Ergonomic Fuzzy Evaluation of Firefighting Operation Motion
Abstract
The firefighting operation motion has an important impact on the safety and comfort of firefighting operation. As a judgment criterion of the firefighting efficiency, the comfort level is hard to judge in that it is completely decided by human feeling, so the comprehensive fuzzy evaluation is utilized for evaluation of comfort level. In this paper, firstly the factor and judgment set of firefighting operation comfort level are determined, and the fuzzy weight evaluation is obtained by questionnaires and analytic hierarchy process. Secondly, the joint angles of some particular motions are determined by motion capture equipment, the moment is obtained by ergonomic engineering software, and then the comprehensive comfort evaluation on firefighting operation motion is completed. Finally, the objective evaluation system of firefighting operation comfort is established.
1. Introduction
Firefighting grows more and more difficult owing to many types of fire accidents nowadays. The operation efficiency becomes the important factor on the firefighting according to statistics of fire accidents. Therefore, the rationality and reliability of firefighting operation directly affect the rescue work.
Motion analysis can be used to optimize and standardize human operation motion by means of detecting and tracking human operation. The motion analysis of firefighting is based on the collection, classification, and evaluation of particular rescue motion of fire men and the research results will be the fundamentals for firefighting product design and fire man training optimization. The motion analysis can be classified into two methods: visual motion observation method and image motion observation method [1].
The ergonomics analysis of firefighting operation and fire men mainly focuses on firefighting training, fire extinguisher, and fire man uniforms. Jiao et al. applied BP neural network to firefighting training evaluation. The comprehensive evaluation on the basic information, training methods, training contents, training management, and achievement of the tested groups are discussed [2]. Based on SAQ+B (Scenario Animation Question and Browse), Chen and Li proposed an evaluation method for simulation of firefighting training. The training process is first divided into several units, and then the training problems are abstracted. Through experts grading, integrating calculation method of AHP by Matlab, the firefighting training evaluation is divided into two parts of knowledge acquisition and capability test. Therefore the quantitative estimation for the training subject is obtained [3]. AHP is short for analytic hierarchy, which is to process a structured technique for organizing and analyzing complex decisions. Comprehensive fuzzy evaluation is applied in plenty of areas. For ergonomic evaluation, Hongzhe and Damin utilized this method in evaluating the comfort level of fighter plane cockpit arrangement. Park et al. conducted evaluation on the comfort level of cab in engineering machines [4].
In the paper, evaluation model for firefighting operation motion will be built by fuzzy integrating method. The human body modeling and motion simulation will be conducted in virtual environment. Through motion capture equipment, the human biomechanics data will be obtained and then an ergonomic software is used for motion simulation, the comfort level judgment for typical firefighting motions. The paper connects the subjective perception and the objective evaluation of firefighters and implements the comfort judgment based on human factors, which play a quite significant role in modern industry [5].
2. Basic Ideas of Comprehensive Fuzzy Evaluation
2.1. Definition of Comfort Level
2.2. Determination of Membership Function
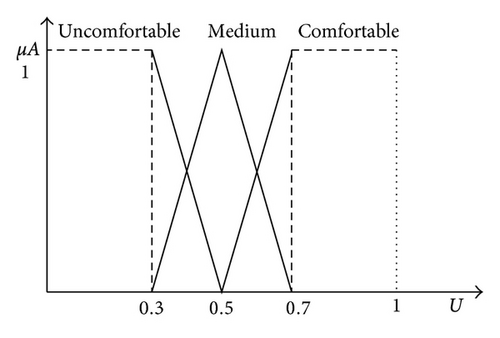
Membership function is used to describe fuzzy set. Research indicates that the energy utilization rate comes to maximum if half used [6], thus human will not feel tired even when working longer. The membership function is described in Figure 1.
2.3. Determination of Factors Set That Influences Motion Comfort
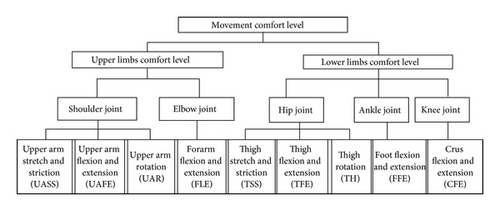
This paper mainly takes body movement into account. Human body consists of joints, which move in different degrees of freedom and combine into motions. Therefore, the judgment factors set is established based on joint movements in the comprehensive comfort evaluation for firefighters (Figure 2).
