α″ Martensitic Twinning in Alpha + Beta Ti-3.5Al-4.5Mo Titanium Alloy
Abstract
The twinning structure of the orthorhombic α′′ martensite phase in alpha + beta Ti-3.5Al-4.5Mo (wt%) titanium alloy was studied using X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscopy by water quenching from below transus temperatures. While water quenching from 910 ∘C induced the formation of {110}∘ twins, quenching from 840 ∘C formed the α′′ martensite with {111}∘ type I twins. The effect of the principle strains on the twinning structure was discussed. As compared to the previous studies, the principle strains play an important role in the formation of the twinning type.
1. Introduction
Commercial α + β titanium alloys are widely used in structural and aerospace applications where the combination of light weight, strength, and room temperature corrosion resistance is highly desired. With different alloy compositions and thermomechanical processing parameters, a wide range of mechanical properties can be achieved in titanium alloys. Beside the enhanced mechanical properties, metastable martensite microstructure can be obtained with fast cooling from body-centered cubic (bcc) β phase region. While near alpha titanium alloys yield only small fraction of martensite structure, alpha + beta titanium alloys can produce a combination of hcp (α′) and c-orthorhombic (α′′) martensite phase [1, 2]. α′′ phase is particularly interesting because it can be thermoelastic, and better understanding of this phase transformation can be used to design smart systems.
There have been extensive studies on the properties of α′ [3–6] and the phenomenological theory martensite crystallography (PTMC) [7, 8]. Unlike the α′ martensite transformation, the α′′ martensite transformation which was first found in a Ti-Nb system [9] can be thermoelastic, and the shape memory effect is present [10–14]. The crystal structure of α′′ martensite is intermediate between bcc β and hcp α phases [9], and the lattice parameters vary with alloy compositions significantly [15]. The morphology of α′′ martensite depends on the magnitude of the lattice deformation. It was found in Ti-Ta alloy that most of the α′′ martensite are not twinned state at a certain Ta content [16], while most literatures concerning the α′′ martensite twin structure in β titanium alloys reported that the α′′ martensite is in {111} twin structure [17, 18]. However, the morphology and crystallography of α′′ martensite twin has not been completely described, especially for the α + β titanium alloys in which the β isomorphic elements are very close to the lower critical concentration of α′′ martensite.
It is well known that twinning is a deformation process of most engineering materials to reduce the overall energy of the system, thus, the determination of twinning structure of the orthorhombic α′′ martensite is essential for better understanding of the deformation mechanism and future development of titanium alloys. In this study, we have investigated an α + β titanium alloy with nominal composition of Ti-3.5Al-4.5Mo (wt%). This alloy is based on Russian Ti-4.5Al-3Mo-1V (VT14) high-strength titanium alloy mainly used for stampings, gear applications [19]. By reducing the aluminum and omitting vanadium contents, we have reduced the amount of β phase so that the martensite microstructure would contain no retained β phase and the identification of α′′ phase would be more pronounced. Considering the β transus temperature of this alloy is about 925°C where the cubic β phase can transform to hexagonal α phase, we have selected 910°C and 840°C as quenching temperatures where they refer to the highest temperature that α′′ phase can be observed and the lowest temperature that the microstructure will be mostly α′′ phase after water quenching, respectively.
2. Experimental Procedure
A titanium alloy ingot with 60 gr weight was prepared in a nonconsumable arc melting furnace under protective argon atmosphere. The ingot was homogenized at 1200°C for 2 hours followed by air cooling and then forged at 900°C to a bar shape with 10 × 10 × 130 mm3 dimensions. The Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS) analysis showed that the composition of the ingot is Ti-3.63Al-4.41Mo (wt%). Two samples with 10 × 10 × 10 mm3 cube shape were cut from the bar and heat-treated at 910°C or 840°C for 1 h followed by water quenching. The α′′ martensite transformation depends on the quenching rate and alloy composition [20, 21]. In present study, the samples were used in identical dimensions so that the quenching rate effect in different samples will be insignificant. Phase distributions and lattice parameters were measured with the Rigaku D/max-2400PC X-Ray diffractometer using Cu-K α radiation at 56 kV voltage and 182 mA current. The microstructures from each quenching temperatures were analyzed with the Technai G220 transmission electron microscope operating at 200 kV. TEM foils were mechanically thinned to about 30 μm in thickness, and further reduction was carried out using MTP-1A magnetic force-driven twin-jet electrolytic polisher in a solution of 20% perchloric acid, 30% butyl alcohol, and 50% methanol (vol.%) at −30°C to −40°C and a current of 15–20 mA.
