A 22-YEAR-OLD MAN WITH INTRACRANEAL HYPERTENSION AND IMPAIRED SENSATION OVER THE PERINEUM AND LEFT FOOT
Henda Foreid
Laboratory of Neuropathology, Hospital de Santa Maria; Institute of Molecular Medicine, Lisbon Faculty of Medicine, Lisbon
Search for more papers by this authorCândida Barroso
Laboratory of Neuropathology, Hospital de Santa Maria; Institute of Molecular Medicine, Lisbon Faculty of Medicine, Lisbon
Search for more papers by this authorHerculano Carvalho
Department of Neurosurgery, Hospital de Santa Maria, Lisbon
Search for more papers by this authorCarlos Morgado
Department of Neurological Imagiology, Hospital de Santa Maria, Lisbon
Search for more papers by this authorLúcia Roque
Laboratory of Cytogenetics, Instituto Português de Oncologia de Francisco Gentil, Lisbon
Search for more papers by this authorJosé Pimentel
Laboratory of Neuropathology, Hospital de Santa Maria; Institute of Molecular Medicine, Lisbon Faculty of Medicine, Lisbon
Search for more papers by this authorHenda Foreid
Laboratory of Neuropathology, Hospital de Santa Maria; Institute of Molecular Medicine, Lisbon Faculty of Medicine, Lisbon
Search for more papers by this authorCândida Barroso
Laboratory of Neuropathology, Hospital de Santa Maria; Institute of Molecular Medicine, Lisbon Faculty of Medicine, Lisbon
Search for more papers by this authorHerculano Carvalho
Department of Neurosurgery, Hospital de Santa Maria, Lisbon
Search for more papers by this authorCarlos Morgado
Department of Neurological Imagiology, Hospital de Santa Maria, Lisbon
Search for more papers by this authorLúcia Roque
Laboratory of Cytogenetics, Instituto Português de Oncologia de Francisco Gentil, Lisbon
Search for more papers by this authorJosé Pimentel
Laboratory of Neuropathology, Hospital de Santa Maria; Institute of Molecular Medicine, Lisbon Faculty of Medicine, Lisbon
Search for more papers by this author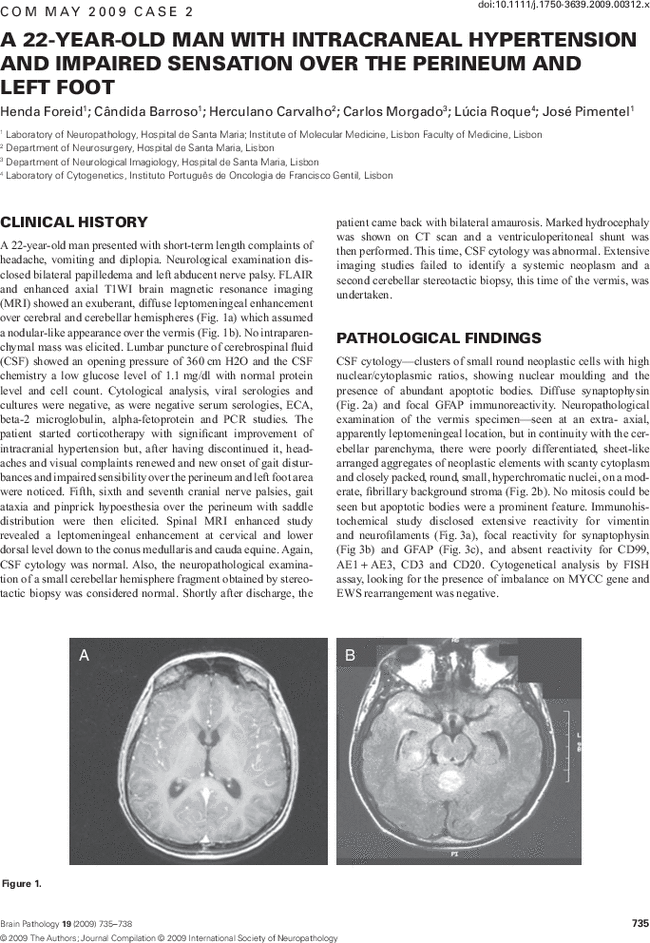
REFERENCES
- 1 Begemann M, Lyden D, Rosenblum MK, Lis E, Wolden S, Antunes NL, Dunkel IJ (2003) Primary leptomeningeal primitive neuroectodermal tumor. J Neurooncol 63: 299–303.
- 2 Connor CL, Cushing H (1927) Diffuse tumors of leptomeninges. Two cases in which the process was revealed only by the microscope. Arch Pathol 3: 374–392.
- 3 Delattre O, Zucman J, Plougastel B, Desmaze C, Melot T, Peter M, Kovar H, Joubert I, De Jong P, Rouleau G, Aurias A, Thomas G (1992) Gene fusion with an ETS DNA-binding domain caused by chromosome translocation in human tumours. Nature 359: 162–165.
- 4 Dirks PB, Harris L, Hoffman HJ, Humphreys RP, Drake JM, Rutka JT (1996) Supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumors in children. J Neurooncol 29: 75–84.
- 5 Ebinger F, Brühl K, Gutjahr P (2000) Early diffuse leptomeningeal primitive neuroectodermal tumors can escape detection by magnetic resonance imaging. Child's Nerv Syst 16: 398–401.
- 6 Fujii M, Orita T, Nishizaki T, Aoki H, Tanaka K (1991) Primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the leptomeninges. Neuroradiology 33: 260–263.
- 7 Jennings MT, Slatkin N, D'Angelo M, Ketonen L, Johnson M, Rosenblum M, Creasy J, Tulipan N, Walker R (1993) Neoplastic meningitis as the presentation of occult primitive neuroectodermal tumors. J Child Neurol 8: 306–312.
- 8 Lamont JM, Mc Manamy CS, Pearson AD, Clifford SC, Elison DW (2004) Combined histopathological and molecular cytogenetic stratification of medulloblastoma patients. Clin Cancer Res 10: 5482–5493.
- 9 Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK (2007) WHO Classification of Tumours of the Central Nervous System. World Health Organization, pp. 132–146. IARC Press, WHO: Lyon.
- 10 Suman R, Santosh V, Anandh BA (2007) Primary leptomeningeal medulloblastoma. Pediatr Neurosurg 43: 544–545.