In view of this, a new assessment based on the National Institutes of Health was explored to provide a reliable guarantee for improving teaching quality [16].
3.5. Analysis of English Deep Learning and Teaching Model
3.5.1. Research on Deep Learning
(1) The Connotation of Deep Learning. Deep Learning is also known as learning deeply. Subsequently, scholars at home and abroad have conducted more extensive and in-depth discussions on the theory and practice of Deep Learning and summarized such views. It summarizes the proven viewpoints. “Surface learning means memorizing isolated facts and accepting scattered information without questioning and developing a surface understanding of concepts that cannot be sustained. By contrast, Deep Learning involves analysis of a new idea critically, the creation of a link is between the new learning materials and previous knowledge, keeping the learned knowledge and the transfer and application in a new and different situation.” Their characteristics are shown in Table 1.
| Deep Learning | Shallow learning | |
|---|---|---|
| Reflective state | Reflective learning by using evidence | Rote learning |
| Focus on | Macro grasping with long-term vision | Learning is driven by fear of failure |
| Knowledge system | Integrating the old with the new | No connection between the old and the new |
| Transfer ability | Solving practical problems based on their own experience | Knowledge is separated from ability |
However, there is no unified view on the definition of Deep Learning at home and abroad. Some people understand it as methods and strategies, while others understand it as goals to be achieved. Therefore, different interpretations such as “Deep Learning mode theory,” “Deep Learning process theory,” and “Deep Learning results theory” have emerged. Some scholars believed that “Deep Learning was the foundation of understanding. Learners were able to critically learn new ideas and facts, integrate them into their existing cognitive structures, make connections between ideas, and transfer existing knowledge to new situations for decision-making and problem-solving.” Some scholars believed that Deep Learning was a kind of study way. The purpose was to construct meaningful learning. On the basis of memory, the learners understood, inducted, grasped, and applied the knowledge. Combined with the original cognitive structure, the learners accepted and learned new knowledge critically and established the correlation between knowledge. Decisions were made and problems were solved through analysis. Deep Learning was a meaningful process of complex cognitive processing and its essence was the construction process of the interaction between structured knowledge and unstructured knowledge. Learners were required to activate the original knowledge, retrieve memories, and analyze, integrate, transfer, and create new knowledge, new information, and new problems. Deep Learning has changed the current situation of low- and middle-level thinking objectives such as memorization, comprehension, and application in teaching, aiming to promote the development of higher-order thinking of learners [17].
(2) Deep Learning and Learning Engagement. Engaged learning typically focuses on students’ academic performance, psychological expectations, and effort levels throughout the learning process. Therefore, the effectiveness of the course and the assessment of learning are limited by student guidance. As teachers and schools produce revised data, they develop and refine student learning strategies based on shared goals. Behavioral investment, knowledge investment, and value investment are our research on investment education, in which investment behavior is the symbol of investment education and the space and equipment for capital investment and stable investment. In the context of the “mobile Internet,” the continuous development of education and the rapid changes in teaching methods also have an impact on students’ learning strategies. Important research from the National College Student Engagement Survey shows that the importance of learning engagement is the interaction between student behavior and the environment, including the time and effort students invest and the policies and procedures schools adopted to advance student learning. “This suggests that the learning process involved is not only about the learner, but also influenced by the learning environment.” In fact, students’ interactions with media or education are also for behavior. Therefore, when researchers design teaching models, in addition to interfering with thinking and intelligence and promoting students’ Deep Learning, they can also use mobile phones to encourage students’ performance in College English classes before, during, and after-class English [18].
