Evaluation of NaTto Red Yeast Rice on Regulating Blood Lipid (ENTRY) Study: A Multicenter, Double-Placebo, Double-Blinded, Randomized Controlled Trial in Chinese Adults
Shufeng Chen and Fangchao Liu contributed equally to this study.
ABSTRACT
Background
Statins are the first line of treatment for dyslipidemia, but their side effects often reduce medication compliance. Natto and red yeast rice are natural ingredients with lipid-lowering effects. However, the efficacy of Natto Red Yeast Rice (NRYR) supplement in combination with statins in regulating blood lipid levels has not been fully evaluated.
Methods
A multicenter, double-blinded, randomized-controlled trial was conducted among individuals with low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) of 3.4 to 5.0 mmol/L at six sites in China, of those at moderate risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) are prioritized. Participants are enrolled and randomly assigned into four groups by a combination of NRYR (or its placebo) and Simvastatin (or its placebo) in a ratio of 1:1:1:1. After examination at baseline, all participants underwent intervention for 3 months and two follow-up visits at 1 month and 3 months after the intervention. The primary outcome is the change in LDL-C level at 3 months, and secondary outcomes include changes in levels of other lipid profiles and biomarkers, as well as calculated 10-year CVD risk. A total of 1136 participants were randomly assigned, of whom 1110 received the intervention.
Discussion
This study may provide new evidence for the efficacy of NRYR supplement in combination with statins to regulate lipid levels and optimize lipid management.
Trial Registration
Chinese Clinical Trial Registry database: registration nos. ChiCTR2200064214, ChiCTR2200064215.
Summary
-
The control rate of dyslipidemia is not satisfactory in Chinese population, and whether dietary supplements may improve the management of blood lipids is unclear.
-
The present study aims to evaluate the efficacy of Natto Red Yeast Rice (NRYR) supplement in combination with statins in regulating blood lipids, especially in individuals with mild or moderate elevated cholesterol levels using a multicenter, double-blind, randomized parallel-controlled trial.
-
This study may provide evidence on the potential role of NRYR supplement in regulation of lipid levels and management of dyslipidemia.
1 Introduction
Dyslipidemia, especially hypercholesterolemia, is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD) in China and globally [1, 2]. It is estimated that elevated total cholesterol levels in the population are expected to lead to approximately 9.2 million additional cardiovascular events in China from 2010 to 2030 when other risk factors maintain a stable prevalence trend [3]. Meanwhile, the prevalence of dyslipidemia in the Chinese population has increased significantly, reaching 35.6% in 2018 [4]. Yet, the awareness, treatment, and control rates of hyperlipidemia in China remain alarmingly low, standing at just 16.1%, 7.8%, and 4.0% in 2015, respectively [4, 5]. It is urgent to take effective measures to control blood lipid levels and reduce the burden of CVD.
Statins, as the first-line clinical treatment for dyslipidemia recommended by guidelines, are proven to effectively lower blood cholesterol levels, and significantly reduce the incidence, and mortality of CVD [6-8]. Nevertheless, recent studies indicated that about 9% of the patients may have statin intolerance, experiencing issues such as muscle symptoms and hepatotoxicity [9, 10]. Notably, adverse effects like elevated liver transaminase and muscle symptoms are more prevalent in the Chinese population, leading to decreased adherence to statin therapy and increased discontinuation rate [11, 12]. In response, the National Lipid Association (NLA) issued a scientific statement advising lower statin dose or use of non-statin therapies to solve the problem [13]. Thus, other well-tolerated lipid-lowering drugs or supplements are urgently needed.
Red yeast rice is a nutraceutical obtained by the fermentation of Oryza sativa with Monascus purpureus [14]. Monacolin K, a natural compound present in red yeast rice, acts as an inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase, sharing the same chemical structure as the active composition in lovastatin, and has been reported to have good lipid-lowing effects in people with dyslipidemia [15-17]. Natto contains nattokinase, a serine endopeptidase that may exert a thrombolytic effect [18, 19]. Previous studies have provided several laboratory evidence of nattokinase for lipid reduction, while evidence from population studies is still limited [20-23]. In addition, a few studies investigated the combined effects of red yeast rice and natto [17, 23-26]. However, it is generally advised against completely substituting statins with alternative non-statin therapy in clinical practice [13]. At present, very few studies have explored the lipid-lowering effect of monascus combined with statins, but these studies have limitations of small sample size, retrospective design, and large population heterogeneity [17, 27-29]. Therefore, it is unclear whether and to what extent Natto Red Yeast Rice (NRYR) supplements have an enhancing effect with statins, and large-scale randomized controlled trials are required.
