The Role of Genetic Variation Near Interferon-kappa in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a systemic autoimmune disease characterized by increased type I interferons (IFNs) and multiorgan inflammation frequently targeting the skin. IFN-kappa is a type I IFN expressed in skin. A pooled genome-wide scan implicated the IFNK locus in SLE susceptibility. We studied IFNK single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in 3982 SLE cases and 4275 controls, composed of European (EA), African-American (AA), and Asian ancestry. rs12553951C was associated with SLE in EA males (odds ratio = 1.93, P = 2.5 × 10−4), but not females. Suggestive associations with skin phenotypes in EA and AA females were found, and these were also sex-specific. IFNK SNPs were associated with increased serum type I IFN in EA and AA SLE patients. Our data suggest a sex-dependent association between IFNK SNPs and SLE and skin phenotypes. The serum IFN association suggests that IFNK variants could influence type I IFN producing plasmacytoid dendritic cells in affected skin.
1. Introduction
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE, OMIM 152700) is an autoimmune disease characterized by production of large quantities of antibodies directed against ubiquitous self-antigens, particularly double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) and small nuclear RNA-binding proteins such as Ro, La, Sm, and nRNP. SLE is characterized by a striking 9 : 1 female to male differential in incidence [1], which remains largely unexplained. Clinically, cutaneous manifestations play a prominent role in SLE. The skin manifestations which include discoid, malar, and photosensitive rashes, are common and comprise 3 of the 11 American College of Rheumatology (ACR) SLE classification criteria [2, 3]. Cutaneous manifestations of SLE commonly precede diagnosis, are among the initial manifestations of SLE in many, and ultimately affect the majority of patients [4–6].
Many recent studies have highlighted the role of the type I interferon (IFN) pathway in SLE pathogenesis and susceptibility [7, 8]. Indeed, serum IFN-alpha (IFN-α) activity was shown to be a heritable risk factor for SLE [9], and many genetic variants associated with SLE susceptibility are associated with increased serum IFN-α activity in lupus patients [10–13]. Additionally, age-related patterns of serum IFN-α activity are present in both lupus patients and their healthy family members which mirror peak SLE incidence rates, with an earlier age of peak serum IFN-α in female patients as compared to male patients [14]. Current models of human SLE pathogenesis place plasmacytoid dendritic cells in a central role, promoting type I IFN production, which leads to the eventual loss of self-tolerance [reviewed in [15]]. Increased production of type I IFN in SLE skin lesions has been observed, and plasmacytoid dendritic cells accumulate in cutaneous lupus lesions [16].
We performed a genome-wide study of 116,204 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in African-Americans using a DNA pooling approach with the goal of identifying general SLE susceptibility genes. Comparing 233 African American SLE cases to 185 African American controls, we found that the rs1031154 SNP 25,000 bp upstream of the promoter for IFNK was associated with SLE (P < .000007; rank number 51 of 116,204 SNPs, Table 1). We did not observe any additional associations in the type I IFN locus or in the type III IFN locus.
| Rank | RS ID | Position | SLE | Control | P-Value (Z2) | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10579 | rs2069031 | 27417257 | 0.24 | 0.18 | .084533 | MOBKL2B |
| 25111 | rs763372 | 27418665 | 0.37 | 0.33 | .233357 | MOBKL2B |
| 30738 | rs1058326 | 27437089 | 0.64 | 0.67 | .295482 | MOBKL2B |
| 96108 | rs10511817 | 27444173 | 0.74 | 0.74 | .991276 | MOBKL2B |
| 58144 | rs1822724 | 27446580 | 0.18 | 0.20 | .587242 | MOBKL2B |
| 86908 | rs10511816 | 27458461 | 0.12 | 0.13 | .892110 | MOBKL2B |
| 29622 | rs7866248 | 27464593 | 0.66 | 0.62 | .282786 | MOBKL2B |
| 51 | rs1031154 | 27488800 | 0.58 | 0.74 | .000007 | MOBKL2B |
| 83966 | rs2783009 | 27504584 | 0.27 | 0.27 | .860562 | MOBKL2B |
| 30667 | rs774354 | 27505967 | 0.66 | 0.62 | .294678 | MOBKL2B |
| 44987 | rs774353 | 27506436 | 0.33 | 0.35 | .445904 | MOBKL2B |
| 51264 | rs10511815 | 27508821 | 0.10 | 0.08 | .513456 | MOBKL2B |
| 3058 | rs700795 | 27510508 | 0.21 | 0.29 | .016545 | MOBKL2B |
| 3280 | rs3849944 | 27550594 | 0.45 | 0.37 | .018332 | C9orf72 |
| 13896 | rs7864840 | 27573468 | 0.21 | 0.17 | .117979 | |
| 96358 | rs590299 | 27591570 | 0.28 | 0.28 | .993607 | |
| 85694 | rs634157 | 27598585 | 0.80 | 0.80 | .878910 |
- Rank: rank order of association in the study, as determined by P-value, position is listed in base pairs on chromosome 9. “SLE” and “Control” indicate the calculated allele frequencies in SLE patients and controls, respectively.
