Review and Bibliographic Analysis of Metaheuristic Methods in Multicriteria Decision-Making: A 45-Year Perspective Across International, Latin American, and Colombian Contexts
Abstract
This study performs a systematic review and analysis of research on the use of multicriteria decision analysis (MCDA) methods for more than 45 years. More than 34,468 documents related to MCDA were identified in more than 130 countries, with an annual increase of 14.15% in scientific production. India, China, and Iran lead in number of publications, covering about 35%. The universities with the most publications include Islamic Azad University and Vilnius Gediminas Technical University. The main journals in this field are Expert Systems With Applications, Sustainability, and Journal of Cleaner Production. The most prolific authors are Zavadskas, E.; Wang, J.; Tzeng, GH; Zavadskas, EK; and Kahraman, C. The most popular methods are TOPSIS, AHP (analytic hierarchy process), VIKOR, PROMETHEE (Preference Ranking Organization Method for Enrichment Evaluation), and ANP. LATAN, which includes countries such as Brazil, Chile, and Mexico, has increased the use of MCDA in recent years. Colombia has also shown a great interest in MCDA, especially in the selection of alternative energy sources and industrial suppliers. This method of literature review provides a comprehensive overview of research at MCDA and offers valuable information for future projects and studies.
1. Introduction
The imminent climate change brought with it the invention of thousands of alternatives to mitigate it and/or take advantage of the renewable resources that our planet brings us as much as possible without the need to pollute it or do it as little as possible [1, 2]. Specifically in the electricity sector, the energy transition is a global fact. In first-world countries, nonconventional energy sources can be seen in large solar or wind farms. Additionally, the implementation of new laws full of incentives and agreements is aimed at encouraging both large and small generators of coal, natural gas, LPG, and other fuels to adopt these alternatives, with the goal of mitigating climate change and making the most of existing oil reserves [3]. However, the path of renewable energy sources still has a long way to go in terms of efficiency, savings, and energy quality [4].
It is of global interest to study all these ecological alternatives in energy because significant amounts of scientific articles on the subject are issued daily in multiple academic journals. Hence, analyzing each of these is almost entirely tricky, hindering the resolution of problems knowing that it involves several competing points of view that must be considered to reach a reasonable decision. Thus, bibliometrics plays a primary role and is an essential tool in the analysis of new knowledge [5], serving as support for decision-making and research direction and better designating economic resources with a measurable base, and also contributes to the excellent prestige of the researcher, thus encouraging the dynamism of research [6].
The importance of bibliometric studies lies in the help that they can provide to assess the current state of science and support decision-making and research direction through their multidisciplinary nature, including statistics, sociology, and computer science, thus representing an instrument for evaluating scientific production and a way to improve and bring excellence to higher levels [7]. In this way, it contributes to the decision-making methods that, in some cases, can be crucial in the direction of companies, economies, and even the very lives of people. Selecting the one with the most minor negative impacts is vitally important. Therefore, if the results matter, then the selection of decision-making methods should also matter even more [8].
Multicriteria decision analysis (MCDA) is a set of methods that, explicitly and systematically, allows additional criteria to be considered, selecting the option with the most significant impact, classifying the alternatives, and ordering the proposed decisions from best to worst [9]. Therefore, this allows the development of a decision-making process with a more holistic, orderly, transparent, and explicit perspective of the different and multiple criteria, making explicit the values or dimensions and their relative importance in this process [10].
MCDA methods are multidisciplinary and can be seen in pharmaceuticals, statistics, business, health technologies, global warming, grid selection, and new electrical projects [11]. Currently, there are different software aimed at performing these types of bibliometric analyses, obtaining graphic results, improving the researcher’s interpretation, and, therefore, directing him to make a decision [12].
This research describes that decision-making is necessary for all human activities based on evaluating the decision-maker’s individual choices, preferences, experience, and other data [13]. Some decisions are simple, while others are complex and must consider multiple competitive viewpoints to arrive at a reasonable decision. In practice, MCDA is used to evaluate possible courses of action or options and select a preferred option or order options from best to worst, which is critical for allocating finite resources between competitive and alternative interests [14].
There are different terms to describe multicriteria decision-making (MCDM) methods, such as MCDA, MCDM, multiobjective decision-making (MODM), or multiattribute decision-making (MADM) [15]. According to this research, the most commonly used MCDA approaches can be divided into two “schools”: the American and the European [16]. The American school is based on a functional approach and employs techniques such as MAUT, AHP (analytic hierarchy process), ANP, SMART, UTA, MACBETH, and TOPSISS. The techniques of the European school are based on a relational concept and use a synthesis of criteria based on overcoming relationships, such as the ELECTRE (Elimination Et Choix Traduisant la Réalité) and PROMETHEE (Preference Ranking Organization Method for Enrichment Evaluation) groups, and other methodologies such as NAIADE, ORESTE, REGIME, ARGUS, TACTIC, MELCHIOR, and PAMSSEM [17].
In addition, there are several areas in which MCDA methods such as information and communication technology, business intelligence, environmental risk analysis, environmental impact assessment and environmental science, water resources, and solid waste management [18] remote sensing, flood risk management, health technology assessment, transport, nanotechnology research, climate change, energy, international law and policy, human resources, financial management, supplier selection, e-commerce and mobile, agriculture and horticulture, chemical and biochemical engineering, software evaluation, network selection, education and social policy, and small-scale energy management and public safety systems [19].
