RELIC THERMOSENSITIVE GENE EXPRESSION IN A TURTLE WITH GENOTYPIC SEX DETERMINATION
Abstract
The evolution of sex determination remains one of the most fascinating enigmas in biology. Transitions between genotypic sex determination (GSD) and temperature-dependent sex determination (TSD) have occurred multiple times during vertebrate evolution, however, the molecular basis and consequences of these transitions in closely related taxa remain unresolved. Here I address a critical question: Do species with GSD derived from ancestors possessing TSD retain any ancestral thermal sensitivity in the developmental pathways underlying gonadal differentiation? Results from an expression study of a gene involved in early gonadogenesis in GSD (Apalone mutica) and TSD (Chrysemys picta) turtles, support the hypothesis that Wt1 in A. mutica displays such a relic thermal sensitivity. This retention is likely enabled by Sf1, a gene immediately downstream from Wt1 whose expression is independent of temperature in this species. My results constitute the first empirical evidence of a GSD vertebrate exhibiting thermal sensitivity in the expression of a gene regulating gonadogenesis. This novel finding reveals an undocumented source of raw material for future evolutionary change that may exist in other GSD taxa, and one that enhances the evolutionary potential of the gene networks underlying sexual differentiation and contributes to the astonishing ability of sex-determining mechanisms.
In most vertebrates sex is determined at conception by the individual's genotype (genotypic sex determination, GSD), whereas in some species sex determination depends on the environmental temperature during development (temperature-dependent sex determination, TSD) (Bull 1983; Valenzuela et al. 2003; Valenzuela and Lance 2004). Why sex is determined by nest temperature in so many reptiles and by the genotype in others remains one of the most fundamental conundrums in evolutionary biology (Shine 1999; Valenzuela 2004). To answer this question it is necessary to understand how sex is determined by temperature or zygotic genotype in closely related taxa. Much effort has been devoted to understanding the molecular control of GSD particularly in model organisms, and studies of nonmodel TSD species such as reptiles are increasing (Morrish and Sinclair 2002; Place and Lance 2004; Ottolenghi et al. 2007). But the molecular underpinnings and consequences of the multiple evolutionary transitions between TSD and GSD in vertebrates remain understudied.
Indeed, little is known about the existence of thermal sensitivity in the gene regulatory network underlying gonadogenesis in GSD species despite its important implications, particularly in those species whose sex ratios are not biased by temperature. For instance, theory predicts that TSD can evolve neutrally from GSD when an ecological change exposes individuals to conditions that allow the expression of a ubiquitously preexisting thermal sensitivity (Bull 1981). On the other hand, it is assumed that in GSD species derived from a TSD ancestor, such as in turtles (Janzen and Krentz 2004), sexual differentiation has lost all thermal sensitivity over evolutionary time. But a critical unexplored alternative is that GSD species retain the thermal sensitivity in the ancestral TSD thermal trigger (the gene that opens the male and female differentiation pathways in a temperature-specific manner), and that this signal is rendered ineffective and selectively neutral by downstream genes in the developmental cascade that stop responding to temperature during GSD evolution.
Here I address this intriguing question by analyzing the expression of the Wilm's tumor-associated gene (Wt1) in Apalone mutica turtles possessing such a derived GSD mechanism (Janzen and Krentz 2004), as well as in Chrysemys picta turtles, a TSD counterpart.
Wt1 plays an important role in early urogenital development through transcriptional regulation and RNA processing (Kent et al. 1995; Spotila and Hall 1998; Hammes et al. 2001; Roberts 2005; Gao et al. 2006). Wt1 encodes a transcription factor protein containing four Kruppel-like zinc-fingers at its C-terminal end with high protein similarity to early growth response genes (Kent et al. 1995). Wt1 is necessary for the establishment of the bipotential gonad and later testis development as it is essential for the maintenance of Sertoli cells and seminiferous tubules in the developing mammalian testis (Gao et al. 2006). Nonmammalian homologs of Wt1 have been identified with similar functions in the development of the urogenital system (Kent et al. 1995; Semba et al. 1996; Spotila and Hall 1998; Spotila et al. 1998; Smith et al. 1999; Yamamura et al. 2005; Ottolenghi et al. 2007). Importantly, Wt1 exhibits temperature-specific expression in Trachemys scripta turtles (TSD) (Spotila et al. 1998). Additionally, Wt1 regulates another gene involved in early gonadogenesis (Sf1) (Roberts 2005), which is a potential TSD thermal trigger in C. picta turtles (Valenzuela et al. 2006). Thus, Wt1 is an excellent target gene to address another still unanswered question of what renders gonadogenesis thermosensitive in TSD vertebrates.
