Hypoxia interferes with aryl hydrocarbon receptor pathway in hCMEC/D3 human cerebral microvascular endothelial cells
Corresponding Author
Aude Jacob
INSERM, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Descartes, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Diderot, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Address correspondence and reprint requests to Aude Jacob, INSERM UMR-S 1144, Faculté des Sciences pharmaceutiques et biologiques, 4 avenue de l'observatoire, 75006 Paris, France. E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorSophie Potin
INSERM, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Descartes, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Diderot, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Search for more papers by this authorBruno Saubaméa
INSERM, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Descartes, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Diderot, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Search for more papers by this authorDominique Crete
INSERM, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Descartes, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Diderot, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Search for more papers by this authorJean-Michel Scherrmann
INSERM, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Descartes, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Diderot, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Search for more papers by this authorEmmanuel Curis
INSERM, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Descartes, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Diderot, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Search for more papers by this authorCarole Peyssonnaux
INSERM, U1016, Institut Cochin, Paris, France
CNRS, UMR8104, Paris, France
Université Paris Descartes, Sorbonne Paris Cité, Paris, France
Search for more papers by this authorXavier Declèves
INSERM, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Descartes, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Diderot, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Aude Jacob
INSERM, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Descartes, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Diderot, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Address correspondence and reprint requests to Aude Jacob, INSERM UMR-S 1144, Faculté des Sciences pharmaceutiques et biologiques, 4 avenue de l'observatoire, 75006 Paris, France. E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorSophie Potin
INSERM, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Descartes, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Diderot, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Search for more papers by this authorBruno Saubaméa
INSERM, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Descartes, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Diderot, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Search for more papers by this authorDominique Crete
INSERM, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Descartes, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Diderot, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Search for more papers by this authorJean-Michel Scherrmann
INSERM, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Descartes, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Diderot, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Search for more papers by this authorEmmanuel Curis
INSERM, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Descartes, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Diderot, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Search for more papers by this authorCarole Peyssonnaux
INSERM, U1016, Institut Cochin, Paris, France
CNRS, UMR8104, Paris, France
Université Paris Descartes, Sorbonne Paris Cité, Paris, France
Search for more papers by this authorXavier Declèves
INSERM, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Descartes, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Université Paris Diderot, UMR-S 1144, Paris, France
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
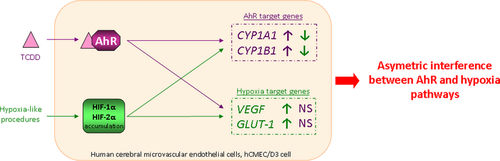
The expression of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) transcription factor was detected at transcript level in freshly isolated human brain microvessels and in the hCMEC/D3 human cerebral microvascular endothelial cell line. Recent studies have demonstrated that AhR pathway is able to crosstalk with other pathways such as hypoxia signaling pathway. Therefore, we used the hCMEC/D3 cell line to investigate the potential crosstalk between AhR and hypoxia signaling pathways. First, we performed two different hypoxia-like procedures in hCMEC/D3 cells; namely, exposition of cells to 150 μM deferoxamine or to glucose and oxygen deprivation for 6 h. These two procedures led to hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α and HIF-2α proteins accumulation together with a significant induction of the two well-known hypoxia-inducible genes VEGF and GLUT-1. Both HIF-1α and -2α functionally mediated hypoxia response in the hCMEC/D3 cells. Then, we observed that a 6 h exposure to 25 nM 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin, a strong AhR ligand, up-regulated CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 expression, and that this effect was AhR dependent. Regarding AhR and hypoxia crosstalk, our experiments revealed that an asymmetric interference between these two pathways effectively occurred in hCMEC/D3 cells: hypoxia pathway interfered with AhR signaling but not the other way around.
We studied the putative crosstalk of AhR and hypoxia pathways in hCMEC/D3 human cerebral microvascular endothelial cells. While hypoxia decreased the expression of the two AhR target genes CYP1A1 and CYP1B1, AhR activation results in no change in hypoxia target gene expression. This is the first sign of AhR and hypoxia pathway crosstalk in an in vitro model of the human cerebral endothelium.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| jnc12972-sup-0001-FigS1-S4.pdfapplication/PDF, 236.4 KB | Figure S1. HIF-1α- and HIF-2α-mediated hypoxia response in hCMEC/D3 cells under DFO exposure. Figure S2. Effect of TCDD on HIF target genes expression following the exposure to 150μM DFO in hCMEC/D3 cells. Figure S3. Effect of DFO exposure on AhR target genes expression in hCMEC/D3 cells. Figure S4. Protein expression of AhR, HIF-1α, and HIF-2α following TCDD and/or DFO exposure in hCMEC/D3 cells. |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- Abbott N. J., Patabendige A. A., Dolman D. E., Yusof S. R. and Begley D. J. (2010) Structure and function of the blood-brain barrier. Neurobiol. Dis. 37, 13–25.