The IFNK gene encodes the precursor for IFN-κ, a recently discovered subclass of type I IFN [17]. IFN-κ is a member of the type I IFN family, which in humans consists of IFN-α, IFN-β, IFN-ε, IFN-ω, and IFN-κ [18]. This family likely arose from gene duplication and differentiation in mammals, and phylogenetically IFN-κ was the first to diverge, exhibiting 30% homology with other type I IFNs [17, 18]. IFN-κ is a multifunctional type I IFN which induces autoimmunity when transgenically expressed in the β cells of the pancreatic islets in mice [19]. IFN-κ is induced following viral infection or treatment of cells with double-stranded RNA [dsRNA] [17], and IFN-κ signaling induces a set of genes (IRF1, STAT1, MXA, PKR, OAS1) common to signaling via the type I interferon receptor [17], and modulates the release of cytokines from monocytes [20]. Unlike other members of the type I IFN family, IFN-κ is constitutively and highly expressed in keratinocytes [17].
Taken together, these data suggested inter-related hypotheses of this study, that: [1] variation at the IFNK locus confers susceptibility to SLE in humans, [2] the same variation could modulate type I IFN levels in patients, and [3] variations affecting the expression of IFN-κ in the skin could alter the response to self-antigens in SLE skin and predispose to cutaneous manifestations of SLE. Based on this evidence and the clear biological plausibility of variation near the promoter of a type I IFN gene as a risk factor for SLE, we considered IFNK a possible candidate gene.
2. Methods
2.1. Genome-Wide Association Scan DNA Pooling Study
Genomic DNA samples for 233 African-American (AA) SLE patients and 185 AA controls were combined in pools stratified first by case/control status and second by the presence or absence of precipitating levels of autoantibodies against Sm or nuclear riboncleoprotein (nRNP) complex autoantigens. Equimolar amounts of DNA (as determined by Nanodrop ND-1000 spectrophotometer [Nanodrop Wilmington, DE]) for each individual in a given pool were combined, which thereafter was treated as a single sample until data analysis. Each pooled sample was evaluated for case versus control signal intensity differences for the SNPs included on the Affymetrix 100 K Gene Chip Mapping Set arrays [Affymetrix Santa Clara, CA] according to manufacturer instructions. SNP allele frequency estimates for each pool were calculated using correction factors, as described in [21], and the significance of the difference between the average allele frequencies between cases and controls was assessed by performing an χ2 test with one degree of freedom on the z2 statistic as described [22]. All subjects in this genome-wide study as well as those in the subsequent portions of the study provided informed consent under the protocols approved by the institutional review board at the respective institution.
2.2. Individual Genotyping and Population Definition in LLAS1
Altogether 21 SNPs in the IFNK region on chromosome 9 between rs10812605 and rs3739526 were selected for followup in this study. We did not include the exact SNPs studied in the initial GWAS screening study described above but instead studied SNPs which correlated with many other SNPs in the locus, and therefore tagging a large proportion of the genetic variation within and near IFNK. The rs1838430 SNP was highly correlated with the rs1031154 SNP which showed the strongest association in the GWAS study (r-squared = 1.0 in EA, 0.59 in AA, and 0.66 in Asian subjects according to the HapMap database). We studied these 21 tagging SNPs in 12,043 DNA samples using custom-designed Illumina bead arrays as part of a larger candidate gene study (Large Lupus Association Study 1 or LLAS1), which tested 19,354 SNPs for association with SLE susceptibility. The quality control for this experiment is described elsewhere in [23]. One SNP assay did not perform well enough for the SNP to be called, and this SNP was not included in the study. Two SNPs could not be automatically called by the Illumina software, but genotype calls could be made clearly by manually reviewing the genotype scatter plots (rs13691 and rs13290599). The remaining SNPs were automatically called by Illumina BeadStudio software [Illumina, Inc. San Diego, CA] and manual inspection confirmed clearly differentiated genotype clusters. The overall call rate for automatically called SNPs was 99.7%, and a single SNP, rs4609281, had a call rate of 98%. Principal component analysis was used to detect population substructure using all successfully called nonrelated samples and SNPs from the larger study, and population outliers were excluded from further analysis as detailed in [23]. This resulted in 242 European ancestry (EA) male cases and 931 controls, 2268 female EA cases and 2036 controls, 629 female African-American (AA) cases and 531 controls, 54 male AA cases and 252 controls, and 843 female Asian cases and 777 Asian controls. Only 69 male Asian cases and 90 male Asian controls were available, which would not provide adequate power to detect even very large genetic effects, and these subjects were not analyzed as a subgroup. All SLE patients met the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria for the diagnosis of SLE [2, 3]. The clinical and serologic information for the SLE cases in each ancestral background is shown in Table 2.
