Dependence of the inner dark matter profile on the halo mass
ABSTRACT
I compare the density profile of dark matter (DM) haloes in cold dark matter (CDM) N-body simulations with 1, 32, 256 and 1024 h−1 Mpc box sizes. I compare the profiles when the most massive haloes are composed of about 105 DM particles. The DM density profiles of the haloes in the 1 h−1 Mpc box at redshift z∼ 10 show systematically shallower cores with respect to the corresponding haloes in the 32 h−1 Mpc simulation at z∼ 3 that have masses, Mdm, typical of the Milky Way and are fitted by a Navarro–Frenk–White (NFW) profile. The DM density profiles of the haloes in the 256 h−1 Mpc box at z∼ 0 are consistent with having steeper cores than the corresponding haloes in the 32 h−1 Mpc simulation, but higher mass resolution simulations are needed to strengthen this result. Combined, these results suggest that the density profile of DM haloes is not universal, presenting shallower cores in dwarf galaxies and steeper cores in clusters. More work is needed to validate this finding at z= 0. Physically, the result sustains the hypothesis that the mass function of the accreting satellites determines the inner slope of the DM profile. However, the result can also be interpreted as a trend with the dynamical state in the assembly process of haloes of different mass. In comoving coordinates, r, the profile
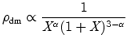
I compare the DM profiles in the 1 h−1 Mpc box with the same simulation including stars, baryons and radiative transfer presented by Ricotti, Gnedin and Shull. Radiative feedback effects produce a larger scatter in the density profile shapes but, on average, do not affect the shape of the DM profiles significantly.




