Intrinsic signal amplification in the application of 2D SENSE parallel imaging to 3D contrast-enhanced elliptical centric MRA and MRV
Corresponding Author
Stephen J. Riederer
MR Research Laboratory, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
MR Research Laboratory, Mayo Clinic, 200 First Street, SW, Rochester, MN 55902===Search for more papers by this authorHouchun Harry Hu
MR Research Laboratory, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
Search for more papers by this authorDavid G. Kruger
MR Research Laboratory, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
Search for more papers by this authorClifton R. Haider
MR Research Laboratory, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
Search for more papers by this authorNorbert G. Campeau
MR Research Laboratory, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
Search for more papers by this authorJohn Huston III
MR Research Laboratory, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Stephen J. Riederer
MR Research Laboratory, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
MR Research Laboratory, Mayo Clinic, 200 First Street, SW, Rochester, MN 55902===Search for more papers by this authorHouchun Harry Hu
MR Research Laboratory, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
Search for more papers by this authorDavid G. Kruger
MR Research Laboratory, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
Search for more papers by this authorClifton R. Haider
MR Research Laboratory, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
Search for more papers by this authorNorbert G. Campeau
MR Research Laboratory, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
Search for more papers by this authorJohn Huston III
MR Research Laboratory, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
The relative signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) provided by 2D sensitivity encoding (SENSE) when applied to 3D contrast-enhanced MR angiography (CE-MRA) is studied. If an elliptical centric phase-encoding order is used to map the waning magnetization of the contrast bolus to k-space, the application of SENSE will reduce the degree of k-space signal modulation, providing a signal amplification A over corresponding nonaccelerated acquisitions. This offsets the SNR loss in R-accelerated SENSE due to
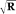 and the geometry (g) factor. The theoretical bound on A is R and is reduced from this depending on the properties of the bolus profile and the duration over which it is imaged. In this work a signal amplification of 1.14–1.23 times that of nonvascular background tissue is demonstrated in a study of 20 volunteers using R = 4 2D SENSE whole-brain MR venography (MRV). The effects of a nonuniform g-factor and inhomogeneity of background tissue are accounted for. The observed amplification compares favorably with the value of 1.31 predicted numerically from a measured bolus curve. Magn Reson Med 58:855–864, 2007. © 2007 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
and the geometry (g) factor. The theoretical bound on A is R and is reduced from this depending on the properties of the bolus profile and the duration over which it is imaged. In this work a signal amplification of 1.14–1.23 times that of nonvascular background tissue is demonstrated in a study of 20 volunteers using R = 4 2D SENSE whole-brain MR venography (MRV). The effects of a nonuniform g-factor and inhomogeneity of background tissue are accounted for. The observed amplification compares favorably with the value of 1.31 predicted numerically from a measured bolus curve. Magn Reson Med 58:855–864, 2007. © 2007 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
REFERENCES
- 1
Pruessmann KP,
Weiger M,
Scheidegger MB,
Boesiger P.
SENSE: sensitivity encoding for fast MRI.
Magn Reson Med
1999;
42:
952–962.
10.1002/(SICI)1522-2594(199911)42:5<952::AID-MRM16>3.0.CO;2-S CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 2 Sodickson DK, Manning WJ. Simultaneous acquisition of spatial harmonics (SMASH): fast imaging with radiofrequency coil arrays. Magn Reson Med 1997; 38: 591–603.
- 3 Griswold MA, Jakob PM, Heidemann RM, Nittka M, Jellus V, Wang J, Kiefer B, Haase A. Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA). Magn Reson Med 2002; 47: 1202–1210.
- 4 Ohliger MA, Grant AK, Sodickson DK. Ultimate intrinsic signal-to-noise ratio for parallel MRI: electromagnetic field considerations. Magn Reson Med 2003; 50: 1018–1030.
- 5 Wiesinger F, Boesiger P, Pruessmann KP. Electrodynamics and ultimate SNR in parallel MR imaging. Magn Reson Med 2004; 52: 376–390.
- 6 Weiger M, Pruessman KP, Kassner A, Roditi G, Lawton T, Ried A, Boesinger P. Contrast-enhanced 3D MRA using SENSE. J Magn Reson Imaging 2000; 12: 671–677.