This study is aimed at presenting a vision of the use of decision methods in Latin America compared to the utility applied in the rest of the world in the field of renewable energies.
A number of 34,468 documents were obtained between the years of 1977 and 2023, of which more than 4000 were published in 2022, an average of 70.8% were scientific articles, of which the National Natural Science Foundation of China sponsored 1071 and obtaining India as the leading exporter of multicriteria method research with a total of 3282 documents; all these data were obtained through the analysis of results obtained in the Scopus database, a website that offers access to databases and citation data in life sciences, social sciences, physical sciences, and health sciences [20]. Elsevier provides access to Scopus, and a subscription is required. It covers three types of sources: series of books, magazines, and specialized magazines. In addition, the searches carried out in Scopus also incorporate searches in patent databases, and the Web of Science (WOS) database highlights a total of 12,339 scientific articles related to the subject of study and highlights the participation of the National Natural Science Foundation of China as the main sponsor of studies related to decision methods. This database, like Scopus, is an online scientific information service, provided by Clarivate Analytics, integrated into ISI Web of Knowledge. Later, a compilation of the main authors found in this research is presented with more references used of the methods of decision worldwide, where you can appreciate the participation of China and you can visualize the number of articles per author; in this way, you can see an initial vision of the subject to analyze, and it represents some of the most outstanding authors.
Kaya et al. [21] addressed the importance of decision-making in energy policies using fuzzy multicriteria (MCDM) decision methods. The usefulness of fuzzy set theory (FST) in solving problems of energy policy and decision-making is highlighted, and numerous articles using fuzzy MCDM methods in this field are analyzed. The results reveal that the diffuse AHP method is the most applied and that evaluations with diffuse type-1 sets are the most preferred. Turkey and China are the countries with the highest number of publications related to diffuse MCDM in energy problems.
On the other hand [22], this paper presents a general review of the development of fuzzy TOPSIS methods in decision-making, exploring different fuzzy models applied in this field and presenting some specific applications of fuzzy TOPSIS.
A systematic review of methodologies and applications of two new MCDM approaches, SWARA and weighted aggregate sum product evaluation (WASPAS), along with their most recent fuzzy extensions is presented in [23]. The results help decision-makers to manage stakeholder preferences, interconnected or contradictory criteria, and uncertain environments.
Russo and Camanho [24] perform a systematic literature review on real cases that applied AHP to evaluate how the criteria are defined and measured. The results show that the literature is the main source for constructing the criteria and that AHP or diffuse AHP is mainly used to calculate their weight.
Si et al. [25] evaluate the application of MCDM methods in the selection of green technologies for the renovation of existing buildings. The applicability of AHP is demonstrated through a case study, showing that it can help formulate the problem and facilitate the evaluation and classification of renovation measures when multiple criteria are considered. An integrated framework for the evaluation and selection of green technologies applicable to existing buildings is proposed.
In [26], evaluating the optimization of machining operations is essential to improve product quality, reduce costs, and increase overall efficiency. This study reviews the application of the entropy weight method (EWM) in machining operations, highlighting its effectiveness in assigning target weights. Eighteen categories of machining operations are identified, and the relevant literature since 2009 is analyzed, providing an overview of EWM applications and their implementation in different fields.
For [27], MCDM is crucial in environments with multiple and often conflicting criteria. This paper examines the methods of diffuse MCDM, classifying them into MADM and MODM and providing tabular and graphical illustrations for each method, focusing mainly on MADM due to the wide availability of MADM methods in the literature.
In [28], MCDM has experienced accelerated growth in recent decades, but the systematic presentation of its theoretical bases and developments is still under discussion. This article reviews the MCDM/MADM methods and highlights the need to investigate the strengths and weaknesses of different decision-making methods.
Kou et al. [29] reviewed the key developments in the peer-to-peer comparison matrix (PCM), focusing on the literature published from 2010 to 2015. Current and future trends in PCM are analyzed, with the aim of providing a comprehensive literature review and summarizing the main developments for future research.
Zavadskas et al. [30] reviewed formal decision-making methods for improving sustainability in different industries and organizations, focusing on hybrid MCDM (HMCDM) methods. The growing application of HMCDM methods to address stakeholder preferences and uncertain environments in sustainability-related decisions is highlighted.
According to Mardani et al. [31], this systematic review analyzes the applications and methodologies of the MCDM techniques, based on 393 articles published from 2000 to 2014. The main application areas and the most used methods are identified, with an emphasis on the AHP method and on research in energy, environment, and sustainability.
De Brito and Evers [32] provided a review of the applications of MCDM in flood risk management, identifying trends and research gaps. The need to address uncertainty and encourage the active participation of multiple stakeholders in the decision-making process is highlighted.
According to Mardani et al. [33], this systematic review analyzes the application of the VIKOR method in areas such as sustainability and renewable energy, highlighting its increasing use and the main areas of application.
Stojčić et al. [34] reviewed the techniques and approaches of MCDM in sustainable and renewable energy system problems, identifying the application areas and the most used methods, with an emphasis on AHP/fuzzy AHP and integrated methods.