Therefore, we aim to perform a multicenter, double-blind, randomized parallel-controlled trial to investigate the effect of NRYR (1950 mg) combined with Simvastatin (20 mg) on blood lipids levels among patients with dyslipidemia and moderate atherosclerotic CVD (ASCVD) risk, so as to evaluate its potential role in management of dyslipidemia and primary prevention of CVD.
2 Methods
2.1 Study Design
The Evaluation of NaTto Red Yeast Rice on Regulating Blood Lipid (ENTRY) Study is a multicenter, double-blind, randomized parallel-controlled trial conducted in six sites in China, including Nangong and Tangshan (Hebei province), Fenyang (Shanxi province), Shenzhen (Guangdong province), Fuzhou (Fujian province), and Shenyang (Liaoning province). After screening by questionnaire and blood sampling, eligible individuals are randomly assigned to one of the four intervention arms: (1) NRYR placebo combined with Simvastatin placebo, (2) NRYR combined with Simvastatin placebo, (3) NRYR placebo combined with Simvastatin, and (4) NRYR combined with Simvastatin. All eligible individuals are randomly assigned into four groups in 1:1:1:1 ratio. Following a baseline assessment, all participants underwent a 3-month intervention. In addition to the baseline examination, follow-up visits are conducted at 1 month and 3 months after intervention. Participants who are taking nutritional supplements (specifically red yeast rice products) at screening are required to complete a 4-week washout period before the intervention. The flow chart of the study is presented in Figure 1.
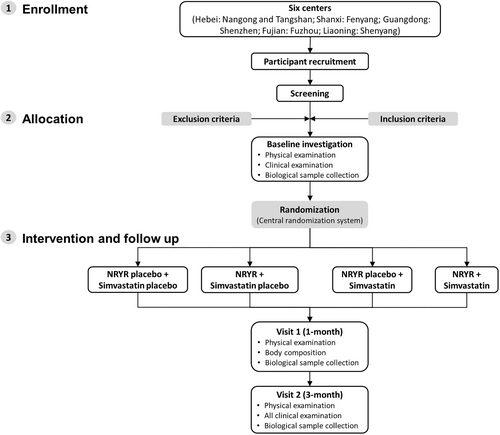
This study is conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Participants can voluntarily withdraw from the present trial at any time for any reason, and may be terminated by the investigator due to safety concerns or failing to meet the inclusion/exclusion criteria. This protocol has been approved by the Ethics Committee of Fuwai Hospital (Approval No.: 2020-1375) and Southern University of Science and Technology (Approval No.: 20210149), and registered in the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry database (registration numbers: ChiCTR2200064214, ChiCTR2200064215) (http://www.chictr.org.cn). All participants signed written informed consents before the screening.
2.2 Study Population and Eligibility Criteria
Individuals with elevated or borderline elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels are recruited from local residents who have lived for more than 6 months and will continue to reside for the next 3 months [30]. Individuals at a moderate level (5%–10%) of 10-year ASCVD risk are preferentially enrolled [30, 31]. Specific inclusion and exclusion criteria are presented in Table 1.
| Inclusion criteria |
|
| Exclusion criteria |
|
- ASCVD, atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
2.3 Recruitment and Screening
Among community residents and outpatients at local hospitals, a preliminary screening for eligible participants is conducted based on personal disease history and family history. Subsequently, a screening investigation is conducted, which included a questionnaire interview regarding demographic information, smoking status, personal medical history, and family history; physical examination of body height, weight, waist circumference, and blood pressure (BP); and biochemical detection of fasting blood lipids, glucose, creatinine, creatine kinase and so on.
2.4 Randomization and Blinding
Enrolled participants are randomly assigned to one of the four intervention groups through an online central randomization system, with a block size of 8. Specifically, an independent statistician generated random codes and allocation results using SAS software, which are then embedded in an Interactive Web Response System (IWRS). After enrollment, each participant is assigned a unique random code via IWRS. The allocation results for each participant are securely kept by the independent statistician in separate sealed envelopes, which are provided to the researcher in case of an emergency. Throughout the study period, participants, researchers, and study supervisors are blinded to the group allocation and treatment.
