A Mutation in the ANK2 Gene Causing ASD and a Review of the Literature
Funding: This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (2015MS08103); Inner Mongolia Medical University youth project (YKD2024QN002); Department of Science and Technology of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Grant numbers (2020GG0139); Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Neurological Disease Clinical Medicine Research Center (MYYXT201903); Major Project of Inner Mongolia Medical University (kjbw2012005); Youth Science and Technology Talents Program-Class A (NJYT-17-A19); National Natural Science Foundation of China (8226050455).
The first two are co-first author “Lu Zhao and Zhi-Dong Qiao”.
ABSTRACT
Objective
To investigate the clinical and genetic characteristics of patients with ANK2(HGNC:493)-associated autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) and epilepsy (EP).
Methods
We identified a novel ANK2 variant in a patient with ASD and EP and summarized the clinical and genetic characteristics of ANK2 gene variants in this patient and those in previous reports.
Results
A novel nonsense variant, ANK2 (NM_001148.6):c.3007C>T/p.R1003* in exon 27, was identified in one patient. We described the clinical features and molecular genetics of this patient and previously reported patients. This was discovered at a follow-up visit to the pediatric neurology department where genetic testing based on condition identified this rare genetic variant. He mainly presents with language delay, intellectual disability, limited learning, and communication skills, and later develops seizures, combined with common childhood neurological disorders such as hyperactivity, behavioral abnormalities, and even self-injury. The patient cohort included 16 patients with a complex array of neurological disabilities: ASD (9 patients); EP (10 patients); ASD with EP (4 patients); intellectual disability and developmental delay (5 patients); poor language communication (11 patients); language and learning impairment (11 patients); anxiety/agitation mood disorder (6 patients); attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (5 patients); cognitive, memory, and adaptability deficits (1 patient); tic disorder (1 patient); electrocardiogram and cardiac damage (1 patient); and abnormal electroencephalography (EEG) (9 patients).
Conclusion
For the first time, we identified a novel variant of the ANK2 gene in China, broadening the genetic spectrum of the ANK2 gene. ANK2 gene mutations can cause ASD, EP, ASD with EP, developmental delay and intellectual disability, poor language communication skills, language and learning disorders, anxiety/agitation mood disorder, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Clinical ASD, EP, common EP should consider the ANK2 gene mutation.
1 Introduction
ANK2(HGNC:493) has 61 exons, is located on chromosome 4q25-q26, and encodes ankyrin B (ANKB), which is important for ion channel localization and membrane stabilization (Teunissen et al. 2023). There are two subtypes of ANKB: one protein is a wild-type 220 kDa protein that is expressed in multiple tissues, and the other protein is 440 kDa, also known as giant ANKB (gANKB), which is caused by alternative splicing. Mutations in this gene can cause various neurological disorders, such as autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) and epilepsy (EP) (Guissart et al. 2023).
ASD is a neurodevelopmental disease that usually manifests symptoms before the age of 3 years and is primarily characterized by impaired social communication, restricted interests, and stereotyped behaviors (Kawano et al. 2022; Hyman et al. 2020). The heterogeneity of the clinical manifestations of ASDs is caused by interactions among multiple genes, gene combinations, epigenetic factors, and environmental regulators (Oztenekecioglu et al. 2021). ANK2 mutations were identified as a functional neurospecific etiology of ASD in 2012 (Iossifov et al. 2012). However, reported cases of ASD associated with ANK2 mutations are rare. In this study, for the first time, we identified a novel ANK2 mutation in a patient with ASD and comorbid EP in China. We searched the literature for reports on ANK2 gene variations and summarized the clinical and genetic characteristics of these patients, aiming to improve the awareness of the gene among clinicians.
2 Materials and Methods
2.1 Ethical Compliance
This study was conducted in accordance with the declaration of Helsinki and from the Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University (No. WZ[2024002]). Written informed consent was obtained from the participant.