- Beischlag T. V., Luis Morales J., Hollingshead B. D. and Perdew G. H. (2008) The aryl hydrocarbon receptor complex and the control of gene expression. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 18, 207–250.
- Brocato J., Chervona Y. and Costa M. (2014) Molecular responses to hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and beyond. Mol. Pharmacol. 85, 651–657.
- Chan S. Y. and Loscalzo J. (2010) MicroRNA-210: a unique and pleiotropic hypoxamir. Cell Cycle 9, 1072–1083.
- Dauchy S., Dutheil F., Weaver R. J., Chassoux F., Daumas-Duport C., Couraud P. O., Scherrmann J. M., De Waziers I. and Decleves X. (2008) ABC transporters, cytochromes P450 and their main transcription factors: expression at the human blood-brain barrier. J. Neurochem. 107, 1518–1528.
- Dauchy S., Miller F., Couraud P. O., Weaver R. J., Weksler B., Romero I. A., Scherrmann J. M., De Waziers I. and Decleves X. (2009) Expression and transcriptional regulation of ABC transporters and cytochromes P450 in hCMEC/D3 human cerebral microvascular endothelial cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 77, 897–909.
- Decleves X., Jacob A., Yousif S., Shawahna R., Potin S. and Scherrmann J. M. (2011) Interplay of drug metabolizing CYP450 enzymes and ABC transporters in the blood-brain barrier. Curr. Drug Metab. 12, 732–741.
- Denison M. S., Soshilov A. A., He G., DeGroot D. E. and Zhao B. (2011) Exactly the same but different: promiscuity and diversity in the molecular mechanisms of action of the aryl hydrocarbon (dioxin) receptor. Toxicol. Sci. 124, 1–22.
- Fradette C., Batonga J., Teng S., Piquette-Miller M. and du Souich P. (2007) Animal models of acute moderate hypoxia are associated with a down-regulation of CYP1A1, 1A2, 2B4, 2C5, and 2C16 and up-regulation of CYP3A6 and P-glycoprotein in liver. Drug Metab. Dispos. 35, 765–771.
- Gradin K., McGuire J., Wenger R. H., Kvietikova I., fhitelaw M. L., Toftgard R., Tora L., Gassmann M. and Poellinger L. (1996) Functional interference between hypoxia and dioxin signal transduction pathways: competition for recruitment of the Arnt transcription factor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16, 5221–5231.
- Hahn M. E., Allan L. L. and Sherr D. H. (2009) Regulation of constitutive and inducible AHR signaling: complex interactions involving the AHR repressor. Biochem. Pharmacol. 77, 485–497.
- Jacob A., Hartz A. M., Potin S., Coumoul X., Yousif S., Scherrmann J. M., Bauer B. and Decleves X. (2011) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent upregulation of Cyp1b1 by TCDD and diesel exhaust particles in rat brain microvessels. Fluids Barriers CNS 8, 23.
- Kallio P. J., Pongratz I., Gradin K., McGuire J. and Poellinger L. (1997) Activation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha: posttranscriptional regulation and conformational change by recruitment of the Arnt transcription factor. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 5667–5672.
- Kaur C. and Ling E. A. (2008) Blood brain barrier in hypoxic-ischemic conditions. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 5, 71–81.
- Kewley R. J., Whitelaw M. L. and Chapman-Smith A. (2004) The mammalian basic helix-loop-helix/PAS family of transcriptional regulators. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 36, 189–204.
- Khan S., Liu S., Stoner M. and Safe S. (2007) Cobaltous chloride and hypoxia inhibit aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated responses in breast cancer cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 223, 28–38.
- Le Vee M., Jouan E. and Fardel O. (2010) Involvement of aryl hydrocarbon receptor in basal and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced expression of target genes in primary human hepatocytes. Toxicol. In Vitro 24, 1775–1781.
- Legendre C., Hori T., Loyer P. et al. (2009) Drug-metabolising enzymes are down-regulated by hypoxia in differentiated human hepatoma HepaRG cells: HIF-1alpha involvement in CYP3A4 repression. Eur. J. Cancer 45, 2882–2892.
- Livak K. J. and Schmittgen T. D. (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25, 402–408.
- Mandl M. and Depping R. (2014) Hypoxia-inducible ARNT (HIF-1beta): a rare exception? Mol. Med. 20, 215–220.
- McIntosh B. E., Hogenesch J. B. and Bradfield C. A. (2010) Mammalian Per-Arnt-Sim proteins in environmental adaptation. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 72, 625–645.
- Nallamshetty S., Chan S. Y. and Loscalzo J. (2013) Hypoxia: a master regulator of microRNA biogenesis and activity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 64, 20–30.