Maity et al. [35] analyzed the application of MCDM methods in sustainable engineering, identifying 108 articles published from 2008 to 2018. It is concluded that sustainable engineering is an appropriate area for the use of MCDM, with a tendency towards the application of uncertainty theories.
Tzeng, G.H. [36] (MADM): A model of ex ante decision-making assesses the sustainability of urban renewal projects based on hybrid MADM from a governmental perspective and includes three classic dimensions: economic (D1), social and cultural (D2), and environment (D3), as well as 13 relevant criteria.
Zavadskas, E.K. [37] (Switzerland 2022 fuzzy MCDM): In this work, a novel integrated model fuzzy MCDM was developed for the evaluation and selection of information technologies for order preparation in a warehouse system, which is one of the most important novelties and contributions of the work.
Kahraman, C. [38] (Turquia 2019 DEVADA, CRITIC): This study first develops the extension of the CRITIC method to IFS, which takes into account the objective weights of the criteria in an uncertain environment for the weighting of the criteria. Then, it is intended to develop the extension of the DEVADA method to IFSs to create a dynamic decision system capable of handling uncertainties. In addition, a stronger system of multiple measures is proposed considering the Euclidean and cosine distances together. To better demonstrate the feasibility and efficiency of the method, the problem of waste disposal site selection, where evaluations are open to temporary changes, is discussed. Next, a complete sensitivity analysis is performed to verify the stability and effectiveness of the method, and a comparative analysis with distance-based MCDM methods is presented, showing the superiority and advantages of the developed method.
Xu, Z. [39] (China 2020 MADM): It develops a new decision evaluation model that integrates OCR and MADM with probabilistic linguistic information to identify these mobile payment usage attributes and use these attributes to evaluate and classify mobile payment services.
Turskis, Z. [40] (Lithuania 2022 SWARA, TOPSISS, TODIM, WASPAS, COPRAS, ARAS, and MULTIMOORA): This paper presents a hybrid decision-making framework for determining the best placement for PPS in Iran using a set of criteria drawn from the literature and expert opinions. An initial list of alternatives for decision-making is drawn up and evaluated using GIS software in terms of criteria. Decision-makers prioritized identified alternatives using MCDM methods, including SWARA and different classification methods (TOPSISS, TODIM, WASPAS, COPRAS, ARAS, and MULTIMOORA). Finally, the CCSD method aggregates the results and identifies the best location. The results correlate greatly with the results of previous methods and demonstrate the robustness of the proposed approach and its ability to overcome the limitations of previous methods.
Büyüközkan, G. [5] (Turkey 2017 SWOT-based fuzzy AHP-MARCOS): This study is aimed at determining and analyzing different DT strategies (DTSs) with the help of a SWOT-based fuzzy AHP-MARCOS methodology that is proposed for the first time in the literature for this purpose. This methodology is validated with a case study on the airline industry in Turkey. SWOT factor weights are determined using the fuzzy AHP method. The fuzzy MARCOS approach is used to select the most suitable DTS. The most appropriate strategy is obtained as “focus on differentiated digital customer experience and quality of service by adapting business models to DT to provide benefits.”
Ishizaka, A. [41] (TODIM): Until now, the MCDS method has rarely considered the psychological behavior of DM during the classification process. This research proposes a TODIM classification method to fill this gap and provides a country risk classification not only to verify the importance of considering the psychological behavior of the DM during the classification process but also to show its application to real-world problems. Finally, the paper presents a related comparison and discussions of the proposed method.
Liu, P. [42] (multiobjective optimization based on ratio analysis (MOORA)): New measures of similarity and divergence are developed for PFS and compared with existing measures to illustrate their efficiency and reliability. In addition, an extended version of MOORA with the full multiplicative form approach (MULTIMOORA) is introduced by employing developed measures of similarity and divergence in PFS information. To reveal the feasibility and usefulness of the approach presented, a problem of selecting medical equipment suppliers from the diffuse perspective of Pythagoras is discussed. Finally, a comparison with previously developed models to certify the applicability and stability of the MULTIMOORA technique is studied.
Wang, C.N. [43]: This study proposes a HMCDM framework that combines spherical fuzzy AHP (SF-AHP) and WASPAS. SF-AHP is used in the first stage to determine the significance levels of the OWPS evaluation criteria. WASPAS is then used to classify OWPS locations. A comprehensive set of evaluation criteria developed based on the concept of sustainable development has been recognized through literature review and expert interviews to practice the two-stage MCDM model. A real case study is conducted for Vietnam to test the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Pedro, G. [44] (SWARA-MOORA-3NAG method): This paper introduces the SWARA-MOORA-3NAG method to enhance the analysis of technical proposals for subsea intervention equipment in oil and gas projects. By addressing the shortcomings in supplier ordering processes, the method offers a new approach to selecting technically suitable suppliers. The study highlights the significance of MCDA methods in improving decision-making processes across industries.
Marcio, P. [45] (EC-PROMETHEE method): This paper presents a hybrid EC-PROMETHEE method for decision-making in policing strategies to reduce crime. It combines objective weighting methods like entropy and CRITIC with the PROMETHEE approach for classifying alternatives. The study is aimed at reducing uncertainty in decision-making processes and providing robust rankings for decision-makers. Future research directions include analyzing preference types in PROMETHEE, integrating more methods, and building a web platform for dissemination.