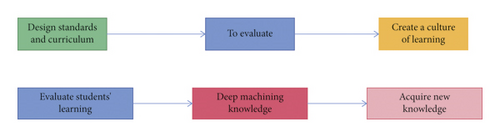
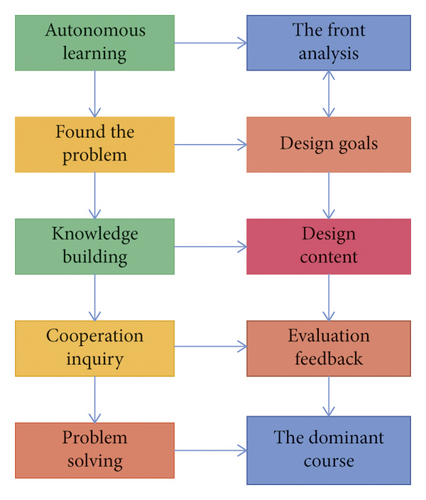
(3) Deep Learning Teaching Mode. As can be seen from Figure 4, the Deep Learning cycle (DELC) is mainly composed of seven key points. They are design standards and curricula to evaluate and create a learning culture, prepare and activate preknowledge, acquire new knowledge and deep machining knowledge, and evaluate students’ learning. These seven key points are called seven powerful strategies of Deep Learning. Evaluating students learning can be seen from the diagram from two routes connecting to acquire new knowledge. The first is that the teacher designs curriculum and standards through the evaluation and analysis of the students’ learning first of all. Then the preliminary assessment is made for the students after the teaching-learning situation. And then, a positive learning culture is created and built for the class design leading to learning. In order to activate students’ previous knowledge, new knowledge is taught. Another is relatively simple: the teacher helps students learn to deeply process knowledge after acquiring new knowledge from the evaluation of student learning. Inspired by the roadmap, a Deep Learning teaching model for College English was constructed [19].
3.6. Design and Implementation of Teaching Mode Pointing to Deep Learning
3.6.1. Construction of Teaching Mode
In the first experimental research, with the goal of Deep Learning as the breakthrough, the learning space into online extracurricular learning space and offline classroom learning space was divided when constructing the teaching mode from the perspective of the learning space. The details of the mode design of each space are as follows.
(1) Teachers’ Teaching Preparation. Before preparing lessons, teachers conducted preassessments based on the accuracy of students, the difficulty of textbooks, and the operation of the teaching platform and determined specific goals. And according to the instructions, the necessary teaching materials are designed, developed, and written. It only has content-related video resources such as tidbits, news, notes, movies, and TED talks, supplemented by text, PPT courseware, audio, pictures, and links to hot tweets. In order to encourage students to participate in learning, teachers continue to carry out online activities, such as tutoring, question-and-answer discussions, voting, brainstorming, and other independent learning. Experienced teachers can download and publish the teaching materials of “Blue Ink Cloud Classroom” anytime, anywhere. Teachers outline individualized assignments and requirements that students must complete before class. Cloud Classroom will automatically send activity alerts to students’ mobile locations.
(2) Students’ Self-Construction. Students can download and set up the “Blue Ink Cloud Classroom” mobile application according to the teacher’s requirements and then visit similar classes by class for self-study. Students can arrange their own learning, personalization, location, progression, and approach and complete their prior knowledge by taking courses and taking online courses. They can also post questions through classroom communication or bring questions to offline classrooms for discussion [20].
(3) Intelligent Management Evaluation. “Blue Ink Cloud Classroom” can compile student courses, grade students according to knowledge value, conduct intelligent assessments on students, group students into groups, and help teachers monitor, control and evaluate. In addition, teachers can encourage students to enjoy learning and build relationships with teachers, mentors, and students through praise, advice, and gifts. Of course, students can also measure up against each other. After the teacher’s work is complete, students can view other students’ responses in real time to expand their thinking, refine the solution, and achieve complete success. See Figure 5.
3.7. Evaluation Design of Deep Learning
3.7.1. Academic Evaluation Method
In order to improve the interactive participation and learning enthusiasm between students and students and between students and teachers, the learning evaluation of this course mainly included two evaluation methods: process evaluation (40%) and final evaluation (60%). Process evaluation included the offline class performance, Cloud Class experience value, and mid-term exam, of which the mid-term exam accounted for 30%. The final evaluation was mainly the result of the final exam. See Figure 6.
