Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes: Synthesis of Meltable and Amphiphilic Derivatives†
Athanasios B. Bourlinos Dr.
Institute of Materials Science, NCSR “Demokritos”, Ag. Paraskevi Attikis, Athens 15310, Greece
Search for more papers by this authorVasilios Georgakilas Dr.
Institute of Materials Science, NCSR “Demokritos”, Ag. Paraskevi Attikis, Athens 15310, Greece
Search for more papers by this authorVasilios Tzitzios Dr.
Institute of Materials Science, NCSR “Demokritos”, Ag. Paraskevi Attikis, Athens 15310, Greece
Search for more papers by this authorNikolaos Boukos Dr.
Institute of Materials Science, NCSR “Demokritos”, Ag. Paraskevi Attikis, Athens 15310, Greece
Search for more papers by this authorRafael Herrera
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853, USA, Fax: (+1) 607-255-2365
Search for more papers by this authorEmmanuel P. Giannelis Prof.
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853, USA, Fax: (+1) 607-255-2365
Search for more papers by this authorAthanasios B. Bourlinos Dr.
Institute of Materials Science, NCSR “Demokritos”, Ag. Paraskevi Attikis, Athens 15310, Greece
Search for more papers by this authorVasilios Georgakilas Dr.
Institute of Materials Science, NCSR “Demokritos”, Ag. Paraskevi Attikis, Athens 15310, Greece
Search for more papers by this authorVasilios Tzitzios Dr.
Institute of Materials Science, NCSR “Demokritos”, Ag. Paraskevi Attikis, Athens 15310, Greece
Search for more papers by this authorNikolaos Boukos Dr.
Institute of Materials Science, NCSR “Demokritos”, Ag. Paraskevi Attikis, Athens 15310, Greece
Search for more papers by this authorRafael Herrera
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853, USA, Fax: (+1) 607-255-2365
Search for more papers by this authorEmmanuel P. Giannelis Prof.
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853, USA, Fax: (+1) 607-255-2365
Search for more papers by this authorWe gratefully acknowledge the support of the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFOSR), the Cornell Center for Materials Research (CCMR), the Office of Naval Research (ONR), and the Fuel Cell Institute at Cornell.
Graphical Abstract
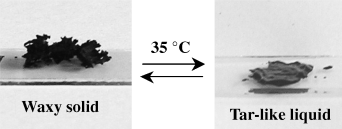
Melt down! A meltable, amphiphilic carbon nanotube derivative was obtained in a two-step functionalization process whereby oxidation of the nanotube was followed by a surface reaction with a polyethylene glycol-substituted tertiary amine. The derivative underwent a reversible solid-to-liquid transition at 35 °C (see image) and was highly dispersible in both aqueous and organic media.
References
- 1
- 1aM. S. Dresselhaus, G. Dresselhaus, P. Avouris, Carbon Nanotubes in Topics in Applied Physics, Springer, Berlin, 2001;
- 1bR. H. Baughman, A. A. Zakhidov, W. A. de Heer, Science 2002, 297, 787–792;
- 1cJ. Kong, N. R. Franklin, C. Zhou, M. G. Chapline, S. Peng, K. Cho, H. Dai, Science 2000, 287, 622–625;
- 1dH. W. C. Postma, T. Teepen, Z. Yao, M. Grifoni, C. Dekker, Science 2001, 293, 76–79.
- 2
- 2aE. W. Wong, P. E. Sheehan, C. M. Lieber, Science 1997, 277, 1971–1975;
- 2bP. M. Ajayan, L. S. Schadler, C. Giannaris, A. Rubio, Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 750–753;
- 2cS. Niyogi, M. A. Hamon, H. Hu, B. Zhao, P. Bhowmik, R. Sen, M. E. Itkis, R. C. Haddon, Acc. Chem. Res. 2002, 35, 1105–1113;
- 2dY. P. Sun, K. Fu, Y. Lin, W. Huang, Acc. Chem. Res. 2002, 35, 1096–1104.
- 3
- 3aJ. L. Bahr, J. M. Tour, J. Mater. Chem. 2002, 12, 1952–1958;
- 3bJ. Chen, M. A. Hamon, H. Hu, Y. Chen, A. M. Rao, P. C. Eklund, R. C. Haddon, Science 1998, 282, 95–98;
- 3cS. Banerjee, M. G. C. Kahn, S. S. Wong, Chem. Eur. J. 2003, 9, 1898–1908;
- 3dV. Georgakilas, V. Tzitzios, D. Gournis, D. Petridis, Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 1613–1617.