In conclusion, the present research refers to the importance of decision-making and the use of MCDM methods in various fields [16]. The aim of the study is to answer a series of research questions related to academic productivity in this topic, and bibliometric techniques were used to analyze the data [19]. The preliminary results reveal the most influential authors, the growth of scientific publishing, the countries with the highest production, the journals with the most publications, the most used methods, and the areas of research in which they are applied. Strategic diagrams are also presented to visualize thematic trends [13]. This research has the following structure: Section 2 briefly describes the methods and materials, Section 3 presents the results, and Section 4 summarizes the main debates used and the conceptual structures of multicriteria methods of decision support. Bibliometric techniques are used to analyze the data, and preliminary results are presented in the article.
Finally, MCDM methods are important to help decision-makers in various fields, so a study has been carried out with the aim of answering six research questions and developing a framework on academic productivity in this area [46, 47]. The questions concern the most influential authors, the growth of scientific publishing, the countries with the highest production, the journals with the most publications, the most used methods in academia and industry, and the impact or application of the MCDA method.
2. Materials and Methods
The increase in the number of scholarly publications has made it increasingly difficult for researchers to stay up-to-date and know the state of the art in a given topic [48]. The authors suggest that literature reviews prevail in the cutting-edge synthesis of several topics. Although structured literature review is a traditional way of analyzing and reviewing the scientific literature, it has limitations, such as time-consuming and the inability to analyze hundreds of documents [49]. With the digitization of scientific journals, bibliometric analysis has become more effective and can handle hundreds, even thousands, of documents to review related literature from a macro perspective [50]. Bibliometric analysis is the quantitative study of bibliographic materials and can characterize developments in a field of research or capture changes in a specific journal. The most commonly used methods are the analysis of social networks specialized in the research and analysis of cowords or keywords [51]. Social network analysis and specialized database is an effective method for assessing the importance of nodes and revealing network structure, while coword analysis is used to group highly relevant keywords into clusters and is used to identify established and emerging research topics or tracking patterns [36].
Performing scientometric studies or bibliometric studies is important for several reasons. First, these studies allow researchers to identify the most relevant research topics in a given field, as well as emerging research trends and patterns [52]. In addition, bibliometric studies can also provide valuable information on the productivity of researchers and institutions, which can be useful in the evaluation of performance and decision-making in the academic and scientific field [5]. Bibliometric studies can also be used to identify collaborative networks between researchers and to evaluate the influence and importance of scientific publications [53]. In general, bibliometric studies are an important tool to assess the state of the art of a research field and to guide decision-making in the scientific and academic field [54].
For this article, we proceeded with an investigation conducted since February 17, 2023. We carried out a search of the WOS database and Scopus using a thematic query. The search was limited to titles, abstracts, keywords, and articles published between the years 1977 and 2023 and produced a series of search terms related to multicharacteristic decision-making and their associated techniques. In particular, the following search equation was devised and entered into the database: TITLE-ABS-KEY (“(“multi-attribute decision making” OR “madm” or “mcda” OR “modm” OR “mcdm” OR “multi-criteria” OR “multi-criteria” OR “multiplecriteria”) AND (“ahp” OR “todim” OR “TOPSISs” OR “promethee” OR “electre” OR “vikor” OR “fahp” OR “fuzzy ahp” OR “decision methods” OR “metaheuristic methods” OR “renewable energy” OR “energy efficiency” OR “analytical network process” OR “anp” OR “simple multi-attribute rating technique” OR “smart” OR “goal programming” OR “thor” OR “cbr” OR “saw” OR “metodos metaheuristicos” OR “drsa” OR “macbeth” OR “modified TOPSISs” OR “metodos de decision” OR “wsm” or “utadis” OR “waspas”)). After the consultation, a total of 34,468 results were obtained. Likewise, the records obtained in RIS format were downloaded and then analyzed. VOSviewer was used for creation and display (version 1.6.19 for a 64-bit data bus). A map based on bibliographic data was created with the records, and a type of author analysis was used with at least five documents for each author.
3. Results
3.1. International Perspective
The conclusions drawn from the bibliometric analysis highlight the following results at the international level: during a period covered from 1977 to 2022, a total of 34,468 documents between both databases. Figure 1 represents the different types of documents found in the Scopus database. The most common in the database is the article, with a total of 15,069 documents, representing about 71% of the sample. Among the less frequent types of documents are books, with a total of 11 documents, and data articles, editorials, notes, letters, and short surveys, with an even smaller number of documents.
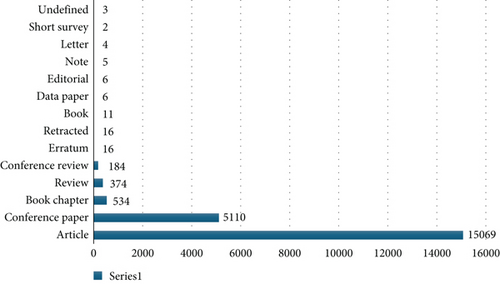
The different types of documents can be thoroughly identified and shown in more detail in Figure 1.