| African-American | European | Asian | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Total | No | Yes | Total | No | Yes | Total | |
| Renal | 0.53 | 0.47 | 507 | 0.72 | 0.28 | 1069 | 0.54 | 0.46 | 674 |
| Malar rash | 0.63 | 0.37 | 508 | 0.44 | 0.56 | 1068 | 0.56 | 0.44 | 674 |
| Discoid rash | 0.76 | 0.24 | 508 | 0.89 | 0.11 | 1069 | 0.92 | 0.08 | 674 |
| Photosensitivity | 0.63 | 0.37 | 507 | 0.34 | 0.66 | 1069 | 0.66 | 0.34 | 674 |
| Arthritis | 0.24 | 0.76 | 508 | 0.18 | 0.82 | 1069 | 0.38 | 0.62 | 674 |
| Oral ulcers | 0.76 | 0.24 | 508 | 0.53 | 0.47 | 1069 | 0.62 | 0.38 | 674 |
| Serositis | 0.48 | 0.52 | 448 | 0.57 | 0.43 | 1025 | 0.72 | 0.28 | 673 |
| Neurologic | 0.87 | 0.13 | 508 | 0.89 | 0.11 | 1069 | 0.93 | 0.07 | 674 |
| Hematologic | 0.28 | 0.72 | 508 | 0.39 | 0.61 | 778 | 0.15 | 0.85 | 674 |
| Immunologic | 0.13 | 0.87 | 505 | 0.26 | 0.74 | 1064 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 674 |
| ANA | 0.01 | 0.99 | 508 | 0.03 | 0.97 | 1069 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 674 |
| Anti-Ro | 0.71 | 0.29 | 475 | 0.80 | 0.20 | 655 | 0.66 | 0.34 | 659 |
| Anti-La | 0.91 | 0.09 | 475 | 0.92 | 0.08 | 661 | 0.92 | 0.08 | 659 |
| Anti-Sm | 0.84 | 0.16 | 384 | 0.98 | 0.02 | 586 | 0.90 | 0.10 | 40 |
| Anti-nRNP | 0.62 | 0.38 | 384 | 0.92 | 0.08 | 586 | 0.65 | 0.35 | 40 |
| Anti-Ribosomal P | 0.98 | 0.02 | 384 | 0.99 | 0.01 | 586 | 0.95 | 0.05 | 40 |
- “No” indicates the proportion of subjects lacking the clinical feature, and “Yes” is the proportion of subjects in whom that feature is present. Total indicates the total number of subjects for whom data is available. The first 11 rows are parameters assessed according to the American College of Rheumatology criteria for SLE [2], while the five rows which begin with “Anti-” indicate particular SLE-associated autoantibody specificities. ANA: anti-nuclear antibody.
2.3. Data Analysis
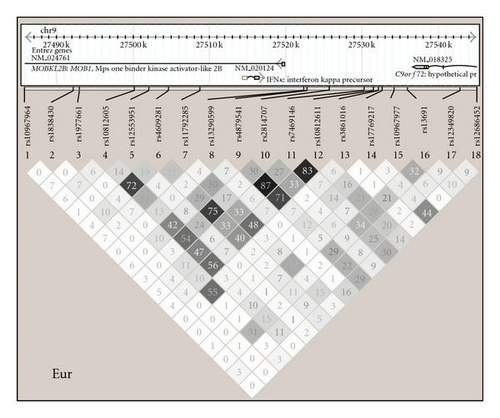
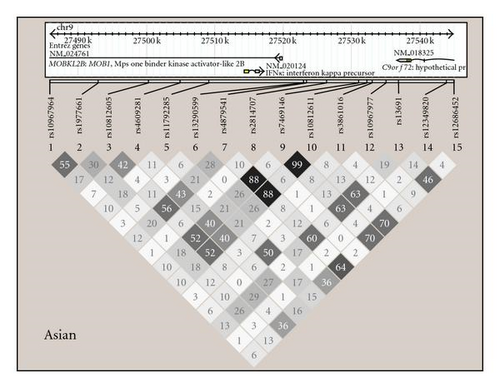
Linkage disequilibrium (LD) analysis was performed using Haploview 4.1 [24] (http://www.broad.mit.edu/mpg/haploview), and diagrams showing haplotype structures in each ancestral background studied are shown in Figure 1. Minor allele frequency <0.05 was used as a cutoff in each population as well as P-value for departure from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium <.001 [23]. Association analysis was performed using the additive genetic model as the primary inference using PLINK v1.07 [25] (http://pngu.mgh.harvard.edu/~purcell/plink/) in each ancestral background and sex category separately. Association analyses were performed as logistic regressions using either SLE affected versus unaffected or SLE subphenotypes as outcome variables and the IFNK SNPs as predictor variables. The first four principal components which were informative for ancestry as described above [23] were incorporated as covariates in all association and subphenotype analyses to control for potential confounding related to population structure. SLE subphenotypes analyzed include the presence or absence of ACR clinical criteria for skin (discoid rash, malar rash, or photosensitivity), high versus low serum type I IFN activity defined as 2SD above healthy donors, as well as presence or absence of positive autoantibody response as determined by positive reactivities against dsDNA or select lupus-associated extractable nuclear antigens. P-values shown are not corrected for multiple comparisons. SNPs were screened for potential influence on serum IFN by logistic regression as above, and then quantitative serum IFN levels were plotted with respect to the SNPs which showed evidence for association in EA and AA, respectively. Two column nonparametric t-tests were performed comparing serum IFN levels in major allele homozygotes versus heterozygotes and minor allele homozygotes combined in each sex in both ancestral backgrounds.

