Taxonomy of two oxypodine genera, Porocallus Sharp and Rhomphocallus Assing, in Korea (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae: Aleocharinae)
Abstract
A taxonomic study of the genera Porocallus Sharp and Rhomphocallus Assing in Korea is presented. The genus Rhomphocallus and two species, Rhomphocallus princeps (Sharp) and Rhomphocallus maruyamai Assing, are reported for the first time in Korea. Porocallus insignis Sharp is recorded for the first time in South Korea. Diagnoses, illustrations of habitus and line drawings of diagnostic characters are provided.
Introduction
The tribe Oxypodini Thomson, 1859, containing approximately 146 genera, is cosmopolitan and one of the most systematically difficult groups of the Aleocharinae (Ashe 2001). It is poorly characterized, but can be recognized by a combination of the following characters: tarsal formula 5-5-5, 4-5-5 or 4-4-4; antennae with 11 articles; mouthparts generalized; head without a neck in most individuals; and median lobe without athetine bridge (Seevers 1978).
The monotypic genus Porocallus Sharp is distributed only in the east Paleartic region. Assing (2001) recorded Porocallus insignis for the first time in Korea. They are found under leaf litter. Members of the genus Porocallus are characterized by the combination of the following characters: moderately large size, densely punctate and dull; maxillary palpomere 3 broad and truncate at the apex, apparently inverted triangle shape, terminal palpomere short and slender; ligula divided into two lobes and lobes rounded; and tarsal formula 5-5-5.
The genus Rhomphocallus Assing, which comprises three species, is restricted to the Palearctic region. Assing (2003) erected the new genus based on Microglotta princeps Sharp and described a new species (Rhomphocallus maruyamai Assing). Members of the genus Rhomphocallus are characterized by the combination of the following characters: large size, body coarsely punctured and pubescent; antennae long and slender, antennomere 11 distinctly longer than wide; ligula not bifid and rounded apically; and tarsal formula 5-5-5.
In the present paper, we report the genus Rhomphocallus and two species, Rhomphocallus princeps (Sharp) and Rhomphocallus maruyamai Assing for the first time in Korea, and record Porocallus insignis Sharp for the first time in South Korea. Given that Assing (2001, 2003) has described these genera and species in detail, we provide here diagnoses, and illustrations of habitus and line drawings of diagnostic characters.
Materials and methods
Preparation of permanent microscopic slides was performed using techniques described by Hanley and Ashe (2003). Terminology for chaetotaxy and microstructures follows Sawada (1972). Materials examined in the present study are deposited in the Chungnam National University Insect Collection, Daejeon, Korea (CNUIC).
Genus Porocallus Sharp, 1888 (Korean name: U-dan-ban-nal-gae-sok)
Porocallus insignis Sharp, 1888 (Korean name: U-dan-ban-nal-gae)
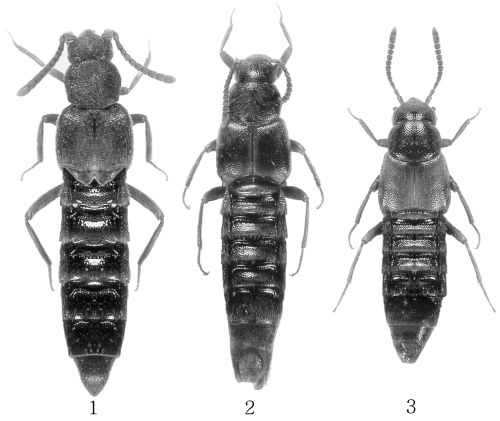
1 Porocallus insignis ; 2 Rhomphocallus princeps ; 3 Rhomphocallus maruyamai .
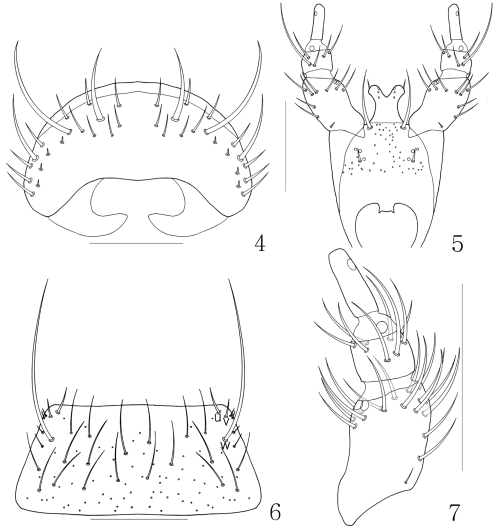
Porocallus insignis : 4 labrum, dorsal aspect; 5 labium, ventral aspect; 6 mentum, ventral aspect; 7 labial palpi, ventral aspect. Scale bars, 0.1 mm.