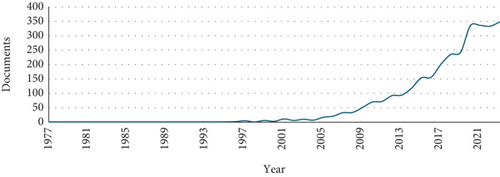
Figure 2 displays the evolution of the number of documents registered in the Scopus database over time, from 1977 to 2022, which are studied in this article. Looking at the graph, it is denoted that the number of documents registered in the database has been increasing steadily over time, with some notable increases in certain years.
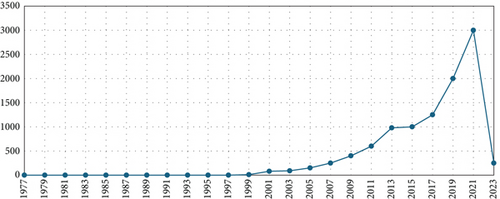
During the first decades, the number of documents was relatively low, with an average of five documents per year between 1977 and 1989. However, in the 1990s, the number of registered documents began to increase significantly, reaching a total of 35 documents in 1999. The most significant change in the curve has been observed since 2005, with a clear upward trend in the number of documents registered.
This increase in the documents’ numbers registered could be explained by several reasons. First, increased access to the Internet and technology has enabled greater dissemination of and access to scientific information. In addition, the number of scientific journals and conferences has been increasing, which could also have contributed to the increase in registered documents.
Figure 3 illustrates the number of documents registered in the Scopus database by country. Asian countries, such as India and China, have significantly higher scientific output than other countries. This could be explained by the size of their population and the investment they make in research and development. However, it is also interesting to note the high level of production of countries such as Iran and Turkey, which might not be as recognized in the research world.
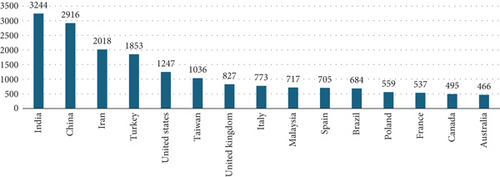
From Figure 3, it can also be concluded that the implementation and development of MCDA methods have had a significant growth worldwide during the last decades. Many researchers have used these methods to analyze complex decision-making problems involving multiple criteria. Globally, MCDA methods have been widely used in different fields, from business and government decision-making to infrastructure project evaluation and urban planning. In recent years, there has been an increase in research on MCDA methods, and new techniques and tools have been developed for their application [55].
In Figure 4, it is possible to observe the authors who have conducted research and utilized MCDA methods in their scientific publications. This provides enhanced visualization of the authors with the most publications in the databases consulted in this research.
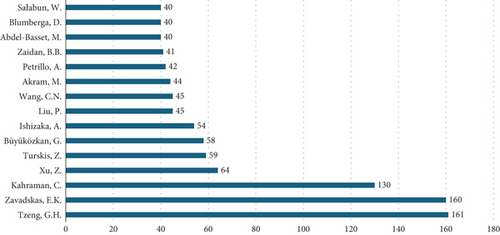
- •
Thomas L. Saaty: He is considered the father of multicriteria decision methods. Saaty is known for his work in AHP. He published numerous articles and books on the subject, including his seminal work The Analytic Hierarchy Process (1980) [56].
- •
Jean-Pierre Brans: Brans is known for his work on the PROMETHEE method, an MCDA method based on comparing pairs of alternatives. Together with his team, he has published numerous articles on the PROMETHEE method and its practical applications [57].
- •
M. Grauer and K. J. Wallenius: These authors have made important contributions around multicriteria classification, including the ELECTRE method and its variants. His work has been widely cited and applied in different areas, such as environmental impact assessment and supplier selection [58].
- •
Ralph E. Keeney: Keeney is known for his work in decision theory and MCDM. He has published numerous articles and books on the subject, including Value-Focused Thinking: A Path to Creative Decisionmaking [59].
- •
Bernard Roy: He is another pioneer in the development of multicriteria decision theory and has developed numerous MCDA methods, including the ELECTRE method and the PROMETHEE method. He has also contributed to the development of multiattribute utility theory [60].
- •
Jyrki Wallenius: He is known for his research around multicriteria decision theory and has developed numerous methods, including the MAUT method and the UTADIS method. He has also researched preference modelling and social choice [58].
- •
Salvatore Greco: He is an active researcher in MCDM and has developed numerous MCDA methods, including the DEA method and the TODIM method. He has also researched the application of MCDA methods in sustainability assessment [61].
- •
Bhattacharyya: He is an expert in multicriteria decision theory and has developed numerous MCDA methods, including the AHP method and the TOPSISS method. He has also researched the application of MCDA methods in transportation planning and supply chain management [62].
These are just some of the many universities that have published research on MCDA methods in recent years. Figure 5 illustrates the number of publications from these 10 top universities in the research of implementing and developing MCDA methods. The University of Tehran leads the ranking, securing the first position with a total of 751 documents, followed by Vilniaus Gedimino Technikos Universitetas (650 documents) and Islamic Azad University (472 documents). The primary documents published by these universities consist of articles and conference papers.