Materials and Methods
SAMPLE COLLECTION
Eggs were collected from freshly laid natural nests of C. picta (seven clutches) and A. mutica (17 clutches), and correspond to the same eggs used previously and collected under permits indicated in Valenzuela et al. (2006). Eggs were brought to the laboratory for incubation at constant temperatures that produce ∼100% male (25°C) and ∼100% female (30°C) C. picta hatchlings. Temperature does not bias sex ratios in A. mutica (GSD) (Janzen 1993).
Eggs from each clutch were uniformly distributed between incubation temperatures. Eggs from each clutch were divided equally among multiple plastic containers filled 3/5 of the way with moistened vermiculite set at −150kPa by adding 338 g of water per 300 g of vermiculite. Boxes containing only the substrate were weighed (± 0.1g), and they were weighed again after adding the eggs and the weight recorded. Eggs were partially buried in the substrate in random positions in the box. Prior to the sampling of any egg (or weekly otherwise), the boxes were reweighed and lost moisture (as determined by weight loss) was replaced. The new weight was recorded after the removal of any eggs. Egg containers were rotated at least weekly to control for the effect of any potential thermal cline in the incubators.
Embryos were collected at several developmental stages prior to and during the thermosentitive period (TSP) (sensu Yntema 1968) equivalent for both temperature treatments and species used: Stage 9 = Before TSP, Stage 12 = Before TSP, Stage 15 = TSP Onset, Stage 19 = Middle TSP, Stage 22 = End TSP (Bull and Vogt 1981). Collection of embryos from each clutch was also distributed across all developmental stages sampled. Sampled embryos were placed immediately in 10 vol of RNAlater (Ambion, Inc., Austin, TX), stored at −20°C and subsequently at −80°C for later use following the manufacturer's recommendations.
CLONING AND QPCR
RNA was extracted from the adrenal-kidney-gonadal complex (whole embryos or trunks were used from stage 9 and 12 embryos, respectively) using QIAGEN's RNeasy Kits (QIAGEN, Valencia, CA), and DNAse-I digested to prevent DNA contamination. RNA was quantified using a NanoDrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (NanoDrop, Wilmington, DE), and its quality was assessed by the presence of ribosomal bands in ethidium-bromide stained agarose gels. Individual samples were kept separate and analyzed without pooling. Total RNA (1 μg per sample) was retro-transcribed with (dT)20 primers using Superscript III (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) following the manufacturer's protocol. For samples that yielded less than 1ug total RNA in 8 μl elute volume, as much as 8 μl were used for the RT-PCR, and the total RNA amount was recorded for standardization during the data analysis as described below.
Degenerate primers were designed for relatively conserved regions of vertebrate Wt1 cDNA sequences as found in GeneBank (Table 1). These primers amplified a 362 bp Wt1 cDNA fragment in both species, which was cloned in a pGEM-T Easy Vector System (Promega, Madison WI) and sequenced. A 343bp β-actin cDNA fragment (Valenzuela et al. 2006) was used to test for the quality of the extracted RNA during QPCR, and for normalization of Wt1 gene expression. Internal primers amplified a 80 bp Wt1 fragment (Table 1) and a 124 bp β-actin fragment (Valenzuela et al. 2006) during real-time QPCR using Brilliant SYBR Green QPCR Master Mix (Stratagene) in an Mx3000P thermocycler (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA). The 80 bp Wt1 fragment is common to all four Wt1 turtle isoforms present in relatively equal proportions during development, but whose total steady state is affected by temperature in TSD species (Spotila and Hall 1998). ROX was used as the reference die for background correction. Standard curves were generated from pure miniprep cloned DNA obtained above by diluting cut inserts at concentrations of 5, 1, 1 × 10−2, 1 × 10−4, 1 × 10−6, 1 × 10−12, 1 × 10−14, and 1 × 10−16 ng/μl, and run in duplicate in each QPCR to ensure technical repeatability of the results. Samples from all clutches, temperatures, and stages were included in each 96-well plate used for the QPCR experiments to avoid any systematic bias. QPCR conditions followed Valenzuela et al. (2006): 1 cycle at 95°C for 10 min; 45 cycles of 95°C for 30 sec, 60°C for 1 min, 72°C for 1 min; and a dissociation-curve cycle of 95°C for 1 min, 55°C for 30 sec, and 95°C for 30 sec. Dissociation profiles obtained at the end of the PCR cycles were inspected to confirm amplification of a single transcript.