Porocallus insignis Sharp, 1888: 286; Fenyes, 1920: 344; Bernhauer and Scheerpeltz, 1926: 733; Assing, 2001: 215; Paśnik, 2001: 227; Smetana, 2004: 486.
Diagnosis. Length 3.5–5.5 mm. Body black, sutural and posterior margin of elytra red, antennae and legs brownish black. Antennae long, antennomere 1 longest and expanded, antennomere 3 longer than two and more than two times as long as wide, antennomeres 4–10 weakly rectangular. Head densely punctured and pubescent. Labrum (Fig. 4) transverse and rounded apically. Mandible pointed, asymmetrical, right mandible with internal tooth and serration between apical tip and internal tooth, apical part strongly curved inward. Maxilla with four palpomeres, palpomere 3 flattened and expanded apically, palpomere 4 small, more or less triangular. Labium with ligula (Fig. 5) weakly bifid, one seta present on it; two medial setae distantly located, setal and basal pores present, pseudopores scattered medially and laterally. Labial palpus (Fig. 7) with three articles, palpomere 1 with 17 setae, palpomere 2 with eight setae and palpomere 3 with distal pore. Mentum (Fig. 6) transverse. Pronotum densely punctured and pubescent. See Assing (2001) for a detailed description.
Material examined. 2♂♂2♀♀, N34°92′50″, E127°09′70″, Mount Dubongsan, Bokrae-myeon, Boseong-gun, Jeonnam Province, Korea, 30.vii.2003, S.J. Park, D.H. Lee, sifting (1♀, on slide); 1♂, Eochi-ri, Daab-myeon, Gwangyang City, Jeonnam Province, Korea, 25.v.2000, H.J. Kim, M.J. Jeon, sifting; 1♀, Eochi-ri, Daab-myeon, Gwangyang City, Jeonnam Province, Korea, 25.v.2000, K.J. Ahn, sifting; 1♂1♀, Cheondong Area, Mount Sobaeksan, Tangyang-gun, Chungbuk Province, Korea, 8–9.v.1999, U.S. Hwang, H.J. Kim, sifting; Mount Paekam, Onjong-myeon, Uljin-gun, Kyeongbuk Province, Korea, 12.vii.1999, U.S. Hwang, ex leaf litter (1♀, on slide); 1♂, Mount Kariwangsan, Jeongsun-gun, Kangwon Province, Korea, 5–7.vii.1998, H.J. Lim, K.L. You, FIT; 1♂, Mount Kariwangsan, Jeongsun-gun, Kangwon Province, Korea, 12–14.viii.1998, H.J. Lim, K.L. You, K.J. Ahn, sifting; 1♂, Ssangryong, Kangwon Province, Korea, 29.viii.1996, Y.B. Cho, ex near stream; Mount Odaesan, Pyeongchang-gun, Kangwon Province, Korea, 28–30.viii.1998, K.L. You, H.J. Lim, K.J. Ahn, sifting (1♂, on slide); 1♀, Mount Oseosan, Sangdam-ri, Kwangcheon-eup, Hongseong-gun, Chungnam Province, Korea, 20.vi.1999, H.J. Kim, sifting; 1♀, Jangoksa Area, Mount Chilgapsan, Cheongyang-gun, Chungnam Province, Korea, 3.vi.2000, U.S. Hwang, K.H. Jung, J.H. Song, sifting; 1♀, Gapsa, Mount Gyeryongsan, Gyeryong-myeon, Gongju City, Chungnam Province, Korea, 3.vi.2000, S.J. Park, M.S. Kim, M.H. Hong, sifting.
Distribution. Korea, Japan, China, Russian Far East.