2.2 Clinical Features
2.2.1 Current Disease History
The patient was born via term vaginal birth (G1P1) and had a birth weight of 3.3 kg. The mother was healthy during pregnancy. There was no history of hypoxia or asphyxiation either before or after birth. The child achieved typical motor milestones, such as rolling over at 3 months, crawling at 8 months, and walking independently at 13 months. Overall, his motor development was similar to that of other children of the same age. However, the child experienced a delay in speech development and was still unable to speak at age 3 years. After seeking medical attention for language delay, he went to the Peking University Sixth Hospital more than 10 years ago when he was 3 years old. He underwent an assessment using the Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS), which yielded a score of 60, indicating a clinical diagnosis of severe ASD. Later, with the growth of age, he showed more serious social disorders, including avoiding eyes and lacking interest in communicating with others. Communication disorders are characterized by impaired language comprehension, emotional and behavioral abnormalities, and unbalanced cognitive development.
Three years ago (March 2020), the child experienced the first seizure episode after fever, characterized by responsiveness (not responding), binocular gaze deviation, cyanosis, and urinary incontinence. The seizure lasted for approximately 3–5 min, and the patient experienced fatigue after remission. He was subsequently diagnosed with EP in March 2020 (10 years old) at our hospital, and oral oxcarbazepine treatment was discontinued.
One year ago, the child started experiencing frequent seizures, each of which presented with similar manifestations, including responsiveness (not responding), cyanosis, eye gaze deviation to the right, head and mouth askew to the right side, limb flexion with jitter, and no incontinence, lasting for approximately 5 min and causing postictal fatigue. In the second year after the diagnosis of EP, the child developed symptoms of involuntary pharyngeal vocalizations and voice clearing. Therefore, our hospital diagnosed the boy with tic disorder (TD) based on the clinical symptoms. Recently, the child has exhibited abnormal behaviors, such as shouting, agitation, and self-injury, and is unable to communicate with others normally. During the disease course, the dosages of oxcarbazepine (OXC), perampanel (PER), and clonazepam were adjusted to control the seizures, and thiopride was added to improve TD symptoms.
2.3 Past History and Family History: No Remarkable History
2.3.1 Physical Examination
His vital signs were stable, and he demonstrated normal development and good nutritional status. There was evidence of hyperactivity, restlessness, and frequent yelling. He exhibited intellectual impairment and was unable to communicate with others in a typical manner. Disconjugate gaze was observed, and the patient could not understand the instructions. The fundus, cardiopulmonary system, and abdominal examinations revealed no abnormalities. He exhibited normal muscle strength and muscle tone in the limbs, physiological reflexes were present, and pathological reflexes were not elicited.
2.3.2 Auxiliary Examination
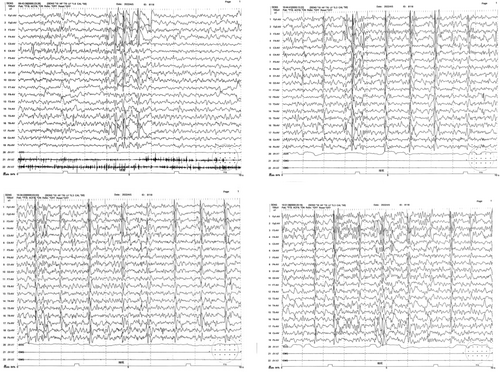
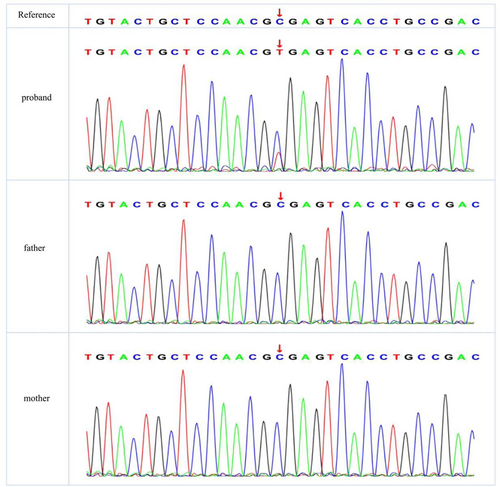
