Two Portuguese Cochlear Implanted Dizygotic Twins: A Case Report
Abstract
Individual’s hearing performance after cochlear implant (CI) is variable and depends on different factors such as etiology of deafness, age at implantation, and social/family hearing environment. Here we report the case of dizygotic twins, boy and girl, presenting with neurosensorial profound deafness prior CI (age of implantation = 3.5 years old). Both parents have severe/profound deafness, since childhood, and use sign language as primary mode of communication. Clinical and genetic characterization was performed, as well as the assessment of the auditory and oral (re)habilitation after CI, applying a battery of audiological, speech, and language tests. The twin girl and the father were homozygous for the c.35delG mutation in the GJB2 gene, while the twin boy and the mother were compound heterozygotes, both monoallelic for c.35delG and for the deletion del(GJB6-D13S1830) in the GJB6 gene. The remaining hearing impaired relatives were c.35delG homozygotes. The genetic cause of deafness was thus identified in this family. Some noteworthy differences were observed regarding twins’ auditory and oral performance after CI. Subsequent follow-up of these children allowed us to conclude that those differences were most likely due to the different environment in which the twins have been living than to their different GJB2/GJB6 genotypes.
1. Introduction
After cochlear implantation (CI) the individual’s hearing performance will vary according to their age at implantation [1], duration of implant use [2], level of residual hearing and mode of communication [3]. However, it has been documented that the contribution of these factors to speech perception after CI explains less than 50% of the variability observed [4], the remaining being related to other factors. One of these factors is thought to be the etiology of deafness [2, 5, 6], namely, connexin-associated deafness [7].
DFNB1 locus was the first nonsyndromic autosomal recessive deafness-related locus to be identified and is located on chromosome 13q11 [8]. It includes GJB2 and GJB6 genes, enconding the gap junction beta-2 protein (connexin 26) and the gap junction beta-6 protein (conexin 30), respectively. Mutations in the GJB2 gene are the most frequent in nonsyndromic recessive deafness, accounting for up to 50% of the cases [9]. The c.35delG mutation, a deletion of a guanine in the GJB2 coding sequence, is the most common recessive deafness-causing mutation in Europe. Two large deletions, del(GJB6-D13S1830) and del(GJB6-D13S1854), identified in the GJB6 gene, are often found in double heterozygosity with mutations in GJB2, which is thought to result in loss of function of the connexin cluster [10]. Most of these genotypes originate severe to profound congenital deafness, which are the cases recommended for cochlear implantation.
This study aimed at performing clinical and genetic characterization, as well as evaluating the oral (re)habilitation, of two nonidentical twins with cochlear implant.
2. Patient Presentation
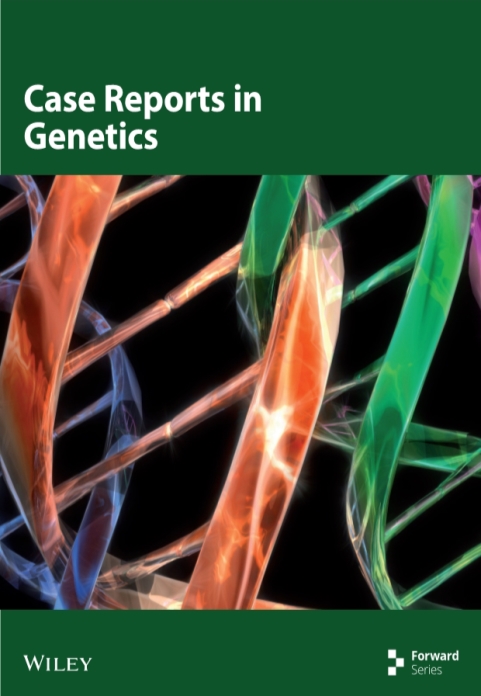
We report the case of dizygotic twins (a boy and a girl), aged 8 years, both with cochlear implants (CI). Both twins (Figure 1: ICC88, III : 7 and ICC89, III : 6) presented with neurosensorial profound hearing loss prior to implantation. Their parents (Figure 1: ICC88A, II : 9 and ICC88B, II : 8) are also severely to profoundly hearing impaired since childhood, use sign language as primary mode of communication, and have one unaffected daughter each, from a prior marriage, as well as several affected and unaffected relatives.