- 4
- 4aM. G. C. Kahn, S. Banerjee, S. S. Wong, Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 1215–1218;
- 4bM. Holzinger, J. Abraham, P. Whelan, R. Graupner, L. Ley, F. Hennrich, M. Kappes, A. Hirsch, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 8566–8580;
- 4cW. Huang, S. Fernando, L. F. Allard, Y.-P. Sun, Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 565–568.
- 5
- 5aB. Zhao, H. Hu, A. Yu, D. Perea, R. C. Haddon, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 8197–8203;
- 5bM. J. Park, J. K. Lee, B. S. Lee, Y.-W. Lee, I. S. Choi, S.-G. Lee, Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 1546–1551.
- 6
- 6aA. B. Bourlinos, A. Stassinopoulos, D. Anglos, R. Herrera, S. H. Anastasiadis, D. Petridis, E. P. Giannelis, Small 2006, 2, 513–516;
- 6bA. B. Bourlinos, R. Herrera, N. Chalkias, D. D. Jiang, Q. Zhang, L. A. Archer, E. P. Giannelis, Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 234–237;
- 6cA. B. Bourlinos, S. Ray Chowdhury, D. D. Jiang, Y.-U. An, Q. Zhang, L. A. Archer, E. P. Giannelis, Small 2005, 1, 80–82;
- 6dA. B. Bourlinos, S. Ray Chowdhury, R. Herrera, D. D. Jiang, Q. Zhang, L. A. Archer, E. P. Giannelis, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 1285–1290;
- 6eB.-H. Han, M. A. Winnik, A. B. Bourlinos, E. P. Giannelis, Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 4001–4009;
- 6fA. B. Bourlinos, K. Raman, R. Herrera, Q. Zhang, L. A. Archer, E. P. Giannelis, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 15358–15359.
- 7
- 7aB. K. Price, J. L. Hudson, J. M. Tour, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 14867–14870;
- 7bT. Fukushima, A. Kosaka, Y. Ishimura, T. Yamamoto, T. Takigawa, N. Ishii, T. Aida, Science 2003, 300, 2072–2074.
- 8
- 8aD. Chattopadhyay, I. Galeska, F. Papadimitrakopoulos, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 3370–3375;
- 8bY. Maeda, S. Kimura, M. Kanda, Y. Hirashima, T. Hasegawa, T. Wakahara, Y. Lian, T. Nakahodo, T. Tsuchiya, T. Akasaka, J. Lu, X. Zhang, Z. Gao, Y. Yu, S. Nagase, S. Kazaoui, N. Minami, T. Shimizu, H. Tokumoto, R. Saito, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 10287–10290.
- 9
- 9aH. Pan, L. Liu, Z.-X. Guo, L. Dai, F. Zhang, D. Zhu, R. Czerw, D. L. Carroll, Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 29–32;
- 9bA. B. Bourlinos, D. Gournis, D. Petridis, T. Szabó, A. Szeri, I. Dékány, Langmuir 2003, 19, 6050–6055;
- 9cT. Ramanathan, F. T. Fisher, R. S. Ruoff, L. C. Brinson, Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 1290–1295.
- 10
- 10aT. J. Singh, S. V. Bhat, Bull. Mater. Sci. 2003, 26, 707–714;
- 10bA. N. Parikh, M. A. Schivley, E. Koo, K. Seshadri, D. Aurentz, K. Mueller, D. L. Allara, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 3135–3143.
- 11
- 11aS. Y. Chen, H. Y. Miao, J. T. Lue, M. S. Ouyang, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2004, 37, 273–279;
- 11bR. Saito, A. Jorio, A. G. S. Filho, A. Grueneis, M. A. Pimenta, G. Dresselhaus, M. S. Dresselhaus, Phys. B 2002, 323, 100–106;
- 11cY. Gogotsi, J. A. Libera, M. Yoshimura, J. Mater. Res. 2000, 15, 2591–2594.
- 12H. Murphy, P. Papakonstantinou, T. I. T. Okpalugo, J. Vac. Sci. Technol., B: Microelectron. Nanometer Struct. 2006, 24, 715–720.
- 13C. A. Furtado, U. J. Kim, H. R. Gutierrez, L. Pan, E. C. Dickey, P. C. Eklund, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 6095–6105.
- 14V. Georgakilas, K. Kordatos, M. Prato, D. M. Guldi, M. Holzinger, A. Hirsch, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 760–761.
- 15C. A. Dyke, J. M. Tour, Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 1215–1218.