2.5 Intervention Program
Simvastatin tablets used in this trial are manufactured by Merck Sharp & Dohme limited (United Kingdom) and contain 20 mg of Simvastatin per tablet. NRYR capsules are manufactured by By-Health Co. Ltd, and 325 mg per capsule. Subsequently, following a standard process, placebo with the same appearance and smell are produced and packaged. Drug packers prepared drugs according to the drug code provided by the independent statistician. Repackaging of Simvastatin and accompanying placebo tablets, and NRYR capsules and accompanying placebo capsules, are provided directly to the local sites by By-Health Co. Ltd. After the randomization, participants received Simvastatin (20 mg) (or placebo) (one tablet once a day at bed-time), and NRYR (1950 mg) (or placebo) (three capsules twice a day, after breakfast and dinner) for 3 months, under the supervision of a physician.
Throughout the study period, all participants are required to maintain a daily Medication Log to record both prescribed and over-the-counter medications during the 3-month intervention period. All participants are not allowed to use any lipid-lowering medications other than the drug provided in this study.
2.6 Data Collection, Management, and Quality Control
Research data are obtained through face-to-face questionnaire interview, physical examination, clinical examination, biological detection, as well as adverse event records. The study schedule is shown in Table 2.
| Items | Screening stage | Investigation stage | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Visit 1 (1 month) | Visit 2 (3 months) | ||
| Informed consent | √ | |||
| Study inclusion and exclusion questionnaire | √ | |||
| Randomization | √ | |||
| Questionnaire interview | √ | √ | √ | |
| Physical examination | ||||
| Body height | √ | √ | √ | |
| Body weight | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Waist circumference | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Hip circumference | √ | √ | ||
| Blood pressure | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Clinical examination | ||||
| 24-h ambulatory blood pressure monitoring | √ | √ | ||
| Body composition | √ | √ | √ | |
| 12-lead electrocardiogram | √ | √ | ||
| Arterial stiffness | √ | √ | ||
| Carotid artery ultrasound | √ | √ | ||
| Ultrasonic cardiogram | √ | |||
| Biological sample collection | ||||
| Blood | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Urine | √ | √ | √ | |
| Stool | √ | √ | √ | |
| Biochemical test | √ | √ | √ | |
| Smart bracelet monitoring | √ | √ | √ | |
- ENTRY, Evaluation of NaTto Red Yeast Rice on Regulating Blood Lipid.
2.6.1 Questionnaire Interview, Physical Examination, and Clinical Examination
A standard questionnaire is used to collect data on demographic information, personal medical history, menstrual history (women only), smoking status, alcohol consumption, dietary behavior, and physical activity information. Body height, weight, waist and hip circumference, and BP are measured according to standardized procedures. Body mass index (BMI) is calculated for each participant based on body weight and height. Body composition, 24-h ambulatory BP monitoring, electrocardiogram (ECG), arteriosclerosis parameters are also measured. Carotid plaque, intima-media thickness (IMT), and stenosis are evaluated using color Doppler ultrasonic diagnosis system in accordance with established standard.
2.6.2 Biological Sample Collection and Detection
Overnight fasting blood samples are drawn by trained professionals at each visit and processed within 3 h of collection, and serum and plasma are separated. Urine and stool samples are also collected. All samples are frozen at the field center until transported to the central laboratory that participated in the Lipid Standardization Program of the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. All biochemical indicators are tested in accordance with standard procedures using the Beckman Coulter AU680 Chemistry Analyzer. LDL-C and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) are determined by the direct surfactant method with reagents produced by Minaris Medical Co. Ltd. Other biochemical indices (including other lipid indicators, glucose, creatinine, liver transaminase, creatine phosphokinase [CK]) are determined using the direct surfactant method with reagents produced by BioSino Bio-Technology and Science Inc. Double serum samples with known concentration (high value and low value) are detected in parallel, and the intra- and inter-assay coefficients of variation are calculated for quality control.
2.6.3 Safety Assessment
Safety assessment is based on clinical signs and symptoms, physical examination, findings from electrocardiogram and laboratory test, as well as the type and severity of adverse events recorded throughout the study. Laboratory tests include alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), creatinine, and creatine kinase. Significant deviations from the normal range in laboratory test results are also considered as adverse events. All adverse events are required to be documented in detail in the case report form (CRF). Researchers should take appropriate measures according to the situations and continue to follow up until symptoms disappear or examination indicators become normal. During the trial period, any serious adverse event that results in hospitalization, serious or permanent disability, impaired ability to work, life-threatening or death should be reported in accordance with regulations [32].