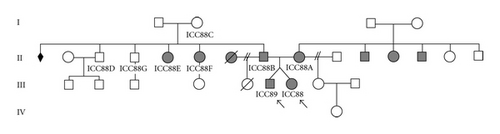
Table 1 presents the clinical history of the twins. It can be observed that both of them were diagnosed, started using hearing aids, and received their cochlear implant at the same time. Likewise, they use the same CI model with the same characteristics.
| ICC088 (III : 7) | ICC089 (III : 6) | |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female | Male |
| Deafness etiology | Congenital | Congenital |
| Suspicion of deafness | 18 months | 18 months |
| Diagnosis | 24 months | 24 months |
| Clinical history |
|
|
| Audiogram | Neurosensorial bilateral profound deafness, stage 3 | Neurosensorial bilateral profound deafness, stage 3 |
| Placement of hearing aids | 24 months | 24 months |
| Gain with hearing aids |
|
|
| Auditory evoked potentials (AEP) | Wave V present above 90 dB nHL on the right and above 100 dB nHL on the left | Absence of AEPs until 110 dB nHL bilaterally |
| Computerized axial tomography scan (CAT scan) |
|
|
| Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) |
|
|
| Age at implantation | 42 months | 42 months |
| Duration of CI use | 56 months | 56 months |
| Age at audiological tests and present study | 8 years | 8 years |
| CI model | CI24R CA Advance | CI24R CA Advance |
| Speech processor | SPRINT | SPRINT |
| Stimulation mode | MP1+2 | MP1+2 |
| Stimulation strategy | ACE | ACE |
| Implanted ear | Right | Right |
Written informed consent was obtained from all individuals and the study was approved by the Ethical Commission of the Hospital.
DNA from the two twins and from affected and unaffected relatives was analysed, by sequencing and multiplex PCR, in respect to the presence of GJB2 coding mutations and GJB6 deletions (del(GJB6-D13S1830) and del(GJB6-D13S1854)). Molecular analysis revealed that the twins present different genotypes: the girl (ICC088, III : 7) is homozygous for the c.35delG autosomal recessive mutation in GJB2 while the boy (ICC089, III : 6) is a compound heterozygote for the c.35delG mutation and the GJB6 large deletion del(GJB6-D13S1830) (Figure 2). Both genotypes are associated with severe congenital deafness phenotype. This genetic evaluation was included in a broader study involving DFNB1 genotype-phenotype correlation in Portuguese CI individuals [7], being the first time that del(GJB6-D13S1830) deletion was found in Portuguese deaf patients.

The different genotypes of the twins justified the genetic analysis of some of the twins’ relatives (Figure 2). The father (ICC088B, II : 8) is a c.35delG homozygote, as the twin girl, and the mother (ICC088A, II : 9) is a c.35delG/del(GJB6-D13S1830) compound heterozygote like the twin boy. Accordingly, the affected relatives from the father’s side (ICC088E, II : 5 and ICC088F, III : 6) are c.35delG homozygotes and the unaffected relatives either present one (ICC088C, I : 2 and ICC088D, II : 3) or none (ICC088G, II : 4) c.35delG alleles. None of them presented the GJB6 deletion. On the mother’s side no relative has been studied.