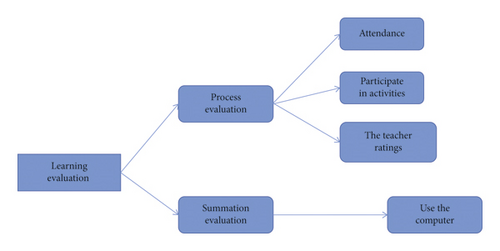
3.7.2. Results’ Evaluation of Deep Learning
Some scholars believed that “although the overall cognitive structure of students cannot be detected, the thinking structure of students in response to a question could be detected, reflecting the conceptual understanding and thinking level of students in specific knowledge points,” which was an important clue to study the quality of learners’ learning results. SOLO (Structure of Observed Learning Outcome) classification theory was proposed and the levels of answering questions were divided into prestructure level, single-point structure level, multipoint structure level, related structure level, and abstract extended structure level [21]. The researcher collected and sorted out the interactive data of students in the Cloud Class during the whole course learning process. SOLO classification theory was used for content analysis, which could reflect the changes in students’ cognitive level in the learning process.
3.8. Analysis of the Implementation Effect
3.8.1. Analysis of Changes in Learning Engagement
The classification dimensions of learning engagement were summarized by consulting a large number of literature materials. Behavior, emotion and cognition were generally recognized evaluation dimensions of learning engagement. In addition, Other relevant research showed that NSSE (academic challenge, active cooperative learning, teacher-student interaction, rich educational experience, campus environment support), UWES-S (vitality, dedication, concentration), OSES (skills, emotion, participation, performance), and other college student engagement scales, which were obviously different from this three-dimensional structure could also be transformed into three dimensions of behavior, emotion, and cognition. Therefore, the study engagement of students was investigated from these three aspects [22]. Students’ learning engagement is investigated, as shown in Table 2.
| Dimension | Items | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Learning engagement | Learning engagement in class | Behavioral engagement | 2–6 |
| Learning engagement after class | Cognitive engagement | 3–8 | |
| Emotion engagement | 22–33 | Cognitive engagement | 10–12 |
After the implementation of the mixed teaching mode based on “Blue Ink Cloud Class + Offline Class” for one semester, a questionnaire survey was conducted on learning engagement among 41 students in Experimental Class A so as to analyze the changes in students’ learning engagement before and after the implementation of the mode. The questionnaire was in the form of a Richter five-level scale, with 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 points from “completely inconsistent” to “completely consistent.” A total of 82 questionnaires were released twice, and a total of 82 valid questionnaires were recovered with a recovery rate of 100%.
First, the reliability and validity analyses of the collected data were performed. As shown in Table 3, the internal consistency of the reliability coefficient value of the questionnaire was 0.962, indicating that the reliability of the questionnaire was ideal and very good. The validity analysis of the questionnaire showed that the value of KMO was 0.946, greater than 0.9, indicating that the questionnaire had good structural validity [23].
| N of items | Cronbach’s alpha | t |
|---|---|---|
| 24 | 0.962 | 0.129 |
Then, the quantitative analysis software SPSS was used to conduct paired sample t-test for the data collected twice and the results are shown in Table 4. Significance (two-tailed) was less than 0.001, namely, P < 0.001, indicating that students in this mixed teaching mode had significantly changed their devotion to College English learning after learning this semester.
