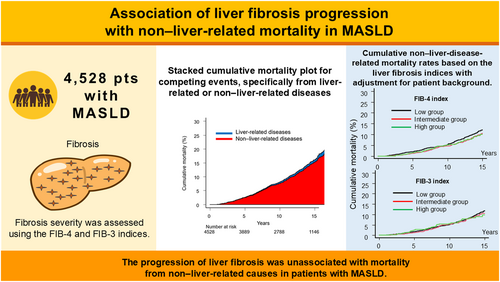
Association of liver fibrosis progression with non–liver-related mortality in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
Abstract
Aim
In patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), the prognosis and outcomes, particularly non–liver-related mortality, remain insufficiently elucidated. We investigated all-cause mortality in patients with MASLD to elucidate the association of the severity of liver fibrosis with liver-related and non–liver-related mortality in MASLD.
Methods
Among 4528 participants with MASLD, we examined the causes of death and analyzed liver-related and non–liver-related mortality, stratified by the degree of fibrosis using the competing risk method. Fibrosis severity was assessed using the Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) and FIB-3 indices.
Results
The median follow-up period was 11.7 years. Of the 4528 participants, 551 died during the follow-up period, with only 37 (6.7%) deaths attributable to liver-related diseases and 514 (93.3%) to non–liver-related causes. For the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma, the hazard ratios (HRs; 95% confidence interval [CI]) for FIB-4 were 5.67 (2.20–14.59) and 32.14 (12.40–83.35) and for FIB-3 were 5.43 (2.73–10.79) and 19.96 (10.50–37.93). For liver-related mortality, the HRs (95% CI) for FIB-4 were 6.32 (2.23–17.85) and 27.62 (9.74–78.37) and for FIB-3 were 7.15 (2.62–19.50) and 19.86 (8.12–48.55), respectively. In contrast, intermediate and high FIB-4 and FIB-3 indices were unassociated with non–liver-related mortality: HRs (95% CI) for FIB-4 were 0.85 (0.70–1.04) and 0.87 (0.64–1.18), and for FIB-3 were 0.96 (0.77–1.20) and 0.92 (95% CI, 0.64–1.31), respectively.
Conclusions
The progression of liver fibrosis was unassociated with mortality from non–liver-related causes in patients with MASLD.
Graphical Abstract
Mortality from disease-specific causes in 4528 metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) was analyzed, stratified by the degrees of liver fibrosis using the Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) and FIB-3 indices. Among the 4528 patients, 514/551 (93.3%) died from non–liver-related causes during the follow-up period. Multivariable analysis showed that the progression of liver fibrosis severity was not associated with mortality from non–liver-related causes in MASLD.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
Toshifumi Tada is an editorial board member of Hepatology Research. Junko Tanaka is the ex-editorial board member of Hepatology Research. The other authors declare no conflict of interests for this article.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The datasets are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.