2.6.4 Data Management and Quality Control
Before the start of the trial, all researchers and staff in the study sites completed a training program and passed the exam. All data from this trial are recorded in the original CRF and then entered twice independently into the electronic database. Researchers at each site regularly summarize their work, give feedback, and solve problems. Clinical researchers periodically review the data to identify and correct any potential omissions or errors. Independent statisticians check data consistency, range, and adherence to logical rules within the database from the electronic data capture (EDC) system. Any traces of modification are retained.
2.7 Outcomes
In this study, the primary outcome is the change in the LDL-C level over a 3-month period. The secondary outcomes include changes in other lipid profiles [TC, triglyceride (TG), HDL-C, non-HDL-C, small dense LDL-C (sdLDL-C), apolipoprotein A1 (apoA1), apolipoprotein B (apoB), apolipoprotein E (apoE), and lipoprotein (a)] and 10-year risk of ASCVD.
Safety outcomes comprise elevated liver transaminase (with ALT and/or AST levels greater than three times the upper limit of the reference range), elevated serum creatinine (> 133 μmol/L), obvious symptoms of liver and muscle (including hepatalgia, myalgia, myositis, hemoglobinuria, muscle discomfort, and/or weakness) and/or elevated serum CK (greater than five times the upper limit of the reference range), gastrointestinal symptoms (abdominal pain, diarrhea and/or indigestion). In addition, participants are asked to report any adverse experience throughout the trial period. And then, physician evaluates the necessity of statin dosage adjustment or discontinuation based on individual clinical conditions and reports to the Adverse Event Review Committee in compliance with established protocols.
2.8 Sample Size Calculation
The estimation of sample size is based on the average LDL-C level after the intervention. The primary hypothesis is that NRYR exhibits lipid-lowering effects compared to placebo. The second hypothesis is that NRYR interacts with Simvastatin in regulating blood lipid profiles. For the primary hypothesis, given that the difference in the average reduction of LDL-C level between placebo group and NRYR group after 3-month interventions is 0.3 mmol/L [33, 34], the estimated sample size of each group is 235 under a two-tailed significance level of 5% and a power of 0.90 set. Taking into account a 20% dropout rate, a minimum of 294 participants are needed in NRYR or placebo group. Thus, a total of 588 individuals are required for two groups of this trial. Similarly, for the second hypothesis, given that the difference in the average reduction of LDL-C level between double placebo group and Simvastatin combined with NRYR group after 3-month interventions is 0.8 mmol/L, the estimated sample size of each group is 198 when further considering interaction between Simvastatin and NRYR under a two-tailed significance level of 5% and a power of 0.90 set. Taking into account a 20% dropout rate, a minimum of 248 participants are needed in each group. Thus, a total of 992 subjects are required for four groups of this trial.
2.9 Drug Distribution and Compliance Monitoring
Monthly medications for each participant are placed in a separate box and dispensed by the drug administrator according to a random number. Participants get their medications monthly and fill in the Medication Log cards. Medication compliance might affect the results of the trial, so the leftover medication is required to be returned at the next visit. Adherence to treatment is determined by pill counting. Good adherence is considered if the participant took ≥ 80% of the provided supplements or medications [35]. For participants who fail to take medication as required, the reasons are carefully documented and appropriate guidance is provided by the research team.
2.10 Statistical Analysis
No interim analyses are planned or conducted for this trial. The statistical analyses of the primary and secondary outcomes will be conducted following the intention-to-treat (ITT) principle. Descriptive analyses will be used to summarize the demographic data and basic characteristics of the participants. Continuous variables will be presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) or median with interquartile range (IQR), and categorical variables will be presented as number and frequency. Generalized linear mixed models will be used to evaluate the effects of interventions. Subgroup analyses take into account factors such as age, sex, living region, socioeconomic status, lifestyle factors, BMI, and so on. In the sensitivity analyses, missing data will be processed through chained multiple imputation [36], producing five imputed datasets. The final estimates will be combined in accordance with Rubin's rules [37]. The per-protocol set (PPS) analysis will be carried out among participants who maintained full compliance during the trial period. Statisticians are blinded to the group allocation of the participants. The analyses will be performed using SAS (V9.4 SAS Institute Inc. Cary NC, USA) and R software (V4.0.2 R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria). A two-tailed p < 0.05 is considered as statistically significant for all tests.
2.11 Monitoring and Inspection
In this study, a coordination center and a steering committee are set up to design the protocol, coordinate the study implementation, and supervise the process. An Independent Data Monitoring Committee (IDMC) is established to monitor the progress in data collection and quality control during the trial to ensure the validity and integrity of the data. Additionally, an Adverse Event Review Committee to review and judge each recorded adverse event, and report those meeting the criteria of adverse event to the Ethics Committee.
