Chemically modified peanut extract shows increased safety while maintaining immunogenicity
Funding information
This study was financially supported by HAL Allergy BV, Leiden, The Netherlands
Abstract
Background
Peanuts are most responsible for food-induced anaphylaxis in adults in developed countries. An effective and safe immunotherapy is urgently needed. The aim of this study was to investigate the immunogenicity, allergenicity, and immunotherapeutic efficacy of a well-characterized chemically modified peanut extract (MPE) adsorbed to Al(OH)3.
Methods
Peanut extract (PE) was modified by reduction and alkylation. Using sera of peanut-allergic patients, competitive IgE-binding assays and mediator release assays were performed. The immunogenicity of MPE was evaluated by measuring activation of human PE-specific T-cell lines and the induction of PE-specific IgG in mice. The safety and efficacy of MPE adsorbed to Al(OH)3 was tested in two mouse models by measuring allergic manifestations upon peanut challenge in peanut-allergic mice.
Results
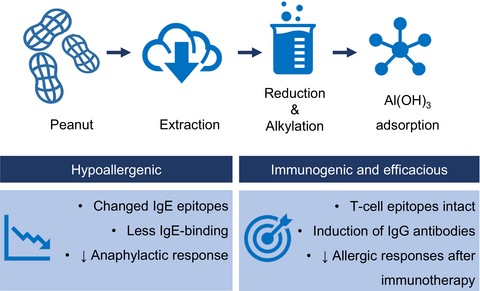
Compared to PE, the IgE-binding and capacity to induce allergic symptoms of MPE were lower in all patients. PE and MPE displayed similar immunogenicity in vivo and in vitro. In mice sensitized to PE, the threshold for anaphylaxis (drop in BT) upon subcutaneous challenge with PE was 0.01 mg, while at 0.3 mg MPE no allergic reaction occurred. Anaphylaxis was not observed when PE and MPE were fully adsorbed to Al(OH)3. Both PE and MPE + Al(OH)3 showed to be efficacious in a model for immunotherapy.
Conclusion
In our studies, an Al(OH)3 adsorbed MPE showed reduced allergenicity compared to unmodified PE, while the efficacy of immunotherapy is maintained. The preclinical data presented in this study supports further development of modified peanut allergens for IT.
Graphical Abstract
A modified peanut extract (MPE), made by reduction and alkylation, followed by aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)3) adsorption was similar or more immunogenic than unmodified peanut extract (PE). MPE demonstrated strongly improved safety compared to PE in relevant in vitro and in vivo assays. MPE showed efficacy in a murine model for immunotherapy, which supports further development of modified peanut allergens for subcutaneous immunotherapy.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
Hanneke P.M van der Kleij, Hans J.M. Warmenhoven, and Dirk Jan E. Opstelten are employees of HAL Allergy. Ronald van Ree is consultant of HAL Allergy, Stef J. Koppelman reports consultancy activities for DBV Technologies and has been a employee of HAL Allergy when part of this work was conducted.