-
First-level comprehensive fuzzy evaluation method:
() -
Second-level comprehensive fuzzy evaluation method:
() -
Third-level comprehensive fuzzy evaluation method:
()
To obtain the membership of operation motion to comfort level, subjective survey is requisite to acquire weight w, and the maximum moment and actual moment of joints are needed according to the comfort level formula. Thus, the first step is to conduct weight acquisition experiment, and the second is to calculate the joint motion angle and actual moment.
3. Weight Index Acquisition
3.1. Subjective Weight Investigation Experiment
When it comes to judge how much joints influence human comfort, joint movement is usually used. The questionnaire is completed through judging the body condition after finishing some movement, taking two joints into comparison. If the body comfort level is lower, which means that this very joint plays an important role in evaluating human body condition, this joint will score high.
To guarantee the accuracy, this research will choose 0–4 scoring method and analytic hierarchy process from various weight set quantized value methods. First, conduct subjective questionnaires among 11 firefighters and use 0–4 scoring method, in which firefighters grade the factors with their subjective judgment. If they are of identical importance, they are 2 points each; if one is more important than the other, then 3 points and 1 point graded; and if one is far more important, then it is graded 4 points and the other 0. After that, analytic hierarchy process is used with the evaluation results by experts.
- (1)
The firefighters should be quite familiar with the procedure and requirement before the experiment.
- (2)
The firefighters should keep up-right and relaxed and move a single joint with other joints fixed. The duration is 3 minutes.
- (3)
Time interval is requisite between two items to prevent tiredness.
3.2. Weight Calculation
The joints are put in order by their importance after data processing. The higher it is graded, the higher it ranks and the more tired it becomes when human is in motion, which indicates its importance to human body. The sequencing results are listed in Table 1.
| N = 5 | Firefighters K = 11 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | Ri | |
| Shoulder | 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 47 |
| Elbow | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 31 |
| Hip | 4 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 45 |
| Ankle | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 16 |
| Knee | 3 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 26 |
| x, y comparison | fy(x) | fx(y) | Illustration |
|---|---|---|---|
| x and y “same importance” | 1 | 1 | x, y contribute the same to some property |
| x “bit more important” | 3 | 1/3 | x contributes a bit more |
| x “bit much more important” | 5 | 1/5 | x contributes a bit much more |
| x “much more important” | 7 | 1/7 | x contributes much ore |
| x “absolutely more important” | 9 | 1/9 | x contributes absolutely more important |
| x, y between two judgments | 2, 4, 6, 8 | 1/2, 1/4, 1/6, 1/8 | Compromise between two judgments |
The weight is obtained after unification. Similarly, the same method is used when calculating the weight of each joint, and the results are shown in Table 3.
| Weight | w1 upper limbs | w2 lower limbs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.488 | 0.512 | ||||
| w11 shoulder | w12 elbow | w21 hip | w22 ankle | w23 knee | |
| 0.284 | 0.204 | 0.2192 | 0.145 | 0.147 | |
| Stretch and striction | 0.463 | — | 0.379 | — | — |
| Flexion and extension | 0.396 | 1 | 0.423 | 1 | 1 |
| Rotation | 0.141 | — | 0.198 | — | — |
4. Firefighting Operation Motion Moment Acquisition
4.1. Method Design
Software JACK is used to acquire the actual movement moment and joint motion angle. JACK is a mature, cross-platform environment for building, running, and integrating commercial-grade multiagent systems, which is built on a sound logical foundation. In JACK, agents are defined in terms of their beliefs, their desires, and their intentions. It is a set of long-term goals as well as an ever-evolving collection of thousands of lines of code and is used for human modeling and simulation in this research.
