Safety and Durability of Accelerated Infliximab Dosing Strategies in Pediatric IBD
A Single Center, Retrospective Study
Meghan Gibson MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorShova Subedi MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorDavid H. Barker PhD
Department of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, Rhode Island Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorSamuel Masur MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Department of Pediatrics, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorMeaghan M. Mallette MPA
Lifespan Biostatistics Core, Rhode Island Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorArchana Lingannan MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorAldo Alejandro Recinos Soto MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorDyadin Esharif MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorSarah H. Maxwell MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Department of Pediatrics, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorMuhammad Safwan Riaz MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorMichael I. Herzlinger MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorLinda B. Shalon MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorCarolina S. Cerezo MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorVania L. Kasper MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorAlbert M. Ross MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorNeal S. Leleiko MD, PhD
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, NY
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jason M. Shapiro MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Address correspondence and reprint requests to Jason M. Shapiro, MD, Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Nutrition and Liver Diseases, Hasbro Children’s Hospital and Rhode Island Hospital, Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, 593 Eddy Street, Providence, RI 02903 (e-mail: [email protected]).Search for more papers by this authorMeghan Gibson MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorShova Subedi MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorDavid H. Barker PhD
Department of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, Rhode Island Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorSamuel Masur MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Department of Pediatrics, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorMeaghan M. Mallette MPA
Lifespan Biostatistics Core, Rhode Island Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorArchana Lingannan MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorAldo Alejandro Recinos Soto MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorDyadin Esharif MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorSarah H. Maxwell MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Department of Pediatrics, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorMuhammad Safwan Riaz MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorMichael I. Herzlinger MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorLinda B. Shalon MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorCarolina S. Cerezo MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorVania L. Kasper MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorAlbert M. Ross MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Search for more papers by this authorNeal S. Leleiko MD, PhD
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, NY
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jason M. Shapiro MD
Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI
Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Providence, RI
Address correspondence and reprint requests to Jason M. Shapiro, MD, Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Nutrition and Liver Diseases, Hasbro Children’s Hospital and Rhode Island Hospital, Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, 593 Eddy Street, Providence, RI 02903 (e-mail: [email protected]).Search for more papers by this authorThe authors report no conflicts of interest.
M.G. and S.S. contributed equally to the article.
Abstract
Objectives:
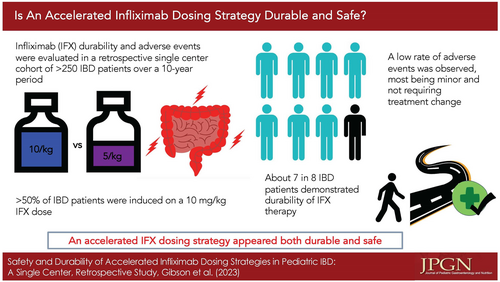
Infliximab (IFX) is commonly used to treat children with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). We previously reported that patients with extensive disease started on IFX at a dose of 10 mg/kg had greater treatment durability at year one. The aim of this follow-up study is to assess the long-term safety and durability of this dosing strategy in pediatric IBD.
Methods:
We performed a retrospective single-center study of pediatric IBD patients started on IFX over a 10-year period.
Results:
Two hundred ninety-one patients were included (mean age = 12.61, 38% female) with a follow-up range of 0.1–9.7 years from IFX induction. One hundred fifty-five (53%) were started at a dose of 10 mg/kg. Only 35 patients (12%) discontinued IFX. The median duration of treatment was 2.9 years. Patients with ulcerative colitis (P ≤ 0.01) and patients with extensive disease (P = 0.01) had lower durability, despite a higher starting dose of IFX (P = 0.03). Adverse events (AEs) were observed to occur at a rate of 234 per 1000 patient-years. Patients with a higher serum IFX trough level (≥20 µg/mL) had a higher rate of AEs (P = 0.01). Use of combination therapy had no impact on risk of AEs (P = 0.78).
Conclusions:
We observed an excellent IFX treatment durability, with only 12% of patients discontinuing therapy over the observed timeframe. The overall rate of AEs was low, the majority being infusion reactions and dermatologic conditions. Higher IFX dose and serum trough level> 20 µg/mL were associated with higher risk of AEs, the majority being mild and not resulting in cessation of therapy.
Graphical Abstract
REFERENCES
- 1.Hyams J, Crandall W, Kugathasan S, et al. Induction and maintenance infliximab therapy for the treatment of moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease in children. Gastroenterology 2007; 132: 863–73; quiz 1165.
- 2.Hyams J, Walters TD, Crandall W, et al. Safety and efficacy of maintenance infliximab therapy for moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease in children: REACH open-label extension. Curr Med Res Opin 2011; 27: 651–62.