- 7 Golay X, Brown SJ, Itoh R, Melhem ER. Time-resolved contrast-enhanced carotid MR angiography using sensitivity encoding (SENSE). AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2001; 22: 1615–1619.
- 8 Maki JH, Wilson GJ, Eubank WB, Hoogeveen RM. Utilizing SENSE to achieve lower station sub-millimeter isotropic resolution and minimal venous enhancement in peripheral MR angiography. J Magn Reson Imaging 2002; 15: 484–491.
- 9 Ohno Y, Kawamitsu H, Higashino T, Takenaka D, Watanabe H, Van Cauteren M, Fuji M, Hatabu H, Sugimura K. Time-resolved contrast-enhanced pulmonary MR angiography using sensitivity encoding (SENSE). J Magn Reson Imaging 2003; 17: 330–336.
- 10 deVries M, Nijenhuis RJ, Hoogeveen RM, de Haan MW, van Engelshoven JM, Leiner T. Contrast-enhanced peripheral MR angiography using SENSE in multiple stations: feasibility study. J Magn Reson Imaging 2005; 21: 37–45.
- 11 Born M, Willinek WA, Gieseke J, von Falkenhausen M, Schild H, Kuhl CK. Sensitivity encoding (SENSE) for contrast-enhanced 3D MR angiography of the abdominal arteries. J Magn Reson Imaging 2005; 22: 559–565.
- 12 Riedy G, Golay X, Melhem ER. Three-dimensional isotropic contrast-enhanced MR angiography of the carotid artery using sensitivity-encoding and random elliptic centric k-space filling: technique optimization. Neuroradiology 2005; 47: 668–673.
- 13 Kramer H, Schoenberg SO, Nikolaou K, Huber A, Struwe A, Winnik E, Wintersperger BJ, Dietrich O, Kiefer B, Reiser MF. Cardiovascular screening with parallel imaging techniques and a whole-body MR imager. Radiology 2005; 236: 300–310.
- 14 Wilman AH, Riederer SJ. Performance of an elliptical centric view order for signal enhancement and motion artifact suppression in breathhold three dimensional gradient echo imaging. Magn Reson Med 1997; 38: 793–802.
- 15 Wilman AH, Riederer SJ, King BF, Debbins JP, Rossman PJ, Ehman RL. Fluoroscopically-triggered contrast-enhanced three-dimensional MR angiography with elliptical centric view order: application to the renal arteries. Radiology 1997; 205: 137–146.
- 16
Griswold MA,
Jakob PM,
Chen Q,
Goldfarb JW,
Manning WJ,
Edelman RR,
Sodickson DK.
Resolution enhancement in single-shot imaging using simultaneous acquisition of spatial harmonics (SMASH).
Magn Reson Med
1999;
41:
1236–1245.
10.1002/(SICI)1522-2594(199906)41:6<1236::AID-MRM21>3.0.CO;2-T CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 17 Jaermann T, Pruessman KP, Valavanis A, Kollias S, Boesinger P. Influence of SENSE on image properties in high-resolution single-shot echo-planar DTI. Magn Reson Med 2006; 55: 335–342.
- 18 Weiger M, Pruessman KP, Boesinger P. 2D SENSE for faster 3D MRI. Magma 2002; 14: 10–19.
- 19
Fain SB,
Riederer SJ,
Bernstein MA,
Huston J.
Theoretical limits of spatial resolution in elliptical-centric contrast-enhanced 3D-MRA.
Magn Reson Med
1999;
42:
1106–1116.
10.1002/(SICI)1522-2594(199912)42:6<1106::AID-MRM15>3.0.CO;2-Q CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 20 Thompson HK, Starmer F, Whalen RE, McIntosh HD. Indicator transit time considered as a gamma variate. Circ Res 1964; 14: 502–515.
- 21 Haacke EM, Brown RW, Thompson MR, Venkatesan R. Magnetic resonance imaging: physical principles and sequence design. New York: Wiley-Liss; 1999. p. 269–272.
- 22 Haider CR, Hu HH, Madhuranthakam AJ, Kruger DG, Campeau NG, Huston IIIJ, Riederer SJ. Time-resolved 3D contrast-enhanced MRA with 2D homodyne and view sharing for contrast bolus dynamics of the brain. In: Proceedings of the 14th Annual Meeting of ISMRM, Seattle, WA, USA, 2006 (Abstract 812).