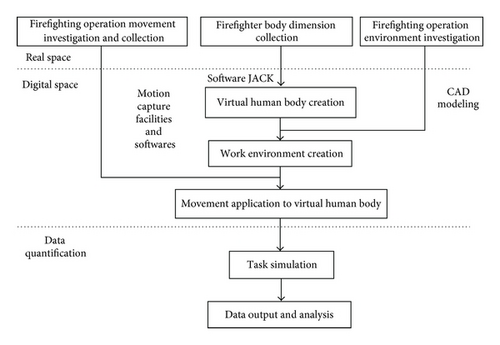
Through the angle simulation result obtained from the calculation of motion experiment by keyframe in JACK, the actual human body model moment is obtained [10]. The whole procedure is divided into three parts, data investigation of actual space, task simulation of virtual space, and quantitative output of simulation results. The implementation process is as Figure 3.
4.2. Joint Movement Angle Acquisition by Capture Experiment
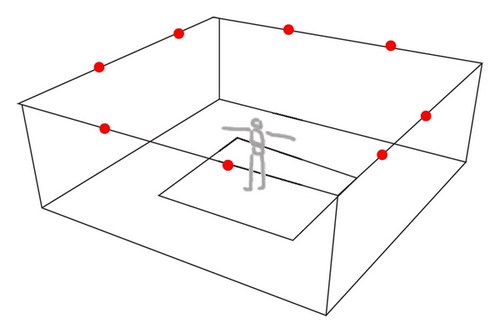
Movement capture system begins from image analysis method, which utilizes humans or other objects similar to animation model to show the movements to be analyzed in a three-dimensional space, and then the computer captures the movement data and quantitatively analyzes the motion track by dealing with the motion sequence. This laboratory is equipped with eight cameras to capture movements, and the location distribution is shown in Figure 4. To guarantee a fine reflection effect, a piece of blue cloth is laid in the center of the room.
During the process of movement capture, two firefighters of identical height are selected to conduct the experiment based on the investigation on firefighter human dimension. The information of the experimenters and the equipment is listed in Table 4.
| Experimenter | Gender | Height | Weight | Age | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Information of experimenter | Experimenter 1 | Male | 170 cm | 60 kg | 22 |
| Experimenter 2 | Male | 173 cm | 65 kg | 22 | |
| Equipment | Weight | Height (diameter) | Length | Pictures | |
| Information of experiment equipment | Water hose | 6.3 kg | 0.12 m | 20 m |  |
| Hydraulic giant | 0.42 kg | 0.10 m | 0.25 m | Water hose | |
| Ladder | 8 kg | 0.45 m | 2 m |  |
|
| Staircase | — | 0.3 m | — | Hydraulic giant | |
11 key points are marked on the body according to the establishment of firefighter mathematical model. Taking into consideration that the human body coordinate system should be established during the movement capture process and the shelter effect of movement to the markers, the markers are selected as in Figure 5.

Through previous task analysis on investigation, four typical movements are extracted among different firefighting motions. 14 training samples are covered in the four movements. The motion track coordinate is established based on motion capture, shown in Table 5.
Ladder carrying training |
Two people carry the ladder, one in the front and the other on the back. The front one lifts the ladder with hands and the back one holds it on shoulder. The ladder in heeling condition. The movements involved are legs running, arms swinging (legs 1), trunk forerake (arm 1), eye level watching (eye 4), and hands holding the ladder (hand 1). |
 |
|---|---|---|
|
One who leans on the corner holds the ladder, and the experimenter climbs it. The movements involved are lower limbs climbing, arms lifting, trunk bending, and hands holding the ladder. |  |
| Water hose training on ground | The motion is divided into throwing the second hose, holding the hydraulic giant, and running. The motions are limbs running (legs 1), arms swinging, holding and clamping (arms 1/3/4), trunk forerake (trunk 1), and hands holding the hose (hand 1) |  |
| Water hose training on high | The motion is divided into two hands alternatively stretching down the hose. The motions are holding and clamping with arms, trunk forerake and bending (trunk 1/3), and hands gripping and cambered open (hand 1/2). |  |
| Rescue | Rescue includes backing, holding, shouldering, and lifting, of which this experiment chooses backing. The motions involved are lower limbs squatting and erecting (leg 4/2), arms holding (arm 3), trunk forerake (trunk 1), and hands gripping with cambered open shape (hand 1/2). | 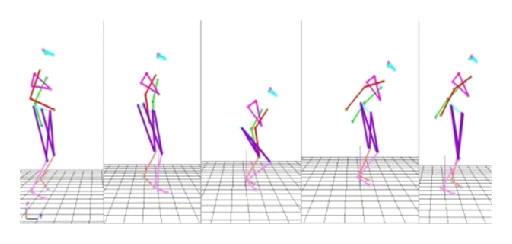 |
According to the analysis above, the coordinate of human body markers and the trajectory diagram are obtained. The calculation of motion angle is divided into two types: projection angle and absolute angle. For a joint with one degree of freedom, absolute angle is suitable; and for a joint with more degrees of freedom, projection angle is used.