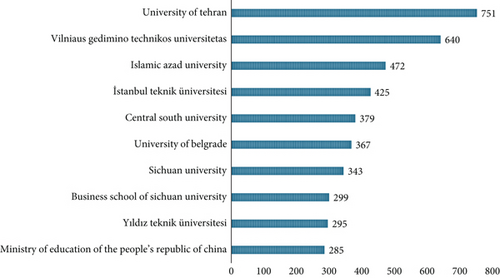
According to the Scopus database, the University of Tehran has published numerous papers, many of which are highly relevant [63–67]. For instance, a paper authored by Rezaei, Khalilpour, and Jahangiri, titled “A Multi-criteria Group Decision-Making Approach for Facility Location Selection Using PROMETHEE Under a Fuzzy Environment,” addresses the issue of uncertainty in decision-making processes. The study proposes the use of Z-numbers to evaluate criteria weights, aiming to represent real-life problems more realistically. Thus, compared to fuzzy models, PROMETHEE with Z-numbers (i.e., Z-PROMETHEE) can better symbolize real-life problems [4].
- •
Stanford University: Stanford University is known for its excellence in research and has published numerous articles on multicriteria decision theory. Stanford professors have worked on developing new methods and applications of MCDA in a variety of fields.
- •
Delft University of Technology: Delft University of Technology is a leader in research in the field of engineering and has published several investigations on MCDA methods in the context of decision-making in infrastructure projects and natural resource management.
- •
University of Navarra: The University of Navarra is recognized for its research in decision-making and has published numerous studies on the application of MCDA methods in the evaluation of sustainability and business management.
- •
University of Massachusetts Amherst: The University of Massachusetts Amherst is a research leader in the field of computer science and has published research on the application of artificial intelligence techniques in MCDM.
- •
University of Manchester: The University of Manchester has published research on the application of MCDA methods in urban planning, supply chain management, and decision-making in the healthcare sector.
- •
University of Sao Paulo: The University of Sao Paulo is a leader in research in Brazil and has published research on the application of MCDA methods in decision-making in the public sector and natural resource management.
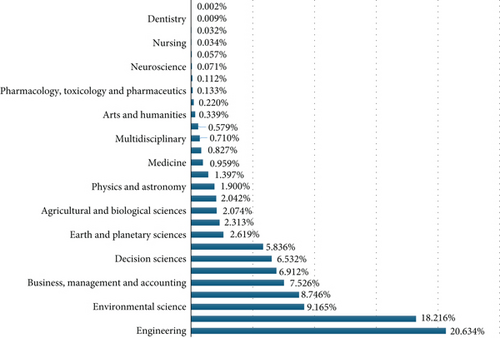
In Figure 6, the percentage classification of these publications according to their area of impact is visualized. The most notable is engineering, comprising approximately 20.634% of the total publications until the year 2022. However, the significant aspect of Figure 6 lies in the breadth of areas where MCDA methods are being applied daily.
- •
Easy to use: The TOPSIS method is relatively easy to understand and apply, making it accessible to people with different skill levels.
- •
Sensitivity to the weight of the criteria: The TOPSIS method is sensitive to the weights of the criteria used in the evaluation, which means that the weights can be adjusted to reflect the relative importance of each criterion.
- •
Based on the ideal solution: The TOPSIS method uses an ideal solution as a benchmark to evaluate options. This means that options that come closest to the ideal solution rank higher in the evaluation.
- •
Flexibility: The TOPSIS method is flexible and can be used to evaluate different types of options, from products and services to policies and strategies.
Overall, the TOPSIS method is an effective tool for MCDM due to its ease of use, sensitivity to the weights of the criteria, focus on the ideal solution, and flexibility. However, like any decision analysis method, the TOPSIS method has its limitations and must be used appropriately and carefully to obtain accurate and useful results.
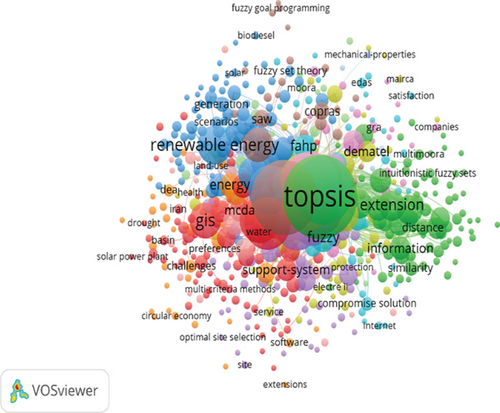
Through the data obtained from the WOS database, the following keywords highlighted in Figure 8 were obtained, in which a large participation of the TOPSIS methods is visualized in the series of documents obtained in this database; in the same way, the relevant simulations were carried out in the software mentioned for the SCOPUS database. Main keywords that stand out in the articles published include decision making, analytical hierarchy process, and the TOPSIS method. These topics are also prominent in the simulations conducted in the previous database.
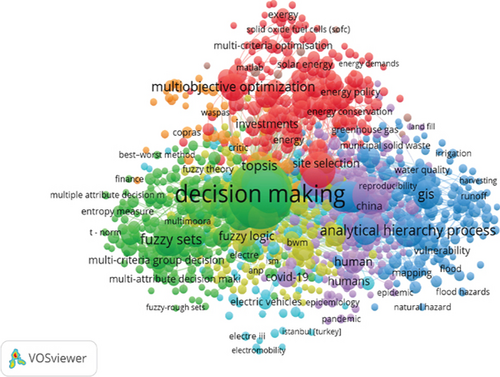
Following the methodology of bibliometric analysis carried out from keywords and most used, the same exercise is carried out, but from the authors with the most impact in Scopus and WOS (Figures 9 and 10).