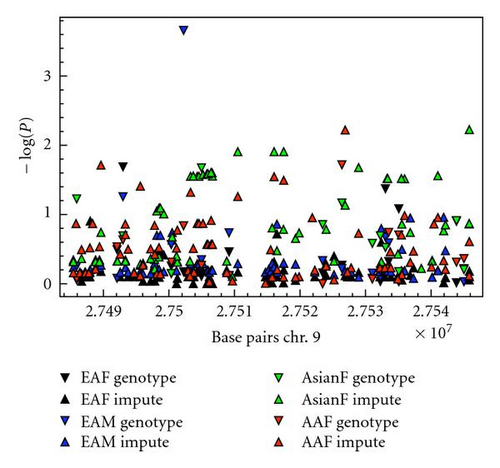
Imputation analysis was performed using the GWAS software suite (gtool, impute, and snptest, http://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/%7Emarchini/software/gwas/gwas.html). Untyped markers for EA and AA samples were imputed using HapMap release number 22 CEU and YRI files, respectively, and Asian samples were imputed using HapMap release number 21 JPT+CHB combined files, all obtained from the above website. SNPs were imputed for the interval between 27485000 bp and 27546000 bp on chromosome 9. Default values for confidence score, buffer size, and suggested values for founder population size were used. Association analysis was performed as above, except that the principal components of ancestry were not included as covariates in the imputed analysis.
2.4. Measurement of Type I IFN in Serum and Analysis of IFN Data
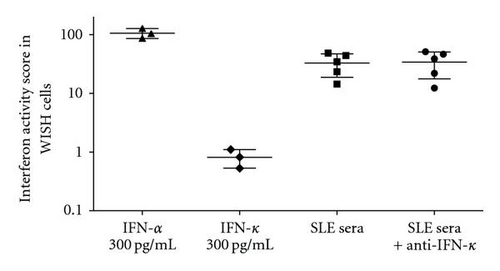
Serum type I IFN activity data were available for 230 EA and 158 AA SLE patients in this study. The reporter cell assay for type I IFN has been described in detail elsewhere in [9, 26]. Reporter cells were used to measure the ability of patient sera to cause IFN-induced gene expression. The reporter cells (WISH cells, ATCC number CCL-25) were cultured with 50% patient sera for 6 hours and then lysed. mRNA was purified from cell lysates, and cDNA was made from total cellular mRNA. cDNA was then quantified using real-time PCR using an Applied Biosystems 7900HT PCR machine with the SYBR Green fluorophore system. Forward and reverse primers for the genes MX1, PKR, and IFIT1, which are known to be highly and specifically induced by IFN-α, were used in the reaction [9]. GAPDH was amplified in the same samples to control for background gene expression. The amount of PCR product of the IFN-induced gene was normalized to the amount of product for the housekeeping gene GAPDH in the same sample. The relative expression of each of the three tested IFN-induced genes was calculated as a fold increase compared to its expression in WISH cells cultured with media alone. Results from the IFN assay were standardized to a healthy multiancestral reference population as previously described, and a serum IFN activity score was calculated based upon the mean and SD of the reference population [9]. This assay could theoretically measure all type I IFNs present in the sample being studied. In SLE sera, type I IFN activity is generally completely blocked by the addition of anti-IFN-α antibodies [9, 26]. Thus, the activity observed in the assay is frequently referred to as serum IFN-α activity. With regard to potential cross-reactivity with the type III IFNs, preincubation of SLE sera with anti-IFN λ1 antibodies did not diminish the capacity of those sera to cause IFN-induced gene expression in the reporter assay [26]. Given that IFN-κ is a type I IFN, we clarified the issue of whether our reporter assay was detecting circulating IFN-κ in lupus sera. Similar to published reports [17], we find that recombinant IFN-κ is capable of inducing some type I IFN-induced gene expression in our reporter assay although this is much less than that induced by the same amount of IFN-α (Figure 2). When lupus sera with high type I IFN activity are preincubated with anti-IFN-κ antibody, there is no decrease in the observed type I IFN activity, supporting the idea that IFN-κ does not contribute to circulating type I IFN activity in SLE sera (Figure 2).