3 Participants Recruitment and Randomization
Among 1136 participants in this study, 285 participants were randomly assigned to the NRYR placebo combined with Simvastatin placebo group (Placebo), 284 participants to the NRYR combined with Simvastatin placebo group (NRYR), 283 participants to the NRYR placebo combined with Simvastatin group (Simvastatin) and 284 participants to the NRYR combined with Simvastatin group (NRYR plus Simvastatin). Among them, 26 participants (7 in placebo group, 9 in NRYR group, 4 in Simvastatin group, and 6 in NRYR plus Simvastatin group) did not take the provided supplement or medication, leaving 1110 participants for the primary analysis.
4 Discussion
Due to the high incidence and mortality of hyperlipidemia and the consumption of medical resources, the control of hyperlipidemia is an important measure for CVD primary prevention [6]. In recent years, NRYR supplement has attracted more attention as an effective, safe, and economical alternative tool for lowering serum cholesterol, but studies are currently limited and results remain inconsistent [34].
A randomized double-blind study of 47 patients with dyslipidemia showed that after 6 months of nattokinase combined with red yeast rice, TC, LDL-C, and TG decreased by 25%, 41%, and 15%, respectively, and HDL-C increased by 7.5% [26]. Another randomized controlled trial involving 113 participants found that the nattokinase-monascus supplement significantly reduced TC and LDL-C levels, while there were no siginificant changes in the levels of TG, HDL-C, and carotid IMT [25]. Notably, these studies had small sample sizes and limited evaluation indices, and no studies have evaluated the lipid-lowering effects of NRYR supplement combined with statins. Thus, we conducted this randomized, double-blind, parallel-controlled trial to evaluate the effect of NRYR supplement combined with statins on the lipid profile, aiming to fill the gaps in the current research.
To our knowledge, this is the first randomized controlled trial to investigate the lipid-lowering effect of NRYR supplement combined with statins in the Chinese population. This study has several advantages, such as a multi-center design, a large sample size, and strict quality control. Additionally, multi-dimensional indices, including laboratory, imaging, and various biological samples, enable a more comprehensive and detailed evaluation of intervention efficacy. The present study is able to compare the combined and independent effects of statins and supplement, providing more evidence for clinical applications. This study has several limitations. First, the intervention duration of this trial is only 3 months, and the long-term effects of the treatment may require to be further evaluated. Second, the molecular mechanism of natto and red yeast rice needs to be further explored. Finally, this study is limited to assessing changes in blood lipid level, serving as an initial exploration for future research on the potential of NRYR supplement in the prevention and treatment of CVDs.
In summary, this study evaluates the effect of NRYR supplement combined with statins on lipid levels among individuals with dyslipidemia. The findings could provide a new idea for the lipid-lowering measures in population with dyslipidemia, and promote the primary prevention of CVD.
Author Contributions
Shufeng Chen: investigation, data curation, manuscript writing, and revision. Fangchao Liu: supervision, methodology, manuscript writing and review, and revision. Jinyue Li: investigation, data curation, visualization, and manuscript writing. Fengchao Liang: data curation, supervision, methodology, and manuscript revision. Jianxin Li: investigation and data curation. Jie Cao: investigation and data curation. Donghua Liu: data curation. Keyong Huang: methodology and manuscript review. Hongfan Li: investigation. Xiangfeng Lu: supervision, funding acquisition, and manuscript revision. Jianfeng Huang: conceptualization, methodology, supervision, and manuscript review. Dongfeng Gu: conceptualization, methodology, supervision, funding acquisition, and manuscript revision. The final manuscript was approved by all authors.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge all participants for their contribution and collaboration to this study. Thanks to BYHEALTH for providing Natto Red Yeast Rice.
Ethics Statement
This protocol has been approved by the Ethics Committee of Fuwai Hospital (Approval No.: 2020-1375) and Southern University of Science and Technology (Approval No.: 20210149). All participants signed written informed consents before the screening.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors declared no conflicts of interests. The trial is partly funded by BYHEALTH Institute of Nutrition and Health, but they did not involve in the study design and study implementation. Professor Dongfeng Gu and Xiangfeng Lu are members of Chronic Diseases and Translational Medicine editorial board and are not involved in the peer review and decision process of this article.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The authors have nothing to report.