The results of routine blood tests, routine urine tests, routine stool tests, and blood biochemical indices showed no obvious abnormalities. Video electroencephalography (Figure 1) revealed a poor background rhythm, increased fast waves, and multiple focal slow waves in each sleep period, particularly in the right frontal region. Cranial magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed no abnormalities. ECG results were normal, and no abnormalities were detected via 24-h Holter ECG monitoring. The patient's score on the Pediatric Autism Rating Scale (2003) (Childhood Autism Rating Scale [CARS]) was 60, indicating a clinical diagnosis of severe ASD. Using trio whole-exome sequencing (WES), we identified a novel de novo mutation in the ANK2 gene: c.3007C>T, p.R1003* (NM_001148.6). To validate the authenticity of this mutation, Sanger sequencing was performed (Figure 2). According to the standards and guidelines of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG), this variant was classified as pathogenic (PVS1 + PS2_Supporting+PM2_Supporting). Additionally, trioCNVseq, capillary electrophoresis testing for dynamic mutations in the fragile X syndrome gene FMR1, and mitochondrial genome analysis were performed, and no abnormal variations were detected.
2.4 Literature Review
Haploinsufficiency of ANK2, as documented in the ClinGen database, is known to cause complex neurodevelopmental disorders, but this relationship was not included in OMIM. According to the in-house database of Chigene (Beijing) Translational Medical Research Center Co. Ltd., ANK2-associated diseases include EP and ASD (ZYDF00139) (Guissart et al. 2023). The main manifestations are nervous system abnormalities, namely, ASD/ASD-like behaviour and seizures. ANK2 has been identified as a key risk gene for ASD (Satterstrom et al. 2020; Willsey et al. 2013) and a potential candidate gene for EP (Peng et al. 2021). A search in PubMed for “ANK2 mutation” and “ANK2 mutation, ASD-EP” yielded four relevant articles, including a total of 15 patients.
The first case described by Guissart et al. (Guissart et al. 2023) involved an 11-year-old boy who exhibited developmental delay at 2 years of age; had several teeth extracted due to caries and periodontal abscess at 8 years of age; and currently presented with severe ASD, anxiety, mood disorders, and speech communication barriers but no seizures. Additional phenotypes included tall stature, macrocephaly, and weight gain. A de novo variant of ANK2 was detected in this patient (c.285 + 1G>T, NM_001148.6), affecting the splice donor site of intron 3 of ANK2.
In the second case, reported by Morais et al. (2023), a 7-year-old girl experienced focal clonic seizures in her left lower limb at 2 months and an abnormal gait (toe walking) at 20 months, in addition to a speech development disorder. Other phenotypes included large mouth deformities and larger teeth. Another de novo variant of ANK2 was detected in this patient (c.3412C>T, p.Arg1138*).
The third case, described by Ji et al. (2019), involved a 5-year-old girl whose main features included severe global developmental delay, seizures, aggressive behavior, and microcephaly.
The other 12 patients with ANK2 mutations were described by Maria W A Teunissen et al. (2023). Their research showed that loss-of-function variants in the ANK2 gene were associated with a novel neurodevelopmental disorder (NDD) with early-onset EP and led to impaired axon initial segment plasticity and hyperactive network activity in human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC)-derived neuronal networks.