| Primers | Chrysemys picta | Apalone mutica |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin forward | 5′-CAGGTCATCACCATYGGCAA-3′ | |
| β-actin reverse | 5′-GCTTGCTGATCCACATCTGC-3′ | |
| Wt1 forward | 5′-AAACGYCCCTTCATGTGTGC-3′ | |
| Wt1 reverse | 5′-CTCTGRTGCATGTTGTGATG-3′ | |
| qmβ-actin forward | 5′-AAGCCCTCTTCCAGCCAT-3′ | 5′-AAGCTCTCTTCCAGCCCT-3′ |
| qmβ-actin reverse | 5′-GACAGCACAGTGTTGGCG-3′ | |
| qmWt1 for | 5′-TGGGTTACAGTGCATTGGC-3′ | |
| qmWt1 rev | 5′-GAGGCCTGGACCAGACAA-3′ |
DATA ANALYSIS
Initial template amount for each sample and each gene was calculated using standard-curve quantification via the algorithms implemented in Mx3000p version 2.0 from Stratagene with background correction. Initial copy numbers were calculated from the molecular weight of the fragments for each gene, and standardized to 1 μg of initial total RNA. Expression of Wt1 was normalized using β-actin expression data, and log2 transformed to correct for the heteroscedasticity and nonnormal distribution characteristic of amplification data. Statistical analysis was carried out on these normalized log2-transformed data keeping individual values separate (Valenzuela et al. 2006). The significance of the temperature treatment effect was determined by testing for differences in the mean gene expression values at each sampled developmental stage via an ANOVA as implemented in Jmp 5.1.2© (SAS Institute, Inc. 2004) with Bonferroni correction (Sokal and Rohlf 1995).
Results
The fragments of Wt1 cloned here from embryonic adrenal-kidney-gonadal tissue encompassed part of the nuclear export and nucleic binding domain regions corresponding to exons 7–10 (Spotila and Hall 1998; Roberts 2005). The sequence of the Wt1 fragment of C. picta's (GenBank EF127640) was 99.97% identical to A. mutica's (GenBank EF127639) excluding the KTS sites, 98.3% to Trachemys scripta's,93.6% to alligator's, 91.2% to chicken's, 87% to human's, 85.4% to mouse's, 64.4% to frog's (80.4% when excluding the KTS sites), and 80.4% to zebrafish's. Differences were also found at the amino acid level (Table 2). The amino acid sequence of C. picta differs by two residues from that of T. scripta (Spotila and Hall 1998) (only one of these changes is present in A. mutica) (Table 2).