| Cases | Mean | Std. deviation | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Front side | 42 | 131.26 | 0.236 |
| Back side | 43 | 169.23 | 0.563 |
In order to explore the more detailed changes within learning engagement, a descriptive statistical analysis of each dimension of the questionnaire on learning engagement was conducted in the research. The statistical results are shown in Table 5. As can be seen from the data in Table 5 (A1 represented pretest and A2 represented posttest), compared with the average value of A1, the value of A2 was greater than A1, indicating that the engagement of each dimension had increased more or less. Among them, the most significant change was emotional engagement; the average value of emotional engagement in the posttest was 4.2793, which was close to 5, indicating that under the teaching mode based on Cloud Class, students had become fond of learning tasks such as accumulating English vocabulary, expanding English reading, making comments in English and writing English compositions. Interest was the best teacher, and the change of emotional engagement was the first step toward the depth of students’ English learning. The next significant change is extracurricular learning; the average changed from 3.4509 to 3.8501. The most significant influence on extracurricular learning engagement was extracurricular behavior engagement. It also indicated that in this class teaching mode based on the cloud, with the increasing tasks completed in extracurricular time, student learning engagement driven by tasks was also increasing. However, the increase in the rate of extracurricular cognition engagement was low, indicating that when preparing teaching resources, teachers should also consider how to associate teaching resources with learning tasks so as to stimulate students’ learning motivation. And the support of the learning strategies was given to help students finish work easier and more efficiently, promoting Deep Learning in College English learning.
| Learning | Cases | Mean | Std. deviation | t | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Curricular learning | A1 | 42 | 3.263 | 0.756 | −1.23 |
| A2 | 43 | 3.269 | 0.369 | −1.23 | |
| Extracurricular learning | A1 | 43 | 3.261 | 0.896 | 0.756 |
| A2 | 41 | 0.963 | 0.369 | 0.239 | |
| Emotion engagement | A1 | 41 | 0.269 | 0.896 | 0.263 |
| A2 | 41 | 0.569 | 0.236 | 0.269 | |
4. Experiment and Research
4.1. The Teaching Mode of Promoting Oral English Deep Learning
4.1.1. Analysis of Learners
In the first round of research, 37 undergraduate students were selected from Experiment Class B, a full-time sophomore of S university in East China, for practical research. The major composition of majors was more complex than that of the first round of the experiment, mainly covering architecture, medicine, and literature. And they were still taught by teacher G. The selected period was the fall semester in 2018-2019, which was the first semester of the sophomore year [24].
4.1.2. Analysis of the Course
In the first round, the elective course Advanced Oral English for full-time College English sophomores was selected. This course was an online open course offered by S University on the platform of Love Course. It mainly used the teaching material “Oral English Communication” and aimed to “improve students’ Oral English Communication ability.” The Ministry of Education College English Curriculum Requirements clearly pointed out that “the teaching aim of College English was to cultivate the students’ English comprehensive application ability, especially listening and speaking skills, to make them communicate effectively in English both written and spoken in the future work and social activities, to improve their ability of independent and the comprehensive cultural quality at the same time, to meet the needs of social development and international exchanges.” Advanced Oral English is aimed at improving college students’ oral English communicative ability more scientifically and effectively. The teaching objectives, teaching contents, teaching methods, teaching material construction, and teaching evaluation of this course have undergone various follow-up and practical teaching reforms. The teaching concept of “teacher-led, student-centered and teacher-student interaction” was implemented in this course, and a multidimensional and three-dimensional teaching model that integrated classroom and extracurricular teaching, in and out of school, face-to-face learning and autonomy, and traditional and modern teaching in one-body teaching was established. Acquiring and developing knowledge and ability were focused on in-classroom or in-school learning [25].
However, there were many restrictions on oral English teaching for online courses, the most prominent of which was the lack of face-to-face communication between students and teachers. Teachers were unable to put forward specific suggestions for the improvement of students’ different oral English situations. Therefore, the second round of mixed-mode research should be carried out by combining offline classes. There were a total of 11 thematic units in the oral English course. Due to time constraints, the second round only lasted for 36 class hours, so only units 1, 3, 8, 9, 10, and 11 were selected by teacher G to carry out teaching. See Table 6.
| 01 | College life and study |
| 02 | Food and health |
| 03 | Friendship |
| 04 | Sports and fitness |
| 05 | D CVTRE |
| 06 | Traveling |
| 07 | Music |
| 08 | Volunteer work |
| 09 | Love and marriage |
| 10 | Science and technology |
| 11 | Career and jobs |
4.2. Teaching Objective Design Pointing to Deep Learning
The objective design of this round was basically similar to that of the first round. Since this round was an applied course of college Oral English, the researchers further strengthened the objective design of oral English by referring to the development objectives in the three-level objective system of the College English Teaching Guide.
