Models of interacting dark energy
ABSTRACT
We investigate the interaction between dark energy and dark matter using a phenomenological model with an interaction proportional to the dark energy density and two physically motivated models, interacting holographic dark energy and mass varying neutrino dark energy. Constraints on the interaction parameters are obtained using observational data including the gold type Ia supernovae set, the cosmic microwave background (CMB) shift parameter 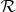 from the 3-yr Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe, the baryon acoustic oscillation parameter A from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey and the time-dependent observables of the lookback time to high-redshift galactic clusters. We find that the available data can be satisfied reasonably well for a wide range of parameters in the models studied and that the CMB
from the 3-yr Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe, the baryon acoustic oscillation parameter A from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey and the time-dependent observables of the lookback time to high-redshift galactic clusters. We find that the available data can be satisfied reasonably well for a wide range of parameters in the models studied and that the CMB 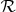 parameter appears to have the most discriminating power between the models.
parameter appears to have the most discriminating power between the models.




