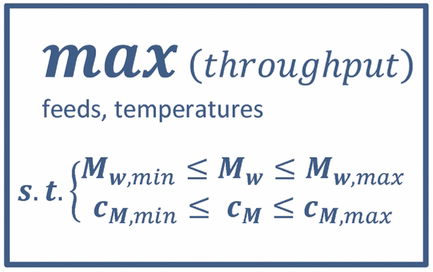Optimizing Control and State Estimation of a Continuous Polymerization Process in a Tubular Reactor with Multiple Side-Streams
INVITE is a not for profit joint venture of Bayer Technology Center Service and TU Dortmund.(http://www.invite-research.com).
Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-2600 CPU @ 3.40GHz, 24GB RAM.
The simulation times stated here are measured when a Matlab implementation of the model and Matlab integrator ode 15 s are used. For the purpose of the control, an MEX implementation of the model with CVODE from sundials TB as integrator are used which increases the simulation speed by a factor of about 100.
Please notice that the monomer injections are described by the amount of the opening control valves which have percent as the unit.
Worker is a MATLAB terminology and refers to the number of the processing units created by MATLAB virtuallyote>
Intel Core i7-2600K CPU @ 3.40GHz - 24.0 GB RAM.
Abstract
In this contribution, a nonlinear model-based optimizing control for continuous polymerization of acrylic acid in tubular reactors with multiple side injections of monomer is developed. The background of this work is to transfer the production of polymers from semibatch to continuous operations. The configuration of the tubular reactor, which imposes long delays between the inputs and the measurements, and the lack of intermediate measurements as well as the nonlinear reaction kinetics and sharp moving fronts of concentrations when the inflows are changed, make the application of the optimizing control very challenging. In order to simulate the sharp fronts of the reactor system faithfully and fast, the spatial domain of the partial differential equations model of the tubular reactor is discretized by applying the weighted essentially non-oscillatory scheme. We formulate the controller such that it optimizes the productivity of the reactor directly, while the product quality parameters are imposed as constraints. A particle filter is implemented to estimate the states of the reactor system and to initialize the process model. The simulation results show that the controller can increase the product throughput considerably compared to an initial operating point and has a robust performance against the measurement noise. Furthermore, the effect of formulating the quality constraints as hard or soft constraints as well as a changeover scenario between the different grades of a polymer are studied.