3. Results and Discussions
The lattice parameters of samples quenched from 840°C or 910°C were calculated from the corresponding X-ray diffraction patterns shown in Figure 1. The lattice parameters consistently changed as compared to previous studies [15]. The lattice parameters of α′′ martensite phase were calculated as a0 = 0.3120 nm, b0 = 0.4990 nm, and c0 = 0.4670 nm after quenched from 910°C and a0 = 0.3130 nm, b0 = 0.4920 nm, and c0 = 0.4640 nm after quenched from 840°C, respectively. The average errors to calculate the lattices parameters were ±0.001 nm. According to the principle of phase equilibrium, the isomorphic β-stable elements (M0 in present alloy) in the β phase are richer when solution treated at 840°C than that at 910°C. Thus, a0 in the unit cell increases while b0 and c0 decrease. Such lattice distortion due to different quenching temperatures was induced by the enriched molybdenum content in the β phase and α′′ phase.
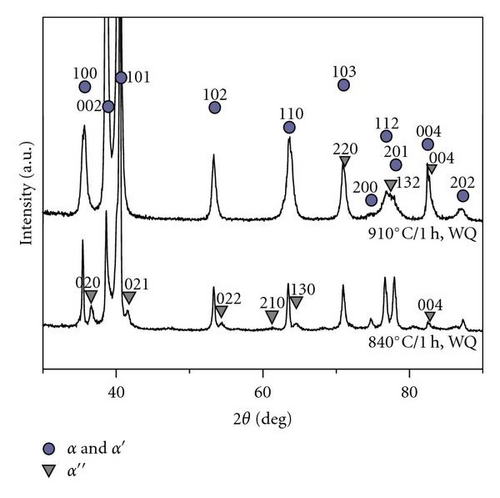
The phase transformation between the β and α′′ martensite phase can be explained with Au-Cd-type transformation [22], as shown in Figure 2 where cubic β transforms to orthrhombic α′′ martensite phase. The twinning relationships can be generally categorized into two classes. Inamura [20] named these classes as “class A” transformation for {111}0 type I twinning and “class B” transformation for {011}0 compound twinning. The twinning planes for class A and B were expressed as {011}β and {100}β, respectively.
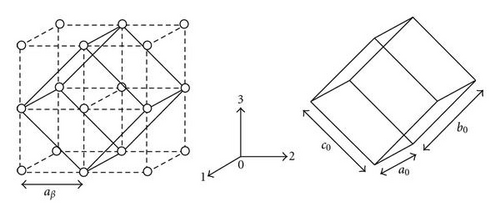
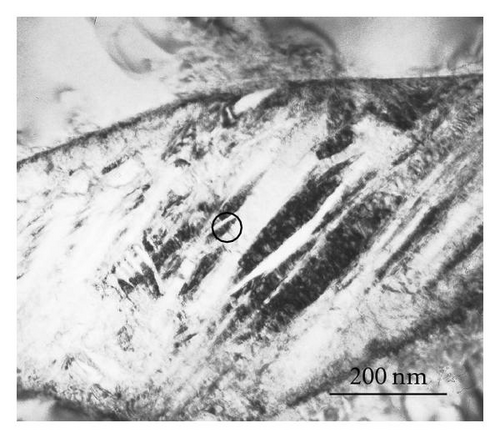
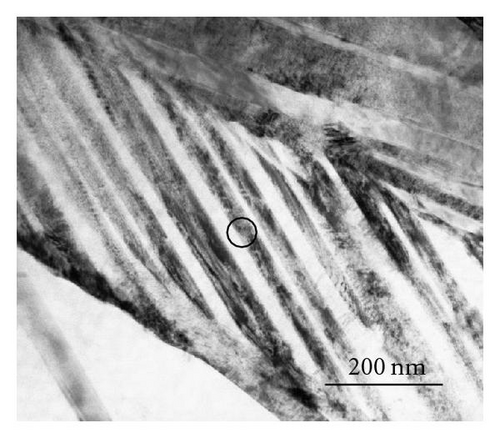
Figure 3(a) shows the TEM bright field image of the sample quenched from 910°C, and Figure 3(b) shows the corresponding selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern taken from the marked area. The α′′ martensite twins locate between α′ laths and is (011) twinning, that is, “class B”. Most of the twins in the α′′ martensite were in “class B” type, and the “class A” type twinning was rarely observed. Figures 3(c) and 3(d) show the TEM bright field image of the sample quenched from 840°C, and the SAED pattern taken from the encircled area in (c), respectively. The α′′ martensite distributes between the remnant β phase laths. The “class A” transformation, namely, the {111}0 type I twinning was confirmed by the Figure 3(d). In contrast with sample quenched from 910°C, the α′′ martensite in the sample quenched from 840°C is almost in “class A” and the “class B” transformation was rarely observed.
