Overexpression of certain transient receptor potential and Orai channels in prostate cancer is associated with decreased risk of systemic recurrence after radical prostatectomy
Corresponding Author
M. A. Perrouin-Verbe MD, PhD
Department of Urology, CHRU-Université de Brest, Brest, France
INSERM UMR1078, Université de Bretagne Occidentale, Brest, France
Department of Urology, CHU-Université de Nantes, Nantes, France
Correspondence Marie-Aimée Perrouin-Verbe, MD, PhD, Department of Urology, CHU-Université de Nantes 1 place Alexis Ricordeau, 44000 Nantes, France.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorN. Schoentgen MD
Department of Urology, CHRU-Université de Brest, Brest, France
INSERM UMR1078, Université de Bretagne Occidentale, Brest, France
Search for more papers by this authorM. Talagas MD, PhD
Department of Pathology, CHRU-Université de Brest, Brest, France
EA 4685 – LIEN, Université de Bretagne Occidentale, Brest, France
Search for more papers by this authorR. Garlantezec MD, PhD
INSERM UMR1085-IRSET, Université Rennes 1, Rennes, France
Search for more papers by this authorA. Uguen MD, PhD
Department of Pathology, CHRU-Université de Brest, Brest, France
Search for more papers by this authorL. Doucet MD
Department of Pathology, CHRU-Université de Brest, Brest, France
Search for more papers by this authorS. Rosec
INSERM UMR1412, Centre d’Investigation Clinique, CHRU-Université de Brest, Brest, France
Search for more papers by this authorP. Marcorelles MD, PhD
Department of Pathology, CHRU-Université de Brest, Brest, France
Search for more papers by this authorM. Potier-Cartereau PhD
INSERM UMR1069, Université François Rabelais, Tours, France
Search for more papers by this authorC. Vandier PhD
INSERM UMR1069, Université François Rabelais, Tours, France
Search for more papers by this authorC. Ferec MD, PhD
INSERM UMR1078, Université de Bretagne Occidentale, Brest, France
Search for more papers by this authorG. Fromont MD, PhD
INSERM UMR1069, Université François Rabelais, Tours, France
Department of Pathology, CHRU-Université de Tours, Tours, France
Search for more papers by this authorG. Fournier MD
Department of Urology, CHRU-Université de Brest, Brest, France
Search for more papers by this authorA. Valeri MD, PhD
Department of Urology, CHRU-Université de Brest, Brest, France
Search for more papers by this authorO. Mignen PhD
INSERM UMR1078, Université de Bretagne Occidentale, Brest, France
INSERM UMR1227, Université de Bretagne Occidentale, Brest, France
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
M. A. Perrouin-Verbe MD, PhD
Department of Urology, CHRU-Université de Brest, Brest, France
INSERM UMR1078, Université de Bretagne Occidentale, Brest, France
Department of Urology, CHU-Université de Nantes, Nantes, France
Correspondence Marie-Aimée Perrouin-Verbe, MD, PhD, Department of Urology, CHU-Université de Nantes 1 place Alexis Ricordeau, 44000 Nantes, France.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorN. Schoentgen MD
Department of Urology, CHRU-Université de Brest, Brest, France
INSERM UMR1078, Université de Bretagne Occidentale, Brest, France
Search for more papers by this authorM. Talagas MD, PhD
Department of Pathology, CHRU-Université de Brest, Brest, France
EA 4685 – LIEN, Université de Bretagne Occidentale, Brest, France
Search for more papers by this authorR. Garlantezec MD, PhD
INSERM UMR1085-IRSET, Université Rennes 1, Rennes, France
Search for more papers by this authorA. Uguen MD, PhD
Department of Pathology, CHRU-Université de Brest, Brest, France
Search for more papers by this authorL. Doucet MD
Department of Pathology, CHRU-Université de Brest, Brest, France
Search for more papers by this authorS. Rosec
INSERM UMR1412, Centre d’Investigation Clinique, CHRU-Université de Brest, Brest, France
Search for more papers by this authorP. Marcorelles MD, PhD
Department of Pathology, CHRU-Université de Brest, Brest, France
Search for more papers by this authorM. Potier-Cartereau PhD