- Oberg M., Bergander L., Hakansson H., Rannug U. and Rannug A. (2005) Identification of the tryptophan photoproduct 6-formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole, in cell culture medium, as a factor that controls the background aryl hydrocarbon receptor activity. Toxicol. Sci. 85, 935–943.
- Pfaffl M. W. (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 29, e45.
- Pollenz R. S. (2002) The mechanism of AH receptor protein down-regulation (degradation) and its impact on AH receptor-mediated gene regulation. Chem. Biol. Interact. 141, 41–61.
- Pollenz R. S. and Buggy C. (2006) Ligand-dependent and -independent degradation of the human aryl hydrocarbon receptor (hAHR) in cell culture models. Chem. Biol. Interact. 164, 49–59.
- Pollenz R. S., Davarinos N. A. and Shearer T. P. (1999) Analysis of aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated signaling during physiological hypoxia reveals lack of competition for the aryl hydrocarbon nuclear translocator transcription factor. Mol. Pharmacol. 56, 1127–1137.
- Puga A., Ma C. and Marlowe J. L. (2009) The aryl hydrocarbon receptor cross-talks with multiple signal transduction pathways. Biochem. Pharmacol. 77, 713–722.
- Quaegebeur A. and Carmeliet P. (2010) Oxygen sensing: a common crossroad in cancer and neurodegeneration. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 345, 71–103.
- Semenza G. L. (2007) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) pathway. Sci. STKE 2007, cm8.
- Semenza G. L. (2010) Vascular responses to hypoxia and ischemia. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 30, 648–652.
- Shawahna R., Uchida Y., Decleves X. et al. (2011) Transcriptomic and quantitative proteomic analysis of transporters and drug metabolizing enzymes in freshly isolated human brain microvessels. Mol. Pharm. 8, 1332–1341.
- Skuli N. and Simon M. C. (2009) HIF-1alpha versus HIF-2alpha in endothelial cells and vascular functions: is there a master in angiogenesis regulation? Cell Cycle 8, 3252–3253.
- du Souich P. and Fradette C. (2011) The effect and clinical consequences of hypoxia on cytochrome P450, membrane carrier proteins activity and expression. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 7, 1083–1100.
- Tang Y. M., Wo Y. Y., Stewart J., Hawkins A. L., Griffin C. A., Sutter T. R. and Greenlee W. F. (1996) Isolation and characterization of the human cytochrome P450 CYP1B1 gene. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 28324–28330.
- Tian H., McKnight S. L. and Russell D. W. (1997) Endothelial PAS domain protein 1 (EPAS1), a transcription factor selectively expressed in endothelial cells. Genes Dev. 11, 72–82.
- Tsuchiya Y., Nakajima M. and Yokoi T. (2003) Critical enhancer region to which AhR/ARNT and Sp1 bind in the human CYP1B1 gene. J. Biochem. 133, 583–592.
- Veldhoen M., Hirota K., Christensen J., O'Garra A. and Stockinger B. (2009) Natural agonists for aryl hydrocarbon receptor in culture medium are essential for optimal differentiation of Th17 T cells. J. Exp. Med. 206, 43–49.
- Vorrink S. U. and Domann F. E. (2014) Regulatory crosstalk and interference between the and hypoxia sensing pathways at the AhR-ARNT-HIF1alpha signaling node. Chem. Biol. Interact. 218, 82–88.
- Vorrink S. U., Severson P. L., Kulak M. V., Futscher B. W. and Domann F. E. (2014) Hypoxia perturbs aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling and CYP1A1 expression induced by PCB 126 in human skin and liver-derived cell lines. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 274, 408–416.
- Wang X., Hawkins B. T. and Miller D. S. (2010) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated up-regulation of ATP-driven xenobiotic efflux transporters at the blood-brain barrier. FASEB J. 25, 644–652.
- Weidemann A. and Johnson R. S. (2008) Biology of HIF-1alpha. Cell Death Differ. 15, 621–627.
- Wenger R. H., Stiehl D. P. and Camenisch G. (2005) Integration of oxygen signaling at the consensus HRE. Sci. STKE 2005, re12.
- Wheeler R. E. (2010) The R project for statistical computing. online at http://www.r-project.org/[accessed on 21 May 2014].
- Whitlock J. P., Jr, Okino S. T., Dong L., Ko H. P., Clarke-Katzenberg R., Ma Q. and Li H. (1996) Cytochromes P450 5: induction of cytochrome P4501A1: a model for analyzing mammalian gene transcription. FASEB J. 10, 809–818.
- Yang X., Solomon S., Fraser L. R., Trombino A. F., Liu D., Sonenshein G. E., Hestermann E. V. and Sherr D. H. (2008) Constitutive regulation of CYP1B1 by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in pre-malignant and malignant mammary tissue. J. Cell. Biochem. 104, 402–417.
- Zhang N. and Walker M. K. (2007) Crosstalk between the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and hypoxia on the constitutive expression of cytochrome P4501A1 mRNA. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 7, 282–290.