Genus Rhomphocallus Assing, 2003 (Korean name: Gom-bo-ban-nal-gae-sok)
Rhomphocallus Assing, 2003: 165.
Type species: Microglotta princeps Sharp, 1874.
Diagnosis. Length 4.5–5.5 mm. Body densely punctate and dull. Antennae long and slender; antennomere 11 longest. Maxillary palpomere 3 broad and truncate at the apex, apparently inverted triangle, terminal palpomere short and slender. Ligula divided into two lobes and rounded. Pronotum transverse, wider than head and widest in the middle. Elytra wider than pronotum, bicolor and latero-basal margin marginated. Tarsal formula 5-5-5. Abdominal tergites III–VII impressed basally. See Assing (2003) for a detailed generic description.
Rhomphocallus princeps (Sharp, 1874) (Korean name: gom-bo-ban-nal-gae)
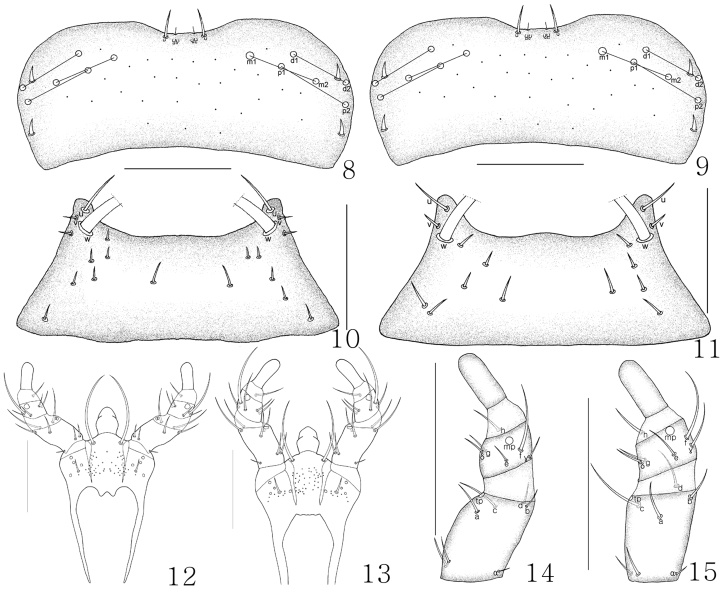
Labrum: 8 Rhomphocallus princeps , dorsal aspect; 9 Rhomphocallus maruyamai , dorsal aspect. Mentum: 10 R. princeps , ventral aspect; 11 P. maruyamai , ventral aspect. Labium: 12 R. princeps , ventral aspect; 13 R. maruyamai , ventral aspect. Labial palpi: 14 R. princeps , ventral aspect; 15 R. maruyamai , ventral aspect. Scale bars, 0.1 mm.
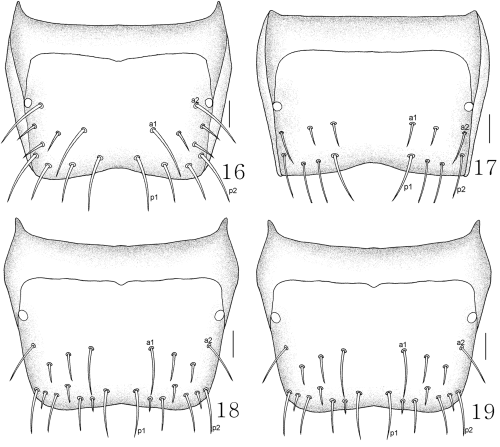
Rhomphocallus princeps : 16 male tergite VIII, dorsal aspect; 17 female tergite VIII, dorsal aspect. Rhomphocallus maruyamai : 18 male tergite VIII, dorsal aspect; 19 female tergite VIII, dorsal aspect. Scale bars, 0.1 mm.
Microglotta princeps Sharp, 1874: 6; Fenyes, 1920: 391; Bernhauer and Scheerpeltz, 1926: 773.
Rhomphocallus princeps : Assing, 2003: 165.
Haploglossa princeps : Smetana, 2004: 473.