3. Results
3.1. rs12553951 C Is Associated with SLE in European Ancestry Males
When each ancestral background was analyzed separately in case-control analysis, there were no strong associations observed (Table 3). Given the precedent for sex differences in the association of type I IFN-pathway genes [13, 27], we also analyzed females and males separately in each background (Table 4). Surprisingly, there was evidence for association between the rs12553951 C allele and SLE in EA males [odds ratio (OR) = 1.93, 95% confidence interval (95% CI) = 1.36–2.74, P = 2.5 × 10−4], but no similar association in EA females. This association would withstand statistical correction for multiple hypothesis testing, such as a Bonferroni correction for the number of SNPs tested within the IFNK locus in this study (P-values < 2.6 × 10−2 would remain significant after this correction). This correction for multiple hypothesis testing is likely too conservative, as independence between the individual measurements is an assumption of this correction, and in fact many of the SNPs tested in this study showed some degree of correlation with other SNPs, as shown in Figure 1. The low number of male subjects tested relates to the low incidence of SLE in males and reduces our confidence to some degree that this will prove to be a robust association to independent replication. However, the observed OR of >1.9 is large for human complex diseases, and genotyping of an independent cohort in an effort to definitively confirm this association would be warranted. No significant effect was observed upon the case-control associations when age was used as a covariate or when analyzing cases separated into age strata as described in the study of the IFN pathway gene SPP1 in [13]. We also imputed SNPs using the IMPUTE program in the Genome-Wide Association Study Software suite by Marchini et al. Using this algorithm we did not observe any additional significant associations with the imputed SNPs which would exceed a Bonferroni correction for the number of SNPs genotyped in the study (Figure 3).
| SNP | MA | European | African-Americans | Asians | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Cont | OR | P | Case | Cont | OR | P | Case | Cont | OR | P | ||
| rs10967964 | A | 0.112 | 0.111 | 1.01 | .88 | 0.022 | 0.025 | 0.85 | .52 | 0.201 | 0.219 | 0.95 | .50 |
| rs1838430 | C | 0.037 | 0.042 | 0.87 | .16 | 0.319 | 0.299 | 1.09 | .27 | — | — | — | — |
| rs1977661 | A | 0.099 | 0.114 | 0.85 | .010 | 0.136 | 0.124 | 1.13 | .29 | 0.307 | 0.318 | 0.99 | .88 |
| rs10812605 | G | 0.352 | 0.351 | 1.00 | .93 | 0.411 | 0.393 | 1.08 | .32 | 0.395 | 0.402 | 0.95 | .50 |
| rs12553951 | C | 0.077 | 0.068 | 1.15 | .06 | 0.016 | 0.009 | 1.79 | .09 | — | — | — | — |
| rs4609281 | C | 0.277 | 0.282 | 0.98 | .57 | 0.483 | 0.462 | 1.09 | .25 | 0.237 | 0.200 | 1.17 | .06 |
| rs11792285 | A | 0.376 | 0.365 | 1.05 | .24 | 0.098 | 0.100 | 0.98 | .89 | 0.287 | 0.295 | 0.98 | .76 |
| rs13290599 | A | 0.069 | 0.066 | 1.05 | .54 | 0.056 | 0.056 | 1.01 | .93 | 0.118 | 0.138 | 0.85 | .10 |
| rs4879541 | A | 0.488 | 0.486 | 1.01 | .87 | 0.165 | 0.166 | 1.01 | .94 | 0.354 | 0.331 | 1.05 | .50 |
| rs2814707 | A | 0.237 | 0.232 | 1.03 | .54 | 0.196 | 0.233 | 0.80 | .014 | 0.059 | 0.043 | 1.27 | .13 |
| rs7469146 | A | 0.490 | 0.488 | 1.01 | .83 | 0.120 | 0.126 | 0.96 | .71 | 0.357 | 0.339 | 1.03 | .73 |
| rs10812611 | G | 0.466 | 0.466 | 1.00 | .97 | 0.127 | 0.134 | 0.95 | .64 | 0.357 | 0.337 | 1.03 | .65 |
| rs3861016 | C | 0.066 | 0.076 | 0.85 | .038 | — | — | — | — | 0.156 | 0.147 | 1.09 | .39 |
| rs17769217 | C | 0.127 | 0.128 | 0.99 | .93 | 0.041 | 0.031 | 1.32 | .18 | — | — | — | — |
| rs10967977 | G | 0.201 | 0.190 | 1.07 | .15 | 0.028 | 0.037 | 0.77 | .22 | 0.193 | 0.202 | 0.97 | .76 |
| rs13691 | A | 0.268 | 0.258 | 1.05 | .27 | 0.079 | 0.080 | 1.02 | .89 | 0.445 | 0.435 | 1.00 | .98 |
| rs12349820 | G | 0.236 | 0.232 | 1.02 | .64 | 0.137 | 0.147 | 0.91 | .40 | 0.109 | 0.096 | 1.09 | .44 |
| rs12686452 | G | 0.243 | 0.246 | 0.98 | .61 | 0.138 | 0.126 | 1.12 | .30 | 0.272 | 0.284 | 0.94 | .42 |
- MA: minor allele, “Case” and “Cont”: allele frequency of the minor allele in cases and controls, respectively, OR: odds ratio, P = P value.