| Trachemys | … .|… .| | … .|… .| | … .|… .| | … .|… .| | … .|… .| | … .|… .| | … .|….| |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 15 | 25 | 35 | 45 | 55 | 65 | |
| KRPFMCAYPG | CNKRYFKLSH | LQMH∼RKHTG | EKPYQCDFKD | CERRFSRSDQ | LKRHQRRHTG | VKPFQCKTCQ | |
| Apalone | … … … . | … … … . | … .S… .. | … … … . | … … … . | … … … . | … … … . |
| Chrysemys | … … … . | … … … . | … .S… .. | … … … . | … … … . | … … … . | … … … . |
| Alligator | … … … . | … … … . | … .S… .. | … … … . | …… … . | … … … . | … … … . |
| Chicken | … … … . | … … … . | … .S… .. | … … … . | … … … . | … … … . | … … … . |
| Human | … … … . | … … … . | … .S… .. | … … … . | … … … . | … … … . | …… … . |
| Mouse | … … … . | … … … . | … .S… .. | … … … . | … … … . | … … … . | … … … . |
| Frog | … … … . | … … … . | … .S… .. | … … … . | … … … . | … … … . | … … … . |
| Zebrafish | … … … . | … … … . | … .S… .. | … … ..T. | .G… … .. | … … … . | … … E… |
| Trachemys | … .|… .| | … .|… .| | … .|… .| | … .|… .| | … .|… .| | … .|… .| |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 75 | 85 | 95 | 105 | 115 | 125 | |
| RKFSRSDHLK | THTRTHTGKT | SEKPFSCRWP | SCQKKFARSD | ELVRHHNMHQ | RNMTKLQLAL | |
| Apalone | … … … . | … … ..– | -… … … | … … … . | … … … . | … … … . |
| Chrysemys | … … … . | … … … . | … … R… | … … … . | … … … . | … … … . |
| Alligator | … … … . | … … … . | … … … . | … … … . | … … … . | … … … . |
| Chicken | … … … . | … … … . | … … … . | … … … . | … … … . | … … … . |
| Human | … … … . | … … … . | … …… . | … … … . | … … … . | … … … . |
| Mouse | … … … . | … … … . | … … … H | … … … . | … … … . | … … HV.. |
| Frog | … … … . | … … ..– | -… … … | … … … . | … … … . | … … … . |
| Zebrafish | … … … . | … … … . | … ..N… . | N… … … | … … … . | ..L… ..TI |
- Trachemys, Trachemys scripta; Chrysemys, Chrysemys picta; Apalone, Apalone mutica; Alligator, Alligator mississippiensis; Chicken, Gallus gallus; Human, Homo sapiens; Mouse, Mus musculus; Frog, Xenopus laevis; Zebrafish, Danio rerio.
Standard curves for β-actin and Wt1 had R2 values of 0.97 and 0.998, respectively, for C. picta, and of 0.98 and 0.996, respectively, for A. mutica. Wt1 expression was significantly higher in C. picta embryos incubated at 25°C (male-producing temperature) than at 30°C (female-producing temperature) during developmental stage 12 that precedes the thermosensitive period (F= 18.32, P= 0.0052, Fig. 1). Notably, in A. mutica, Wt1 expression was also significantly higher at 25°C than at 30°C during stage 12 (F= 10.0532, P= 0.008, Fig. 1).

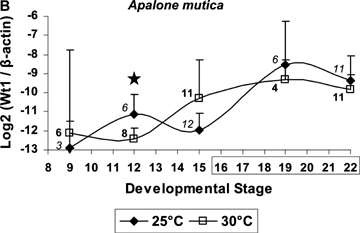
Developmental expression of Wt1 in Chrysemys picta (TSD) and Apalone mutica turtles (GSD). y-axis represents Wt1 initial copy number normalized to β-actin (+ SD). Boxed stages correspond to C. picta's thermosensitive period. Sample sizes at 25°C (italics) and at 30°C (bold) are presented per sampling time. Stars denote significant differential expression. Results are robust irrespective of outliers. The magnitude of difference in expression at stage 12 is greater in C. picta than in A. mutica. Differences in transcript abundance at all other stages are not statistically significant and thus, no biological significance can be attributed to the crossing of the expression profiles.
Significance of the results is not due to any systematic bias generated by a small number of clutches represented, nor to clutch-mates being over-represented in any particular developmental stage or temperature. For A. mutica, 17 clutches were represented, and a single egg per clutch was sampled at all temperature-by-stage combinations. For C. picta, seven clutches were represented, and only in stages 19 and 22 did two of the total eggs sampled at each temperature come from the same clutch. Importantly, readings from these clutch-mate pairs were not more similar than from any pair of unrelated individuals sampled at the same temperature-by-stage combination. Additionally, although duplicate readings from embryonic samples were precluded because the limited total RNA amount per sample was used to profile seven different genes (Valenzuela et al. 2006; Valenzuela and Shikano 2007, N. Valenzuela unpubl. data), duplicate readings from the standard curves were 98–99.9% identical, thus ensuring the technical reliability of the transcript abundance readings. The only exception was one duplicate standard for A. mutica whose readings were 92.2% identical. However, results were robust to removing this one particular standard duplicate for transcript abundance quantification.