The condition in which people stand with two arms up-right down is treated as the initial movement and the joints are regarded as vectors. According to the vector formula, , the movement range and angles are calculated. The joint angle takes the initial condition as benchmark, so the bending angle of single degree of freedom is 180° − θ.
Taking water hose on high, for example, the angles of joints in this kind of motion are calculated as in Figure 6. Since this kind of motion mainly relates to shoulder joint and elbow joint with separately one degree of freedom and three degrees, the calculation results are shown in Figures 7 and 8.
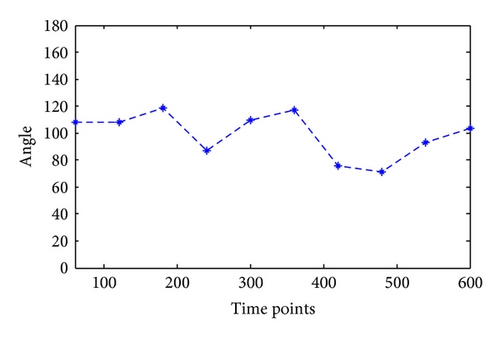
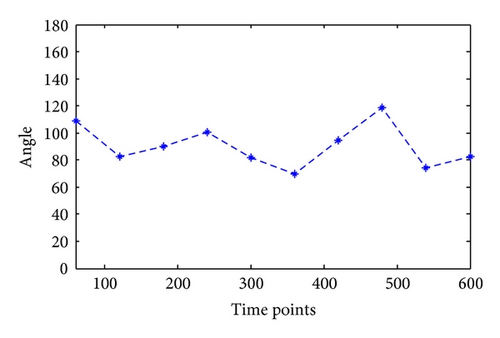
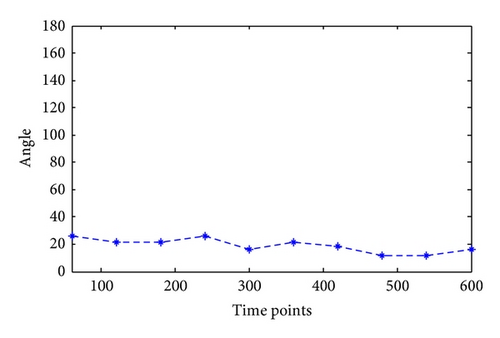
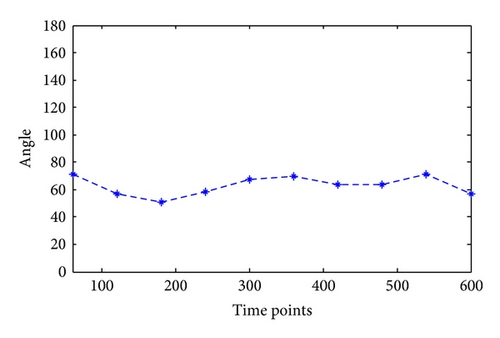

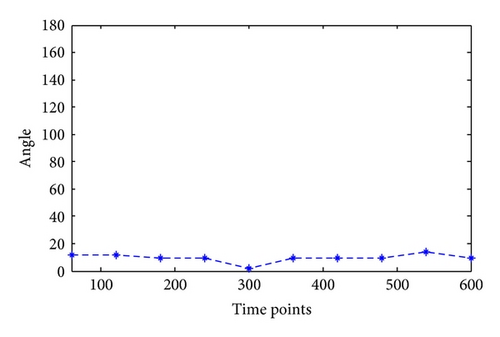
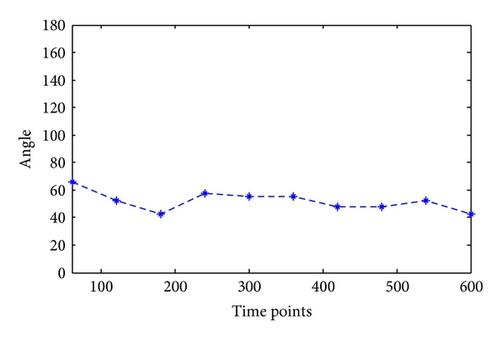
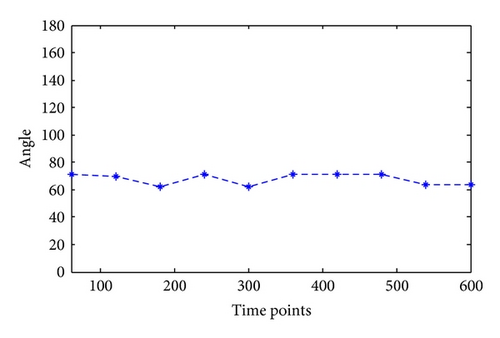
Similarly, the joint angles change in different motions can be calculated through motion trail. The angle not only provides foundation for the following motion simulation, but also the joint movement maximum moment can be calculated through NASA power model; besides, it can provide data foundation for firefighting product design, such as clothing and equipment.
4.3. Firefighter Typical Movement Simulation
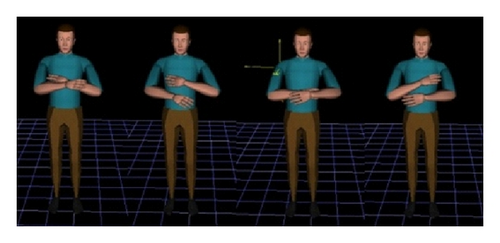
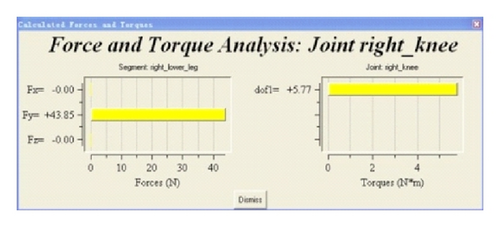
The ergonomic software JACK is used for simulation. The firefighting operation motion is simulated through key frame, which is utilized to be adjusted manually to change the motion of the virtual human. Ten key frames are chosen to simulate the joint angle, in order to acquire the moments in different time. Taking the motion of the disengaging water hose on high, for example, the motion simulation is shown in Figure 9. The joint moment output is illustrated in Table 6.