4.2.1. Oral Presentation Skills
(1) Picture Speaking. The learners are able to describe the main content of the situation orally, to guess the depth of information the picture conveys, and to clarify their own views based on their own experience.
(2) Dialogue Skills. The learners are able to skillfully use some communication strategies to control the content and topic trend of two-person conversations or multiperson group discussions.
(3) Speech Skills. The learners are able to make impromptu speeches on various topics and in various situations.
(4) Debate Skills. The learners are able to use debate skills to deal with various debate topics, master the debate process, organize debate activities, and cooperate with team members to elaborate their own views and complete group debate.
(5) Transfer of Application. The learners are able to communicate effectively in English in daily life, study, and future work. The specific objectives of each topic unit are shown in Table 7.
| Unit | Topic | Learning objectives | Ability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unit1 | College life and study | (1) Complete basic reading tasks | Listening, speaking, reading, and writing |
| (2) Master common words and phrases in the text | |||
| (3) Understand your views on the purpose of education | |||
| (4) Practice oral expression | |||
| (5) Discuss the purpose of education | |||
| (6) Learn presentation skills | |||
| Unit2 | Friends and friendship | (1) Complete basic reading tasks | Listening, speaking, reading, and writing |
| (2) Master common words and phrases in the text | |||
| (3) Practice your listening ability | |||
| (4) Strengthen oral expression | |||
| (5) Cultivate teamwork skills | |||
| (6) Learn to reflect on yourself and others | |||
| Unit3 | Charity and volunteer work | (1) Complete basic reading tasks | Listening, speaking, reading, and writing |
| (2) Master common words and phrases in the text | |||
| (3) Strengthen oral expression ability | |||
| (4) Cultivate teamwork skills | |||
| (5) Learn to reflect on yourself and comment on others | |||
| Unit4 | Love and marriage | (1) Complete basic reading tasks | Listening, speaking, Reading and writing |
| (2) Master common words and phrases in the text | |||
| (3) Learn presentation skills | |||
| (4) Strengthen oral expression ability | |||
| (5) Cultivate teamwork skills | |||
| (6) Learn to reflect on yourself and comment on others | |||
| Unit5 | Science and technology | (1) Complete basic reading tasks | Listening, speaking, reading, and writing |
| (2) Master common words and phrases in the text | |||
| (3) Learn presentation skills | |||
| (4) Strengthen oral expression ability | |||
| (5) Cultivate teamwork skills | |||
| (6) Learn to reflect on yourself and comment on others | |||
4.3. Optimization and Implementation of Pointing to Deep Learning Mode
4.3.1. Optimization of the Teaching Mode
In the process of optimization, the teaching model from the dimension of learning time was designed, dividing the learning time into three periods: pre-class, in-class, and after-class. In order to make teaching resources and teaching activities associated in any period, the importance of group tasks was highlighted and the group task module was placed after the after-class period. The optimization diagram of the mixed mode is shown in Figure 7 and the specific details of mode design for each part are as follows.