Diagnosis. Length 4.5–5.5 mm. Body brown; antennae, marginal elytra, posterior tergites, and legs yellowish brown. Antenna long, antennomeres 1–3 similar in size, 4 weakly rectangular, 5 subquadrate, 6–10 transverse, 11 longest. Head densely punctured and pubescent. Labrum as in Figure 8. Mandible asymmetrical. Mentum as in Figure 10. Labium as in Figure 12. Galea wide, proximal sclerite transverse. Labial palpi (Fig. 14) with three articles, additional two setae present on opposite side of α-seta and β-seta absent. Pronotum densely punctured and pubescent. Abdominal tergite VIII of male as in Figure 16, and female as in Figure 17. See Assing (2003) for a detailed description.
Material examined. 2♂1♀, Dongseon-dong, Seongbuk-gu, Seoul, Korea, 9.v.1988, Y.S. Kim, bait; 1♂1♀, Dongsan-ri, Jinbu-myoen, Pyeongchang-cun, Kangwon Province, Korea, 2.vii.1985, Y.S. Kim, bait; Dongseon-dong, Seongbuk-gu, Seoul City, Kyeongki Province, Korea, 24.v.1988, K.S. Jang, bait (1♀, on slide); 1♂, Guam-ri, Sacheon City, Gyeongnam Province, Korea, 16.v.1986, K.S. Lee; 1♂, Piagol, Mount Jirisan, Gurye-gun, Jeonnam Province, Korea, 24.v.2000, H.J. Kim, M.J. Jeon, sifting.
Distribution. Korea, Japan.
Rhomphocallus maruyamai Assing, 2003 (Korean name: min-mu-nui-gom-bo-ban-nal-gae)
Rhomphocallus maruyamai Assing, 2003: 165.
Diagnosis. Length 4.5–4.8 mm. Body brown; antennae, marginal elytra, posterior tergites, and legs yellowish brown. Antenna long, antennomeres 1–3 similar in size, 4 and 5 subquadrate, 6–10 transverse, 11 longest. Head densely punctured and pubescent. Labrum as in Figure 9. Mentum as in Figure 11. Labium as in Figure 13. Galea wide, proximal sclerite transverse. Labial palpi (Fig. 15) with three articles, additional two setae present on opposite side of α-seta, and β-seta absent. Pronotum densely punctured and pubescent. Abdominal tergite VIII of male as in Figure 18, and female as in Figure 19. See Assing (2003) for a detailed description.
Material examined. Guam-ri, Sacheon City, Gyeongnam Province, Korea, 16.v.1986, K.S. Lee (1♀, on slide); Seoguipo Beach, Jeju Province, Korea, 12.xii.1984, K.S. Lee (1♀, on slide); 1♂, Jinju City, Gyeongnam Province, Korea, 28.iv.1983, J.I. Kim; 1♂, Jang-dong, Daejeon City, Chungnam Province, Korea, 26.xi.1996, Y.B. Cho.
Distribution. Korea, Japan.
Remarks. Rhomphocallus maruyamai can be distinguished from R. princeps by a weakly emarginated posterior margin of abdominal tergite VIII, aedeagal differences and mouthpart structures (Table 1).
| Rhomphocallus princeps | Rhomphocallus maruyamai | |
|---|---|---|
| Body length | 4.5–5.5 mm | 4.5–4.8 mm |
| Color (elytra) | Sutural and posterior margin red | Yellowish brown |
| Antennomere 4 | Weakly rectangular | Subquadrate |
| Labrum | Figure 8 | Figure 9 |
| Mentum | Figure 10 | Figure 11 |
| Labium | Figure 12 | Figure 13 |
| Labial palpi | Figure 14 | Figure 15 |
| Posterior margin of abdominal tergite VIII | Distinctively emarginated (Figs 16,17) | Weakly emarginated (Figs 18,19) |
| Median lobe | Figure 3 (Assing 2003) | Figure 12 (Assing 2003) |
| Spermatheca | Figure 6 (Assing 2003) | Figures 14 and 15 (Assing 2003) |
Acknowledgments
We thank Volker Assing (Hanover, Germany) for providing valuable reprints. We also thank Mr Seung-il Lee for taking the habitus photos. This research was supported by a Korea Research Foundation Grant (KRF-2004-015-C00518) to K.-J. Ahn.