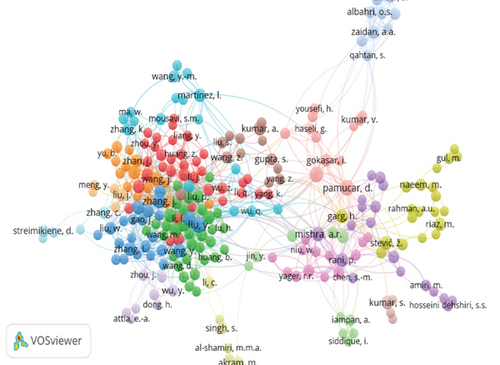
3.2. Latin American Perspective
In Latin America, there has been a noticeable rise in the utilization of MCDA methods, as depicted in Figure 11. In Figure 12, research projects developed in five main Latin American countries—Brazil, Mexico, Chile, Colombia, and Argentina—are showcased, highlighting the relevance of these countries in research pertaining to MCDA methods applied across various areas of application. The primary fields applying this methodology are computer science (18.4%), engineering (18.1%), and environmental science (10.0%).
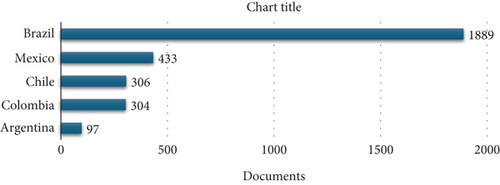
In Latin American, the implementation and development of MCDA methods have been less frequent compared to other parts of the world. However, there are some notable examples of its use in the region. For example, in Mexico, the AHP method has been used to evaluate the effectiveness of public policies in the health sector [69]. Regarding Brazil, the PROMETHEE method has been used for the evaluation of infrastructure projects.
According to Figure 12, Brazil stands out significantly in scientific production compared to other countries on the list, being the only Latin American country represented. This highlights Brazil’s substantial effort in scientific research and development, indicating its relevance in the international arena. It is essential to note that this observation does not necessarily reflect the quality or impact of the research from each country but provides insight into the most productive countries in publications regarding multicriteria methods.
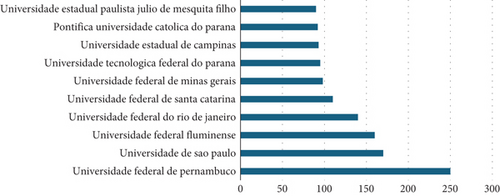
Among the top 10 universities with the most publications involving the MCDA method between 1977 and 2023, the leading one has been the Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, standing out with a total of 250 documents, followed by the Universidade de São Paulo (USP) with approximately 200 documents. It is worth noting that the top 10 universities researching and applying MCDA methods are Brazilian institutions.
In Figure 13, the most relevant authors in the field are listed. The primary author in the region is Adiel Teixeira de Almeida from the Center for Decision Systems and Information Development (CDSID), Federal University of Pernambuco (PE, Recife, Brazil), with a total of 56 documents published in the area. Among his key works is the article titled “Portfolio-Based Decision Model for Enhancing the Mitigation of Multidimensional Risks in Hydrogen Pipeline Sections,” where this paper presents a multicriteria decision model to support organizations responsible for transporting hydrogen in a pipeline in risk management under a multidimensional perspective. They developed a search algorithm to select sections within the set that makes up the pipeline network (a portfolio-based approach), with a view to identifying the most critical areas in terms of risks and to optimizing the allocation of resources for mitigation while respecting current requirements. In other works by Almeida, he applies methods such as FITradeoff, MCDM/A, and Alpha-Theta Diagram as decision neuroscience tools for analyzing holistic evaluation in decision-making, as well as multicriteria decision methods for RRM models [70–73].
On the other hand, Mexico has published 270 documents between the years 2000 and 2023, with a considerable increase in the year 2023. This number of documents corresponds to works published by 15 universities, with the top three being Tecnológico de Monterrey, Universidad Autónoma de Sinaloa, and Universidad Autónoma de Ciudad Juárez. Among the main authors from each university are Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, Navarro, Jorge, and Alejandro Alvarado-Iniesta. The main methods used by the authors include an integrated SWARA-WASPAS framework based on spherical fuzzy set, the Pythagorean fuzzy TOPSIS method, and the THESEUS method, among others [74–76].
The Universidad Católica del Norte, the Universidad de Santiago de Chile, and the Pontifical Catholic University of Chile have a total of 121 documents registered in the Scopus database between 2006 and 2023. Among the most relevant authors from Chile is Hashemkhani Zolfani, with over 46 documents and 6000 citations and with significant works such as “Integrated QFD-MCDM Framework for Green Supplier Selection” and “New Application of SWARA Method in Prioritizing Sustainability Assessment Indicators of Energy System” [77, 78]. Yazdani et al. have published works integrating various methods, such as a novel hybrid SWARA and VIKOR methodology, an integrated approach with SWARA and COPRAS-G methods, and the integration of MCDM methods and QFD [77, 79, 80]. On the other hand, other authors such as Macuada, Oddershede, and Cordova and Quezada et al. have also contributed relevant works [81–83].