| SNP (ancestry) | MA | Females | Males | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cases | Cont | OR (95% CI) | P | Cases | Cont | OR (95% CI) | P | ||
| rs1977661 (EA) | A | 0.101 | 0.117 | 0.85 (0.74–0.98) | .023 | 0.080 | 0.109 | 0.69 (0.48–0.99) | .047 |
| rs12553951 (EA) | C | 0.074 | 0.072 | 1.04 (0.88–1.23) | .62 | 0.107 | 0.060 | 1.93 (1.36–2.74) | .00025 |
| rs3861016 (EA) | C | 0.067 | 0.078 | 0.85 (0.72–1.00) | .05 | 0.056 | 0.071 | 0.75 (0.49–1.16) | .20 |
| rs2814707 (AA) | A | 0.195 | 0.235 | 0.79 (0.65–0.96) | .020 | 0.204 | 0.229 | 0.85 (0.51–1.40) | .52 |
- EA: European ancestry, AA: African-American ancestry, MA: minor allele, “Case” and “Cont”: allele frequency of the minor allele in cases and controls respectively, OR: odds ratio, 95% CI = 95% confidence interval of the odds ratio, P = P value.
3.2. IFNK SNPs Are Associated with Skin Phenotypes in SLE
We next tested for associations between IFNK SNPs and skin phenotypes in a case-case analysis of the SLE patients. In female EA and AA SLE patients, seven SNPs demonstrated evidence for association with discoid rash and malar rash, respectively (Tables 5(a) and 5(b), resp.). More than one SNP showed at least nominal (P < .05) evidence for association, however, conditioning on the strongest association in each background abolished the marginal significance observed at the other SNPs (Tables 5(a) and 5(b)). Interestingly, the allele frequencies of the most strongly associated SNP in each background in males showed a strong trend toward an opposite association as compared to that found in females (Table 5(c)). Thus, the allele associated with a skin phenotype in female patients shows evidence of being protective against the same skin phenotype in males of the same ancestral background. The low number of males limits the statistical strength of these findings although these preliminary allele frequency differences are of large magnitude, and this parallel sex-skewing of genetic associations with skin phenotypes in two different ancestral backgrounds is intriguing. Photosensitivity was not associated with IFNK SNPs, and no associations were observed with SLE-associated antibodies (data not shown).
| SNP | MA | OR (95% CI) | P | Conditioned on rs4879541 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | P | ||||
| rs4609281 | C | 1.35 (1.03–1.78) | .030 | 1.28 | .091 |
| rs11792285 | A | 0.60 (0.37–0.98) | .043 | 0.92 | .81 |
| rs4879541 | G | 0.58 (0.39–0.85) | .0061 | — | — |
| rs7469146 | A | 0.57 (0.36–0.89) | .015 | 0.84 | .66 |
| rs10812611 | A | 0.57 (0.36–0.89) | .014 | 0.80 | .56 |
| SNP | MA | OR (95% CI) | P | Conditioned on rs2814707 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | P | ||||
| rs4609281 | C | 1.47 (1.08–1.98) | .013 | 1.04 | .91 |
| rs2814707 | A | 1.55 (1.13–2.12) | .0063 | — | — |
| rs12686452 | G | 0.65 (0.45–0.94) | .023 | .73 | .11 |
| SNP | Allele | Female − | Female + | Male − | Male + | Female OR | Male OR | Phenotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs4879541 (AA) | G | 0.192 | 0.124 | 0.048 | 0.447 | 0.58 | 6.36 | Malar |
| rs2814707 (EA) | A | 0.220 | 0.312 | 0.281 | 0.156 | 1.55 | 0.45 | Discoid |
3.3. Serum Type I IFN Levels Are Related to IFNK SNPs in EA and AA SLE Patients
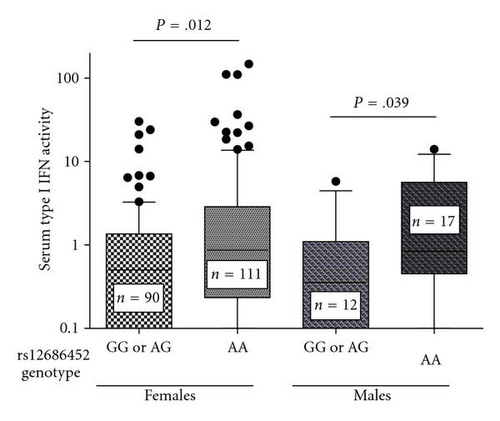
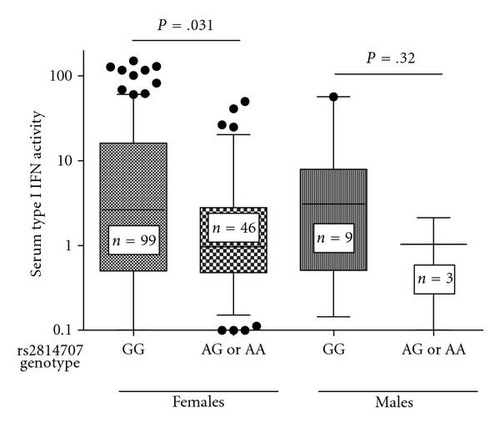
We next analyzed serum type I IFN activity in subjects with data available for this phenotype, which included 230 European-American and 158 African-American SLE patients. We first used logistic regression models with ancestry covariates to detect associations with high serum type I IFN activity as a categorical trait (high IFN was defined as >2SD above healthy controls). In both EA and AA, there was a single SNP associated with high serum type I IFN activity in female patients. The rs12686452 A allele was associated with high serum IFN in EA females (OR = 2.79, 95% CI = 1.48–5.29, P = 1.6 × 10−3) and the rs2814707 G allele was associated with high serum IFN in AA females (OR = 2.69, 95% CI = 1.30–5.56, P = 7.6 × 10−3). Quantitative serum type I IFN activity in each ancestral background stratified by SNP genotype is shown in Figure 4.