Of the 16 patients (Table 1), 10 had EP, including one who was diagnosed with West syndrome, five with focal seizures, one with generalized seizures, and three with seizures of unknown cause. Additionally, nine patients were diagnosed with ASD, four of whom had seizures. Five patients exhibited developmental delay and intellectual disability. Eleven patients had difficulties in verbal communication, language, and learning, and 11 patients had abnormal behavioral problems, including anxiety, agitation, mood disorders, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, TD, sleep disorders, self-injury, and aggressive behavior. One patient had an abnormal electrocardiogram (ECG), and nine had an abnormal electroencephalogram (EEG), mainly characterized by multifocal epileptiform discharge and spike-wave distribution. We analyzed all 16 patients based on sex, EP, ASD, intellectual disability, language and learning disabilities, language communication skills, abnormal behaviors (including anxiety, agitation, mood disorders, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and TD), cognitive memory adaptability issues, and ECG and EEG abnormalities (Table 2). Among the 16 patients, there were significant differences in eight parameters: ASD diagnosis, EP diagnosis, poor language communication, language and learning disabilities, cognitive memory adaptability issues, TD, ECG abnormalities, and EEG abnormalities (p < 0.05). However, there were no significant differences in sex, intellectual disability, anxiety, mood disorders, or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder among the 16 patients (p > 0.05).
| Patient | Sex | Age | Variant | DD, ID | LLD | Poor language and communication skills | Anxiety, agitation, MD | ADHD | LCA, LMA and adaptability | EP | ASD | TD | ECG | PH | EEG | Other | Diagnosis | Reference (PMID) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | M | 11 | c.285+1G>T | + | + | + | − | + | + | − | + | − | − | − | − | Extensive tooth decay | None | 37088467 |
| P2 | F | 7 |
c.3412C>T p.Arg1138* |
+− | + | + | − | − | − | + | + | − | − | Levetiracetam; phenobarbital | The background was normal, and the interictal and ictal epileptiform discharges were confined to the midline central and right central regions (Cz-P30) | Abnormal gait (toe walking), wide teeth deformity | Focal EP with focal seizures and focal clonic seizures of the left lower limb | Morais et al. (2023) |
| P3 | F | 5 |
c.1417C>T p.Arg473* |
+ | UK | UK | UK | UK | UK | + | UK | UK | UK | UK | UK | Microcephaly and aggressive behaviour | Unknown type of EP with unknown seizures | 32023981 |
| P4 | F | 13 | c.2797-1G>A | − | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | − | − | Lamotrigine | Multifocal seizure discharges | UK | Unknown type of EP with unknown seizures | 37195288 |
| P5 | M | 15 | c.922C>T | + | + | + | − | + | − | + | − | − | + | − | Normal | − | Unknown type of EP with unknown seizures | 37195288 |
| P6 | M | 12 | c.2179-1G>A | − | + | + | − | − | − | + | − | − | Valproic acid 500/500 mg and clonidine 0.1 mg | Right-side epileptiform discharge | − | Focal EP with focal seizures with left eye deviation and impaired consciousness | 37195288 | |
| P7 | M | 18 | c.3019C>T | − | + | + | + | − | − | + | + | − | − | Ketogenic diet, clonazepam, lufenamide, clobazam, cannabidiol, valproic acid, and VNS | Abundant multifocal epileptiform activity; left>right deceleration. | − | West syndrome associated with infantile spasticity and Lennox–Gastaut syndrome | 37195288 |
| P8 | F | 14 | c.1159-1160del | − | + | + | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | Lamotrigine, VNS | Generalized 3 Hz spikes and waves during sleep | Sleep apnoea | Generic EP/seizures with myoclonic absence | 37195288 |