| Time | Left elbow | Right elbow | Left shoulder | Left shoulder | Left shoulder | Right shoulder | Right shoulder | Right shoulder |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | Z | Y | Y | Z | |||
| 60 | 2.48 | 2.39 | 4.76 | 13.59 | 3.11 | 5.50 | 15.62 | 5.73 |
| 120 | 4.19 | 4.14 | 4.19 | 11.66 | 6.83 | 4.92 | 15.94 | 6.46 |
| 180 | 4.19 | 4.97 | 3.63 | 10.28 | 6.95 | 4.14 | 12.58 | 8.19 |
| 240 | 3.91 | 3.45 | 5.11 | 15.96 | 7.38 | 5.24 | 15.23 | 6.35 |
| 300 | 3.73 | 4.30 | 4.58 | 12.83 | 6.03 | 4.62 | 15.13 | 10.65 |
| 360 | 3.54 | 3.89 | 4.42 | 12.63 | 4.39 | 4.69 | 17.57 | 6.49 |
| 420 | 3.73 | 4.51 | 5.04 | 17.07 | 7.82 | 4.62 | 13.80 | 6.23 |
| 480 | 4.16 | 3.84 | 4.65 | 16.35 | 9.11 | 4.21 | 11.91 | 5.59 |
| 540 | 3.77 | 4.30 | 5.06 | 14.97 | 6.74 | 4.69 | 16.65 | 7.52 |
| 600 | 4.60 | 5.01 | 3.93 | 10.95 | 7.71 | 4.09 | 13.23 | 7.82 |
5. Fuzzy Judgment Result Analysis
The comfort membership is calculated in Matlab according to fuzzy comfort evaluation method. Taking the disengaging water hose on high at one moment, for example, the first-order comprehensive fuzzy evaluation is conducted firstly. The factor set U11 = { U111, U112, U113} = {Upper arm stretch and striction, upper arm flexion and extension, upper arm rotation}, U12 = {U121} = {Front arm flexion and extension} is calculated the membership rij = (ri1, ri2, ri3) (j = 1, 2, 3) of this motion is determined, and then the evaluation matrix is obtained.