INSERM UMR1069, Université François Rabelais, Tours, France
Search for more papers by this authorC. Vandier PhD
INSERM UMR1069, Université François Rabelais, Tours, France
Search for more papers by this authorC. Ferec MD, PhD
INSERM UMR1078, Université de Bretagne Occidentale, Brest, France
Search for more papers by this authorG. Fromont MD, PhD
INSERM UMR1069, Université François Rabelais, Tours, France
Department of Pathology, CHRU-Université de Tours, Tours, France
Search for more papers by this authorG. Fournier MD
Department of Urology, CHRU-Université de Brest, Brest, France
Search for more papers by this authorA. Valeri MD, PhD
Department of Urology, CHRU-Université de Brest, Brest, France
Search for more papers by this authorO. Mignen PhD
INSERM UMR1078, Université de Bretagne Occidentale, Brest, France
INSERM UMR1227, Université de Bretagne Occidentale, Brest, France
Search for more papers by this authorThis work was performed at INSERM UMR1078, Université de Bretagne Occidentale and at the Department of Urology, CHRU-Université de Brest, 29200 Brest, France.
Abstract
Background: Several studies had suggested the potential role of calcium signaling in prostate cancer (PCa) prognosis and agressiveness. We aimed to investigate selected proteins contributing to calcium (Ca2+) signaling, (Orai, stromal interaction molecule (STIM), and transient receptor potential (TRP) channels) and involved in cancer hallmarks, as independent predictors of systemic recurrence after radical prostatectomy (RP).
Methods: A case-control study including 112 patients with clinically localized PCa treated by RP between 2002 and 2009 and with at least 6-years’ follow-up. Patients were divided into two groups according to the absence or presence of systemic recurrence. Expression levels of 10 proteins involved in Ca2+ signaling (TRPC1, TRPC4, TRPV5, TRPV6, TRPM8, STIM1, STIM2, Orai1, Orai2, and Orai3), were assessed by immunohistochemistry using tissue microarrays (TMAs) constructed from paraffin-embedded PCa specimens. The level of expression of the various transcripts in PCa was assessed using quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) analysis. RNA samples for qPCR were obtained from fresh frozen tissue samples of PCa after laser capture microdissection on RP specimens. Relative gene expression was analyzed using the 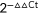 method.
method.
Results: Multivariate analysis showed that increased expression of TRPC1, TRPC4, TRPV5, TRPV6, TRPM8, and Orai2 was significantly associated with a lower risk of systemic recurrence after RP, independently of the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level, percentage of positive biopsies, and surgical margin (SM) status (P = .007, P = .01, P < .001, P = .0065, P = .007, and P = .01, respectively). For TRPC4, TRPV5, and TRPV6, this association was also independent of Gleason score and pT stage. Moreover, overexpression of TRPV6 and Orai2 was significantly associated with longer time to recurrence after RP (P = .048 and .023, respectively). Overexpression of TRPC4, TRPV5, TRPV6, and Orai2 transcripts was observed in group R− (3.71-, 5.7-, 1.14-, and 2.65-fold increase, respectively).
Conclusions: This is the first study to suggest the independent prognostic value of certain proteins involved in Ca2+ influx in systemic recurrence after RP: overexpression of TRPC1, TRPC4, TRPV5, TRPV6, TRPM8, and Orai2 is associated with a lower risk of systemic recurrence. TRPC4, TRPV5, and TRPV6 appear to be particularly interesting, as they are independent of the five commonly used predictive factors, that is, PSA, percentage of positive biopsies, SM status, Gleason score, and pT stage.
REFERENCES
- 1Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017; 67: 7-30.
- 2Kattan MW, Eastham JA, Stapleton AMF, Wheeler TM, Scardino PT. A preoperative nomogram for disease recurrence following radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998; 90: 766-771.