| P9 | M | 1.5 | c.12881G >A | − | + | + | + | + | − | + | − | − | − | Oxcarbazepine | Multifocal, mainly central (parietal lobe) spines | Aggressive behaviour | Focal EP with focal motor seizures (clonic and myoclonic) with impaired consciousness | 37195288 |
| P10 | F | 1.6 | c.10768G>T | − | + | + | + | + | − | + | − | − | − | − | Focal central spike | Aggressive behaviour | Focal EP with focal motor seizures (clonic and myoclonic) with impaired consciousness | 37195288 |
| P11 | M | UK | c.3632-3633del | UK | UK | UK | + | UK | UK | − | + | UK | UK | UK | UK | − | UK | 37195288 |
| P12 | F | UK | c.-288710-8555700del | UK | UK | UK | UK | UK | UK | − | + | UK | UK | UK | UK | Severe feeding difficulties | UK | 37195288 |
| P13 | F | UK | c.-65884-2476923del | UK | UK | UK | UK | UK | UK | − | + | UK | UK | UK | UK | − | UK | 37195288 |
| P14 | M | UK | c.7360-7361delTCinsA+ | UK | UK | UK | UK | UK | UK | − | − | UK | UK | UK | UK | Aggressive behaviour | UK | 37195288 |
| P15 | M | UK | c.862C>T | UK | UK | UK | UK | UK | UK | − | + | UK | UK | UK | UK | UK | 37195288 | |
| P16 | M | 13.5 | c.3007C>T (exon27 NM_001148)p.R1003*,2955 | + | + | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | Clonazepam; perampanel; oxcarbazepine | Background rhythm is poor, fast waves increase, multifocal slow waves, and multiple slow waves in the waking and sleeping periods in the right frontal lobe | Pyogenic gingivitis; self-injury behaviour | EP (focal seizures) | This study |
- Abbreviations: ADHD, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder; DD, developmental delay; ID, intellectual disability; LCA, low cognitive ability; LLD, language and learning disabilities; LMA, low memory ability; MD, mood disorders; PH, pharmacy; UK, unknown.
| Parameter | Yes | No | χ 2 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Man | 9 (60.00) | 6 (40.00) | 1.200 | 0.273 |
| Woman | 6 (40.00) | 9 (60.00) | |||
| Developmental delay and intellectual disability | Yes | 5 (45.45) | 6 (54.54) | 0.182 | 0.670 |
| No | 6 (54.54) | 5 (45.45) | |||
| Language and learning disabilities | Yes | 11 (100.00) | 0 (0.00) | 20.000 | 0.000* |
| No | 0 (0.00) | 11 (100.00) | |||
| Poor language and communication skills | Yes | 11 (100.00) | 0 (0.00) | 20.000 | 0.000* |
| No | 0 (0.00) | 11 (100.00) | |||
| Anxiety, agitation, and mood disorders | Yes | 6 (54.50) | 5 (45.50) | 0.182 | 0.670 |
| No | 5 (45.50) | 6 (54.50) | |||
| Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder | Yes | 5 (50.00) | 5 (50.00) | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| No | 5 (50.00) | 5 (50.00) | |||
| Low cognitive memory and adaptability | Yes | 1 (10.00) | 9 (90.00) | 12.800 | 0.000* |
| No | 9 (90.00) | 1 (10.00) | |||
| Epilepsy | Yes | 10 (76.92) | 3 (23.08) | 7.538 | 0.006* |
| No | 3 (23.08) | 10 (76.92) | |||
| ASD | Yes | 9 (69.23) | 4 (30.77) | 3.846 | 0.049* |
| No | 4 (30.77) | 9 (69.23) | |||
| Tic disorder | Yes | 1 (10.00) | 9 (90.00) | 12.800 | 0.000* |
| No | 9 (90.00) | 1 (10.00) | |||
| ECG abnormalities and cardiac damage | Yes | 1 (10.00) | 9 (90.00) | 12.800 | 0.000* |
| No | 9 (90.00) | 1 (10.00) | |||
| Electroencephalogram abnormalities | Yes | 9 (90.00) | 1 (10.00) | 12.800 | 0.000* |
| No | 1 (10.00) | 9 (90.00) | |||
- * p < 0.05 is considered statistically significant.
Therefore, when we find that the main manifestation of autism combined with epilepsy, intellectual development disorders, behavioral abnormalities, and EEG abnormalities in the clinic, we must not let go of the possibility of ANK2 gene mutation.