- 23 Fain SB, Riederer SJ. Dependence of venous enhancement on the field of view in 3D contrast-enhanced MRA using the elliptical centric view order. Magn Reson Med 2001; 45: 1134–1141.
- 24 Farb RI, Scott JN, Willinsky RA, Wright GA, terBrugge KG. Intracranial venous system: gadolinium-enhanced three-dimensional MR venography with auto-triggered elliptic centric-ordered sequence—initial experience. Radiology 2003; 226: 203–209.
- 25 Wetzel SG, Law M, Lee VS, Cha S, Johnson GA, Nelson K. Imaging of the intracranial venous system with a contrast-enhanced volumetric interpolated examination. Eur Radiol 2003; 13: 1010–1018.
- 26 Mermuys KP, Vanhoenacker PK, Chappel P, Van Hoe L. Three-dimensional venography of the brain with a volumetric interpolated sequence. Radiology 2005; 234: 901–908.
- 27 Nael K, Fenchel M, Salamon N, Duckwiler GR, Laub G, Finn JP, Villablanca JP. Three-dimensional cerebral contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance venography at 3.0 Tesla. Invest Radiol 2006; 41: 763–768.
- 28 Haacke EM, Brown RW, Thompson MR, Venkatesan R. Magnetic resonance imaging: physical principles and sequence design. New York: Wiley-Liss; 1999. p 340.
- 29 Rosner B. Fundamentals of biostatistics. Duxbury Press, Belmont CA: Thomson Learning; 2000. p 275–278.
- 30 Henkelman RM. Measurement of signal intensities in the presence of noise in MR images. Med Phys 1985; 12: 232–233.
- 31 Riederer SJ, Bernstein MA, Breen JF, Busse RF, Ehman RL, Fain SB, Hulshizer TC, Huston J, King BF, Kruger DG, Shah S. Three-dimensional contrast-enhanced MR angiography with real-time fluoroscopic triggering: design specifications and technical reliability in 330 patient studies. Radiology 2000; 215: 584–593.
- 32 Farzaneh F, Riederer SJ, Pelc NJ. Analysis of T2 limitations and off-resonance effects on spatial resolution and artifacts in echo-planar imaging. Magn Reson Med 1990; 14: 123–139.
- 33 Constable RT, Gore JC. The loss of small objects in variable TE imaging: implications for FSE, RARE, and EPI. Magn Reson Med 1992; 28: 9–24.
- 34 Willinek WA, Gieseke J, Conrad R, Strunk H, Hoogeveen R, von Falkenhausen M, Keller E, Urbach H, Kuhl CK, Schild HH. Randomly segmented central k-space ordering in high-spatial-resolution contrast-enhanced MR angiography of the supraaortic arteries: initial experience. Radiology 2002; 225: 583–588.
- 35 Finn JP, Baskaran V, Carr JC, McCarthy RM, Pereles FS, Kroeker R, Laub G. Thorax: low-dose contrast-enhanced three-dimensional MR angiography with subsecond temporal resolution—initial results. Radiology 2002; 224: 896–904.
- 36 Riederer SJ, Tasciyan T, Farzaneh F, Lee JN, Wright RC, Herfkens RJ. MR fluoroscopy: technical feasibility. Magn Reson Med 1988; 8: 1–15.
- 37 van Vaals JJ, Brummer ME, Dixon WT, Tuithof HH, Engels H, Nelson RC, Gerety BM, Chezmar JL, denBoer JA. “Keyhole” method for accelerating imaging of contrast agent uptake. J Magn Reson Imaging 1993; 3: 671–675.
- 38 Korosec FR, Frayne R, Grist TM, Mistretta CA. Time-resolved contrast-enhanced 3D MR angiography. Magn Reson Med 1996; 36: 345–351.
- 39 Cashen TA, Carr JC, Shin W, Walker MT, Futterer SF, Shaibani A, McCarthy FM, Carroll TJ. Intracranial time-resolved contrast-enhanced MR angiography at 3T. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2006; 27: 822–829.