Discussion
The partial cDNA fragments of A. mutica and C. picta cloned here exhibit high, but not perfect homology to other vertebrate Wt1 cDNAs (Table 2). Because the two amino acid substitutions detected among turtles include a missing serine in T. scripta that is a very polar amino acid present in all other vertebrates, and another change from a neutral cystein to a positively charged arginine, these few differences in this highly conserved zinc-fingers region (Spotila and Hall 1998) may be functionally important.
Wt1 is associated with testis development in mammals and it expression is higher in males (Gao et al. 2006). Consistently, significant differential Wt1 expression is higher at male- than at the female-producing temperatures in T. scripta turtles (Spotila and Hall 1998; Spotila et al. 1998), as was observed for C. picta in the present study. However, the timing of Wt1 differential expression varied between these two TSD turtles. Particularly, Wt1 was not differentially expressed in T. scripta at stage 12 as determined by in situ hybridization (and no expression was detected at this stage by Northern blot analysis), but levels were higher at male- than at female-producing temperatures during stages ≥14. This contrasts with the sexually monomorphic Wt1 expression of chickens (Smith et al. 1999), alligators (Western et al. 2000), and frogs (Yamamura et al. 2005). Because all these studies on reptiles and frogs used entire gonadal/kidney complexes, differences in expression patterns in general, and during the thermosensitive period of C. picta and T. scripta in particular, cannot be attributed to the masking effect that gene expression in whole complexes can have on subtle but biologically significant differential expression in the gonads alone (Pieau and Dorizzi 2004). Similarly contrasting expression patterns among TSD, and across TSD and GSD species, exist for other genes involved in gonadogenesis such as Sf1 and Aromatase, and as in Wt1 they likely reflect evolutionarily divergence in expression (Valenzuela et al. 2006; Valenzuela and Shikano 2007). Such divergence of the gene regulatory networks underlying sex determination and differentiation would represent an example of developmental systems drift (True and Haag 2001), in direct contrast with the consistent gene expression across species expected if sex determining systems (TSD or GSD) were pleisiomorphic and developmentally conserved.
The concordance in expression at stage 12 for Wt1 from this study and for Sf1 (Valenzuela et al. 2006) in C. picta supports the hypothesis that early developmental stages are important in activating temperature-specific pathways in C. picta. Because Wt1 is known to regulate Sf1 in other vertebrates (Wilhelm and Englert 2002), this result adds Wt1 to Sf1 as another candidate master thermal switch in TSD turtles (Valenzuela et al. 2006) that warrants further testing. As such, this finding points in a promising direction in the quest for the elusive key regulator that bestows thermal sensitivity to vertebrate sexual differentiation. Future studies should explore Wt1 and Sf1 regulation and downstream effects to test their specific roles in opening the sex differentiation pathways in a temperature-specific manner in TSD taxa.
Even more remarkably, the GSD turtle A. mutica exhibited differential Wt1 expression. The potential explanation that Wt1 differential expression in A. mutica is due to a general effect of temperature on the kinetics of gene expression, for example, can be ruled out. Under this hypothesis, such general effects should be observable across other sex differentiation and housekeeping genes, yet the expression of two other genes involved in gonadogenesis, Sf1 and Aromatase, and of β-actin is independent of temperature in this species (Valenzuela et al. 2006; Valenzuela and Shikano 2007). The alternative that the significance of the results in C. picta or A. mutica may be due to an experimental bias can also be ruled out because care was taken to use eggs from multiple clutches (17 for A. mutica and seven for C. picta) and to distribute eggs from each clutch uniformly across temperatures, incubation boxes, and sampling times as detailed in the methods section.
