Local Fractional Laplace Variational Iteration Method for Solving Linear Partial Differential Equations with Local Fractional Derivative
Abstract
The local fractional Laplace variational iteration method was applied to solve the linear local fractional partial differential equations. The local fractional Laplace variational iteration method is coupled by the local fractional variational iteration method and Laplace transform. The nondifferentiable approximate solutions are obtained and their graphs are also shown.
1. Introduction
Fractional calculus [1] has successfully been used to study the mathematical and physical problems arising in science and engineering. Fractional differential equations are applied to describe the dynamical systems in physics and engineering (see [2, 3]). It is one of the hot topics for finding the solutions for the fractional differential equations for scientists and engineers. There are many analytical and numerical methods for solving them, such as the spectral Legendre-Gauss-Lobatto collocation method [4], the shifted Jacobi-Gauss-Lobatto collocation method [5], the variation iteration method [6], the heat-balance integral method [7], the Adomian decomposition method [8], the finite element method [9], and the finite difference method [10].
The above methods did not deal with some nondifferentiable problems arising in mathematics and physics (see [11–13]). Local fractional calculus (see [12–14] and the cited references) is the best choice to deal with them. Some methods for solving the local fractional differential equations were suggested, such as the Cantor-type cylindrical-coordinate method [15], the local fractional variational iteration method [16, 17], the local fractional decomposition method [18], the local fractional series expansion method [19], the local fractional Laplace transform method [20], and local fractional function decomposition method [21, 22]. More recently, the coupling schemes for local fractional variational iteration method and Laplace transform were suggested in [23]. However, the results are very little. In this paper, our aim is to use the local fractional Laplace variational iteration method to solve the linear local fractional partial differential equations. The structure of the paper is suggested as follows. In Section 2 the basic theory of local fractional calculus and local fractional Laplace transform are introduced. Section 3 is devoted to the local fractional Laplace variational iteration method. In Section 4, the four examples for the local fractional partial differential equations are given. Finally, the conclusions are considered in Section 5.
2. Local Fractional Calculus and Local Fractional Laplace Transform
In this section, we present the basic theory of local fractional calculus and concepts of local fractional Laplace transform.
3. Analysis of the Method
In this section, we introduce the idea of local fractional variational iteration method [16, 17], which is coupled by the local fractional variational iteration method and Laplace transform.
4. The Nondifferentiable Solutions for Linear Local Fractional Differential Equations
In this section, we present the examples for linear local fractional differential equations of high order.
Example 1. The local fractional differential equation is presented as
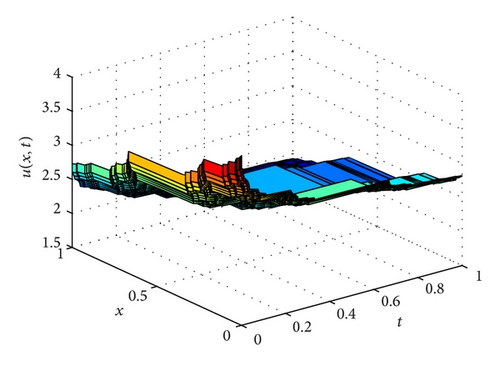
Example 2. We report the following local fractional partial differential equation:
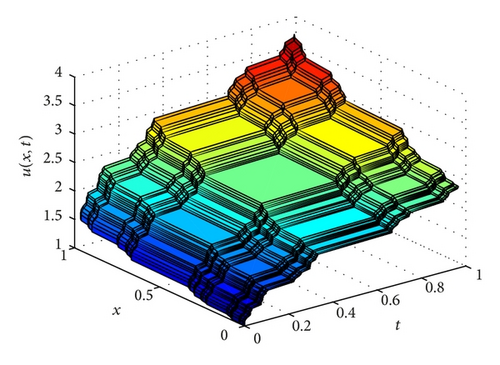
Example 3. The following local fractional partial differential equation
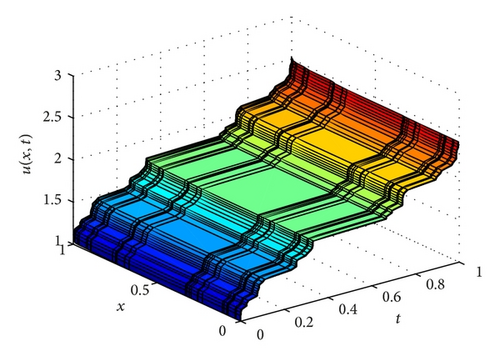
5. Conclusions
Local fractional calculus was successfully applied to deal with the nondifferentiable problems arising in mathematical physics. In this work we considered the coupling method of the local fractional variational iteration method and Laplace transform to solve the linear local fractional partial differential equations and their nondifferentiable solutions were obtained. The results are efficient implement of the local fractional Laplace variational iteration method to solve the partial differential equations with local fractional derivative.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this paper.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Scientific and Technological Support Projects (no. 2012BAE09B00), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 51274270), and the National Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (no. E2013209215).