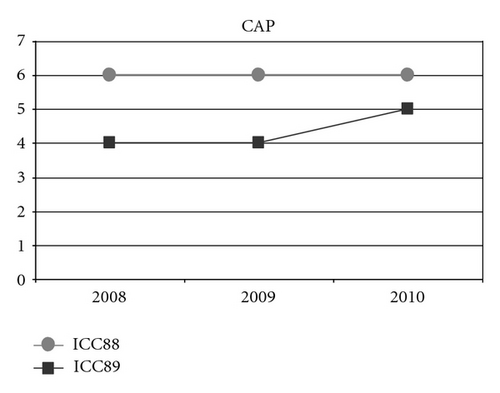
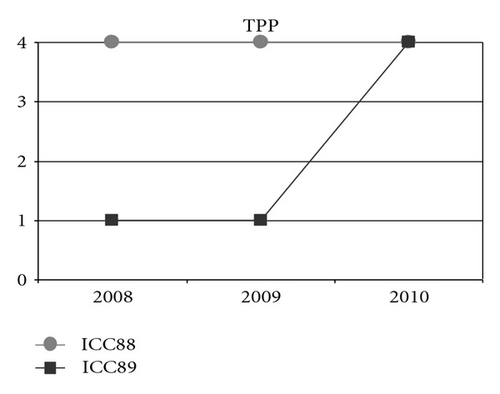
Assessment of the twins’ global auditory and oral performance after cochlear implantation was carried out by applying a battery of audiological, speech, and language tests at the ENT Department from the Centro Hospitalar de Coimbra such as disyllabic words test discrimination score, monosyllable test, monosyllable phoneme test, number test, number phoneme test, sentences test, categories auditory performance (CAP), closed-set word perception test (with real objects, images, or written words), verbal articulation test (evaluates 19 consonants and 3 consonant groups, calculated as percentage of phonemes correctly produced), percentage of accurate vowels, vocal characteristics test (voice intensity, pitch, nasal resonance, intonation and breathing, phonation and articulation coordination), and speech intelligibility rating (SIR).
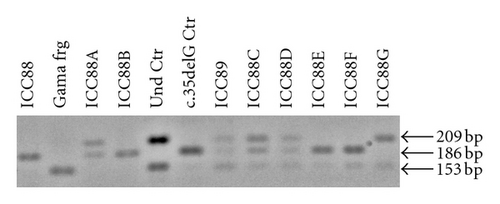
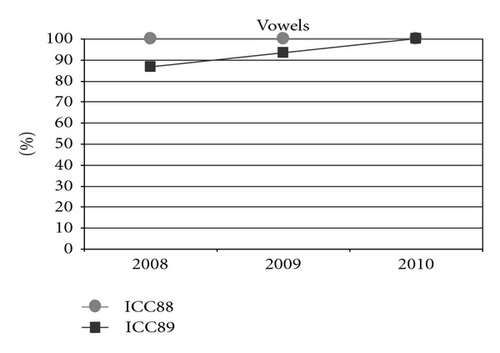
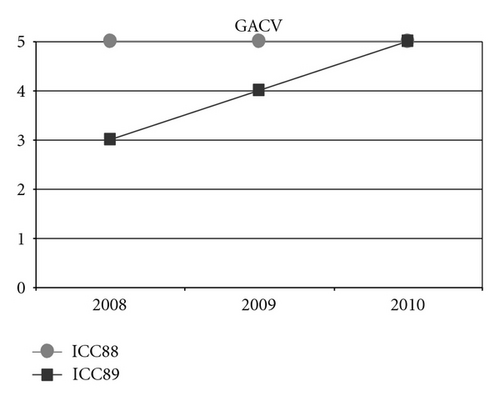
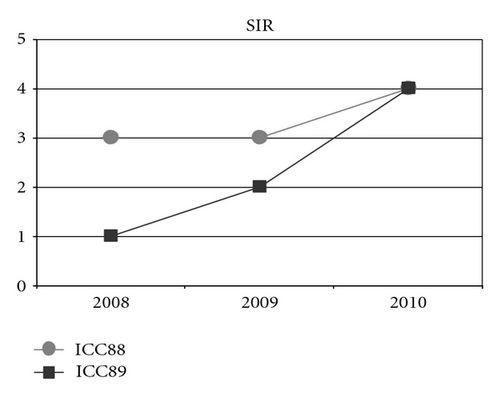
When observing the twins’ audiograms at 3.5 years old, just after CI, (Figure 3), the pure tone thresholds for most frequencies were very similar. Thus, it would be reasonable to assume their auditory and oral performance scores would also be similar. However the speech perception tests performed after 5 years of CI use (Figure 4), show that the twin girl (ICC88, III : 7) had an overall good performance throughout the tests while the twin boy (ICC89, III : 6) got poorer results, had difficulties regarding some of the age appropriate tests that are part of the standard evaluation, and was not even able to respond to some of the tests.