Alternatively, this differential Wt1 expression in A. mutica combined with the observation that temperature does not bias sex ratios from the 1:1 expected under GSD in this species (Janzen 1993), and given that GSD is a derived trait in turtles (Janzen and Krentz 2004), is consistent with the hypothesis that A. mutica's Wt1 thermal sensitivity is a relic from a TSD ancestor. Two questions follow. First, why this temperature-specific signal does not result in biased sex ratios in A. mutica? And second, why has this thermal sensitivity persisted over evolutionary time? The answer to both questions may lay in Sf1's thermal insensitivity in this species (Valenzuela et al. 2006). Specifically, studies on TSD and GSD taxa indicate that when differentially expressed, Wt1 levels are higher in males than in females (Spotila and Hall 1998; Spotila et al. 1998; Du et al. 2002; Gao et al. 2006). Thus Wt1 differential expression in A. mutica, which mimics that of C. picta at that same developmental stage, is consistent with this expectation. Additionally, higher levels of Wt1 upregulate Sf1 (Roberts 2005). Because Sf1 lays downstream of Wt1 in the sex determination pathway, Sf1's lack of differential expression by temperature in A. mutica (Valenzuela et al. 2006) indicates that Sf1 is not responding to Wt1's thermal signal. This would render Wt1's differential expression functionally inoperative to bias sex ratios and consequently, selectively neutral, such that there would be no selection for its rapid or complete loss. Under this scenario, variation should be free to accumulate, leading to the testable prediction that there ought to be higher levels of standing variation in the levels of expression among individuals in Wt1 than in Sf1 as a result of neutral evolution. Consistent with this prediction, the coefficients of variation (Sokal and Rohlf 1995) of individual expression were higher for Wt1 than for Sf1 (26.9 and 14.9 absolute values, respectively), and it should be noted that both genes were profiled in the same set of embryos (this study and Valenzuela et al. 2006).
The protein WT1 is localized in Sertoli cells and has been proposed as a contributor to the differential cell proliferation between putative testis and ovaries observed in T. scripta (Schmahl et al. 2003). WT1 is also expressed in the central nervous system at multiple locations in the cephalic region (Roberts 2005). The significant differences in Wt1 expression detected in C. picta and A. mutica in this study cannot be due to cephalic expression because trunks were used at stage 12. However, because Wt1 is also involved in the development of other internal organs (Hohenstein and Hastie 2006), future analyses on isolated gonads are required to rule out the possibility that differential expression at stage 12 could have extragonadal localization. Nonetheless, irrespective of the tissue source, a differential pattern was detected in a temperature-specific manner in C. picta, which in this species is also sex-specific because each temperature used produces a single sex.
The possibility that differential Wt1 expression in A. mutica is due to sex-specific differences that coincide with the temperature treatments (e.g., most/all stage-12 embryos from 26° happened to be males and from 30° happened to be females) could not be addressed here directly as no molecular marker exists to sex embryos of this species. However, although ruling out this alternative conclusively awaits the development of appropriate markers, this scenario seems unlikely. If such bias existed, it would be expected that other genes known to be involved in sexual differentiation such as Sf1 and Aromatase, will exhibit a concordant differential expression pattern, which was not detected in this very set of embryos (Valenzuela et al. 2006; Valenzuela and Shikano 2007).
The finding of Wt1differential expression by temperature in a GSD vertebrate for the first time is paramount for understanding the evolution of sex-determining mechanisms because it shows that GSD species can harbor differential thermal sensitivity in genes important for gonadogenesis even when such sensitivity is nonfunctional for temperature-specific sexual differentiation (because temperature does not affect sex ratios in A. mutica[Janzen 1993]). This is critical because theoretical models for the evolution of TSD (Bull 1981; 1983, reviewed in Valenzuela 2004) rely on the premise that GSD taxa posses an ubiquitous thermal sensitivity that can be co-opted during the evolution of phenotypic plasticity (TSD), and my results provide the first empirical evidence for the existence of such sensitivity at the level of gene expression. Similar cases may await discovery in other GSD taxa and thus, more studies are needed that focus not only on the effect that temperature has on gene expression in TSD species but also in their GSD counterparts.
Associate Editor: B. Swalla
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
I thank T. Shikano and A. LeClere for their assistance with some data collection. This study was partially funded by the Center for Integrative Genomics at Iowa State University.




