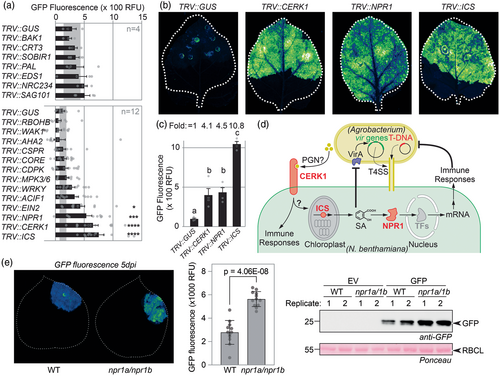
Immunity gene silencing increases transient protein expression in Nicotiana benthamiana
The infiltration of Nicotiana benthamiana with Agrobacterium tumefaciens (agroinfiltration) has become a routine expression platform for plant science and molecular pharming, yet this platform remains to be further optimized. We recently showed that N. benthamiana silenced for the cold shock protein (CSP) receptor (CORE) enables 8-fold more GFP production in older, 6–8-week-old plants, which are normally not used because of low transient expression efficiencies (Dodds et al., 2023). Here, we investigated whether we can also increase transient protein expression levels in routinely used younger, 5-week-old juvenile plants, by silencing immunity-related genes.
We selected 21 immunity-related genes encoding proteins that act at different levels in the plant immune system (Table S1). Besides CORE, we silenced receptor-encoding genes WAK1 (Wall-associated Protein Kinase), CERK1 (Chitin Elicitor Receptor Kinase-1), BAK1 (BRI1-associated Receptor Kinase-1), SOBIR1 (Suppressor of BIR1-1) and RE02 (Receptor of SCPs). We also tested silencing of immune signaling components such as F-box protein ACIF1 (Avr/Cf-induced F-box-1); lipase-like proteins EDS1 (Enhanced Disease Susceptibility-1) and SAG101 (Senescence-associated Gene-101); CDPK (Calcium-dependent Protein Kinase), MPK3/6 (MAP protein kinases-3 and -6), Nod-like helper receptors NRC2/3/4 (NLR Required for Cf Signaling) and chaperone CRT3a (Calreticulin-3a). We also included genes required for stress hormone signaling, including PAL (Phenylalanine Ammonia Lyase), ICS (Isochorismate Synthase), NPR1 (Nonexpressor of PR genes-1), EIN2 (Ethylene-insensitive-2) and WRKY transcription factors. Finally, we included genes encoding AHA2 (Arabidopsis H+-ATPase 2) and RBOHB (Respiratory Burst Oxidase Homolog B). Genes encoding phytoene desaturase (PDS) and ß-glucuronidase (GUS) were included as positive and negative controls for silencing, respectively. We resynthesized the silencing fragments as published previously (Table S1) and selected novel fragments targeting ACIF1, CDPK, CORE, ICS and AHA2 (Dodds et al., 2023, Tables S2 and S3).
Tobacco Rattle Virus (TRV) vectors, each carrying a fragment of these 21 immunity genes and the controls were agroinfiltrated into 2-week-old seedlings and plants were tested for transient expression three weeks later. Transcript levels of the targeted genes were downregulated with novel silencing fragments (Figure S1). At that stage, no strong phenotypes were observed in TRV-inoculated plants, except for photobleaching in TRV::PDS plants, dwarfed TRV::BAK1 and TRV::CDPK plants, and small, chlorotic TRV::ICS plants (Figure S2). Leaf discs of TRV::RBOHB and TRV::BAK1 plants showed a reduced oxidative burst upon flg22 treatment (Figure S3), consistent with the effective silencing of these genes.
Silenced plants were agroinfiltrated with a 1:1:1 mixture of Agrobacteria delivering three ‘traffic light’ reporters: bioluminescent AgroLux bacteria (Jutras et al., 2021, orange), mixed with Agrobacteria delivering expression cassettes for cytonuclear GFP (cGFP, green) and secreted RFP (sRFP, red). GFP fluorescence in leaf discs taken at 5 days post-infiltration (5 dpi) was significantly higher in TRV::ICS, TRV::CERK1, TRV::NPR1 and TRV::EIN2 plants, when compared to TRV::GUS plants (Figure 1a). The same silenced plants also showed more RFP fluorescence when compared to TRV::GUS control plants (Figure S4a). No altered fluorescence was detected in TRV::CORE plants, consistent with low CORE expression in juvenile plants (Wang et al., 2016). AgroLux bioluminescence was similar between these silenced plants (Figure S4b), indicating that silencing these immunity genes does not increase Agrobacterium population levels. Scanning of agroinfiltrated leaves in subsequent experiments confirmed that silencing CERK1 or NPR1 increased GFP-fluorescence by >4-fold and ICS silencing even >10-fold, when compared to the GUS silencing control (Figure 1b,c). Also, a significant, 1.7-fold increased GFP fluorescence was detected in TRV::EIN2, when compared to TRV::GUS plants (Figure S5), consistent with the initial screen.
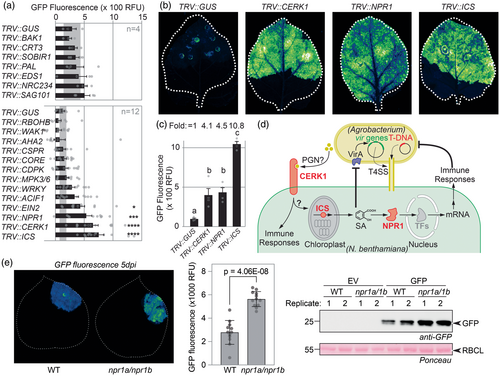
The observed effects imply that immunity genes CERK1, NPR1 and ICS encode important barriers for transient expression (Figure 1d). CERK1 is a receptor-like kinase involved in the perception of chitin (Miya et al., 2007) and peptidoglycan (Willmann et al., 2011). NPR1 is a transcriptional regulator of responses induced by salicylic acid (SA) (Spoel and Dong, 2024). ICS is a chloroplastic enzyme producing isochorismate, a precursor of SA (Spoel and Dong, 2024). The unaltered GFP fluorescence in TRV::PAL plants indicates that SA restricting transient expression is not produced via phenylalanine, but through isochorismate in agroinfiltrated leaves (Spoel and Dong, 2024). The effect of ICS silencing is twice as strong compared to NPR1 silencing might be because ICS depletion would not only reduce immune signalling, but also reduce SA levels that negatively regulate vir gene expression in Agrobacterium (Yuan et al., 2007).
To enhance transient expression without relying on VIGS, we are disrupting the open reading frames of these immunity-related genes using genome editing and stacking mutant genes. So far, the deletion of the two silenced NPR1 genes (Figure S6), has indeed caused increased GFP fluorescence and accumulation (Figure 1e) and enhanced IgG accumulation (Figure S7). These genome-edited lines hold important potential for boosting transient gene expression for protein production in N. benthamiana.
Acknowledgements
We thank Urszula Pyzio for excellent plant care, and Sarah Rodgers, Caroline O'Brien and Patricia Bowman for technical support.
Funding
This project was financially supported by the Interdisciplinary DTC project DDT00060 (ID) and DDT00230 (EW); BBSRC projects BB/R017913/1 (PB) and BB/S003193/1 (MS); and ERC project 101019324 (RH).
Author contributions
RALH conceived the project; ILD and ECW performed most experiments with the help of MS and PB and SS; YT, MHAJJ and TB provided VIGS constructs and JS provided the npr11/npr1b mutant; ILD, ECW and RALH wrote the manuscript with all authors.
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Open Research
Data availability statement
The data that supports the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.