In the ranking of Latin American countries that have contributed to research applying the MCDM approach, Colombia and Argentina rank fourth and fifth, respectively. In the case of Colombia, the statistics will be presented in the following section. Meanwhile, in Argentina, the Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas and the Universidad Nacional de Salta stand out, where works such as “A Mixed Usability Evaluation on a Multi-criteria Group Decision Support System in Agriculture” and “Goal Programming and Multi-criteria Methods in Remanufacturing and Reverse Logistics: Systematic Literature Review and Survey” have been published [84, 85].
3.3. Colombian Perspective
In the case of Colombia, although there is a growing interest in the use of MCDA methods, their implementation and development are still at an early stage. Although there have been some studies using these methods in areas such as environmental management and public policy evaluation, there is still a long way to go for their widespread adoption [86]. In Colombia, there have also been some applications of MCDA methods in different fields. For example, in the energy sector, the PROMETHEE method has been used for the evaluation of power generation alternatives [87].
The first work registered in the Scopus database was “Towards an Evaluation of Chemicals” in 2005. The work was published through a partnership between the Universidad de Pamplona in Pamplona, Colombia, and the Leibniz-Institute of Freshwater Ecology and Inland Fisheries in Berlin, Germany [88]. The work in question deals with the assessment of chemicals for environmental risks, highlighting the need for a comprehensive database to support risk assessment models like EUSES. Although it does not explicitly focus on MCDA methodologies, it implicitly addresses the principles of this approach in dealing with a multicriteria problem. The author describes the process of characterizing chemicals and their environmental behavior using different models and available data. Additionally, it highlights the identification of hazardous chemicals and the use of a generalized ranking scheme by partial orders. While specific MCDA techniques are not employed, the work underscores the multifaceted nature of decision-making in the context of environmental risk assessment.
For the year 2023, Colombia appears with a record of 39 documents registered in Scopus, with Universidad de la Costa in Barranquilla leading the national ranking, followed by Universidad del Valle (Figure 14).
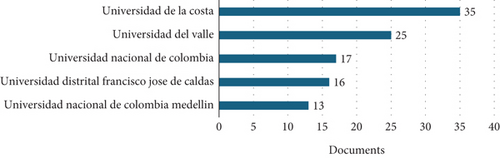
The authors Miguel Angel Ortiz-Barrios, Mateo Barrera Zapata, Iván D. Gill, and Christian Manuel Moreno Rocha have been reported to produce significant works in the field. The main methods applied for the authors include AHP, AHP-DEMATEL, fuzzy MCDM, and TOPSIS, among others [46, 47, 89–91].
4. Conclusions
Currently, Latin America is experiencing an increase in research and the application of MCDM methods. However, this progress is uneven across the region and varies significantly from country to country. Some Latin American countries, such as Brazil, Chile, Colombia, and Mexico, have made important advances in the research and application of these methods in different fields, including natural resource planning and management, risk management, and business decision-making. Other countries in the region, however, have a limited presence in this area.
Overall, it can be said that the implementation and research in MCDM methods in Latin America are in a phase of growth and consolidation and is likely to continue to increase in the coming years due to the growing demand for effective decision-making tools in different fields. Compared to other regions of the world, Latin America still has a long way to go in terms of research and application of MCDM methods. However, there are ongoing initiatives to address this gap, including networking of researchers and collaboration with international experts. Over time, Latin America is likely to reach the same level of competition as other regions in this field.
Colombia has shown progress in the implementation and research of MCDM methods in recent years. According to the scientific literature, various applications of these methods have been developed in the country, in fields such as project evaluation, territorial planning, and environmental management.
In addition, research groups have been created in Colombian universities dedicated to the application and development of these methods, which has generated scientific publications in specialized journals and presentations at international conferences. Although there is still a gap compared to more advanced countries in this field, such as the United States or some European countries, Colombia is on an upward path in the implementation and research of MCDM methods.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Funding
The financing of this research was with the support of the company Soluciones Energeticas Ambientales Renovables; in addition, the possible payment of APC will be assumed by the University of Santiago de Compostela.
Appendix
The main contribution of a research titled “Review and Bibliographic Analysis of Metaheuristic Methods in Multicriteria Decision-Making: A 45-Year Perspective Across International, Latin American, and Colombian Contexts” could be its ability to provide a comprehensive and updated overview of the research status in multicriteria decision-making methods (MCDA) with a focus on metaheuristics. Some specific aspects that could be highlighted as significant contributions may include the compilation and synthesis of literature by gathering a wide range of relevant studies and documents in the field of MCDA and metaheuristics, providing readers with a complete view of trends, advancements, and areas of interest in multicriteria decision-making over 45 years; additionally, identifying emerging trends, research leaders, and geographical areas of high activity in the use of MCDA methods and metaheuristics through bibliometric analysis and data visualization tools, offering valuable insights into the current and future state of this field, with a focus on international contexts, including Latin America and Colombia, highlighting the application and relevance of MCDA methods and metaheuristics in different international contexts, providing a global and regional perspective on their adoption, development, and practical applications; and finally, by providing a comprehensive review and bibliographic analysis of MCDA methods and metaheuristics, generating knowledge and useful recommendations for professionals, academics, and decision-makers in various fields, helping them make more informed and effective decisions.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data of this investigation rest on the PC of the principal investigator; if at any time they require to be seen, there is no problem in sharing them.