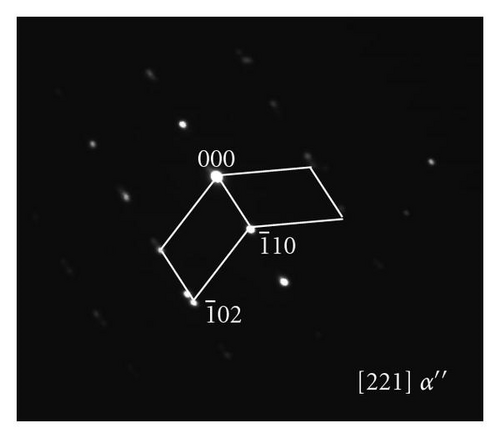

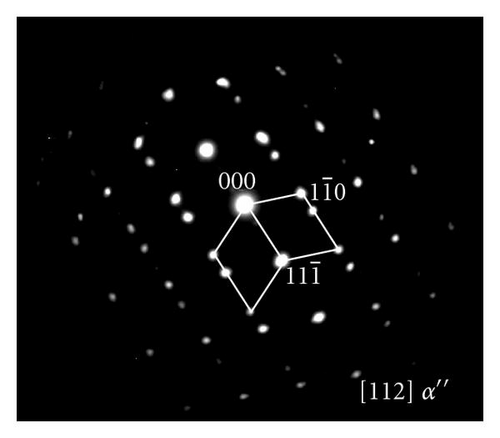
As shown in Figure 1, the β phase transformed to α′ + α′′ and α′′ + β phases due to the isomorphic β stable elements after water quenched from 910°C and 840°C, respectively. The Burgers orientation relationship (OR) between β and α′ is //{110}β and //〈110〉β, the OR of β and α′′ is //{110}β and //〈001〉β [15]. When the partial β phase transforms into a set of parallel α′ laths during quenching, the (011)β twin plane extends along the [011]β direction with a formation of residual stress. If the α′′ martensite twin phase nucleates in this region, the newly formed twins will form by making 45° with the habit plane as the preferred slide plane will make a maximum Schmidt factor. By referring to Figure 2, the possible slide plane is {100}β. When the product of α′′ + β is obtained during quenching, the remnant β phase shrinks and compressive stress is developed. While the remnant β phase shrinks, newly formed α′′ phase will develop and tensile stresses appear along {001} direction families to reduce the overall energy of the system. The discussion about the elastic strain energy reduction follows in the next section.
In the process of β − α′′ martensite transformation, one unit cell of the α′′ martensite corresponds to two unit cells of the β phase, the volume of a unit cell of α′′, V0, is a0 × b0 × c0, and the volume of two unit cells, Vβ, is 2 × aβ × aβ × aβ. VO is about 1.2% larger than Vβ in the sample quenched from 910°C, while VO is about 1.0% smaller than Vβ in the sample quenched from 840°C. When the local twin structure expands, the higher magnitude of the elastic strain energy would decrease the free energy in the α′′ martensite due to increased molybdenum content. In shrinking regions, a lower free energy state can be obtained with larger magnitude of W. Thus, W{100}β is thermodynamically favorable when the sample is quenched from 910°C. When the local twin structure shrinks, the elastic strain energy would be positive, a larger W can also make a lower energy condition, and W{011}β is thermodynamically favorable when the sample is quenched from 840°C.
Different W may introduce different twinning systems into the alloys. As described before that the main twinning system of α′′ martensite in the sample quenched from 910°C is class B, while class A in the sample quenched from 840°C. This yields to a conclusion that low isomorphic β-stable elements can introduce a high strain in the water quenched microstructure, and {011}0 compound twinning is likely to form. {111}0 type I twinning is preferred in a water quenched microstructure with high β-stable elements. In fact, most of the observed α′′ martensite twin structure in β titanium alloys are {111}0 twin structure [17, 18].
It is also important to note that not all research finds the {111}0 compound twinning as the predominant twin structures in β titanium alloys. Based on the theory of deformation twinning given by Bilby and Crocker, Ping [21], the possible deformation twinning is mainly {110}0 compound twinning in β-Ti alloys, and the result was confirmed by his investigation. This would be another proof that the strain induces the formation of {110}0 twinning when principle strain η3 is plus. Similarly, increased content of the isomorphic β-stable elements distorts the lattice with a negative η3 and promotes the formation of the {111}0 type I twinning. The results from both quenching temperatures consistently show these twin structures.
4. Conclusions
The orthorhombic α′′ martensite twinning was investigated in the Ti-3.5Al-4.5Mo (wt%) alloy. Quenching from 910°C induced the formation of {110}0 compound twinning, while the α′′ martensite is mainly the {111}0 type I twinning in the sample quenched from 840°C. The type of α′′ martensite twin structure is highly dependent on the principle strain, that is, a tensile η3 leads to form {110}0 twinning while a compressive η3 induces the formation of the {111}0 type I twinning. The contents of the isomorphic β-stable elements in the titanium alloy is the main effect on the formation of the principle strains and determines the type of α′′ martensite twin structure.
Acknowledgment
The authors wish to thank Institute of Metal Research staff for the help in the TEM and X-ray diffraction measurements.