- 3.Hyams J, Damaraju L, Blank M, et al. Induction and maintenance therapy with infliximab for children with moderate to severe ulcerative colitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012; 10: 391–99.e1.
- 4.Hanauer SB, Feagan BG, Lichtenstein GR, et al. Maintenance infliximab for Crohn’s disease: the ACCENT I randomised trial. Lancet 2002; 359: 1541–9.
- 5.Rutgeerts P, Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, et al. Infliximab for induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 2462–76.
- 6.Zitomersky NL, Atkinson BJ, Fournier K, et al. Antibodies to infliximab are associated with lower infliximab levels and increased likelihood of surgery in pediatric IBD. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2015; 21: 307–14.
- 7.Naviglio S, Lacorte D, Lucafò M, et al. Causes of treatment failure in children with inflammatory bowel disease treated with infliximab: a pharmacokinetic study. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2019; 68: 37–44.
- 8.Kennedy NA, Heap GA, Green HD, et al. Predictors of anti-TNF treatment failure in anti-TNF-naive patients with active luminal Crohn’s disease: a prospective, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019; 4: 341–53.
- 9.Church PC, Guan J, Walters TD, et al. Infliximab maintains durable response and facilitates catch-up growth in luminal pediatric Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2014; 20: 1177–86.
- 10.Vahabnezhad E, Rabizadeh S, Dubinsky MC. A 10-year, single tertiary care center experience on the durability of infliximab in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2014; 20: 606–13.
- 11.Winter DA, Joosse ME, de Wildt SN, Taminiau J, de Ridder L, Escher JC. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and immunogenicity of infliximab in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and revised dosing considerations. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2020; 70: 763–76.
- 12.Singh N, Rosenthal CJ, Melmed GY, et al. Early infliximab trough levels are associated with persistent remission in pediatric patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2014; 20: 1708–13.
- 13.Van Hoeve K, Dreesen E, Hoffman I, et al. Adequate infliximab exposure during induction predicts remission in paediatric patients with inflammatory bowel disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2019; 68: 847–53.
- 14.Lega S, Phan BL, Rosenthal CJ, et al. Proactively optimized infliximab monotherapy is as effective as combination therapy in IBD. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2019; 25: 134–41.
- 15.Papamichael K, Cshachu KA, Vajravelu RK, et al. Improved long-term outcomes of patients with inflammatory bowel disease receiving proactive compared with reactive monitoring of serum concentrations of infliximab. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017; 15: 1580–8.
- 16.Bonovas S, Fiorino G, Allocca M, et al. Biologic therapies and risk of infection and malignancy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016; 14: 1385–97.
- 17.Holmer A, Singh S. Overall and comparative safety of biologic and immunosuppressive therapy in inflammatory bowel diseases. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 2019; 15: 969–79.
- 18.Haens G, Reinisch W, Colombel J, et al. Five-year safety data from ENCORE, a European observational safety registry for adults with Crohn’s disease treated with infliximab [Remicade®] or conventional therapy. J Crohns Colitis 2017; 11: 680–9.
- 19.Hyams JS, Dubinsky MC, Baldassano RN, et al. Infliximab is not associated with increased risk of malignancy or hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in pediatric patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 2017; 152: 1901.
- 20.Shapiro JM, Subedi S, Machan JT, et al. Durability of infliximab is associated with disease extent in children with inflammatory bowel disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2016; 62: 867–72.
- 21.Turner D, Mack D, Leleiko N, et al. Severe pediatric ulcerative colitis: a prospective multicenter study of outcomes and predictors of response. Gastroenterology 2010; 138: 2282–91.
- 22.Turner D, Ruemmele FM, Orlanski-Meyer E, et al. Management of paediatric ulcerative colitis, part 2: acute severe colitis--an evidence-based consensus guideline from the European Crohn’s and Colitis Organization and the European Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2018; 67: 292–310.
- 23.Greener T, Kabakchiev B, Steinhart AH, Silverberg MS. Higher infliximab levels are not associated with an increase in adverse events in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2018; 24: 1808–14.
- 24.Lichtenstein GR, Feagan BG, Cohen RD, et al. Infliximab for Crohn’s disease: more than 13 years of real-world experience. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2018; 24: 490–501.
- 25.Huang VWM, Dhami N, Fedorak D, et al. A study investigating the association of dermatological and infusion reactions to infliximab and infliximab trough levels. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015; 29: 35–40.
- 26.Dipasquale V, Romano C. Biosimilar infliximab in paediatric inflammatory bowel disease: efficacy, immunogenicity and safety. J Clin Pharm Ther 2020; 45: 1228–34.