- 3D'Amico AV. Biochemical outcome after radical prostatectomy, external beam radiation therapy, or interstitial radiation therapy for clinically localized prostate cancer. JAMA. 1998; 280: 969-974.
- 4D'Amico AV, Whittington R, Malkowicz SB, et al. Biochemical outcome after radical prostatectomy or external beam radiation therapy for patients with clinically localized prostate carcinoma in the prostate specific antigen era. Cancer. 2002; 95: 281-286.
- 5Stephenson AJ, Scardino PT, Eastham JA, et al. Postoperative nomogram predicting the 10-year probability of prostate cancer recurrence after radical prostatectomy. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23: 7005-7012.
- 6Shariat SF, Karakiewicz PI, Roehrborn CG, Kattan MW. An updated catalog of prostate cancer predictive tools. Cancer. 2008; 113: 3075-3099.
- 7Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Roderick HL. Calcium signalling: dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003; 4: 517-529.
- 8Prevarskaya N, Ouadid-Ahidouch H, Skryma R, Shuba Y. Remodelling of Ca2+ transport in cancer: how it contributes to cancer hallmarks? Philos Trans R Soc B. 2014; 369: 20130097.
- 9Fiorio Pla A, Kondratska K, Prevarskaya N. STIM and ORAI proteins: crucial roles in hallmarks of cancer. Am J Physiol – Cell Physiol. 2016; 310: C509-C519.
- 10Vashisht A, Trebak M, Motiani RK. STIM and Orai proteins as novel targets for cancer therapy. A review in the theme: Cell and molecular processes in cancer metastasis. Am J Physiol-Cell Physiol. 2015; 309: C457-C469.
- 11Mignen O, Thompson JL, Shuttleworth TJ. The molecular architecture of the arachidonate-regulated Ca2+-selective ARC channel is a pentameric assembly of Orai1 and Orai3 subunits: molecular architecture of the ARC channel. J Physiol. 2009; 587: 4181-4197.
- 12Prakriya M, Feske S, Gwack Y, Srikanth S, Rao A, Hogan PG. Orai1 is an essential pore subunit of the CRAC channel. Nature. 2006; 443: 230-233.
- 13Thebault S, Flourakis M, Vanoverberghe K, et al. Differential role of transient receptor potential channels in Ca2+ entry and proliferation of prostate cancer epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 2006; 66: 2038-2047.
- 14Mignen O, Constantin B, Potier-Cartereau M, et al. Constitutive calcium entry and cancer: updated views and insights. Eur Biophys J. 2017; 46: 395-413.
- 15Cahalan MD. STIMulating store-operated Ca2+ entry. Nat Cell Biol. 2009; 11: 669-677.
- 16Mignen O, Thompson JL, Shuttleworth TJ. Both Orai1 and Orai3 are essential components of the arachidonate-regulated Ca2+-selective (ARC) channels: Orai1 and Orai3 are both required for functional ARC channels. J Physiol. 2008; 586: 185-195.
- 17Thompson JL, Shuttleworth TJ. Molecular basis of activation of the arachidonate-regulated Ca2+(ARC) channel, a store-independent Orai channel, by plasma membrane STIM1: Mechanism of ARC channel activation by plasma membrane STIM1. J Physiol. 2013; 591: 3507-3523.
- 18Hogan PG, Lewis RS, Rao A. Molecular basis of calcium signaling in lymphocytes: STIM and ORAI. Annu Rev Immunol. 2010; 28: 491-533.
- 19Prevarskaya N, Skryma R, Shuba Y. Calcium in tumour metastasis: new roles for known actors. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011; 11: 609-618.
- 20Shapovalov G, Skryma R, Prevarskaya N. Calcium channels and prostate cancer. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2012; 8: 18-26.
- 21Prevarskaya N, Skryma R, Bidaux G, Flourakis M, Shuba Y. Ion channels in death and differentiation of prostate cancer cells. Cell Death Differ. 2007; 14: 1295-1304.
- 22Flourakis M, Lehen'kyi V, Beck B, et al. Orai1 contributes to the establishment of an apoptosis-resistant phenotype in prostate cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2010; 1: e75.