4. Discussion
In this study we analyzed the role of genetic variation near the IFNK locus in SLE susceptibility and the clinical expression of cutaneous and autoantibody manifestations of SLE. While evidence supporting a genetic association was observed in EA males with SLE, EA females with discoid rash, AA females with malar rash, and EA and AA females with serum type I IFN activity, the specific associated SNPs were not the same for each phenotype and were not shared across the different ancestral backgrounds examined in this study. This could be due to spurious association, although there are other potential explanations as well. It is possible that the associations we observe are due to linkage between the marker SNPs we have genotyped and one or more as yet unknown causal genetic variants in the IFNK locus. Further examination of this locus with fine mapping and sequencing in multiple ancestral backgrounds will help to answer this question. Also, it is possible that the causal variant may be in the Mps One Binder kinase activator-like 2B (MOBKL2B) gene, which is also within this locus on the opposite strand from IFNK (Figure 1). The MOBKL2B gene is homologous to the yeast MOB1 gene, which is involved in regulating mitotic spindle checkpoints, and it seems that IFNK is a more likely candidate gene in this locus given our current understanding of the biology of these two genes.
Despite the differences we observe in genetic associations between different ancestral backgrounds, it is still possible that the causal genetic elements are the same in all ancestral backgrounds, and the differences in associations we observe could relate to different chromosomal linkage patterns between the SNPs we genotyped and untyped causal variants in different backgrounds. Alternatively, it is possible that different causal variants in the IFNK locus are present in different ancestral backgrounds and predispose subjects to different subphenotypes. There is some precedent for this phenomenon with SLE-risk loci [11, 13, 28].
If the association between rs12553951 C and SLE in EA males is confirmed in independent cohorts, this may provide greater insight into the pathogenesis of male SLE, which is not well understood at present. Interestingly, we have previously observed evidence for sex-differences in genetic associations in another type I IFN pathway gene, osteopontin (SPP1) [13, 27]. In the largest study of SPP1 to date, an association of the previously reported risk allele was only observed in male SLE patients [27]. This was surprising, as males represented approximately 10% of the population studied, similar to most studies of SLE. Another study recently described sex-related differences in associations between the same risk variant of SPP1 and serum cytokine patterns, which may provide some explanation of the observations in previous studies in [13]. In this study of SPP1, young female SLE patients were enriched for the risk allele of SPP1 and demonstrated increased serum osteopontin and type I IFN levels related to the risk variant, while older female patients did not. Male patients, while few in number, demonstrated a robust pattern of increased serum cytokines related to the SPP1 risk allele, similar to the younger female patients [13]. Given these data, we explored age as a variable in this study although this did not resolve the differences in IFNK associations we observed between males and females.
The potential associations of SNPs in the IFNK locus with skin phenotypes in SLE is interesting, as IFN-κ is expressed in the skin [17] and could conceivably play a role in the skin inflammation characteristic of the SLE disease process. The sex-skewing of allele frequencies observed in the associated SNPs in relation to skin phenotypes is striking and also warrants further validation in a greater number of male subjects. While the reasons underlying the sex-differences in association we observe at the IFNK locus are not clear, the type I IFN system is crucial for placental reproduction [29]. Additionally, the type I IFN gene family has diversified extensively in placental mammals [18]. It is possible that sex differences in the regulation of type I IFNs could relate to the differences in associations we observe between disease states and some type I IFN pathway genes [30, 31].
If variants in the IFNK locus do not truly confer susceptibility or alter the clinical expression of its various manifestations, IFNK may yet play an important role in SLE via modulation of serum type I IFN and other cytokines. In this study we observe evidence for associations between IFNK SNPs and serum type I IFN activity. We show that IFN-κ does not contribute directly to the serum type I IFN activity being measured, consistent with previous observations that IFN-α has been the predominant type I IFN inducing the serum activity observed in SLE patients [9, 26]. Alternatively, it is possible that IFN-κ could exert an influence upon serum type I IFN levels by acting locally in the skin. In this regard, it has been noted that IFN-κ can bind strongly to heparin, which would facilitate retention of the cytokine close to the site of production in the skin [20]. The major IFN-α producing cells are plasmacytoid dendritic cells. These cells are frequently found SLE-affected skin [16], and it seems possible that IFN-κ could be involved in activating and “priming” these cells. This type of feed-forward mechanism has been described with other type I IFNs [32], and could potentially explain an association of the IFNK locus with serum levels of type I IFN, even if the type I IFN being measured in serum is predominantly IFN-α.