3 Discussion
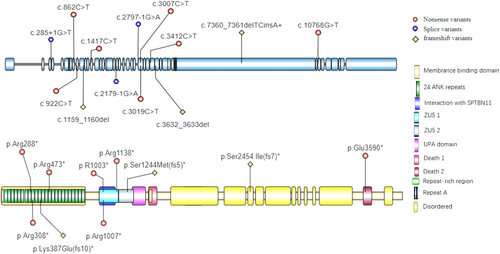
The ankyrin protein family includes ankyrin-R (AnkR), ankyrin-B (AnkB), and ankyrin-G (AnkG) (Sucharski et al. 2020; Bennett and Stenbuck 1979), which are encoded by ANK1, ANK2, and ANK3, respectively (Otto et al. 1991; Lambert et al. 1990). AnkR is important for maintaining the structural integrity and organization of red blood cell (RBC) membranes. Loss-of-function variants in ANK1 are associated with approximately 50% of hereditary spherocytosis cases and are characterized by abnormal shaping and fragility of RBCs (Narla and Mohandas 2017). ANK2 is highly conserved and can be expressed in multiple organs, especially in the brain, heart, and kidney. ANK2 has two major transcripts that produce 220-kDa (normal) and 440-kDa (giant) proteins. The 220-kDa AnkB protein has two isoforms, AnkB-188 and AnkB-212, both of which exhibit similar and unique patterns of alternative splicing: exons 7, 24, 30, and 40 are removed in both isoforms; exons 28, 38, and 46–50 are removed in AnkB-18; and exons 12–13 and 17 are removed in AnkB-212 (Sucharski et al. 2020; Wu et al. 2015). The 440 kDa AnkB protein is the result of the insertion of a 6.4-kb exon between the spectrin-binding domain (SBD) and death domain (DD). AnkG plays an important role in various excitable tissues. The expression and localization of βIV spectrin and NaV 1.5 were disrupted in mouse cardiomyocytes lacking AnkG, leading to a significant reduction in voltage-gated NaV channel activity. These mice exhibited a decreased heart rate, impaired atrioventricular conduction, increased PR interval, and increased QRS interval (Sato et al. 2011; Makara et al. 2014). ANKB, as well as other ankyrins, consists of four main domains: a membrane-binding domain (MBD), an SBD, a DD, and a C-terminal domain (Figure 3B). The MBD contains 24 consecutive ANK repeats and can interact with membrane proteins such as ion channels and transporters. The SBD contains highly conserved ZU5-ZU5-UPA domains and can interact with βII-spectrin. The function of the DD is still unknown, but reports in the literature suggest that it plays a role in cell apoptosis and inflammation (Park et al. 2007). The DD and C-terminal domain together constitute the regulatory domain, which can directly bind to the MBD and have inhibitory effects (Abdi et al. 2006; Xie et al. 2022).
Although AnkB and AnkG have similar structures, they are associated with different diseases. The specificity of ankyrins is partly determined by the autoinhibitory linker peptide between the MBD and SBD, which prevents AnkB from binding to molecular chaperones (He et al. 2013).
AnkB is widely expressed in both excitatory and inhibitory neurons of the brain, as well as in glial cells (Saunders et al. 2018; Jin et al. 2020). AnkB is considered an axon protein because it is highly concentrated in the axon initial segment (AIS), Ranvier node (NOR), and axon terminals. Within axons, it participates in the transport of organelles, including synaptic vesicles. At the AIS and NOR, AnkB interacts with multiple calcium channels, IP3R, and ion transport proteins (Yoon et al. 2023). Studies investigating the loss of ANK2 function suggest that it is associated with axonal morphology, connectivity, and calcium signaling in excitatory neurons (Yoon et al. 2023; Kline et al. 2014).