- 23Dubois C, Vanden Abeele F, Lehen’kyi V, et al. Remodeling of channel-forming ORAI proteins determines an oncogenic switch in prostate cancer. Cancer Cell. 2014; 26: 19-32.
- 24Faouzi M, Hague F, Potier M, Ahidouch A, Sevestre H, Ouadid-Ahidouch H. Down-regulation of Orai3 arrests cell-cycle progression and induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells but not in normal breast epithelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 2011; 226: 542-551.
- 25Faouzi M, Kischel P, Hague F, et al. ORAI3 silencing alters cell proliferation and cell cycle progression via c-myc pathway in breast cancer cells. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) – Mol Cell Res. 2013; 1833: 752-760.
- 26Hoth M, Niemeyer BA. The neglected CRAC proteins: Orai2, Orai3, and STIM2. Curr Top Membr. 2013; 71: 237-271.
- 27Diez-Bello R, Jardin I, Salido GM, Rosado JA. Orai1 and Orai2 mediate store-operated calcium entry that regulates HL60 cell migration and FAK phosphorylation. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) – Mol Cell Res. 2017; 1864: 1064-1070.
- 28Perrouin Verbe MA, Bruyere F, Rozet F, Vandier C, Fromont G. Expression of store-operated channel components in prostate cancer: the prognostic paradox. Hum Pathol. 2016; 49: 77-82.
- 29Hoenderop JGJ, Nilius B, Bindels RJM. Epithelial calcium channels: from identification to function and regulation. Pflügers Archiv – Eur J Physiol. 2003; 446: 304-308.
- 30Lehen’kyi V, Flourakis M, Skryma R, Prevarskaya N. TRPV6 channel controls prostate cancer cell proliferation via Ca2+/NFAT-dependent pathways. Oncogene. 2007; 26: 7380-7385.
- 31Peng JB, Zhuang L, Berger UV, et al. CaT1 expression correlates with tumor grade in prostate cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001; 282: 729-734.
- 32Landowski CP, Bolanz KA, Suzuki Y, Hediger MA. Chemical inhibitors of the calcium entry channel TRPV6. Pharm Res. 2011; 28: 322-330.
- 33Henshall SM, Afar DE, Hiller J, et al. Survival analysis of genome-wide gene expression profiles of prostate cancers identifies new prognostic targets of disease relapse. Cancer Res. 2003; 63: 4196-4203.
- 34Bidaux G. Evidence for specific TRPM8 expression in human prostate secretory epithelial cells: functional androgen receptor requirement. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005; 12: 367-382.
- 35Yang ZH, Wang XH, Wang HP, Hu LQ. Effects of TRPM8 on the proliferation and motility of prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Asian J Androl. 2009; 11: 157-165.
- 36Zhang L, Barritt GJ. Evidence that TRPM8 is an androgen-dependent Ca2+ channel required for the survival of prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004; 64: 8365-8373.
- 37Sobin L. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours. Chichester, West Sussex, UK: Wiley-Blackwell; 2010.
- 38Boccon-Gibod L, Djavan B, Hammerer P, et al. Management of prostate-specific antigen relapse in prostate cancer: a European Consensus. Int J Clin Pract. 2004; 58: 382-390.
- 39Heidenreich A, Bastian PJ, Bellmunt J, et al. EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Part 1: screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent-update 2013. Eur Urol. 2014; 65: 124-137.
- 40Jhaveri FM, Klein EA. How to explore the patient with a rising PSA after radical prostatectomy: defining local versus systemic failure. Semin Urol Oncol. 1999; 17: 130-134.
- 41Pound CR. Natural history of progression after PSA elevation following radical prostatectomy. JAMA. 1999; 281: 1591-1597.
- 42D’Amico AV, Whittington R, Malkowicz SB, et al. Utilizing predictions of early prostate-specific antigen failure to optimize patient selection for adjuvant systemic therapy trials. J Clin Oncol. 2000; 18: 3240-3246.