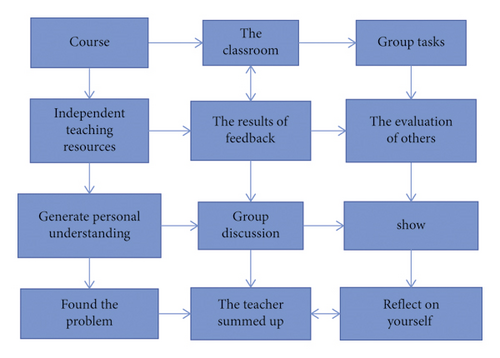
(1) Project-Based Learning (PBL) Strategy. In the stage of independent learning before class, students completed the learning of learning resources and self-construction of the knowledge system according to the task information released by teachers, finding derivative problems encountered in the learning process while generating personal understanding and bringing the unsolvable problems into groups or classes for communication. Different from the first round, the Project-based Learning (PBL) strategy was adopted to intervene students’ independent learning before class. Students needed to carry out learning tasks (individual tasks or group tasks) for learning resources. For example, before the theme unit of Unit4 Love and Marriage, the teacher assigned a pre-class task: Read Amal Clooney's Speech on her husband George Clooney. Write one or two paragraphs to your future spouse anything. Students were asked to read all the tweets and videos about Mrs. Jo first and then write a paragraph or two to their future partner. The importance of students’ internal motivation was emphasized in Deep Learning, which was the premise of autonomous learning. Project-based Learning was purposeful and efficient, which was conducive to cultivating students’ cognitive competence.
(2) Cooperation-Based Learning Strategies. In the stage of classroom sharing and discussion, motivation strategies and cooperation-based Learning strategies were mainly used to cultivate students’ interpersonal skills. Classroom learning was the stage of face-to-face communication between teachers and students. Teachers could use the forms of individual questioning, team discussion, group discussion, and so on to promote collaboration and communication between group members during classroom activities. Motivation strategies were mainly reflected in that teachers could adopt new English activities such as debate, performance, dubbing, and situational dialogue to teach, so as to stimulate students’ learning motivation, to improve their classroom participation and enthusiasm, and to promote Deep Learning.
(3) Reflection-Based Learning Strategies. In the stage of the after-class reflection evaluation, the evaluation was optimized on the basis of the first round. According to the group mutual evaluation, the teacher divided the scoring dimensions and set the score values in advance so that students had standards and directions for evaluation. As for learning reflection, reflection activities were launched in the mid-term and final stages, respectively, in this round. Mid-term reflection could help students find their own shortcomings and promote the understanding of learning content. Teachers could adjust teaching plans timely according to the opinions of students. The final reflection was mainly to train students’ reflective learning ability and help teachers carry out the next lesson better, as shown in Figure 7.
4.4. Optimization of Deep Learning Evaluation Design
Similar to the first round of courses, the two evaluation methods of the process evaluation and the final evaluation were still adopted in the learning evaluation of this course. But the difference was that the process evaluation increased to 60%, and the final evaluation accounted for 40% in order to improve students’ participation and enthusiasm in process learning. The process evaluation included offline class performance, Cloud Class experience value, and mid-term exam. The mid-term exam accounted for 30%. The score was the average score of teaching assistants and teachers. The learning record and classroom performance of Cloud Class accounted for 30%. The final evaluation was mainly the result of the final computer exam. See Figure 8.
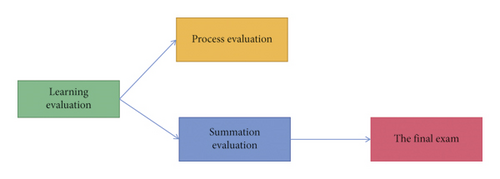
4.5. Analysis of Implementation Effect
4.5.1. Analysis of Changes in Deep Learning
The questionnaire about learning strategies in Research on Undergraduates’ Deep Learning Process and Teaching Strategies was adapted and revised according to the course characteristics of College English. The specific dimensions and questions are set as shown in Table 8.
| Variable | Question |
|---|---|
| Shallow motivation | 1∼8 |
| Shallow strategy | 6∼9 |
| Deep motivation | 10∼19 |
| Deep strategy | 13∼14 |
After the first round of optimization design, the model was implemented in Experimental Class B for 18 weeks. In order to understand the changes in students’ learning motivation and strategies before and after the implementation of the model, a questionnaire survey on the learning motivation and strategies of 37 students in Experiment Class B was conducted. The questionnaire was in the form of the Richter scale, in which 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 points were used from “completely inconsistent” to “completely consistent.” A total of 74 questionnaires were released twice and a total of 74 valid questionnaires were collected, 37 for the first time and 37 for the second time, with a recovery rate of 100%.