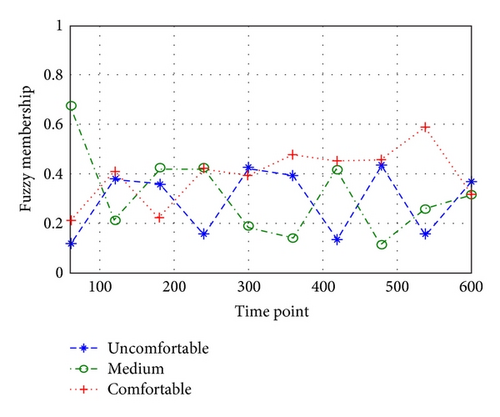
The comfort of some continuous motion is evaluated by the relationship of joint comfort change with time by Matlab. The membership of motion to comfort level is shown in Figures 10 and 11.
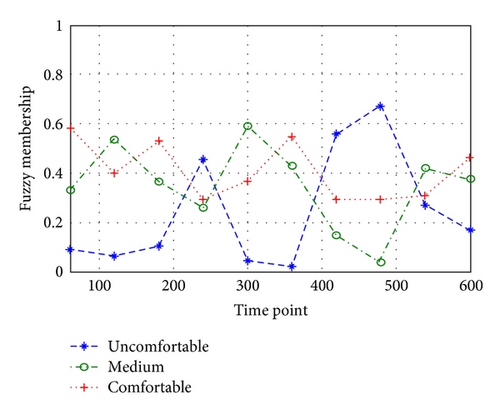
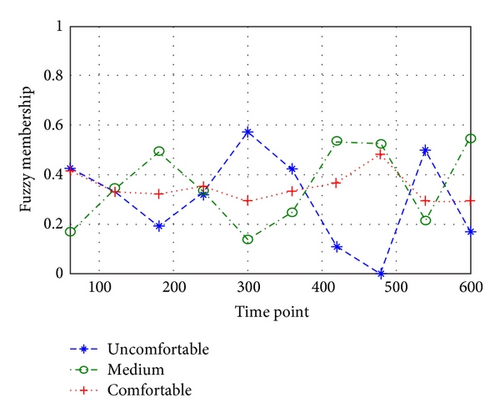
This motion involves two shoulders and two elbows and eight degrees of freedom, which forms the evaluation on upper limb movement. Through the previous weight calculation and proper unification, the comprehensive comfort level is evaluated.
From Figures 10, 11, and 12, the average of comprehensive comfort level in the latter half is higher than in the former half. Since this motion is of cyclicity, so the joint angle in the latter half fits comfort level effect better. Therefore, the latter half is always selected to conduct the experiment. According to this motion, the improvement in comfort means the improvement of work efficiency and safety. At the same time, when many experimenters take part, the best-comfortable motions will be taken as the model samples through comprehensive comfort evaluation.
6. Conclusion
- (1)
The comprehensive fuzzy evaluation model of firefighting operation motion comfort level is established, which then is applied in the comfort evaluation.
- (2)
Joint weight determination through investigation experiments.
- (3)
The joint angles in every degree of freedom of typical motions are calculated in Matlab through the firefighter motion trails acquired by the motion capture equipment, which provide foundation to design firefighting equipment and clothing.
- (4)
The joint motion moment is acquired through motion simulation of disengaging water hose in JACK, and then the comprehensive fuzzy evaluation of comfort is conducted. The membership of joints to comfort level is obtained too.
This paper used the method of objective skeleton motion ergonomic evaluation, thus the results are objective and reliable. The research ideas will be applied in the future work to complete the database of motion evaluation, and the evaluation results will be dealt with statistically to build standard evaluation system.