Loss of AnkB in mice causes severe neurological defects, such as hypoplasia of the corpus callosum and pyramidal tract and lateral ventricle dilatation (Scotland et al. 1998). Yoon et al. (2023) reported that changes in the synaptic proteome caused by the loss of ANK2 impair neuronal activity and synchrony, leading to behavioral disorders associated with NDDs. Yang et al. (2019) elucidated a mechanism that typically restricts axonal branching: giant AnkB is localized to the periodic axonal plasma membrane domain through its interaction with the L1 cell adhesion molecule protein (L1CAM). This interaction allows AnkB to couple microtubules to the plasma membrane and prevents microtubules from entering nascent axon branches (Chen et al. 2020; Fransen et al. 1997). Furthermore, several studies have suggested that ANK2 mutants exhibit dysregulated intracellular calcium homeostasis and altered expression of calcium channels in excitatory neurons (Yoon et al. 2023; Kline et al. 2014). Homologues of ankyrin proteins are known to interact with ion channels in various types of neurons (Tseng et al. 2015). Loss of AnkB has been shown to lead to decreased expression of voltage-gated calcium channel 2.1 (Cav 2.1) compared to voltage-gated calcium channel 2.2 (Cav 2.2) in the cortex, cerebellum, and brainstem. ANK2 mutations may be associated with seizures (Choi et al. 2019).
We identified a nonsense mutation, c.3007C>T, p.R1003*, in the patient. This mutation results in an amino acid change from Arg to Ter at position 1003 of AnkB, leading to the production of a truncated protein that lacks the subsequent 2955 amino acids due to abnormal translation; this mutation may cause nonsense-mediated decay (NMD) or may prevent interaction with L1CAM, thus preventing the inhibition of axonal growth. Therefore, we propose that this variant is a strong candidate for explaining the patient's clinical phenotype. Additional published data are needed to further support the correlation between the variant and the phenotype (Ji et al. 2019). Other reported variants of the ANK2 gene are shown in Figure 3A.
4 Conclusion
ANK2 gene variants have rarely been reported; to date, only 15 patients have been reported worldwide. Our patient is the 16th patient and the first such patient reported in China. We also summarized the genetic and disease spectra of all 16 patients. ANK2 variants were associated with a series of phenotypes: ASD (9/16 patients); EP (10/16 patients); ASD with EP (4/16 patients); developmental delay and intellectual disability (5/16 patients); poor language communication skills and language and learning disabilities (11/16 patients); abnormal behavior problems (11/16 patients, including anxiety, agitation, mood disorders, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, TD, sleep disorder, self-injury and aggressive behaviour); poor cognition, memory, and adaptability (1 patient); ECG abnormalities and cardiac damage (1 patient); and abnormal EEG results (9 patients). Prompt performance of genetic testing is important for patients with EP in ASDs with intellectual disability, behavioral abnormalities, and EEG abnormalities. ANK2 mutations should also be considered when an exon 27 mutation is detected. There are no specific guidelines or consensus on the treatment of neurological diseases associated with the ANK2 gene. For children experiencing seizures, it is important to develop individualized treatment plans based on factors such as seizure type, EEG, and craniocerebral imaging. For children diagnosed with ASDs, appropriate psychological and behavioral interventions or pharmacological treatments should be implemented according to the corresponding diagnosis and treatment guidelines. For individuals with intellectual disability, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, or TD, it is crucial to conduct prompt evaluations and implement active intervention measures. When necessary, rehabilitation training can be provided to support their needs. In conclusion, ANK2 is a novel gene associated with EP and related neurological disorders, primarily manifesting as ASDs, intellectual development disorders, behavioral abnormalities, and electroencephalogram abnormalities. Genetic testing should be promptly conducted to elucidate the underlying cause, and ANK2 gene mutations should be considered.
Author Contributions
Lu Zhao and Zhi-Dong Qiao wrote the article; Yue-Xin Jia, Jun-Xian Fu, and Tian-Xia Li edited the data; Kai-Ru Jia, Xiao-Fan Yang, and Hao Pan collected the data; Hong Zhao and Jin-Ping Bao improved and modified the article; and Guang-Lu Yang, as the corresponding author, gave comprehensive guidance to the writing of the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the patient and his family who shared the case, and all those who contributed to the data of our team.
Ethics Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the declaration of Helsinki and from the Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University (No. WZ[2024002]).
Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the participant.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request from the authors. The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.