A recent genome-wide association scan of differential response to anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) treatment in rheumatoid arthritis showed strong preliminary evidence of association of a number of SNPs in the IFNK locus with response or nonresponse to anti-TNF-α therapy (ORs range from 4.9 to 5.4, P-values in the 4-5 × 10-4 range) [33]. Cross-regulation of type I IFN and TNF-α has been observed in SLE [12] and other conditions [34], and treatment with anti-TNF-α agents has been shown to increase serum type I IFN activity [35]. Upregulation of type I IFNs is one mechanism proposed for lack of response to anti-TNF-α agents [36], and it is possible that IFNK variants could contribute to dysregulation of the type I IFN pathway in the setting of TNF-α inhibition. Anti-IFN-α therapy has showed promise in recent trials in [37], as having therapies modulating B-cell activating factor (BAFF) [38]. Indeed, studies suggest that type I IFN exposure upregulates BAFF in humans [35, 39], further supporting the idea that type I IFN is related to a number of important pathological cytokines in human disease. These data taken together suggest that IFNK variants could play an important role in cytokine regulation in SLE and consequently the pharmacogenetics of anti-cytokine therapies, even if a role for IFNK variants in SLE susceptibility is not confirmed.
Financial Disclosures and Conflict of Interest
The authors report no financial conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
Isaac T. W. Harley and Timothy B. Niewold had equal contribution to this paper. I. T. W. Harley received an HD07463, NICHD Training in Developmental and Perinatal Endocrinology, GM063483 NIGMS Medical Scientist Training Program. T. B. Niewold gained NIH K08 AI083790, NIAID Clinical Research Loan Repayment AI071651, Arthritis National Research Foundation Eng Tan Scholar Award, Lupus Research Institute Novel Research Grant, Alliance for Lupus Research Target Identification in Lupus Grant, University of Chicago CTSA Core Subsidy Grant, and Collaborative University of Chicago/Northshore University Health System Translational Research Pilot Grant from UL1-RR024999. J. A. Kelly obtained Lupus Family Registry and Repository – NIH AR62277, research Grants from NIH (AR42460, AI24717). J. C. Edberg was given research Grants from the NIH (P01 AR49084, R01 AR33062, R01 AR42476, and UL1-M01RR00052). G. McGwin Jr. received research Grants from IH (AR49084). M. A. Petri was awarded with research Grants from the NIH (AR43727, P01-AR49084) and the Institute for Clinical and Translational Research UL1-RR025005. R. Ramsey-Goldman received research Grants from NIH (K24 AR002138, P60 AR30692, P01 AR49084, MO1-RR00048, and UL1-RR025741), J. D. Reveille from NIH (P01 AR49084), and L. M. Vila-Perez from NIH (P01 AR49084). G. S. Gilkeson has NIH (P60 AR049459) and the Medical Research Service, Ralph H Johnson VAMC. T. J. Vyse was given A Wellcome Trust Senior Fellowship, support for sample collection from a Grant from the NIH (AI065687), and a grant from the NIHR Comprehensive Biomedical Research Centre, Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust. M. E. Alarcón-Riquelme gained Swedish Research Council, Torsten and Ragnar Söderbergs Foundation and the Gustaf Vth-80th year Jubilee, research Grants from the NIH (P20 RR020143, P01 AI083194, R01 CA141700, and RC1 AR058621) and the Instituto de Salud Carlos III de el Ministerio de Innovacióny Ciencia and the Consejería de Salud de Andalucía. G. S. Alarcón was offered NIH (P01 AR49084). P. M. Gaffney obtained research Grants from NIH (AR052125, AI063274). R. P. Kimberly received research Grants from NIH (P01 AR49084, R01 AR33062, and R01 AR42476). S-C. Bae gained was with the Korea Healthcare technology R & D project, Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs, Republic of Korea (A010252, A080588). J. B. Harley had Lupus Family Registry and Repository –NIH AR62277, research Grants from NIH (AR42460, AI53747, AI31584, DE15223, RR20143, AI24717, AI62629, AR48940, AI83194, and AR49084), and research grants from the US Department of Veterans Affairs, Alliance for Lupus Research, and Rheuminations, Inc. J. M. Guthridge was given OHRS award for Project no. HR08-037 from the Oklahoma Center for the Advancement of Science & Technology, research Grants from NIH (N01 AI050026-001). J. A. James received research Grants from NIH (RR15577, AR48940, AR045084, AR053483, AR058554, and AI082714), Mary Kirkland Scholar, and Lou Kerr Chair in Biomedical Research.