- 43Heidenreich ABM, Joniau S, Mason MD, et al. Guidelines on Prostate Cancer 2011; https://uroweb.org/wp-content/uploads/08_Prostate_Cancer-September-22nd-2011.pdf
- 44Leuner K, Kraus M, Woelfle U, et al. Reduced TRPC channel expression in psoriatic keratinocytes is associated with impaired differentiation and enhanced proliferation. PLoS One. 2011; 6: e14716.
- 45van de Graaf SFJ. Functional expression of the epithelial Ca2+ channels (TRPV5 and TRPV6) requires association of the S100A10-annexin 2 complex. EMBO J. 2003; 22: 1478-1487.
- 46Yang H, Choi KC, Hyun SH, Jeung EB. Coexpression and estrogen-mediated regulation of TRPV6 and PMCA1 in the human endometrium during the menstrual cycle. Mol Reprod Dev. 2011; 78: 274-282.
- 47Klejman ME, Gruszczynska-Biegala J, Skibinska-Kijek A, et al. Expression of STIM1 in brain and puncta-like co-localization of STIM1 and ORAI1 upon depletion of Ca2+ store in neurons. Neurochem Int. 2009; 54: 49-55.
- 48Skibinska-Kijek A, Wisniewska MB, Gruszczynska-Biegala J, Methner A, Kuznicki J. Immunolocalization of STIM1 in the mouse brain. Acta Neurobiol Exp. 2009; 69: 413-428.
- 49McCarl CA, Picard C, Khalil S, et al. ORAI1 deficiency and lack of store-operated Ca2+ entry cause immunodeficiency, myopathy, and ectodermal dysplasia. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 124: 1311-1318.
- 50Shukla CJ, Pennington CJ, Riddick ACP, Sethia KK, Ball RY, Edwards DRW. Laser-capture microdissection in prostate cancer research: establishment and validation of a powerful tool for the assessment of tumour-stroma interactions. BJU Int. 2008; 101: 765-774.
- 51Rubin MA. Use of laser capture microdissection, cDNA microarrays, and tissue microarrays in advancing our understanding of prostate cancer. J Pathol. 2001; 195: 80-86.
- 52Kube DM, Savci-Heijink CD, Lamblin AF, et al. Optimization of laser capture microdissection and RNA amplification for gene expression profiling of prostate cancer. BMC Mol Biol. 2007; 8: 25.
- 53Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 2001; 25: 402-408.
- 54Flourakis M, Prevarskaya N. Insights into Ca2+ homeostasis of advanced prostate cancer cells. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) – Mol Cell Res. 2009; 1793: 1105-1109.
- 55Gkika D, Prevarskaya N. TRP channels in prostate cancer: the good, the bad and the ugly? Asian J Androl. 2011; 13: 673-676.
- 56Shapovalov G, Ritaine A, Skryma R, Prevarskaya N. Role of TRP ion channels in cancer and tumorigenesis. Semin Immunopathol. 2016; 38: 357-369.
- 57Nijenhuis T, Hoenderop JGJ, Nilius B, Bindels RJM. Pathophysiological implications of the novel epithelial Ca2+ channels TRPV5 and TRPV6. Pflügers Archiv – Eur J Physiol. 2003; 446: 401-409.
- 58Tsavaler L, Shapero MH, Morkowski S. Laus R. Trp-p8, a novel prostate-specific gene, is up-regulated in prostate cancer and other malignancies and shares high homology with transient receptor potential calcium channel proteins. Cancer Res. 2001; 61: 3760-3769.
- 59Wang Y, Wang X, Yang Z, Zhu G, Chen D, Meng Z. Menthol inhibits the proliferation and motility of prostate cancer DU145 cells. Pathol Oncol Res. 2012; 18: 903-910.
- 60Hull GW, Rabbani F, Abbas F, Wheeler TM, Kattan MW, Scardino PT. Cancer control with radical prostatectomy alone in 1,000 consecutive patients. J Urol. 2002; 167: 528-534.