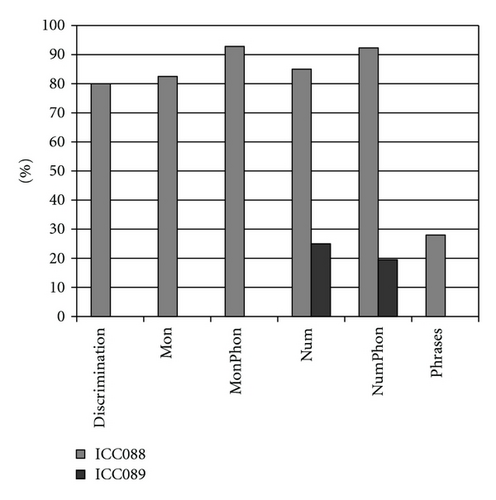
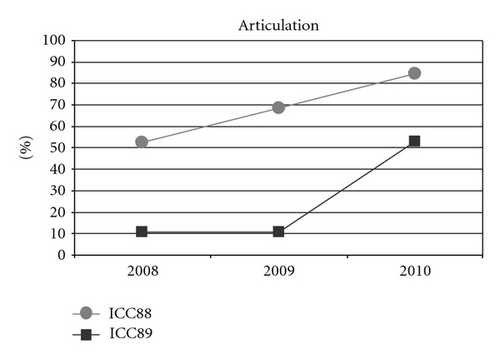
Could the differences in auditory and oral outcomes on post-CI rehabilitation be related to the different DFNB1 genotypes? Further analysis of the family history showed that other factors could be playing an important role and contributing for the differences observed. The twins had not lived together in the same hearing environment as previously assumed. On the contrary, each of them came from a different social background. The twin girl has lived since she was 6 months-old with their hearing aunt, and uncle (II : 1 and II : 2) and has been educated in a regular school with special education and speech therapy while the twin boy lived until 7 years-old with the hearing impaired parents, who only used sign language as mode of communication, thus in a poor auditory stimulating environment, only having contact with other deaf children, and with some household problems. In 2009, through legal decision, he moved in with his sister, aunt and uncle (II : 1 and II : 2) and integrated regular school with special education and speech therapy. The audiological tests from the last three years revealed the twin boy’s favourable evolution since this social alteration (Figure 5). The positive effect of the auditory and oral stimulation observed in the twin since he moved to his aunt highlights the importance of the auditory stimulating environment in the success of the post-CI rehabilitation.
3. Conclusion
The nonidentical twins here analysed, aged 8 years-old presented different genotypes, c.[35delG]+[35delG] and [c.35delG]+[del(GJB6-D13S1830)], and different speech perception results after CI. The twin boy presented weaker verbal outcomes and worse level of residual hearing before he was implanted (absence of AEP’s). However, both twins’ audiograms were very alike after CI, revealing that their hearing thresholds, unlike their auditory and oral performance, were similar.
As such, the observed differences in the oral performance are most likely due to the different social context in which the twins have been living and not to their different GJB2/GJB6 genotype. The oral outcome of the twin boy improved from the moment he started living in a hearing stimulating environment, which is a strong evidence of this factor’s importance in the success of the oral rehabilitation after CI, namely, in DFNB1-associated hearing loss cases.
The remaining twins’ affected relatives studied carried the c.35delG mutation in homozigosity. Molecular diagnosis and genetic counselling is thus very important to a family such as this one, namely, to the twins’ unaffected half-sister still alive.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the family for their contribution to the investigation. The present study was financially supported by Cochlear.