First, the reliability and validity analyses of the collected data were performed. As shown in Table 9, the reliability coefficient value of questionnaire a was 0.883, indicating that the reliability of the questionnaire was good, as shown in Table 9.
| N of items | Cronbach’s alpha | t |
|---|---|---|
| 17 | 0.553 | −7.236 |
In order to explore the more detailed changes in learning engagement, the quantitative analysis software SPSS was used to conduct paired sample t-test on the data collected twice and the statistical results were shown in Table 10 (B1 represented pretest and B2 represented posttest). As can be seen from the data in the table, compared with the average value of B1, the average value of B2 was greater than that of B1 for Shallow Motivation and the average value of B2 was less than that of B1 for Shallow Strategy. While the average value of B2 was greater than that of B1 for both Deep Motivation and Deep Strategy and the significance value was less than 0.05, namely, P < 0.05, which indicated that under the optimized teaching mode, students’ learning motivation and learning strategy were slowly transferred from shallow to deep, and the difference of the pre-and posttest data was significant. See Table 10.
| Variable | Mean | Std. deviation | t | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shallow motivation | B1 | 0.236 | 0.236 | −1.369 | 0.456 |
| B2 | 2.25 | 0.264 | −1.236 | 0.859 | |
| Deep motivation | B1 | 2.37 | 0.23 | −0.239 | 0.896 |
| B2 | 2.26 | 0.296 | −0.258 | 0.259 | |
In terms of specific questions of Shallow Motivation, the item “I think the purpose of learning English is to pass CET-4, CET-6, IELTS or TOEFL, which may be helpful when looking for a job” changed the most from 3.22 to 2.92. As for Deep Motivation, the item “I’ll find more information about the interesting English academic topic after class” changed the most from 2.86 to 3.39, which showed that the understanding of the college students for English not only was confined to treating it as a test and a work necessity but also felt that learning English was a kind of fun. I began to actively engage in English reading after class. As for Shallow Strategy, the item that “I think that the best way to pass the English examination is to keep high frequency words in mind” changed most significantly from 3.3 to 2.68. As for Deep Strategy, the most significant change was in the item “It can be very interesting for almost all the oral English topics as long as you engage in it actively.” The value increased from 3.31 to 3.97, which was almost close to 4. From the comparison, it could be found that the students changed from memorizing English words mechanically and passively in order to pass the exam to engaging in the oral English situation actively to solve problems so as to obtain self-satisfaction. As a language, English can reflect a unique cultural heritage. It is different from Chinese culture, which can improve learners’ spiritual and cultural accomplishments subtly. In addition, we should try to solve problems with English logical thinking, which can train our critical thinking and oral expression ability, enhance our self-confidence, and improve our sense of self-efficacy.
5. Conclusion
- (1)
The deeply mixed teaching mode based on “Blue Ink Cloud Class + Offline Class” was helpful in increasing students’ learning engagement, stimulating students’ learning motivation, and improving students’ learning strategies so as to improve the college undergraduates’ comprehensive application ability and promote the Deep Learning of College English.
- (2)
College students were highly receptive to emerging technologies and could accept the College English class based on the deeply mixed teaching mode of “Blue Ink Cloud Class + Offline Class.”
- (3)
As a mixed learning support tool, “Blue Ink Cloud Class” could effectively connect online and offline teaching spaces, facilitate students’ learning, increase the communication and interaction between teachers and students, enhance the special friendship between teachers and students, and contribute to the construction of a good teaching atmosphere.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Hebei Vocational College of Rail Transportation.
Open Research
Data Availability
The labeled dataset used to support the findings of this study is available from the corresponding author upon request.




